0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views3 pagesJim Davis Meeting: Water Treatment Calculations
The document provides information to calculate:
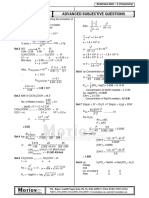
1) The amount of precipitate formed and alkalinity consumed from adding 68 mg/L of copperas. It calculates 0.0435 g/L of precipitate and 24.4736 mg/L of alkalinity consumed as CaCO3.
2) The alum dosage, mass of solids removed, and alkalinity consumed for treating 14.5 MGD of water with 650 mg/L TSS. It calculates 4910.5395 kg/day of alum, 569787.066 kg of solids removed, and 42.9293 mg/L of alkalinity consumed as CaCO3.
3) The amount of
Uploaded by
JHuvieCLaireCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views3 pagesJim Davis Meeting: Water Treatment Calculations
The document provides information to calculate:
1) The amount of precipitate formed and alkalinity consumed from adding 68 mg/L of copperas. It calculates 0.0435 g/L of precipitate and 24.4736 mg/L of alkalinity consumed as CaCO3.
2) The alum dosage, mass of solids removed, and alkalinity consumed for treating 14.5 MGD of water with 650 mg/L TSS. It calculates 4910.5395 kg/day of alum, 569787.066 kg of solids removed, and 42.9293 mg/L of alkalinity consumed as CaCO3.
3) The amount of
Uploaded by
JHuvieCLaireCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd