Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mcat F S: Kinematics and Mechanics
Uploaded by
Wollo NeftegnawOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mcat F S: Kinematics and Mechanics
Uploaded by
Wollo NeftegnawCopyright:
Available Formats
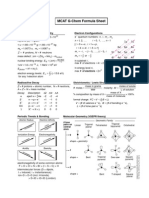
MCAT FORMULA SHEET: This formula sheet is to be used as a
reference tool. DO NOT MEMORIZE these formulas, instead, understand the
concepts behind the equations and the relationships they represent.
Kinematics and Mechanics
1 v2 mv 2
d = vt v f = v0 + at v 2f = v02 + 2a∆x ∆x = v0 t + at 2 ac = , Fc =
2 r r
distance vat vax tax centripetal motion
GM 1 M 2 Fk = µ k FN
F= F net = ma τ = Fl sin θ F = −k x
r2 Fs ≤ µ s FN
Newton's 2nd law torque hooke's Law
law of gravitation friction
Work, Energy, Momentum Thermodynamics
1 2 1 2 ∆Q = mc∆T ∆Q = mL
KE = mv PE grav = mgh PEelastic = kx
2 2 heat energy latent heat
gravitational PE
kinetic energy spring PE
∆U = Q − W
W first law of
P= W = Fd cos θ
t
work thermodynamics
power
p = mv m1v1i + m2 v2i = m1v1 f + m2 v2 f
∆G = ∆H - T ∆S ∆G° = − RT ln K eq
momentum conservation of momentum
Gibbs free energy equilibrium
Fluids and Solids
m ρ substance F
ρ= s.g . = Fb = ρ fluid Vsubmerged g P=
V ρ water A
buoyant force
density specific gravity pressure
π = MRT Ptotal = Patm + Pgauge Pfluid = ρ fluid gh
osmotic pressure total pressure on fluid fluid gauge pressure
1 2 rate A MM B ∆L = α L∆T
A1v1 = A2 v2 P+ ρ v + ρ gh = const. =
2 rate B MM A ∆V = β V ∆T
continuity equation
Bernoulli's equation Graham's Law thermal expansion
Rev. 2A Rev. Date: 2/7/2003
Electricity & Magnetism
kq kq
E= V=
kq q F r2 ∆U r
Fe = 12 2 E= ∆V =
r q0 electric field due q0 electrical potential
electrostatic force electric field to point charge electrical potential of a point charge
1 µI µI
U = CV 2 B= 0 B= 0
2 2π r F = qvB sin θ 2r
q = VC
energy stored magnetic field F = ILB sin θ magnetic field @
capacitance
by capacitor around a wire magnetic force center of wire loop
Electric Power & Circuits Light and Optics
P = IV c hc
n= E = hf =
∆q I max Vmax v λ
V = IR I= I rms = , Vrms =
∆t 2 2 index of refraction photon energy
electrical power &
current AC circuits
Ohm's Law
n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ 2
1 1 1 Rs = R1 + R2 + Snell's Law
= + +
CS C1 C2 1 1 1
= + + 1 1 1
CP = C1 + C2 + RP R1 R2 n2
sin θ crit = , n2 < n1 = +
capacitors in series resistors in series n1 f o i
and in parallel and in parallel total internal reflection lensmaker's eq.
