Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notebook 1 Genral Physics Vocab
Uploaded by
api-335583967Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notebook 1 Genral Physics Vocab
Uploaded by
api-335583967Copyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL PHYSICS FORMULAS
SI Base Units
Base Quantity
Unit Name
Amount of substance
Mole
Unit
Symbol
Mol
Electric current
Ampere
Length
Centimeters
Or
Inches
Cm
Luminous intensity
Candela
Cd
Mass
Kilogram
Kg
Time
Second
in
When Are They Used
The amount of a
chemical substance that
contains as many
elementary entities
(atoms, molecules, ions,
electrons, or photons)
In radiology we use
Amperage in our mAs.
We stepdown from
amperage to
milliamperage (mA) for
the use of how many
protons are projected
towards the patient.
We may sometimes use
cm or inches to measure
the thickness of a
patient or to measure
the SID (source to image
distance)
Luminous Intensity, in a
given direction, a source
that emits
monochromatic
radiation of frequency
540x10^12 Hertz and
has a radiant intensity in
the direction of 1/683
Watt per steradian.
Kilograms is a unit of
measurement to weigh
something/someone
Used with mA stated
above, we combine
seconds with mA to
create mAs. Which is the
amount of photons
projected to a patient
Temperature
Kelvin
per x amount of
seconds.
Used along side with
Fahrenheit and Celcius
to measure temperature
SI Derived Units
Name
Square meter
Cubic meter
Meter per
second
Meter per
second squared
Hertz
Symbol
M2
M3
m
s
m
s2
Hz
Newton
Pascal
Joule
Watt
N
Pa
J
W
Coulomb
Volt
C
V
When Are They Used
Area
Volume
Speed and Velocity
Acceleration
Hertz is typically used to measure the current in the
x-ray tube
Force
Pressure and stress
Energy, work, quantity of heat
Watts is used to measure the amount of electrical
power and radiant flux.
Electric charge and quantity of electricity.
Volts are used in the xray circuit but are upgraded to
Kilovolts inside the tube through the step up
transformer to increase the current inside the tube.
(used for the kVp which determines the penetrability
of the photons)
As well as electrical potential difference and
electromotive force
Ohm
Electrical resistance
Weber
Telsa
Becquerel
Gray
Sievert
Wb
T
Bq
Gy
Sv
Magnetic Flux
Magnetic Flux Density
Activity of the radionuclide
Absorbed dose, specific energy
Dose equivalent
Prefixes used to designate multiples of base units
Pref
x
Symb
ol
Meaning
Multiple of base
unit
Tera
Giga
Meg
a
Kilo
Centi
Milli
T
G
M
Trillion
Billion
Million
1,000,000,000,000
1,000,000,000
1,000,000
Scientif
c
Notation
1012
109
106
k
c
m
1,000
1/100 or .01
1/1000 or .001
103
10-2
10-3
Micro
Thousand
One hundredth
One
thousandth
One millionth
10-6
Nano
One billionth
pico
One trillionth
1/1000000 or .
000001
1/1000000000000
or .000000001
1/1000000000000
or .000000000001
10-9
10-12
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Notebook 2Document4 pagesNotebook 2api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 5Document2 pagesNotebook 5api-335583967No ratings yet
- Final Notebook 10 3Document2 pagesFinal Notebook 10 3api-335583967100% (1)
- Notebook 11Document4 pagesNotebook 11api-335583967No ratings yet
- Digital vs. Film-Screen Radiography: Notebook 7Document5 pagesDigital vs. Film-Screen Radiography: Notebook 7api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document6 pagesNotebook 12api-335583967No ratings yet
- Final Notebook 10 2Document3 pagesFinal Notebook 10 2api-335583967No ratings yet
- Final Notebook 10Document2 pagesFinal Notebook 10api-335583967No ratings yet
- Single Emulsion Notebook 3Document1 pageSingle Emulsion Notebook 3api-335583967100% (1)
- Notebook 8Document2 pagesNotebook 8api-335583967No ratings yet
- Sensitivity SpeckDocument2 pagesSensitivity Speckapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Double Emulsion Notebook 3Document1 pageDouble Emulsion Notebook 3api-335583967No ratings yet
- Parallel Grid Notebook 2Document1 pageParallel Grid Notebook 2api-335583967No ratings yet
- Intensifying Screen Notebook 3Document1 pageIntensifying Screen Notebook 3api-335583967No ratings yet
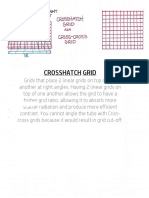
- Crosshatch Grid Notebook 2Document1 pageCrosshatch Grid Notebook 2api-335583967No ratings yet
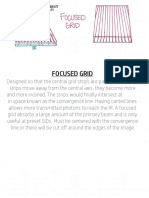
- Focused Grids Notebook 2Document1 pageFocused Grids Notebook 2api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document3 pagesNotebook 3api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 9Document7 pagesNotebook 9api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 9 GeneratorsDocument2 pagesNotebook 9 Generatorsapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 15 All The StepsDocument2 pagesNotebook 15 All The Stepsapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 4Document1 pageNotebook 4api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 6 X Ray CircuitDocument1 pageNotebook 6 X Ray Circuitapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 5 - Fleming Hand RuleDocument3 pagesNotebook 5 - Fleming Hand Ruleapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document1 pageNotebook 12api-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 10 Anode Cooling ChartDocument1 pageNotebook 10 Anode Cooling Chartapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 9 GeneratorsDocument2 pagesNotebook 9 Generatorsapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 2 Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesNotebook 2 Atomic Structureapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Notebook 4 Electrical CircuitDocument4 pagesNotebook 4 Electrical Circuitapi-335583967No ratings yet
- Home PageDocument1 pageHome Pageapi-335583967No ratings yet