Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Operations Management
Uploaded by
Asma Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views30 pagesvalue analysis and value engineering
Original Title
valueanalysisandvalueengineering-130308105420-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentvalue analysis and value engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views30 pagesOperations Management
Uploaded by
Asma Khanvalue analysis and value engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Name Roll No.
Ayush Dixit 2012005
Steffi Fernandes 2012022
Seema Popat 2012068
Mukesh Singh Rajput 2012033
Value Analysis
1. Cost reduction technique.
2. Organised creative approach.
3. Main focuses.
4. Birth Second World War.
5. Recent years -
Value Engineering.
Molecular Engineering.
Vertical Thinking.
What is Value
The minimum
money which has
to be expended in
purchasing or
manufacturing a
product to create
the appropriate
use of esteem
factors.
Division Of Value
1. Use of functional Value.
2. Esteem Value.
3. Cost Value.
4. Exchange Value.
Advantages of Value Analysis
It leads to improvements in product design so that, most
appropriate products are produced .
High quality (value) is maintained.
All-round efficiency is achieved by eliminating waste of various
types.
Cost savings provide a measure for judging managerial
effectiveness.
New ideas are generated and incorporated.
Teams spirit and morale are improved.
Areas requiring attention and improvement are pin pointed.
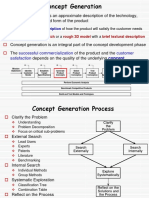
Procedure of Value Analysis
There is no standard approach or procedure
Ascertaining the needs and wants of customers.
Specifying the function of products and
components.
Determining the appropriate cost of desired
performance.
Identifying better alternatives in terms of works
procedures.
Implementation of Value
Analysis
Identifying the function:-
Primary.
Secondary.
Evaluation of the function by comparison :-
Basic question
does the function accomplish reliability at the best cost
Develop Alternatives.
Value Analysis Steps
1. Gather Information.
2. Measure Performance.
3. Analyse Functions.
4. Generate Ideas.
5. Evaluate and Rank Ideas.
6. Develop and Expand Ideas.
7. Present Ideas.
Value Engineering
Value engineering is a total of management
which approaches the question of saving cost
from the point of view of value.
Requires co-operation of all functional
departments.
In large organisations, there are value
engineering teams having full time jobs.
Value Engineering
Value and cost
Value = Function
Cost
Value: What the product is worth to the customer.
Function: Properties and qualities of product.
Cost: Money value of materials used, Labour &
indirect costs.
Value Engineering
Suggestion schemes
Suggestion scheme facilitates the work of
value engineering team.
The scheme helps in the changes of value
engineering and makes it implementation
easier.
Value Engineering
Requirement of a product
Use.
Esteem.
It is essential to be considered how much to
be added in order to sell the part.
The reasonable price of a product can be
obtained by comparing with a comparative product.
Value Engineering Approach
No standard approach discuss with team
members.
Subject Basic question Analysis Answer
Function What functions 1) Is there any possibility of elimination?
are performed? 2) What alternative methods are
available?
Material What is the 1) Can alternative material be used?
material 2) Can the specification be amended?
specification?
What quantity of 1) Is the size or weight of material
material should excessive?
be used? 2) Can the quality be reduced?
3) Will a cheaper material serve the same
purpose?
4) Is the cutting done economically
without waste?
Value Engineering Approach
Subject Basic question Analysis Answer
Labour Which are the 1) Are all the operations necessary?
direct labour 2) Will alternative operations be cheaper?
costs? 3) Can certain assembly operations be
modified?
Process Are the best 1) Are all the operations necessary?
Processes being 2) Will alternative operations be cheaper?
used? 3) Can certain assembly operations be
modified?
Standardizatio Are the materials 1) Can the materials be standardized?
n or components 2) Can a number of product use standard
standard? (common) parts?
3) Can methods be standardized?
Waste Control
Reasons for wastages in industry
Obsolescence
Surplus
Scrap
Role of Management in waste control
Proper inventory control
Materials management
Effective Co-ordination among departments
Input-Output Analysis
Systematic study of production structure.
Predict total production of each year.
Production structure of all the industries are to
be grouped together.
Output material of 1 sector becomes input raw-
materials for the other.
Original Information Innovation Evaluation Choice Implementation Review
Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase Phase
1. Product Design and
Development
1. Factors considered in product design :-
Customers requirement.
Operators Convenience.
Types of materials.
Work methods and equipment.
1. Product Design and
Development
2. Design.
3. Planning.
4. Specialized function.
5. Visible in long run.
2. Application of Value
Engineering
Overall quality and performance.
Work together to reduce cost.
Latest developments.
Service function.
Desired objective.
3. Simplification of Product
1. Elimination of undesirable features.
2. The main purpose is to improve quality and to
reduce unit costs.
Reduce cost and prices.
Reduction of undesirable materials.
3. Benefits.
You might also like
- Microbial OOS InvestigationsDocument12 pagesMicrobial OOS InvestigationsSairam EdupugantiNo ratings yet
- Operation AnalysisDocument16 pagesOperation AnalysisLyne LerinNo ratings yet
- Materials Enabled Designs: The Materials Engineering Perspective to Product Design and ManufacturingFrom EverandMaterials Enabled Designs: The Materials Engineering Perspective to Product Design and ManufacturingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Software Quality Chapter 1 2 3Document78 pagesSoftware Quality Chapter 1 2 3Thalia SerranoNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument25 pagesNOTESRonah Abigail BejocNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis and Value EngineeringDocument30 pagesValue Analysis and Value EngineeringAbhinav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis AND Value EngineeringDocument24 pagesValue Analysis AND Value EngineeringKumar KnNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis and ValueengineeringDocument27 pagesValue Analysis and ValueengineeringShyam Suryawanshi100% (1)
- Value Analysis and Value EngineeringDocument4 pagesValue Analysis and Value EngineeringrenuNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Value Engineering Use CaseDocument25 pagesGroup 5 - Value Engineering Use CaseParesh SwamiNo ratings yet
- Valueengineering 141206000637 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument36 pagesValueengineering 141206000637 Conversion Gate02 PDFRachanesh GhatgeNo ratings yet
- Mba Ii Unit IvDocument22 pagesMba Ii Unit IvrabindrakumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis 2 Reduce Cost Thru Value Engineering of Furniture ProductDocument8 pagesAnalysis 2 Reduce Cost Thru Value Engineering of Furniture Productgeoffrey g. monsantoNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering ExplainedDocument14 pagesValue Engineering Explainedalfred100% (1)
- Oct 22 Value Analysis & Engineering r1Document46 pagesOct 22 Value Analysis & Engineering r1syed wahid aliNo ratings yet
- Study On Value Engineering in Construction ProjectsDocument5 pagesStudy On Value Engineering in Construction ProjectsEditor IJRITCC100% (1)
- Lesson 10 Case Study on Value EngineeringDocument16 pagesLesson 10 Case Study on Value EngineeringarunNo ratings yet
- Ijser: An Analytical Way To Reduce Cost of A Product Through Value Engineering Employment (Case Study: Walton)Document7 pagesIjser: An Analytical Way To Reduce Cost of A Product Through Value Engineering Employment (Case Study: Walton)Shashank DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument13 pagesValue EngineeringSangivikumar S100% (1)
- Unit 3 PPCDocument49 pagesUnit 3 PPCRama Narasimha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Defining Business Need and Value AnalysisDocument39 pagesDefining Business Need and Value AnalysisRoshanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Process SelectionDocument9 pagesAssignment-1: Process SelectionSuhans BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Products and ProcessesDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Products and ProcessesKamble AbhijitNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument21 pagesMechanical Engineering DesignFarid AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis and Value EngineeringDocument22 pagesValue Analysis and Value EngineeringSuyash BiradarNo ratings yet
- 5th LectureDocument24 pages5th Lecturekhushboo58No ratings yet
- Operations Managment Part-4Document20 pagesOperations Managment Part-4Sai Rock SaiNo ratings yet
- 3-Types of Questions in EnglishDocument31 pages3-Types of Questions in EnglishDhimas AdharasetaNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument18 pagesValue Engineeringjohnplaya1234100% (1)
- The Concept of Value Analysis Was Developed During World War II by Lawrence D. Miles of General Electric CompanyDocument15 pagesThe Concept of Value Analysis Was Developed During World War II by Lawrence D. Miles of General Electric Companyrealguy556789No ratings yet
- ACCT2522 - Topic 3 - Introduction - Lecture 2023 Student Slides - 1 Per PageDocument47 pagesACCT2522 - Topic 3 - Introduction - Lecture 2023 Student Slides - 1 Per PageFreda DengNo ratings yet
- Value AnalysisDocument6 pagesValue AnalysisAMIYA KUMAR SAMALNo ratings yet
- Operation Management MidTermDocument10 pagesOperation Management MidTermNicholas ChiewNo ratings yet
- OM Unit IIDocument16 pagesOM Unit IIJagadish MaturuNo ratings yet
- R Chapter Design QuestionsDocument15 pagesR Chapter Design QuestionsBo RaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Case StudyDocument15 pagesLecture 10 Case StudyMrinalini ChopadeNo ratings yet
- W12 Module 10 - VeringJust-in-TimeDocument14 pagesW12 Module 10 - VeringJust-in-TimeLid AlessandreNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering and Value AnalysisDocument14 pagesValue Engineering and Value AnalysisZulfikar AfdholaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 IntroductionDocument59 pagesUNIT 1 Introductioncuajohnpaull.schoolbackup.002No ratings yet
- Value Analysis Technique to Reduce Costs While Retaining Product PerformanceDocument11 pagesValue Analysis Technique to Reduce Costs While Retaining Product PerformanceRuban ThomasNo ratings yet
- CVENG 423 - Module 4 - Construction Estimates and Values EngineeringDocument7 pagesCVENG 423 - Module 4 - Construction Estimates and Values EngineeringLester BiñasNo ratings yet
- Product Design and Development 1516079078 20707Document24 pagesProduct Design and Development 1516079078 20707Er Dinesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh: Product Design and DevelopmentDocument24 pagesChandigarh: Product Design and DevelopmentEr Dinesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4RUSYDUDDIN QUSYAIRINo ratings yet
- Sesi 9-DesignDocument22 pagesSesi 9-DesignViki SapriantoNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument6 pagesTotal Quality Managementahmed radwanNo ratings yet
- Industrial ManagementDocument14 pagesIndustrial Managementthefooox1No ratings yet
- AMED 01e PDFDocument22 pagesAMED 01e PDFAbenesh KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Decision MakingDocument39 pagesGroup 1 Decision Makinglyka.fermaaa100% (1)
- Implementation of Functional Analysis Using Value Analysis Value Engineering (Vave) On Car Outside HandleDocument6 pagesImplementation of Functional Analysis Using Value Analysis Value Engineering (Vave) On Car Outside HandleEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- OPERATION MANAGEMENT ANSWERSDocument17 pagesOPERATION MANAGEMENT ANSWERSCheru TerefeNo ratings yet
- Product DesignDocument27 pagesProduct DesignrubensNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs & VariancesDocument30 pagesStandard Costs & VariancesMaruelle Kate Jordan ParillaNo ratings yet
- The EcoDesign ChecklistDocument1 pageThe EcoDesign ChecklistPaolo BartoliNo ratings yet
- Operation AnalysisDocument22 pagesOperation AnalysisJahmmil A RamastaNo ratings yet
- OCT 2022 valueengineering-UNITDocument36 pagesOCT 2022 valueengineering-UNITsyed wahid aliNo ratings yet
- Product and Service DesignDocument30 pagesProduct and Service DesignElaine YapNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis.3980264.PowerpointDocument8 pagesValue Analysis.3980264.PowerpointAllied EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Human-Computer Interaction: Evaluation - Part IDocument18 pagesHuman-Computer Interaction: Evaluation - Part IaliumerNo ratings yet
- Theme 5 Management Science and Financial Management Course GuideDocument48 pagesTheme 5 Management Science and Financial Management Course Guidedanielnebeyat7No ratings yet
- Pune Bus ServiceDocument122 pagesPune Bus ServiceAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- A One-Equation Turbulence Model For Aerodynamic Flows: January 1992Document18 pagesA One-Equation Turbulence Model For Aerodynamic Flows: January 1992Asma KhanNo ratings yet
- Cost Control Cost ReductionDocument59 pagesCost Control Cost Reductionahmed nawazNo ratings yet
- Power Transmitting ElementsDocument20 pagesPower Transmitting ElementsAsma Khan100% (1)
- Lathe MachineDocument8 pagesLathe MachineAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Annual Calendar 2018 EnglDocument1 pageAnnual Calendar 2018 EnglSaketNo ratings yet
- Fasteners List.Document4 pagesFasteners List.Asma KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculation and Identification of The Aerodynamic ParametersDocument18 pagesCalculation and Identification of The Aerodynamic Parametersgustavo12No ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument13 pagesRefrigerationAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Grinding ProcessDocument5 pagesGrinding ProcessAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument7 pagesClutchesAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- System Suspension Simulink ModelDocument1 pageSystem Suspension Simulink ModelAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Redwood ViscometerDocument4 pagesRedwood ViscometerAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Ost ReductionDocument8 pagesOst ReductionAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Ost ReductionDocument8 pagesOst ReductionAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Study of IC EngineDocument11 pagesStudy of IC EngineAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Qualifications of A Product Design EngineerDocument10 pagesQualifications of A Product Design EngineerAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- R.L. MurtyDocument55 pagesR.L. MurtyAsma Khan0% (1)
- Block Diagram RepresentationDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram RepresentationAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Solid ModellingDocument14 pagesSolid ModellingAsma Khan100% (1)
- Design of ExperimentsDocument2 pagesDesign of ExperimentsAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Qualifications of A Product Design EngineerDocument10 pagesQualifications of A Product Design EngineerAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Control System - Thermal System TFDocument13 pagesControl System - Thermal System TFAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Cim DBMSDocument4 pagesCim DBMSAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit Response Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesUnit Response Analysis PDFAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Plate BendingDocument7 pagesPlate BendingAnonymous Clm40C1No ratings yet
- Stability & Routh Hurwitz CriteriaDocument18 pagesStability & Routh Hurwitz CriteriaAsma Khan100% (1)
- Unit Response Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesUnit Response Analysis PDFAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram RepresentationDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram RepresentationAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Manager-Job Description and Person SpecDocument3 pagesQuality Control Manager-Job Description and Person SpecPageduesca RouelNo ratings yet
- Sungov CatalogueDocument32 pagesSungov Cataloguepkrishna984No ratings yet
- Quality Manual ExampleDocument23 pagesQuality Manual ExampleMuhammad HaroonNo ratings yet
- Final Report 7Document61 pagesFinal Report 7syamlyNo ratings yet
- Data Visualization, Volume IIDocument33 pagesData Visualization, Volume IICharleneKronstedtNo ratings yet
- Performance Management System of KFC-with-cover-page-V2Document16 pagesPerformance Management System of KFC-with-cover-page-V2Tài Trần TấnNo ratings yet
- (2009) Satisfaccion Definition of QualityDocument17 pages(2009) Satisfaccion Definition of QualityCarlosOchoaNo ratings yet
- OPCRF School HeadDocument1 pageOPCRF School HeadJanus SalinasNo ratings yet
- TQM Definition, Approaches, Purpose, Gurus & BenefitsDocument9 pagesTQM Definition, Approaches, Purpose, Gurus & BenefitsMd Rabbi KhanNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Certification of Blowout Preventers (CAODC)Document18 pagesInspection and Certification of Blowout Preventers (CAODC)Carlos MunizagaNo ratings yet
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) & It S ImplementationDocument46 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance (TPM) & It S ImplementationDeep DaveNo ratings yet
- BidyutDocument137 pagesBidyutChao Bidyut Bikash GogoiNo ratings yet
- Engineer Materials Research Design in Greater Chicago IL Resume Christopher WhiteDocument3 pagesEngineer Materials Research Design in Greater Chicago IL Resume Christopher WhiteChristopher WhiteNo ratings yet
- 2SK 2371 - 2372 - NecDocument8 pages2SK 2371 - 2372 - NecStevenNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visit Report: Precitek, Sidhakala, Jayshree PolymersDocument48 pagesIndustrial Visit Report: Precitek, Sidhakala, Jayshree PolymersNarendra Chaudhari100% (1)
- Metro Project (Islamabad & Rawal Pindi)Document59 pagesMetro Project (Islamabad & Rawal Pindi)zoomlens100% (1)
- Modelo de Articulo-Adm MelissaDocument8 pagesModelo de Articulo-Adm MelissaAna Roxana Benavides MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 2008 StandardDocument90 pagesIso 9001 2008 StandardArun KumarNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 - Quality Management: This Section Concisely Describes The Essential Features of The ISO 9000 FamilyDocument5 pagesISO 9000 - Quality Management: This Section Concisely Describes The Essential Features of The ISO 9000 FamilyElya RosaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Software QualityDocument29 pagesUnit 5 Software Qualitykansis aslksnNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management: Submitted To: Mrs. Kavita Aggarwal Submitted By: Nikhlesh Partap Singh Mba 1 SemDocument40 pagesSoftware Project Management: Submitted To: Mrs. Kavita Aggarwal Submitted By: Nikhlesh Partap Singh Mba 1 SemVidyut VatsNo ratings yet
- CheckList - IsO 9001-2015Document39 pagesCheckList - IsO 9001-2015Guilherme AugustoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document25 pagesChapter 1Jinnatul RaihanNo ratings yet
- Broadband Installation (Fixed Wireless) NC IIDocument63 pagesBroadband Installation (Fixed Wireless) NC IIKliu Senior Selestre Villanueva67% (3)
- Scan Profile For EmailDocument100 pagesScan Profile For EmailZaheer Ahamed100% (1)
- Export Import Procedures & Documents SummaryDocument402 pagesExport Import Procedures & Documents SummaryRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- Low voltage panel board installationDocument7 pagesLow voltage panel board installationuddinnadeemNo ratings yet