Professional Documents
Culture Documents
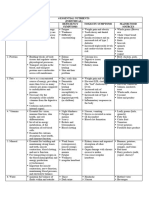
Nutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Rda or Dri Food Sources Deficiency Toxicity
Nutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Rda or Dri Food Sources Deficiency Toxicity
Uploaded by
Danilo Clerigo Sr.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Rda or Dri Food Sources Deficiency Toxicity
Nutrient Chart: Nutrient Function Rda or Dri Food Sources Deficiency Toxicity
Uploaded by
Danilo Clerigo Sr.Copyright:
Available Formats
NUTRIENT CHART
NUTRIENT FUNCTION RDA or DRI FOOD SOURCES DEFICIENCY TOXICITY
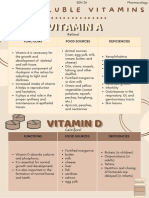
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
VITAMIN A Preserves integrity of Males: 1000 ug RE Breast milk, infant Night blindness, dry eyes, Fatigue; night sweats;
(Retinol) epithelial cells; formation Females: 800 ug RE formula, liver, egg yolk, poor bone growth, vertigo; headache; dry and
of rhodopsin for vision in dark green and deep impaired resistance to fissured skin; lips;
dim light; necessary for yellow vegetables and infection, papillary hyperpigmentation;
wound healing, growth, fruits. hyperkeratosis of the skin. retarded growth; bone
and normal immune pain; abdominal pain;
function. vomiting; jaundice;
hypercalcemia.
VITAMIN D Necessary for the Males: 5.0 ug Infant formula, egg yolk, Rickets (symptoms: Abnormally high blood
(Calciferol) formation of normal bone; Females: 5.0 ug liver, fatty fish, sunlight costochondral beading, calcium (hypercalcemia),
promotes the absorption (activation of 7- epiphyseal enlargement, retarded growth,
of calcium and dehydrocholesterol in the cranial bossing, bowed vomiting,
phosphorus in the skin). legs, persistently open nephrocalcinosis.
intestines. anterior fontanelle).
VITAMIN E May function as an Males: 10 mg -TE Breast milk; infant Hemolytic anemia in the May interfere with
(Tocopherol) antioxidant in the tissues; Females: 8 mg -TE formula; vegetable oils; premature and newborn; vitamin K activity leading
may also have a role as a liver; egg yolk; butter; hyporeflexia, and to prolonged clotting and
coenzyme; neuromuscular green leafy vegetables; spinocerebellar and retinal bleeding time; in anemia,
function. whole-grain breads, degeneration. suppresses the normal
cereals, and other fortified hematologic response to
or enriched grain iron.
products; wheat germ.
VITAMIN K Catalyzes prothrombin Males: 80 ug Infant formula, vegetable Prolonged bleeding and Possible hemolytic
(Phylloquinone) synthesis; required in the Females: 65 ug oils, green leafy prothrom- bin time; anemia; hyper-
synthesis of other blood vegetables, pork, liver. hemorrhagic manifesta- bilirubinemia (jaundice).
clotting factors; synthesis tions (especially in
by intestinal bacteria. newborns).
WATER-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
VITAMIN B1 Combines with Males: 1.2 mg Breast milk; infant Beriberi, neuritis, edema, There are NO TOXIC
(Thiamine) phosphorus to form Females: 1.1 mg formula; lean pork; wheat cardiac failure. LEVELS of Thiamine
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 1
thiamin pyrophosphate germ; whole-grain and known today. However,
(TPP) necessary for enriched breads, cereals, drowsiness or
metabolism of protein, and other grain products; hypersensitivity to
carbohydrate, and fat; legumes; potatoes. Thiamine is possible but
essential for growth, rare.
normal appetite, digestion,
and healthy nerves.
VITAMIN B2 Essential for growth; Males: 1.3 mg Breast milk; infant Photophobia, cheilosis, No toxic levels have been
(Riboflavin) plays enzymatic role in Females: 1.1 mg formula, meat; dairy glossitis, corneal established for
tissue respiration and acts products; egg yolk; vascularization, poor Riboflavin. However,
as a transporter of legumes; green growth. very high doses may
hydrogen ions; synthesis vegetables; whole-grain cause a passing itching,
of FMN and FAD. breads, cereals, and numbness, or tingling
fortified or enriched grain sensation.
products.
