Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Number System
Uploaded by
Ashutosh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageThis document provides an overview of key concepts in number systems including rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It defines various types of numbers such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. Rational numbers have decimal expansions that are either terminating or recurring, while irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-recurring decimals. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers. The document also notes that the sum, difference, or product of a rational number and irrational number is irrational, but the quotient may be either rational or irrational. It provides an example of rationalizing the denominator of a fraction.
Original Description:
notes
Original Title
09 Maths Key Notes Ch 01 Number System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of key concepts in number systems including rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It defines various types of numbers such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. Rational numbers have decimal expansions that are either terminating or recurring, while irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-recurring decimals. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers. The document also notes that the sum, difference, or product of a rational number and irrational number is irrational, but the quotient may be either rational or irrational. It provides an example of rationalizing the denominator of a fraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 page09 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Number System
Uploaded by
AshutoshThis document provides an overview of key concepts in number systems including rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It defines various types of numbers such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. Rational numbers have decimal expansions that are either terminating or recurring, while irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-recurring decimals. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers. The document also notes that the sum, difference, or product of a rational number and irrational number is irrational, but the quotient may be either rational or irrational. It provides an example of rationalizing the denominator of a fraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Key Notes
CHAPTER 1
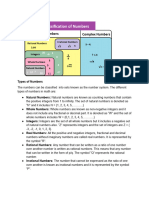
NUMBER SYSTEMS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Rational Numbers
Irrational Numbers
Real Numbers and their Decimal Expansions
Operations on Real Numbers
Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers
Natural numbers are - 1, 2, 3, . denoted by N.
Whole numbers are - 0, 1, 2, 3, denoted by W.
Integers - . -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, denoted by Z.
Rational numbers - All the numbers which can be written in the form r / s p / q, are called
rational numbers where p and q are integers.
Irrational numbers - A number s is called irrational, if it cannot be written in the form p / q
where p and q are integers and
The decimal expansion of a rational number is either terminating or non-terminating
recurring. Thus we say that a number whose decimal expansion is either terminating or nonterminating recurring is a rational number.
The decimal expansion of a irrational number is non terminating non-recurring.
All the rational numbers and irrational numbers taken together.
Make a collection of real number.
A real no is either rational or irrational.
If r is rational and s is irrational then r+s, rs, r.s are always irrational numbers but r/s may
be rational or irrational.
Every irrational number can be represented on a number line using Pythagoras theorem.
Rationalization means to remove square root from the denominator.
3+ 5
1
to remove we will multiply both numerator & denominator by 2
its
2
a b
rationalization factor a b
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Real Numbers PresentationDocument43 pagesReal Numbers PresentationitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Numbers Rational Numbers & IntegersDocument36 pagesNumbers Rational Numbers & IntegersKuthubudeen T MNo ratings yet
- Primary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) - Maths - Counting Practice – Ages 5-7’ eBookFrom EverandPrimary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) - Maths - Counting Practice – Ages 5-7’ eBookNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AptitudeDocument137 pagesQuantitative AptitudeJack P0% (1)
