Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rate of Chemical Reaction
Uploaded by
whitneyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rate of Chemical Reaction
Uploaded by
whitneyCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 : Rate of reaction
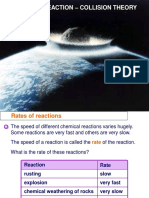
What is rate of reaction ?
Measures the speed at which reactants are converted into products in a chemical reaction
Time taken for a fast reaction is short whereas time taken for short reaction is long
When a reaction occurs , the quantity of a reactant decrease with time and quantity of product increase
with time
Rate of reaction is defined as the change in a selected quantity during a reaction per unit time
Reaction between magnesium and diute sulphuric acid
Two changes is observed
Mass of magnesium ( the reactant ) decrease with time
Volume of hydrogen gas increase with time
Rate of reaction can be measured change in the mass of magnesium or the volume of hydrogen
gas
Rate of reaction can be measured in two ways :
a) average rate of reaction
b) rate of reaction at a given time
Factors affecting the rate of reaction
- Total surface area / particle size ( size smaller , total exposed surface area larger , rate increase)
- Concentration of a reactant ( conc increase , rate increase )
- Temperature
- Use of catalyst ( a substance use to increase the rate )
- Pressure of the reactants ( pressure increase , rate also increase )
Characteristic of catalyst
- Remains chemically uncanged
- Does not change the quantity of product
- Specific in its action
- Small amount of catalyst needed to achieve increase In rate
Exercise :
1. 1 g of excess magnesium powder is added to 50cm3 of 0.5mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid at room
temperature . Figure below shows the curve obtained when the volume of hydrogen gas
liberated against time is plotted .
The experiment is repeated using 25cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 HCL at 80oC to replace 50 cm3 of 0.5mol
dm-3 hydrochloric acid at room temperature . Copy and sketch the graph that you will expect to
obtained from the second experiment.
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of Reaction: Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Kadar Tindak BalasDocument10 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of Reaction: Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Kadar Tindak BalasameermxNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChemical KineticsitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Document 61Document2 pagesDocument 61Keandra JordanNo ratings yet
- AS-Level Reaction Kinetics Chapter NotesDocument8 pagesAS-Level Reaction Kinetics Chapter NotesArslnNo ratings yet
- Topic.6 Chemical ReactionsDocument22 pagesTopic.6 Chemical ReactionsJoyce AmirNo ratings yet
- IA - Metals and AcidsDocument3 pagesIA - Metals and Acids14nganhc1No ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesRate of Reactionnatasha_muslim93No ratings yet
- Rates of Chemical Reaction - PowerpointDocument16 pagesRates of Chemical Reaction - Powerpointmerezemenike272No ratings yet
- Speed of Reactions PDFDocument8 pagesSpeed of Reactions PDFafoo1234No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesChapter 8 Chemical ReactionsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Rates of chemical reactionsDocument11 pagesRates of chemical reactions류성의No ratings yet
- Rate NotesDocument16 pagesRate NotesMegan GohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Form 5Document2 pagesChemistry - Form 5Vasantha SowndappanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument4 pagesChemical ReactionaleezaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F5C1Document9 pagesChemistry F5C1Mohammad Nur SyafiqNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument12 pagesKineticsElvis NgandweNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument71 pages1.1 Rate of ReactionyiosahhNo ratings yet
- Unit - The Periodic TableDocument20 pagesUnit - The Periodic TableMaurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesChemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDon Amaru SarmaNo ratings yet
- Saturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsDocument6 pagesSaturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsKingford MwesoNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument22 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument10 pagesRates of ReactionAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Speed of Reaction SummaryDocument3 pagesSpeed of Reaction Summarychong5660% (5)
- Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChemical KineticsWiktoria KaczmarzykNo ratings yet
- Effect of Catalyst On The Rate of ReactionDocument9 pagesEffect of Catalyst On The Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriNo ratings yet
- Notes DECEMBER-2021 CH 10 - The Speed of A Reaction Grade: 9 Sub: ChemistryDocument4 pagesNotes DECEMBER-2021 CH 10 - The Speed of A Reaction Grade: 9 Sub: ChemistryAnish KanthetiNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument5 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumDocument22 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumChemistryKlipz100% (7)
- 2.2.4 Rate of Chemical ReactionDocument12 pages2.2.4 Rate of Chemical Reactiondansochristiana574No ratings yet
- Kinetics and Equilibria: Factors Affecting Reaction RatesDocument57 pagesKinetics and Equilibria: Factors Affecting Reaction RatesJana Abo elfotohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5 - Physical ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistry 5 - Physical Chemistryolivia.mar.sanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - ROR ReversibleDocument44 pagesChemical Reactions - ROR ReversibleAlia AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument10 pagesChap 7 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Activity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSDocument2 pagesActivity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSkiara menesesNo ratings yet
- (1123) Nat 5 Unit 1 RevisionDocument35 pages(1123) Nat 5 Unit 1 Revisions9dijdjiNo ratings yet
- Definition N FactorsDocument37 pagesDefinition N FactorsJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical KineticsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Chemical KineticsGodwin EdekheNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Rates of ReactionDocument4 pagesChemical Kinetics Rates of ReactionBobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical KineticsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Chemical KineticsGodwin EdekheNo ratings yet
