Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future Proofing Procurement 2017
Uploaded by
coloradoresourcesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Future Proofing Procurement 2017
Uploaded by
coloradoresourcesCopyright:
Available Formats
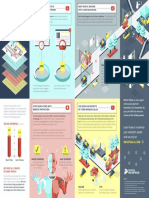
BATTLING MODERN SLAVERY Uzbekistan 1.
24
WORLD CUP EXPLOITATION
The construction programme for the FIFA 2022 World Cup in Qatar
has fuelled the demand for foreign labour, predominantly from
South Asia. However, as every migrant worker must be sponsored
by an employer and are unable to change jobs or leave the
EASTERN PROMISES
Disparities in work opportunities
between rural and urban populations
have resulted in an extremely high
internal migrant population, creating
Despite vast improvements in the global fight against modern- own role to play. Ensuring transparency and accountability country without their employers permission, employees are at opportunities for traffickers. The
day slavery over the past decade, more than 45 million people across globalised supply chains from direct providers to risk from systemic corruption and abuse. While the Arab state has government has issued a National
passed laws to protect workers rights and welfare standards, the Action Plan to Combat Human
remain victims of forced labour worldwide, with 58 per cent of indirect third-party sourcing is key, and the procurement sponsorship system continues to undermine the effectiveness of Trafficking, though its effectiveness is
those from five countries alone. While government intervention function is pivotal to not only safeguarding firms from big fines, these labour protections thought to be undermined by local
protectionism by regional officials
can have the biggest immediate impact, businesses have their but helping nations eradicate modern slavery once and for all Russia 1.05 prioritising economic performance over
anti-trafficking efforts
Myanmar 0.52
GOVERNMENT RESPONSE North Korea 1.1
Of the 161 countries analysed by the
Walk Free Foundation, just four engage
with businesses and investigate public
procurement the UK, Brazil, United States
and Australia. The UKs Modern Slavery Act, Cambodia 0.26
enacted in 2015, requires large, commercial
organisations to prepare a slavery
DIRECT LABOUR and human trafficking statement each
financial year, holding them accountable
Poland 0.18
Current systems of outsourced recruitment and
management of foreign migrant workers often for violations across their domestic and
put employees at risk of forced labour and human international supply chains UK
trafficking. In 2014 HP became the first IT company Turkey 0.48
to require direct employment of foreign migrant
workers across its supply chain. The transition to Ukraine 0.21
direct employment means that all foreign migrant
workers of HPs suppliers must be employed and Syria 0.26
paid directly by the supplier, not by agents, sub-
United
agents or third parties
States Japan 0.3
Afghanistan 0.37
Morocco 0.22
Iraq 0.4
China 3.39
Algeria 0.25 Nepal 0.23
Qatar South Korea 0.2
Mexico 0.38
India 18.35
CHANGING THE LAW Yemen 0.31
In 2016 the United States closed a
loophole in legislation that had previously
allowed goods made through forced Venezuela 0.2
labour to enter the country. Historically, Ethiopia 0.41
a consumptive demand clause in trade
laws meant forced labour-produced Colombia 0.31
Philippines 0.4
goods were legally imported if they were Uganda 0.24
not produced in such quantities in the Iran 0.5
United States as to meet the consumptive Kenya 0.19
Indonesia 0.74
demands of the United States
Peru 0.2
Nigeria 0.88 Egypt 0.57
Thailand 0.43
Argentina 0.18 Tanzania 0.34
CONFLICT MINERALS
Madagascar 0.41
Cobalt is an essential component
PREVALENCE OF MODERN SLAVERY in lithium-ion batteries used by
Estimated percentage of total population in modern slavery technology and car companies
worldwide. Around half of the
0% 5%
worlds supplies come from the Sudan 0.45
Democratic Republic of the
Congo, where substandard
Number of people in mining conditions and child labour Bangladesh 1.53