- Chapter - 1Document10 pagesChapter - 1May Yadanar Nwe100% (1)
- 9th Maths DISHADocument538 pages9th Maths DISHANikhil Kumar100% (1)
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Counting Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookFrom EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Counting Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Disha - Quantitative Aptitude PDFDocument137 pagesDisha - Quantitative Aptitude PDFअतुल्य भारतNo ratings yet
- Final Report Business MathematicsDocument70 pagesFinal Report Business MathematicsSifatShoaebNo ratings yet
- Primary School ‘KS2 (Key Stage 2) - Maths – Counting Practice - Ages 7-11’ eBookFrom EverandPrimary School ‘KS2 (Key Stage 2) - Maths – Counting Practice - Ages 7-11’ eBookNo ratings yet
- Elementary School ‘Grades 1 & 2: Math – Number – Ages 6-8’ eBookFrom EverandElementary School ‘Grades 1 & 2: Math – Number – Ages 6-8’ eBookNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument1 pageNumber SystemRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument2 pagesNumber SystemZakir AhemadNo ratings yet
- Maths Presentation Made by Kirti Pratap RanaDocument29 pagesMaths Presentation Made by Kirti Pratap RanaBOGNo ratings yet
- Math 11Document10 pagesMath 11Cheyene Reli GloreNo ratings yet
- Class-Ix - Notes & Practice Questions Chapter - 1 (Term-SA-I) MathematicsDocument2 pagesClass-Ix - Notes & Practice Questions Chapter - 1 (Term-SA-I) Mathematicsapi-294144440No ratings yet
- Rational and Irrational NumbersDocument8 pagesRational and Irrational Numbersabaan2610No ratings yet
- Number Systems Cla.s 9 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 1 (PDF)Document4 pagesNumber Systems Cla.s 9 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 1 (PDF)Muhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Real NumbersDocument39 pagesLecture 1 Real NumbersFelix blayNo ratings yet
- Revisi 1Document10 pagesRevisi 1reyvad.a.mbiNo ratings yet
- Rational Numbers: ©ncert Not To Be RepublishedDocument20 pagesRational Numbers: ©ncert Not To Be RepublishedrekshanaNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers and Imaginary NumbersDocument19 pagesReal Numbers and Imaginary NumbersTimothy LeronNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Natural NumbersDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Natural Numbershello.fordnjNo ratings yet
- Number SlideDocument33 pagesNumber SlideCristeena Merin MathewNo ratings yet
- Number: A Number Is A Mathematical Object Used To Count, Label and Measure The EntitiesDocument6 pagesNumber: A Number Is A Mathematical Object Used To Count, Label and Measure The EntitiesShan MajeedNo ratings yet
- Arranges Real Number in Increasing and Decreasing OrderDocument4 pagesArranges Real Number in Increasing and Decreasing OrderMaricel Pablico GamboaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Session 1 Chapter 1 Reviewing Number ConceptsDocument31 pagesGrade 10 Session 1 Chapter 1 Reviewing Number ConceptsReham IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Real Number LineDocument25 pagesThe Real Number LineMr. AulisioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 - Set of Real NumbersDocument21 pagesChapter 1 2 - Set of Real Numbersapi-263209117No ratings yet
- Sets - Numbers BasicsDocument2 pagesSets - Numbers BasicsFarishta SNo ratings yet
- Types of NumbersDocument2 pagesTypes of NumbersKenji LogieNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AptitudeDocument81 pagesQuantitative AptitudeSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- RatnoDocument26 pagesRatnoKartik chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Can Irrational Numbers Be NegativeDocument4 pagesCan Irrational Numbers Be NegativenishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Complete Sets of NumbersDocument2 pagesComplete Sets of NumbersHazel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Math Is Fun-WPS OfficeDocument29 pagesMath Is Fun-WPS OfficeIp NetworkNo ratings yet
- Real NumberDocument15 pagesReal NumberSaksham Business SolutionsNo ratings yet
- NumbDocument25 pagesNumbZulkifli Paldana AkbarNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude: WWW Upscmantra COMDocument12 pagesQuantitative Aptitude: WWW Upscmantra COMSuresh GangavarapuNo ratings yet
- Number Theory (Krishna Sir)Document52 pagesNumber Theory (Krishna Sir)Anonymous nJB6aNTswZ100% (2)
- Basic Maths 1Document2 pagesBasic Maths 1Nandhini RanimohanNo ratings yet
- Number Systems 1Document16 pagesNumber Systems 1Priyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Number Systems 1Document19 pagesNumber Systems 1Priyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- GMAT Club Math Book June5Document95 pagesGMAT Club Math Book June5anilk12345No ratings yet
- Concept of Number System: - : by Rafay Sheikh Class 9 Summer Vacation HomeworkDocument9 pagesConcept of Number System: - : by Rafay Sheikh Class 9 Summer Vacation HomeworkRafay SheikhNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Maths 03-08-18Document9 pagesStudy Notes Maths 03-08-18Ajesh mohan100% (1)
- AQA Computer Science A-Level 4.5.1 Number Systems: Advanced NotesDocument5 pagesAQA Computer Science A-Level 4.5.1 Number Systems: Advanced Notestrickster jonasNo ratings yet
- Theory of NumbersDocument106 pagesTheory of NumberspreetyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Numbers: Numbers and Number LineDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Numbers: Numbers and Number LinerajatNo ratings yet
- Measurement GR 11Document8 pagesMeasurement GR 11Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- GMAT Club Math Book v3 - Jan-2-2013Document126 pagesGMAT Club Math Book v3 - Jan-2-2013prabhakar0808No ratings yet
- Methods and Techniques For Business Data Analysis: Unit-1 Number SystemDocument23 pagesMethods and Techniques For Business Data Analysis: Unit-1 Number System24.7upskill Lakshmi V75% (4)
- Two Irrational Numbers Whose Sum Is RationalDocument4 pagesTwo Irrational Numbers Whose Sum Is RationalnishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1 The Set of Real NumbersDocument59 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1 The Set of Real NumbersJeloubelle DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About Math in This Big Fat BookDocument12 pagesEverything You Need To Know About Math in This Big Fat BookRosalin HuynhNo ratings yet
- Elementary School ‘Grades 1 & 2: Math - Counting Practice – Ages 6-8’ eBookFrom EverandElementary School ‘Grades 1 & 2: Math - Counting Practice – Ages 6-8’ eBookNo ratings yet
- Trivia and Fun Facts 50 Random Facts That You Won't Believe Are TrueDocument7 pagesTrivia and Fun Facts 50 Random Facts That You Won't Believe Are TrueAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Narayana: Common Practice Test-7Document13 pagesNarayana: Common Practice Test-7AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.KDocument6 pagesFokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.K Fokfir@Lfkkukurj.KAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Some Interesting Fun Facts Fun Facts For Kids: Credit: CanvaDocument6 pagesSome Interesting Fun Facts Fun Facts For Kids: Credit: CanvaAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Nationalism in India: ST THDocument13 pagesNationalism in India: ST THAshutosh100% (1)
- Ch-4 Climate NotesDocument8 pagesCh-4 Climate NotesAshutoshNo ratings yet
- English Comm MSDocument8 pagesEnglish Comm MSAshutoshNo ratings yet
- DFGHJ: VBNJNKDocument2 pagesDFGHJ: VBNJNKAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Letter To Editor (Sample) : Sender's AddressDocument1 pageLetter To Editor (Sample) : Sender's AddressAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Pascal's Rule For Any Positive Integers N and KDocument1 pagePascal's Rule For Any Positive Integers N and KAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Popular Struggles and MovementsDocument6 pagesPopular Struggles and MovementsAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Parliament: Compost DustbinsDocument1 pageParliament: Compost DustbinsAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Mayurvihar-1 Class X Holiday HomeworkDocument6 pagesMayurvihar-1 Class X Holiday HomeworkAshutoshNo ratings yet
- ZxywqqwertyDocument2 pagesZxywqqwertyAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Yankii's Despacitoo .. Justin Bieber Also Sang Good Than Original .Crossed 2.9B Views On Utube Becoming No1Document1 pageYankii's Despacitoo .. Justin Bieber Also Sang Good Than Original .Crossed 2.9B Views On Utube Becoming No1AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Cleanliness Project Class - XB: (In Case The Model Depicts Practices From Outside India)Document1 pageCleanliness Project Class - XB: (In Case The Model Depicts Practices From Outside India)AshutoshNo ratings yet
- OggyDocument2 pagesOggyAshutoshNo ratings yet
- ZxywqqwertyDocument2 pagesZxywqqwertyAshutoshNo ratings yet
- Think +veDocument7 pagesThink +veAshutoshNo ratings yet