Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer The Following Questions:: 1.) Explain Your Observation
Uploaded by
Jose Mari Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesExperiment on Magnets
Original Title
Science Experiment Magnet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentExperiment on Magnets
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesAnswer The Following Questions:: 1.) Explain Your Observation
Uploaded by
Jose Mari SantosExperiment on Magnets
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:
1. ) Explain your observation.
I observed that when the compass is near the north and
south pole of bar magnet, the compass will directly point in
north-north pole and south-south pole. Its the compass who
move around or rotate in the bar magnet. The point of
direction of compass will also rotate depends on any point
around the magnetic bar. The compass needle is
magnetized and mounted in a way that allows it to move in
response to magnetic fields.
2.) Why did the compass behave that way?
The behavior of the compass might be a bit different in the
real world when you place it on top of the magnet. The
compass needle is magnetized and mounted in a way that
allows it to move in response to magnetic fields. When the
magnet is present, the north end of the needle (colored red)
is attracted to its magnetic field and aligns itself so that it is
pointing toward the object. The closer the magnet is to the
compass, the more powerful the effect. Even when the
magnet is removed, the compass is still being affected by
magnetic forces those associated with the Earth.
3.) What is magnetic field?
A magnetic field is a picture that we use as a tool to
describe how the magnetic force is distributed in the space
around and within something magnetic.
The magnetic field is described mathematically as a vector
field. An alternative way to represent the information
contained within a vector field is with the use of field lines.
Magnetic fields can be defined in a number of ways,
depending on the context. However, in general terms, it is
an invisible field that exerts magnetic force on substances
which are sensitive to magnetism. Magnets also exert forces
and torques on each other through the magnetic fields they
create.
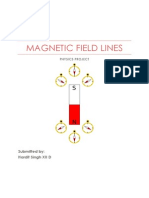
PART C: magnetic field direction
BAR MAGNET
UNLIKE POLES
LIKE POLES
A. MAGNETIC FIELD OF BAR MAGNET
B. MAGNETIC FIELD OF UNLIKE POLES
C. MAGNETIC FIELD OF LIKE POLES
You might also like
- The Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Magnetic PildDocument6 pagesMagnetic PildZephyr MikaealNo ratings yet
- What are Magnets? A Child's Guide to Understanding Magnets - Science Book for Elementary School | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandWhat are Magnets? A Child's Guide to Understanding Magnets - Science Book for Elementary School | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet
- Magnet and Magnetic Field Saraa Private SchoolDocument11 pagesMagnet and Magnetic Field Saraa Private Schoolmal7182281No ratings yet
- Question 1 MagnetismDocument44 pagesQuestion 1 MagnetismRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Report On Magnetic Field LinesDocument3 pagesReport On Magnetic Field LinesrafiullahNo ratings yet
- Module1 - MagnetismDocument35 pagesModule1 - MagnetismJoicsha Nicole FerrerNo ratings yet
- Physics Art ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Art Projectbetsy10245No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar MagnetDocument2 pagesMagnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar Magnetheartbreakkid132No ratings yet
- Our Magnetic Earth: The Science of GeomagnetismFrom EverandOur Magnetic Earth: The Science of GeomagnetismRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Chapter 2 Magnetic Effects of Current XDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Magnetic Effects of Current XPawan Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- What Is A Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Magnetic Fieldruxandra tudorascuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Curre-NotesDocument11 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Curre-Notesbassantsss93% (14)
- 11th WeekDocument6 pages11th WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- HE Agnetic Ompass: Arab Academy For Science, Technology &maritime TransportDocument50 pagesHE Agnetic Ompass: Arab Academy For Science, Technology &maritime Transportنزهة الكاتبةNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields and Magnetic Field Lines - Physics 101 - OpenStax CNXDocument1 pageMagnetic Fields and Magnetic Field Lines - Physics 101 - OpenStax CNXJin ChenNo ratings yet
- 312 Physics Eng Lesson18Document39 pages312 Physics Eng Lesson18Muthu PandiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 - Magnetic Field and Magnetic ForcesDocument12 pagesLesson 2.1 - Magnetic Field and Magnetic ForcesClyde EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Theories of MagnetismDocument6 pagesTheories of MagnetismAnonymous xZCFQbQ4No ratings yet
- Null 5Document8 pagesNull 5victormwamwaziNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanThế Anh Đỗ100% (1)
- Magnets Are CoolDocument5 pagesMagnets Are Coolhenryosullivan082No ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument13 pagesPhysics Notesemirben803No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Force: Alexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocument15 pagesMagnetic Field and Force: Alexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & TechnologyAli ElkilanyNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISM: Magnetic Fields: Laboratory Report of Group 2Document32 pagesMAGNETISM: Magnetic Fields: Laboratory Report of Group 2MelbertNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument82 pagesMagnetism and ElectromagnetismschlemielzNo ratings yet
- GRP1 Q4AA1 Magnetic-Field-LinesDocument8 pagesGRP1 Q4AA1 Magnetic-Field-LinesJoyce AmanteNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Notes - Unit 4, Part I: MagnetismDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Physics Notes - Unit 4, Part I: MagnetismAaron Kebede100% (1)
- CHAP 13-Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument19 pagesCHAP 13-Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentrakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- More Free Powerpoints at HTTPDocument56 pagesMore Free Powerpoints at HTTPhamang khullafah100% (1)