- Effect of Catalyst Amount on Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition RateDocument74 pagesEffect of Catalyst Amount on Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition RateSao BăngNo ratings yet
- KINETICSDocument47 pagesKINETICSMarilia BonorinoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Rate of Reaction (1.2d)Document74 pages1.4 Rate of Reaction (1.2d)Amirul NaqibNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reaction NotesDocument13 pagesRates of Reaction NotesNia RamNo ratings yet
- Chemistrylabreport 2Document16 pagesChemistrylabreport 2api-361536038No ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument13 pagesRate of Reactionmakah2711No ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2Document48 pagesChemistry Paper 2Matty PNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5Document3 pagesChemistry Form 5alliey75% (8)
- Chemical Kinetics o Level 1Document8 pagesChemical Kinetics o Level 1Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- SPM Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesSPM Rate of ReactionAfida HamsaniNo ratings yet
- Revision For Short Test 2, 9ig, CH 8,9Document9 pagesRevision For Short Test 2, 9ig, CH 8,9husseinrabihhijaziNo ratings yet
- 1a Rates of Reaction Slides PDFDocument26 pages1a Rates of Reaction Slides PDFArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsryankyleacostaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionDocument19 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of ReactionRasidah Abd Samat100% (1)
- RatesDocument22 pagesRatesPeterNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument48 pagesRate of ReactionHAFSAH AHMADNo ratings yet
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- LCCI Examiniation Timetable January 2016Document8 pagesLCCI Examiniation Timetable January 2016whitneyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentwhitneyNo ratings yet
- MTDocument2 pagesMTwhitneyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentwhitneyNo ratings yet
- Num. Scoring Criteria MarksDocument12 pagesNum. Scoring Criteria MarkswhitneyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentwhitneyNo ratings yet
- 0e2048045 Acts-StudyDocument116 pages0e2048045 Acts-StudywhitneyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentwhitneyNo ratings yet
- Mission Trip Helping Others AbroadDocument1 pageMission Trip Helping Others AbroadwhitneyNo ratings yet
- Indices Log PDFDocument18 pagesIndices Log PDFwhitneyNo ratings yet
- Basic Words in Rungus LanguageDocument2 pagesBasic Words in Rungus LanguagewhitneyNo ratings yet
- MTDocument2 pagesMTwhitneyNo ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ReactionDocument2 pagesRate of Chemical ReactionwhitneyNo ratings yet
- High-Solids Epoxy Systems For Protective and Marine CoatingsDocument6 pagesHigh-Solids Epoxy Systems For Protective and Marine CoatingsJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- PH Ysicsguide: Basic Concepts of Statistical MechanicsDocument14 pagesPH Ysicsguide: Basic Concepts of Statistical MechanicsMNo ratings yet
- The Otto Schmidt's Inter-Stellar Dust TheoremDocument1 pageThe Otto Schmidt's Inter-Stellar Dust TheoremKC CampilanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionImdad JalaliNo ratings yet
- Yemigeba DocumentDocument78 pagesYemigeba DocumentDemelashNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Product Specification - RZBC (JUXIAN) - CAADocument1 page2017 - Product Specification - RZBC (JUXIAN) - CAAediasianagri100% (1)
- Squamocin-O and Squamocin-O, New Adjacent Bis-Tetrahydrofuran Acetogenins From The Seeds of Annona SquamosaDocument6 pagesSquamocin-O and Squamocin-O, New Adjacent Bis-Tetrahydrofuran Acetogenins From The Seeds of Annona SquamosaamensetNo ratings yet
- 301 Lab2Document9 pages301 Lab2Ryan BaleNo ratings yet
- Astm D971Document4 pagesAstm D971JORGE SANTANDERNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instruments in Water-Steam-Cycles: An Introduction For The Non-ChemistDocument27 pagesAnalytical Instruments in Water-Steam-Cycles: An Introduction For The Non-ChemistMaxi MaxiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument19 pagesChapter - 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsTilahun ArfichoNo ratings yet
- Metal Corrosion Causes and PreventionDocument23 pagesMetal Corrosion Causes and PreventionAman NikhareNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 SimpleDistillationDocument52 pagesTopic 2 SimpleDistillationJA NableNo ratings yet
- Pre-Final Examination Feb 2023Document1 pagePre-Final Examination Feb 2023Arun AchalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1Document27 pagesChapter 2.1wendye13No ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Elements (2nd Edition)Document14 pagesChemistry of The Elements (2nd Edition)mycomiccityNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785322035441 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2214785322035441 MainMohammad Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- Mariner 910 S - ENGDocument2 pagesMariner 910 S - ENGNindi Widia Devi RahmasariNo ratings yet
- The Astronet Infraestructure RoadmapDocument178 pagesThe Astronet Infraestructure RoadmapALNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Document24 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Mohmmad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- En 13237-2003 Terms and Definitions For Equipment and Protective Systems Intended For Use in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresDocument26 pagesEn 13237-2003 Terms and Definitions For Equipment and Protective Systems Intended For Use in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresGargiulo AnitaNo ratings yet
- APITECH 03 DecryptedDocument23 pagesAPITECH 03 Decryptedjokerveloz100% (2)
- EMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andDocument4 pagesEMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andChong Leong GanNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument2 pagesMeteorologyIoniță AndreeaNo ratings yet
- IS 401.2001 - Preservation of Timber PDFDocument30 pagesIS 401.2001 - Preservation of Timber PDFMehul BansalNo ratings yet
- Pericyclic ReactionsDocument5 pagesPericyclic ReactionsNurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument20 pagesClass Notesrockybhaighost97No ratings yet
- Absolute Dating PowerpointDocument15 pagesAbsolute Dating PowerpointJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulations of Gas-Solid Flow in An Industrial-Scale Circulatingfluidized Bed Furnace Using Subgrid-Scale Drag ModelsDocument10 pagesCFD Simulations of Gas-Solid Flow in An Industrial-Scale Circulatingfluidized Bed Furnace Using Subgrid-Scale Drag ModelsMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity ChartDocument2 pagesElectronegativity ChartDana FransenNo ratings yet