Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atmospheric Pressure
Uploaded by
Sadashiw Patil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageAtmospheric pressure at sea level is equal to 1 bar, which is also equivalent to 1 atmosphere (ATA) or 14.7 pounds per square inch (PSI). Absolute pressure is calculated by adding gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure. Pressure increases by 1 ATA for every 10 meters or 33 feet of depth below the surface.
Original Description:
Pressure unit conversion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAtmospheric pressure at sea level is equal to 1 bar, which is also equivalent to 1 atmosphere (ATA) or 14.7 pounds per square inch (PSI). Absolute pressure is calculated by adding gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure. Pressure increases by 1 ATA for every 10 meters or 33 feet of depth below the surface.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageAtmospheric Pressure
Uploaded by
Sadashiw PatilAtmospheric pressure at sea level is equal to 1 bar, which is also equivalent to 1 atmosphere (ATA) or 14.7 pounds per square inch (PSI). Absolute pressure is calculated by adding gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure. Pressure increases by 1 ATA for every 10 meters or 33 feet of depth below the surface.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
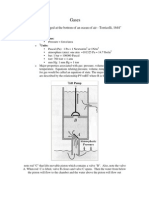
the pressure at sea level is called 1 atmosphere (ata) of pressure, and it is equal to 760mmHg /
30inHg / 14.7psi or 1 bar.
Absolute pressure = Gauge Pressure + Atmospheric Pressure. Atmospheric pressure at sea level= 1 Bar
which also equals 1 ATM (Atmosphere) which also = 14.7 PSI. All those three are equivalent, just in
different units. So in order to get an Absolute pressure, one has to add the gauge pressure + the
atmospheric Pressure. ATA is absolute.
Example, at a depth of 0 meters (Sea level) a gauge would read 0 Bar/0ATM/0PSI. In order to get the
absolute pressure at sea level you need to add the Gauge pressure of 0 and the atmospheric pressure of
1 BAR/1 ATM. 0 ATM (gauge) + 1 ATM (atmosphere) = 1 ATA. So the ATA at sea level is 1 ATA.
Pressure increases by 1 ATA for every 10M or 33FT.
Now at a depth of 10 meters the gauge pressure is now 1 BAR/1ATM. In order to get the absolute
pressure at this depth, you need to take the gauge pressure of 1 BAR/1ATM and add atmospheric
pressure which remains constant at 1BAR/1ATM. That is how you get the 2 ATA at a depth 10 M or 33FT.
You might also like
- Gauge Pressure AbsoluteDocument3 pagesGauge Pressure AbsoluteWin AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Details of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)Document3 pagesDetails of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)chockalingam athilingamNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?Document2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?reach_arindomNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Static Fluid PressureDocument5 pagesExperiment 7 Static Fluid PressureDham DoñosNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesFluid Statics Lecture NotesChailynn CanilaoNo ratings yet
- MANOMETERS NotesDocument5 pagesMANOMETERS NotesKawie AñeroNo ratings yet
- CHPTERTHREEFluidStaticandItsApplicationsDr SalahN Farhan PDFDocument20 pagesCHPTERTHREEFluidStaticandItsApplicationsDr SalahN Farhan PDFHana ShenNo ratings yet
- ME LabDocument32 pagesME LabiamjemahNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pressure MeasurementDocument49 pagesIndustrial Pressure MeasurementArjay T. EspinoNo ratings yet
- 48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsDocument29 pages48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsHussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- 3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFDocument7 pages3.) Principles of Hydrostatics PDFShan Yi HaiNo ratings yet
- Notes Chem FinalsDocument20 pagesNotes Chem FinalsShirley Anne ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9Document23 pagesUnit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesDocument47 pagesFluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesSin Za DolaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticsDocument82 pagesTopic 2 - Ecw 211-Fluid StaticssonghahoonNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 PressureDocument5 pagesTopic 4 PressureRaymund SuaybaguioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8-FluidDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 8-FluidRN Builder IpohNo ratings yet
- O'level Physics PressureDocument11 pagesO'level Physics PressureToretto100% (1)
- PressureDocument65 pagesPressuremh3611462No ratings yet
- SIALANA Pressure of GasDocument14 pagesSIALANA Pressure of GasTito V. Bautista Jr.No ratings yet
- PressureDocument62 pagesPressureZehra FarhanNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument32 pagesHydrostaticsdaphcosiNo ratings yet
- LO8 Session 01Document52 pagesLO8 Session 01Abo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- 5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentDocument1 page5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentAlessandroNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit PressureDocument51 pages3 Unit PressureRalph Ian GodoyNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocument20 pages5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureTrixia DuazoNo ratings yet
- HYDROSTATICDocument8 pagesHYDROSTATICryan valerioNo ratings yet
- Gauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)Document3 pagesGauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)SherwinNo ratings yet
- AtmosphericDocument3 pagesAtmosphericTalha GorsiNo ratings yet
- PleteDocument47 pagesPletediamantechennieNo ratings yet
- M11 - Principle of HydrostaticsDocument15 pagesM11 - Principle of HydrostaticsAlessandra SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter1 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 InstrumntdfsDocument4 pagesChapter2 InstrumntdfsdfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter1 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter2 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument10 pagesPressureklaudioajdini9No ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument3 pagesPRESSUREchristianjamestimNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Stationary FluidsDocument8 pagesPressure in Stationary FluidsHIPAPNo ratings yet
- Ther 1 - 111114Document33 pagesTher 1 - 111114So Nny0% (1)
- Konversi TekananDocument4 pagesKonversi TekananHuyuth HuyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Physics Reporting 2ND Sem 1Document48 pagesFluid Mechanics Physics Reporting 2ND Sem 1Ma Faustina GeronaNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument1 pagePressureDevineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lvijayabharathi_vijivijiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3آڃمْڊ آلُنْمْرNo ratings yet
- 01.hazards of Trapped Pressure & Vacuum-4Document2 pages01.hazards of Trapped Pressure & Vacuum-4rahulNo ratings yet
- Fluid - Is A Substance That ContinuallyDocument8 pagesFluid - Is A Substance That ContinuallybenjerickNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Marine Hydrodynamics I - Fluid Statics - Part 2Document20 pagesLecture 3 Marine Hydrodynamics I - Fluid Statics - Part 2Khalid BaragaNo ratings yet
- Special Section - Temperature & Pressure - The Physics of Pressure - IsADocument3 pagesSpecial Section - Temperature & Pressure - The Physics of Pressure - IsAkumar_chemicalNo ratings yet
- 0-1air TheoryDocument132 pages0-1air TheorylearningzabatNo ratings yet
- 5 2018 03 05!01 13 43 PMDocument40 pages5 2018 03 05!01 13 43 PMquike6041-150% (2)
- KhalidDocument3 pagesKhalidSyed Adnan AqibNo ratings yet
- CHPTERTHREEFluidStaticandItsApplicationsDr Salahn FarhanDocument21 pagesCHPTERTHREEFluidStaticandItsApplicationsDr Salahn FarhanAnonymous ldkl4EXqefNo ratings yet
- Notes Lecture 2 Fluid StaticsDocument42 pagesNotes Lecture 2 Fluid StaticsPranavMehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a GasesDocument12 pagesChapter 1a GasesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREZoteloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PRESSURE - January 2015 1Document25 pagesChapter 5 PRESSURE - January 2015 1MustaphaNo ratings yet
- HSSRptr-Plus One Chapter10 PhysicsDocument24 pagesHSSRptr-Plus One Chapter10 PhysicsSPARTANo ratings yet
- Example. Average Molecular Weight of AirDocument10 pagesExample. Average Molecular Weight of AirLinda Leon TomaNo ratings yet
- Pressure 130723134649 Phpapp02Document76 pagesPressure 130723134649 Phpapp02Syazwana ElleasNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Refractory Inspection-3Document2 pagesRefractory Inspection-3Sadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Apendix ADocument1 pageApendix ASadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Risk MGMT Thrugh Process ApproachDocument1 pageRisk MGMT Thrugh Process ApproachSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Recognition of Competent Person Under SMPV 0Document6 pagesRecognition of Competent Person Under SMPV 0Sadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Safety Goggles 1) Sure Safety 1.1) 3M Indoor - Outdoor Safety EyewearDocument2 pagesSafety Goggles 1) Sure Safety 1.1) 3M Indoor - Outdoor Safety EyewearSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- The Static and Mobile Pressure VesselsDocument28 pagesThe Static and Mobile Pressure VesselsSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Metric UnitsDocument47 pagesMetric UnitsSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument4 pagesProject Quality ManagementSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- EOI For Competent Persons Under SMPV (U) Rules 2016Document2 pagesEOI For Competent Persons Under SMPV (U) Rules 2016Sadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Pressure Conversion PDFDocument1 pagePressure Conversion PDFSadashiw Patil100% (1)
- Boilers and Hrsgs 171: Fig. 7.4 Pressure ConversionsDocument1 pageBoilers and Hrsgs 171: Fig. 7.4 Pressure ConversionsSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Plate InspectionDocument5 pagesPressure Vessel Plate InspectionSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Dail Indicator Shaft Alignment (Sag)Document3 pagesDail Indicator Shaft Alignment (Sag)Sadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Travel Camera Comparison TableDocument1 pageTravel Camera Comparison TableSadashiw Patil0% (1)
- Company ProfileDocument9 pagesCompany ProfileSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Determination of Necessary Preheating Temperature in Steel WeldingDocument7 pagesDetermination of Necessary Preheating Temperature in Steel WeldingKelvin LabarezNo ratings yet
- 04 Welding Consumables Control (Welder)Document1 page04 Welding Consumables Control (Welder)Sadashiw PatilNo ratings yet