- p13.1 Magnetic Fields 11X1Document21 pagesp13.1 Magnetic Fields 11X1Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- What Are Magnetic FieldsDocument7 pagesWhat Are Magnetic FieldsIsaac KnarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document19 pagesChapter 13anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- Class X Phymagnetic Effects of Current SessiononeDocument3 pagesClass X Phymagnetic Effects of Current SessiononeAtharv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Notes Magnetic EffectDocument9 pagesNotes Magnetic EffectanandsahuNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetismtshiamo.dintweNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current ( (Term I)Document15 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current ( (Term I)Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 12Document7 pagesPhysics Project Class 12Keith Payne60% (20)
- Mod 3 Book 2 Magnetism InductanceDocument34 pagesMod 3 Book 2 Magnetism Inductanceranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Magnet and Earth MagnetismDocument36 pagesMagnet and Earth MagnetismSaurabh PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Science STD 7 Science Chapter 19 - Properties of A Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesScience STD 7 Science Chapter 19 - Properties of A Magnetic FieldRiddhi RaneNo ratings yet
- Magnets Class6Document34 pagesMagnets Class6Moumita DasNo ratings yet
- Physics-2 Q4-Student SDocument39 pagesPhysics-2 Q4-Student Sjohnella gutayNo ratings yet
- Makalah MagnetDocument29 pagesMakalah MagnetAinur RokhNo ratings yet
- BHAVANADocument5 pagesBHAVANADeepanya ReswinNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - MagnetismDocument5 pagesCSEC Physics - MagnetismCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Magnetism StudentDocument41 pagesMagnetism StudentSmurf TanNo ratings yet
- MODULE-NAVIGATION-leigh PagulayanDocument20 pagesMODULE-NAVIGATION-leigh Pagulayanleigh pagulayanNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Magnetism and Matter - 2604f953 23e2 48aa 87b8 9be454a9f4deDocument5 pagesChap 5 Magnetism and Matter - 2604f953 23e2 48aa 87b8 9be454a9f4dekushwahakailash348No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism (Autosaved)Document45 pagesElectromagnetism (Autosaved)Melai Rodriguez IbardalozaNo ratings yet
- AB Project PhyDocument8 pagesAB Project Phy1932-Adwait BobhateNo ratings yet
- Magn Tis LíthosDocument10 pagesMagn Tis Líthosgritchard4No ratings yet
- Magnets and Electromagnets - QuizizzDocument17 pagesMagnets and Electromagnets - QuizizzSelva Jothy GunasaigaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Class 12 Physics NCERT PART 1Document31 pagesChapter 5 Class 12 Physics NCERT PART 1krittinkalraNo ratings yet
- Physics - MagnetismDocument5 pagesPhysics - Magnetismpedromanaka59No ratings yet
- Prayers To St. Joseph of CupertinoDocument2 pagesPrayers To St. Joseph of CupertinoJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Fixed End MomentsDocument1 pageFixed End MomentsHarold DeanNo ratings yet
- Concrete VolumeDocument1 pageConcrete VolumeJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix EstimateDocument1 pageConcrete Mix EstimateJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Problem 7.10 Non-Uniform Beam ElementDocument1 pageProblem 7.10 Non-Uniform Beam ElementJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Problem 7.10 Non-Uniform Beam ElementDocument1 pageProblem 7.10 Non-Uniform Beam ElementJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Novena Pray Booklet PDFDocument3 pagesNovena Pray Booklet PDFJose Mari SantosNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures 5th Edition Solutions Manual PDFDocument131 pagesSteel Structures 5th Edition Solutions Manual PDFÍslàm Ñåbïl89% (18)
- Neville Goddard Master Course to Manifest Your Desires Into Reality Using The Law of Attraction: Learn the Secret to Overcoming Your Current Problems and Limitations, Attaining Your Goals, and Achieving Health, Wealth, Happiness and Success!From EverandNeville Goddard Master Course to Manifest Your Desires Into Reality Using The Law of Attraction: Learn the Secret to Overcoming Your Current Problems and Limitations, Attaining Your Goals, and Achieving Health, Wealth, Happiness and Success!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (284)
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYFrom EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthFrom EverandThe Three Waves of Volunteers & The New EarthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (179)
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1457)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)From EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- No Mud, No Lotus: The Art of Transforming SufferingFrom EverandNo Mud, No Lotus: The Art of Transforming SufferingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (174)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Deep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!From EverandDeep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Leveraging the Universe and Engaging the MagicFrom EverandLeveraging the Universe and Engaging the MagicRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Notes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendFrom EverandNotes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)
- The Afterlife Frequency: The Scientific Proof of Spiritual Contact and How That Awareness Will Change Your LifeFrom EverandThe Afterlife Frequency: The Scientific Proof of Spiritual Contact and How That Awareness Will Change Your LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (46)
- A New Science of the Afterlife: Space, Time, and the Consciousness CodeFrom EverandA New Science of the Afterlife: Space, Time, and the Consciousness CodeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Bedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsFrom EverandBedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- The Basics of a Course in MiraclesFrom EverandThe Basics of a Course in MiraclesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (226)
- The Beginner's Guide to the Akashic Records: The Understanding of Your Soul's History and How to Read ItFrom EverandThe Beginner's Guide to the Akashic Records: The Understanding of Your Soul's History and How to Read ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Workings of Energy in the Human Energy Field: A Psychic's PerspectiveFrom EverandThe Workings of Energy in the Human Energy Field: A Psychic's PerspectiveRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Heal: Discover Your Unlimited Potential and Awaken the Powerful Healer WithinFrom EverandHeal: Discover Your Unlimited Potential and Awaken the Powerful Healer WithinRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (38)
- The Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsFrom EverandThe Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (549)