modern slavery (millions) are prevalent, often controlled
South Africa 0.25 RANA PLAZA AFTERMATH
by armed groups involved in
conflict. The OECDs due diligence More than a thousand workers died in 2013 after the
Modern slavery refers to the exploitation of people who cannot refuse
or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, abuse of power or standard covering minerals from collapse of the eight-story Rana Plaza commercial
deception, with treatment akin to a farm animal, according to the Walk conflict-affected and high-risk building. Following the disaster, brands and retailers joined
Free Foundation. This can take the form of human trafficking, forced labour, forces to establish common human rights standards on
areas means firms must do basic
debt bondage, forced or servile marriage, and the sale and exploitation of
checks to ensure the minerals they factory safety in the Bangladeshi garment industry. The
children. Pakistan 2.13
buy do not contribute to conflict Bangladesh Accord on Fire and Building Safety has now
Those in grey were not included in the index finance, human rights abuses been signed by more than 200 apparel brands, retailers
or corruption and importers worldwide
Democratic
Republic
Global Slavery Index 2016, Walk Free Foundation of the Congo 0.87
You might also like
- Don T Stop Til You Get Enough Michael JacksonDocument8 pagesDon T Stop Til You Get Enough Michael JacksonJose San MartinNo ratings yet
- SystemsDocument1 pageSystemsumNo ratings yet
- Rules of EngagementDocument4 pagesRules of EngagementSYED JUNAID AHMEDNo ratings yet
- B) Consent of The Contracting Parties, Object Certain and Cause or Consideration and Delivery of The ObjectDocument30 pagesB) Consent of The Contracting Parties, Object Certain and Cause or Consideration and Delivery of The ObjectSam Mie0% (1)
- Lab #10: Create A Cirt Response Plan For A Typical It InfrastructureDocument3 pagesLab #10: Create A Cirt Response Plan For A Typical It InfrastructureHờ Bờ LờNo ratings yet
- Gro Strategy 1Document1 pageGro Strategy 1emissimaNo ratings yet
- Denah Pelat, Kolom Dan Balok Full UIII-Elv 11.95Document1 pageDenah Pelat, Kolom Dan Balok Full UIII-Elv 11.95site engineer wkNo ratings yet
- Underwater Terrain Reconstruction From Forward-Looking Sonar ImageryDocument7 pagesUnderwater Terrain Reconstruction From Forward-Looking Sonar Imagery张啊康No ratings yet
- Peta Lintasan MkalDocument1 pagePeta Lintasan MkalFilzha Leeman FilzhaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Programming Case StudyDocument2 pagesCultural Programming Case Studydjb932661No ratings yet
- Safety Vest InformationDocument2 pagesSafety Vest InformationSyafiq KhalilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Micro MacroDocument1 pageChapter 5 - Micro MacroShayna ButtNo ratings yet
- LPUMC News & Views-March 2010Document6 pagesLPUMC News & Views-March 2010LafayetteParkUMCNo ratings yet
- Leupold 2005 CatalogDocument38 pagesLeupold 2005 CatalogCraig ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Housing For Fishermen Community (2019, DS-8, PUCAD)Document1 pageLow Cost Housing For Fishermen Community (2019, DS-8, PUCAD)Adnan Akhtar100% (1)
- Project No.3 (Plumbing) CAD File (JLCAE) - TRACING 01Document1 pageProject No.3 (Plumbing) CAD File (JLCAE) - TRACING 01Kurt Laurhon CabahugNo ratings yet
- M007 MML Arc DWG Ucstedu Aa 00007 - Rev4.0Document1 pageM007 MML Arc DWG Ucstedu Aa 00007 - Rev4.0whalet74No ratings yet
- INYT Frontpage Global.20201229Document1 pageINYT Frontpage Global.20201229Hong KuangNo ratings yet
- RCC Slab Culvert Widening 1X3.0Document1 pageRCC Slab Culvert Widening 1X3.0Shivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- ABAC - 01-11 - Updated - Splited - LoRes - EN - FORMULADocument7 pagesABAC - 01-11 - Updated - Splited - LoRes - EN - FORMULAIoan Emil VostinarNo ratings yet
- CTFC EnglishDocument2 pagesCTFC EnglishSomclauNo ratings yet
- Asst. Nodal Officer Nagar Panchayat Koora (Kunra) Architect C.M.O / Nodal Officer Nagar Panchayat Koora (Kunra)Document1 pageAsst. Nodal Officer Nagar Panchayat Koora (Kunra) Architect C.M.O / Nodal Officer Nagar Panchayat Koora (Kunra)SHOAIB MEMONNo ratings yet
- Board - Conceptual SiteDocument1 pageBoard - Conceptual SiteRaizel CustodioNo ratings yet
- FT UsDocument16 pagesFT UsMARIO M TORRESANo ratings yet
- Typ. 2Nd and 3Rd Floor Framing Plan: E I K C A F B G D J HDocument1 pageTyp. 2Nd and 3Rd Floor Framing Plan: E I K C A F B G D J HSherly PocotNo ratings yet
- E-06.2 Misc - Ao180315Document1 pageE-06.2 Misc - Ao180315Jhoanna CalloNo ratings yet
- DMM 1 e 007Document1 pageDMM 1 e 007mahesh reddy mNo ratings yet
- Perspective A: KarevDocument1 pagePerspective A: KarevJohn Paul GutierrezNo ratings yet
- IndiaDocument1 pageIndiahshanthiNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit 4storey PDFDocument1 pageShort Circuit 4storey PDFmayasNo ratings yet
- JABINES - PDF 1 1Document1 pageJABINES - PDF 1 1ice iceNo ratings yet
- Vdocument - in - Architect Pinehurst Elementary School Roof Roof A101 Roof Plan A102 Roof DetailsDocument6 pagesVdocument - in - Architect Pinehurst Elementary School Roof Roof A101 Roof Plan A102 Roof DetailsReden H. ArgawanonNo ratings yet
- ARCH 400 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesARCH 400 Lecture Notesrida.haider2002No ratings yet
- Architectural Updated Plans 2-23-21Document71 pagesArchitectural Updated Plans 2-23-21itamarNo ratings yet
- Of Door Of Door: Pdf 檔案使用 "Pdffactory Pro" 試用版本建立Document1 pageOf Door Of Door: Pdf 檔案使用 "Pdffactory Pro" 試用版本建立Mico FranceNo ratings yet
- Dumalag Original SignedDocument23 pagesDumalag Original Signedclark ian manuel ongchuaNo ratings yet
- Spectrin - Prashant Sir - RCC Foundation - R3-CLDocument1 pageSpectrin - Prashant Sir - RCC Foundation - R3-CLMadhavi GanbavaleNo ratings yet
- Komal Art Auction NoticeDocument7 pagesKomal Art Auction Noticeashutosh ranjan JhaNo ratings yet
- Estructura de Nomina 15-06-2022 - Ajustada Corregida - Multi Serviciosub-CeroDocument25 pagesEstructura de Nomina 15-06-2022 - Ajustada Corregida - Multi Serviciosub-CeroBRYAN NOGUERANo ratings yet
- Perspective: Office Blow Up PlanDocument1 pagePerspective: Office Blow Up Planmichael jan de celisNo ratings yet
- Latoza Auditorium 1Document1 pageLatoza Auditorium 1John Kerby EnmanuelNo ratings yet
- Top Beam Details1Document13 pagesTop Beam Details1AATVIK SHRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- A-28 Storey 998 Center-For Conts.-Updated112720Document30 pagesA-28 Storey 998 Center-For Conts.-Updated112720Allan AyesNo ratings yet
- 1GYKPRRLXRZ113138 WindowstickerDocument1 page1GYKPRRLXRZ113138 Windowstickerorca51588No ratings yet
- FTB65 EngDocument8 pagesFTB65 Engalfredo gutierrez del cerroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ClassificationDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - ClassificationShayna ButtNo ratings yet
- Structural - Pit Os S1Document1 pageStructural - Pit Os S1Kurt jan Bacon DamandamanNo ratings yet
- Planning Tech StoryDocument2 pagesPlanning Tech StoryHazel KwonNo ratings yet
- 9 Jones ST - Building Review - 200227 - PL PDFDocument8 pages9 Jones ST - Building Review - 200227 - PL PDFLeonardo Jr. SasingNo ratings yet
- Ngwebu Zaka RDocument1 pageNgwebu Zaka RMunyaradziNo ratings yet
- Proposed Scaffold Layout For Loading Gantry at 392-394 Seven Sister's Road, LondonDocument1 pageProposed Scaffold Layout For Loading Gantry at 392-394 Seven Sister's Road, LondonjmsNo ratings yet
- 03 Precitech 2.0 9 March 2024Document5 pages03 Precitech 2.0 9 March 2024ankeshp.pnaNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document26 pagesBook 2Anish NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram LVMDP-GP DomestikDocument1 pageSingle Line Diagram LVMDP-GP DomestikYasdiansyah Arya DinataNo ratings yet
- Proposed Second Storey Extension Residencial Project: Office of The Building Official D C B A C' B'Document1 pageProposed Second Storey Extension Residencial Project: Office of The Building Official D C B A C' B'JesusAntonioJugosNo ratings yet
- S1 PDFDocument1 pageS1 PDFRec Alfonso CincoNo ratings yet
- KURVA SadadadadadDocument1 pageKURVA Sadadadadadichsanadhip.itsNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz For Blueprint Checking 12-05-2022Document14 pagesDela Cruz For Blueprint Checking 12-05-2022Patrick Jerald CamilonNo ratings yet
- Foundation P L A N: E I K C F A B G J D HDocument1 pageFoundation P L A N: E I K C F A B G J D HSherly PocotNo ratings yet
- Lubigan Residence Working Drawings - Bidding DocumentsDocument23 pagesLubigan Residence Working Drawings - Bidding Documentsklent jalecoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation Rev-B After UpdationDocument100 pagesHydraulic Calculation Rev-B After UpdationkarthiNo ratings yet
- The World of ABAC Join The ABAC Advantage The Reference WorkstationDocument2 pagesThe World of ABAC Join The ABAC Advantage The Reference WorkstationSaša ŽivićNo ratings yet
- STEM Fair Careers InfographicDocument1 pageSTEM Fair Careers InfographicnandhunNo ratings yet
- Milliken's Complete Book of Instant Activities - Grade 4: Over 110 Reproducibles for Today's Differentiated ClassroomFrom EverandMilliken's Complete Book of Instant Activities - Grade 4: Over 110 Reproducibles for Today's Differentiated ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Blue FlowerDocument1 pageBlue FlowercoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Man I Feel Like A WomanDocument6 pagesMan I Feel Like A WomancoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- American GirlDocument7 pagesAmerican GirlcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Old Time Rock and RollDocument3 pagesOld Time Rock and RollcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Country FieldDocument1 pageCountry FieldcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Infographic Creation2Document1 pageInfographic Creation2coloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Education Around The WorldDocument1 pageEducation Around The WorldcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Black EmeraldDocument1 pageBlack EmeraldcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Connected LearningDocument1 pageConnected LearningcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Creative ActivitiesDocument1 pageCreative ActivitiescoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- The Daily Advertising Journey: Minute SecondsDocument1 pageThe Daily Advertising Journey: Minute SecondscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- User'S Guide: ImageclassDocument621 pagesUser'S Guide: ImageclasscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Infographic Creation 3Document1 pageInfographic Creation 3coloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- What Is Paralanguage InfographicsDocument1 pageWhat Is Paralanguage InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- 6 Principals of Conncted Learning InfographicsDocument1 page6 Principals of Conncted Learning InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Infographic CreationDocument1 pageInfographic CreationcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- 5 Tips For Creating InfographicsDocument1 page5 Tips For Creating InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Infographics of InfographicsDocument1 pageInfographics of InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Hordes For The Holidays InfographicsDocument1 pageHordes For The Holidays InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- The Worldwide Report InfographicDocument1 pageThe Worldwide Report InfographiccoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Education Around The World InfographicsDocument1 pageEducation Around The World InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Future of Outsourcing 2016Document1 pageFuture of Outsourcing 2016coloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Derelict Crab Pots in The Chesapeake Bay InfographicDocument1 pageImpacts of Derelict Crab Pots in The Chesapeake Bay InfographiccoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- The Ugly Co-Pay Surprise InfographicsDocument1 pageThe Ugly Co-Pay Surprise InfographicscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Workplace PensionsDocument1 pageWorkplace PensionscoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- The Best Word in The English DictionaryDocument1 pageThe Best Word in The English DictionarycoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Powering The Future 2016Document1 pagePowering The Future 2016coloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Made in FranceDocument1 pageMade in FrancecoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- Uk FintechDocument1 pageUk FintechcoloradoresourcesNo ratings yet
- 2 Actionable Items On National E-MPO Oversight Committee MeetingDocument2 pages2 Actionable Items On National E-MPO Oversight Committee MeetingOperation Isabela PPONo ratings yet
- Motion To Quash Practice CourtDocument7 pagesMotion To Quash Practice CourtSayeret MatkalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between IDS and IPS and FirewallDocument3 pagesDifference Between IDS and IPS and Firewall07939312No ratings yet
- C3e - 3 - Doldol v. PeopleDocument2 pagesC3e - 3 - Doldol v. PeopleAaron AristonNo ratings yet
- Violations of Traffic Rules QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesViolations of Traffic Rules QuestionnaireZubaer Ahmed Jewel100% (1)
- Case Study On Bhushan Steel Fire Accident, 2013Document15 pagesCase Study On Bhushan Steel Fire Accident, 2013pratikNo ratings yet
- Out - 28 IT FraudDocument41 pagesOut - 28 IT FraudNur P UtamiNo ratings yet
- East Orange OPRA Request FormDocument4 pagesEast Orange OPRA Request FormThe Citizens CampaignNo ratings yet
- 969 - Farrington Motion For AcquittalDocument8 pages969 - Farrington Motion For AcquittalJason TrahanNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law OutlineDocument13 pagesCriminal Law OutlineThomas Jefferson100% (1)
- Border Patrol Rape and Attempted Murder CaseDocument37 pagesBorder Patrol Rape and Attempted Murder Caseildefonso ortizNo ratings yet
- Manuel Figueroa v. The People of Puerto Rico, 232 F.2d 615, 1st Cir. (1956)Document8 pagesManuel Figueroa v. The People of Puerto Rico, 232 F.2d 615, 1st Cir. (1956)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CAMPANILLA CRIM November 15, 2018Document10 pagesCAMPANILLA CRIM November 15, 2018Eva TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Report of Attorney Discipline Board Hearing For Ralph KimbleDocument3 pagesReport of Attorney Discipline Board Hearing For Ralph KimbleWWMTNo ratings yet
- Hindus in South Asia and The Diaspora: A Survey of Human Rights, 2012Document267 pagesHindus in South Asia and The Diaspora: A Survey of Human Rights, 2012Hindu American FoundationNo ratings yet
- Legal Memorandum Mary Grace Merca Slight Physical InjuryDocument6 pagesLegal Memorandum Mary Grace Merca Slight Physical InjuryPat P. MonteNo ratings yet
- International Efforts To Combat Corruption: Prof. Dr. Mark PiethDocument18 pagesInternational Efforts To Combat Corruption: Prof. Dr. Mark PiethsemarangNo ratings yet
- News Reading ScriptDocument2 pagesNews Reading ScriptTASHANo ratings yet
- Gurwinder Singh v. State of Punjab PDFDocument14 pagesGurwinder Singh v. State of Punjab PDFHURI BABANo ratings yet
- Firefighters Arrive For Convention: Elphos EraldDocument10 pagesFirefighters Arrive For Convention: Elphos EraldThe Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Strict Liability - ProjectDocument7 pagesStrict Liability - ProjectRushabh Lalan100% (1)
- People Vs TuangcoDocument12 pagesPeople Vs TuangcoJan Veah CaabayNo ratings yet
- USTA Grievance ComplaintDocument4 pagesUSTA Grievance ComplaintIrene EngNo ratings yet
- Paper IVDocument13 pagesPaper IVNouman MumraizNo ratings yet
- Spring 2023 - PSY101 - SabahatDocument2 pagesSpring 2023 - PSY101 - SabahatMalikSabahatHussainAwanNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime & Security ElementsDocument21 pagesCyber Crime & Security ElementsLALIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- COMPLEX CrimeDocument29 pagesCOMPLEX CrimeJoebueyNo ratings yet