VITAMIN B3 Part of the enzyme system Males: 16 mg NE Breast milk; infant Pellegra: dermatitis, Transient due to the
(Niacin) for oxidation, energy Females: 14 mg NE formula; meat; poultry; diarrhea, dementia. vasodilating effects of
release; necessary for fish; whole-grain breads, niacin (does not occur
synthesis of glycogen and cereals, and fortified or with niacinamide)-
the synthesis and break- enriched grain products; flushing, tingling,
down of fatty acids. egg yolk. dizziness, nausea; liver
abnormalities;
hyperuricemia; decreased
LDL and increased HDL
cholesterol.
VITAMIN B5 Functions in the synthesis Males: 5.0 mg Breast milk; infant Fatigue; sleep Diarrhea; water retention.
(Pantothenic Acid) and breakdown of many Females: 5.0 mg formula; meat; fish; disturbances; nausea;
vital body compounds; poultry; liver; egg yolk; muscle cramps; impaired
essential in the yeast; whole-grain breads, coordination; loss of
intermediary metabolism cereals, and other grain antibody production.
of carbohydrate, fat, and products; legumes;
protein. vegetables.
VITAMIN B6 Aids in the synthesis and Males: 1.3 mg Breast milk; infant Microcytic anemia; Sensory neuropathy with
(Pyridoxine) breakdown of amino acids Females: 1.3 mg formula; liver; meat; convulsions; irritability. progressive ataxia;
and unsaturated fatty acids whole-grain breads, photosensitivity.
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 2
from essential fatty acids; cereals, or other grain
essential for conversion of products; legumes;
tryptophan to niacin; potatoes.
essential for normal
growth.
VITAMIN B7 Essential component of Males: 30 ug Breast milk, infant Seborrheic dermatitis; Although Biotin is very
(Biotin) en- zymes; important in Females: 30 ug formula, liver, meat, egg glossitis; nausea; potent and only very small
reactions involving the yolk, yeast, bananas, most insomnia. quantities are required,
lengthening of car- bon vegetables, strawberries, Biotin shows NO
chains; coenzyme carrier grapefruit, watermelon. TOXICITY.
of carbon dioxide; plays
an impor- tant role in the
metabolism of fatty acids
and amino acids.
VITAMIN B12 Essential for biosynthesis Males: 2.4 ug Infant formula, breast Pernicious anemia; Vitamin B12 has NO
Cyanocobalamin of nucleic acids and Females: 2.4 ug milk, meat, fish, poultry, neurologic deterioration. known toxicity from
(Cobalamin) nucleoproteins; red blood cheese, egg yolk, liver. excess intakes of food and
cell maturation; involved supplements. However,
with folate metabolism; acne, diarrhea, hives,
central nervous system itchy skin, peripheral
metabolism. vascular thrombosis may
exist from IV megadoses.
Furthermore, large doses
of Vit. B12 & B9 might
stimulate tumour growth.
FOLIC ACID Essential in the Males: 400 ug Breast milk; infant Poor growth; Masking of B12
(Folacin, Folate) biosynthesis of nucleic Females: 400 ug formula; liver; green leafy megaloblastic anemia deficiency symptoms in
acids; necessary for the vegetables; legumes; (concurrent deficiency of those with pernicious
normal maturation of red whole-grain breads, vitamin B12 should be anemia not receiving
blood cells. cereals, and fortified or suspected); impaired cyanocobalamin.
enriched grain products; cellular immunity.
legumes; oranges;
cantaloupe; lean beef.
VITAMIN C Essential in the synthesis Males: 60 mg Breast milk, infant Scurvy, pinpoint Nausea, abdominal
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 3
(Ascorbic Acid) of collagen (thus, Females: 60 mg formula, fruits (especially peripheral hemorrhages, cramps, diarrhea, possible
strengthens tissues and citrus fruits, papaya, bleeding gums, osmotic formation of kidney
improves wound healing cantaloupe, strawberries), diarrhea. stones.
and resistance to vegetables (potatoes,
infection);iron absorption cabbage).
and transport; water-
soluble antioxidant;
functions in folacin
metabolism.
MAJOR MINERALS/MACROMINERALS
SODIUM Helps regulate acid-base Males: 1500 mg Sodium chloride (table Nausea; cramps; Swelling in the
equilibrium and osmotic Females: 1500 mg salt), abundant in most vomiting; dizziness; extremities, high blood
pressure of body fluids; foods except fruit. apathy; exhaustion; pressure; increase risks for
plays a role in normal possible respiratory osteoporosis.
muscle irritability and failure.
contractility; influences
cell permeability.
CHLORIDE Helps regulate acid-base No RDA or DRI Breast milk, infant Usually accompanied by Can cause some problems
equilibrium and osmotic formula, sodium chloride sodium depletion; see with fluid retention and
pressure of body fluids; (table salt). Sodium. altered acid-base balance
component of gastric (although the main
juices. problem lies with the
sodium).
POTASSIUM Helps regulate acid-base Males: 4700 mg Breast milk; infant Muscle weakness; Decreased blood pressure,
equilibrium and osmotic Females: 4700 mg formula; fruits especially decreased intestinal tone stomach cramps, diarrhea,
pressure of body fluids; orange juice, bananas, and and distension; cardiac vomiting, irritability,
influences muscle activity, dried fruits; yogurt; arrhythmias; respiratory fatigue; irregular
especially cardiac muscle. potatoes; meat; fish; failure. heartbeat; tingling
poultry; soy products; sensation in the hands,
vegetables. feet & tongue; respiratory
failure, flaccid paralysis.
CALCIUM Builds and maintains Males: 1000 mg Breast milk, infant Rickets abnormal Excessive calcification of
bones and teeth; essential Females: 1000 mg formula, yogurt, cheese, development of bones. bone; calcification of soft
in clotting of blood; fortified or enriched grain tissue; hypercalcemia;
influences transmission of products, some green vomiting; lethargy.
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 4
ions across cell leafy vegetables (such as
membranes; required in collards, kale mustard
nerve transmission. greens, and turnip greens),
tofu (if made with calcium
sulfate), sardines, salmon.
PHOSPHORUS Builds and maintains Males: 700 mg Breast milk; infant Phosphate depletion Hypocalcemia (when
bones and teeth; Females: 700 mg formula; cheese; egg yolk; unusual effects renal, parathyroid gland not
component of nucleic ac- meat; poultry; fish; whole- neuromuscular, skeletal fully functioning).
ids, phospholipids; as grain breads, cereals, and systems as well as blood
coenzyme functions in other grain products; chemistries.
energy metabolism; legumes.
buffers intracellular fluid.
MAGNESIUM Required for many Males: 420 mg Breast milk; infant Muscle tremors; Diarrhea; transient
coenzyme oxidation- Females: 320 mg formula; whole-grain convulsions; irritability; hypocalcemia.
phosphorylation reactions, breads, cereals, and other tetany; hyper or
nerve impulse grain products; tofu; hypoflexia.
transmissions, and for legumes; green
muscle contraction. vegetables.
TRACE MINERALS/MICROMINERALS
IRON Essential for the formation Males: 10 mg Breast milk; infant Hypochromic microcytic Hemochromatosis;
of hemoglobin and Females: 15 mg formula; meat; liver; anemia; malabsorption; hemosiderosis.
oxygen trans- port; legumes; whole- grain irritability; anorexia;
increases resistance to breads, cereals, or pallor, lethargy.
infection; functions as part fortified or enriched grain
of enzymes involved in products; and dark green
tissue respiration. vegetables.
ZINC Component of many Males: 11 mg Breast milk; infant Decreased wound healing, Acute gastrointestinal
enzyme systems and Females: 8 mg formula; meat; liver; egg hypogonadism, mild upset; vomiting; sweating;
insulin. yolk; oysters and other anemia, decreased taste dizziness; copper
seafood; whole-grain acuity, hair loss, diarrhea, deficiency.
breads, cereals, and other growth failure, skin
fortified or enriched grain changes.
products; legumes.
IODINE Helps regulate thyroid Males: 150 ug Breast milk, infant Endemic goiter; depressed Possible thyroid
hormones; important in Females: 150 ug formula, seafood, iodized thyroid function; enlargement.
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 5
regulation of cellular salt. cretinism.
oxidation and growth.
SELENIUM May be essential to tissue Males: 55 ug Whole-grain breads, Myalgia; muscle Nausea; vomiting; nail
respiration; associated Females: 55 ug cereals, and other fortified tenderness; cardiac discoloration, brittleness,
with fat metabolism and or enriched grain myopathy; increased & loss; hair
vitamin E; acts as an products; onions; meats; fragility of red blood loss; fatigue; irritability;
antioxidant. seafood; dependent on soil cells; de- generation of and foul breath odor/garlic
content vegetables pancreas. breath.
COPPER Facilitates the function of No RDA or DRI Liver; kidney; poultry; Pallor, retarded growth, Wilsons disease copper
many enzymes and iron; shellfish; legumes; whole- edema, anorexia. de- posits in the cornea;
may be an integral part of grain breads, cereals, and cirrhosis of liver;
RNA, DNA molecules. other grain products. deterioration of
neurological processes.
MANGANESE Essential part of several No RDA or DRI Whole-grain breads, Impaired growth; skeletal In extremely high
enzyme systems involved cereals, and other grain abnormalities; neonatal exposure from
in protein and energy products; legumes; fruits; ataxia. contamination: severe
metabolism. vegetables (leafy). psychiatric and neurologic
disorders.
FLUORIDE Helps protect teeth against Males: 3.8 mg Fluoridated water. Increased dental carries. Mottled, discolored teeth;
tooth decay; may Females: 3.1 mg possible increase in bone
minimize bone loss. density; calcified muscle
insertions and exotosis.
CHROMIUM Required for normal No RDA or DRI Meat; whole-grain breads, Glucose intolerance; Severe gastrointestinal
glucose metabolism; cereals, and other fortified impaired growth; irritation/ulcers, nausea,
insulin cofactor. or enriched grain peripheral neuropathy; vomiting, diarrhea, fever,
products; brewers yeast; negative nitrogen balance; vertigo, cramping of
corn oil. de- creased respiratory muscles, intravascular
quotient. hemolysis, circulatory
collapse, liver damage.
MOLYBDENUM Part of the enzymes No RDA or DRI Organ meats; breads, Goutlike syndrome.
xanthine oxidase and cereals, and other grain
aldehyde oxidase, products; dark green leafy
possibly helps reduce vegetables; legumes.
incidence of dental
carries.
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 6
DANIELLE FAYE F. CLERIGO Page 7
You might also like
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel KairupanNo ratings yet
- XMP1 System Description R5.5 PDFDocument374 pagesXMP1 System Description R5.5 PDFIan CutinNo ratings yet
- Buying Homes in ForeclosureDocument182 pagesBuying Homes in Foreclosurermendgle100% (1)
- DOH HealthbeatDocument52 pagesDOH Healthbeatpurple0920No ratings yet
- Lipid-Lowering Agents: Critical FactsDocument22 pagesLipid-Lowering Agents: Critical Factsjyothi100% (1)
- Module 3 Reproductive Life Planning 2023Document13 pagesModule 3 Reproductive Life Planning 2023AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Vitamin MicronutrientsDocument11 pagesVitamin Micronutrientsprabhjot singhNo ratings yet
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Appendix C: Nutrient Chart - Function, Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms, and Major Food SourcesDocument5 pagesAppendix C: Nutrient Chart - Function, Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms, and Major Food SourcesMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Infant Nutrition and Feeding Infant Nutrition and FeedingDocument5 pagesInfant Nutrition and Feeding Infant Nutrition and FeedingGarv JainNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Unit ThreeDocument49 pagesNutrition Unit ThreeMelchizedek Tagarino TorioNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)Document1 pageFat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)Satyam AnandNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument15 pagesVitaminsFrederick E. EurolfanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument3 pagesVitamins Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 4 - VitaminsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 4 - VitaminsDahria CatalanNo ratings yet
- Presented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda SyaedDocument33 pagesPresented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda Syaedbobovovo bobovovoNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument61 pagesVitamins and MineralsMackoy LoganNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument6 pagesNutritionrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- Vitamin AsDocument37 pagesVitamin AsmarcelaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument5 pagesVITAMINSdetectionisimpressionNo ratings yet
- Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsDocument3 pagesKeratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsNimish BajareNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument5 pagesVitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Retinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin ADocument2 pagesRetinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin AsashellNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocument5 pages6 Essential NutrientsRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Rickets in Children, Osteomalacia in Adults, Osteoporoisis in Oldage Retards Growth. Hairfall & Change in Skin. Reproduction FailureDocument3 pagesRickets in Children, Osteomalacia in Adults, Osteoporoisis in Oldage Retards Growth. Hairfall & Change in Skin. Reproduction FailureHarshan VPNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument8 pagesVitaminsecho tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: Treatment of MalnutritionDocument4 pagesPediatrics: Treatment of Malnutritionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- Minerals Notes-CHAP 4Document4 pagesMinerals Notes-CHAP 4DIey ChokiEyNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy-Diet ChartDocument1 pagePregnancy-Diet Chartsathyag1No ratings yet
- Diet & NutritionDocument117 pagesDiet & NutritionSubbalekshmiNo ratings yet
- Essential Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesEssential Amino Acidssania ziaNo ratings yet
- IMP BiologyDocument22 pagesIMP Biologyvolesa9875No ratings yet
- 105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Document5 pages105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- जीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -Document2 pagesजीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -adityasjadhav2505No ratings yet
- A B C D E K: Functions of Food Guide Pyramid As A Guideline For A Well-Balanced DietDocument1 pageA B C D E K: Functions of Food Guide Pyramid As A Guideline For A Well-Balanced DietminasoonNo ratings yet
- Nur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikDocument7 pagesNur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikSyahirah YusriNo ratings yet
- Minerals TableDocument4 pagesMinerals Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- Shafiya Fatiha Rahmi 11181330000023Document2 pagesShafiya Fatiha Rahmi 11181330000023Shafiya RahmiNo ratings yet
- SM 6 NutritionDocument10 pagesSM 6 Nutritionrahul royNo ratings yet
- Vitamins in Human BodyDocument3 pagesVitamins in Human BodyJawad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Nutrition 6.1 Type of NutritionDocument9 pagesChapter 6: Nutrition 6.1 Type of NutritionmariposillasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of Foodpclim2010No ratings yet
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Yi YingNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietDocument27 pages6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-Lesson 3Document10 pagesNutrition-Lesson 3Lucrezia BordiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Table FormDocument7 pagesVitamins Table FormR-Chian Jose GermanpNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Purpose Deficiency Comments Source Water Soluble: Beriberi: PolyneuropathyDocument1 pageVitamin Purpose Deficiency Comments Source Water Soluble: Beriberi: PolyneuropathyArely CrzNo ratings yet
- MCHN Week 1november-18Document46 pagesMCHN Week 1november-18cyrilperry1No ratings yet
- Week 3 Biology Lesson Note SS1Document10 pagesWeek 3 Biology Lesson Note SS1Opeyemi AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument6 pagesVitamin and Mineral Chartsellitt ngNo ratings yet
- Digestive System, BookletDocument10 pagesDigestive System, BookletMikhael Devalino 1537036No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- Nutrient Chart Deficiency and ToxicityDocument7 pagesNutrient Chart Deficiency and Toxicityapi-256577647No ratings yet
- Nutrient Function Deficiency Symptoms Toxicity Symptoms SourcesDocument1 pageNutrient Function Deficiency Symptoms Toxicity Symptoms SourcesSatyam AnandNo ratings yet
- Vit EDocument2 pagesVit EkingpinNo ratings yet
- 5th Vitamins & MineralsDocument5 pages5th Vitamins & MineralsKennedy HouseNo ratings yet
- Nutrilite RefChartDocument4 pagesNutrilite RefChartgirishkumarhm50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- TOPIC: Health Education On Preventions of HIV and AIDS DefinitionDocument7 pagesTOPIC: Health Education On Preventions of HIV and AIDS DefinitionDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- ReqsDocument4 pagesReqsDanilo Clerigo Sr.100% (2)
- Severe Pre-Eclampsia Diagnostic TestsDocument2 pagesSevere Pre-Eclampsia Diagnostic TestsDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Parents Say Baby's Head Severed While Being Born in Cebu HospitalDocument2 pagesParents Say Baby's Head Severed While Being Born in Cebu HospitalDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics 2nd Edition Gould Test BankDocument21 pagesIntroductory Statistics 2nd Edition Gould Test Bankodilemelanie83au100% (31)
- SAP Finance NotesDocument131 pagesSAP Finance NotesMohammed MisbahuddinNo ratings yet
- Final 2023 Announcement Bcu 2023Document26 pagesFinal 2023 Announcement Bcu 2023I G. A. Ratna DewiNo ratings yet
- Panera Bread Company Case AnalysisDocument18 pagesPanera Bread Company Case AnalysisAmmar Yahya82% (11)
- AIR Modeller - Issue 73 (2017 08-09)Document68 pagesAIR Modeller - Issue 73 (2017 08-09)604457060100% (1)
- Pleiger Tank Measuring SystemDocument12 pagesPleiger Tank Measuring SystemPamellaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer's Perception Towards Honda Activa in Muzaffarpur CityDocument34 pagesA Study On Consumer's Perception Towards Honda Activa in Muzaffarpur CityabhaybittuNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test and Polarization Index TestDocument3 pagesInsulation Resistance Test and Polarization Index TestJoeDabidNo ratings yet
- Too Much Safety Ebook Rev 01Document16 pagesToo Much Safety Ebook Rev 01desurkarbNo ratings yet
- Handbook ISA 530Document17 pagesHandbook ISA 53025 - Trương Cao Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- Xslicer-SMX 160 KVDocument16 pagesXslicer-SMX 160 KVDoanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Process Design: Norsok StandardDocument29 pagesProcess Design: Norsok StandardRam MurtyNo ratings yet
- Msd80/81 Dme Flash Instructions: Please Read The Following NotesDocument10 pagesMsd80/81 Dme Flash Instructions: Please Read The Following NotesBolinha's Wash ClubNo ratings yet
- CG3 PDFDocument198 pagesCG3 PDFMauricio Arboleda ZapataNo ratings yet
- Trees of IndiaDocument6 pagesTrees of IndiaKonstantino LeoNo ratings yet
- Derivatives 304Document105 pagesDerivatives 304Fazal RehmanNo ratings yet
- Kendall's Coefficient of Colleration TDocument14 pagesKendall's Coefficient of Colleration TJoshua ArmestoNo ratings yet
- Jbase Editor Find and ReplaceDocument1 pageJbase Editor Find and ReplaceFolakunmi OjemuyiwaNo ratings yet
- Sheraton HRM Case SolutionDocument64 pagesSheraton HRM Case SolutionMohammad Rafi100% (4)
- Artificial Neural Networks in Data MiningDocument4 pagesArtificial Neural Networks in Data MiningAmitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- JAYSON Feasibility 3 PDFDocument68 pagesJAYSON Feasibility 3 PDFReyes Je AnNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1 Demand EstimationDocument9 pagesAssignment #1 Demand EstimationAnonymous PyzvD6No ratings yet
- Directory Sugar Refineries 2021 2022Document2 pagesDirectory Sugar Refineries 2021 2022J Paul VarelaNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras' & Trigonometry Past Paper QuestionsDocument46 pagesPythagoras' & Trigonometry Past Paper QuestionsinternationalmakkhayarNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris "Roleplay Ambulation": OlehDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris "Roleplay Ambulation": Olehnono NonoNo ratings yet
- CE On Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument2 pagesCE On Events After The Reporting PeriodalyssaNo ratings yet