Periodic Motion, Waves and Sound Chemistry and Biology
1 k V1 V
f = ω = 2π f = PV = nRT = 2 1 1 = P2V2
PV
T m T1 T2
wave freq., period ideal gas law Boyle's Law
spring angular freq Charles' Law
g n1 n2
ω = 2π f = v= fλ = pH = − log H +
L V1 V2
wave speed pH
pendulum angular freq Avogadro's Law
v ∓ vD
f '= f n2 a
v ± vS M iVi = M f V f P + (V - nb ) = nRT
V2
Doppler effect dilution
Van der Waals equation of state
EMF = E °red + E °ox Ecell = Ecathode - Eanode
Atomic and Nuclear electromotive force EMF
A
Z X →ZA −− 42 Y + α
alpha decay p + q =1
p + 2 pq + q 2 = 1
2
A
Z X→ A
Z +1 Y+ e
0
−1
A
Z X→ A
Z −1 Y+ e
0
+1 Hardy-Weinberg equations
beta-minus decay beta-plus decay
Rev. 2A Rev. Date: 2/7/2003
You might also like
- The Premed Playbook Guide to the Medical School Application Process: Everything You Need to Successfully ApplyFrom EverandThe Premed Playbook Guide to the Medical School Application Process: Everything You Need to Successfully ApplyNo ratings yet
- The Premed Playbook: Guide to the Medical School Personal StatementFrom EverandThe Premed Playbook: Guide to the Medical School Personal StatementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber0971% (7)
- Mnemonics For The MCATDocument11 pagesMnemonics For The MCATsujsam100% (2)
- Garrett Biehle The MCAT Physics Book PDFDocument440 pagesGarrett Biehle The MCAT Physics Book PDFAdalat Adel100% (8)
- 500 Review Questions For MCAT OC&BC PDFDocument273 pages500 Review Questions For MCAT OC&BC PDFGALANG ANUGERAH P. LAMATO100% (3)
- Testing Solutions CARS Test 7Document444 pagesTesting Solutions CARS Test 7JjjjmmmmNo ratings yet
- Mcat Mnemonics 2017Document57 pagesMcat Mnemonics 2017Blinka199100% (2)
- MCAT CARS Practice Passages & ReviewDocument15 pagesMCAT CARS Practice Passages & ReviewSadek Mowakket100% (2)
- MCAT MnemonicsDocument14 pagesMCAT Mnemonicskmulqs100% (1)
- 500 Review Questions For The MCAT General Chemistry 2EDocument208 pages500 Review Questions For The MCAT General Chemistry 2EBurning Phenom100% (1)
- 16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula SheetDocument2 pages16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula SheetNathan Korean Kim100% (7)
- Practice MCAT Test 1Document42 pagesPractice MCAT Test 1Rowena Concepcion Penafiel67% (12)
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 1 PowerPointDocument46 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 1 PowerPointLaurie Gardner100% (8)
- 500 Review Questions For The MCAT Behavioral SciencesDocument177 pages500 Review Questions For The MCAT Behavioral Sciencesimperiouxx100% (5)
- 500 Review Questions For The MCAT Biology, 2 EditionDocument192 pages500 Review Questions For The MCAT Biology, 2 EditionAaron GohNo ratings yet
- MCAT ShortcutsDocument12 pagesMCAT ShortcutsShafqat Shakeel100% (2)
- 2015 MCAT Study PlanDocument14 pages2015 MCAT Study PlanSeanNo ratings yet
- 100 MCAT TipsDocument23 pages100 MCAT TipsJhilianne Batino100% (1)
- Complete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3Document172 pagesComplete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3Panda Panda100% (7)
- MCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsFrom EverandMCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNo ratings yet
- Jack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryDocument52 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryLora100% (2)
- MCAT Power Practice PDFDocument239 pagesMCAT Power Practice PDFOseas Medina100% (6)
- Free MCAT ResourcesDocument2 pagesFree MCAT ResourcesGeorges KoberianosNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- MCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideFrom EverandMCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 1 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (3)
- MEDICAL COLLEGE ADMISSION TEST (MCAT): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMEDICAL COLLEGE ADMISSION TEST (MCAT): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- ENG590 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit PDFDocument3 pagesENG590 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit PDFTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bDocument4 pagesEXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- Testing Solutions Section Bank Notes V1.8Document85 pagesTesting Solutions Section Bank Notes V1.8megNo ratings yet
- 1 MCAT Leah4scimcatcheatsheetcollection2017Document50 pages1 MCAT Leah4scimcatcheatsheetcollection2017JD Ampaya100% (2)
- MCAT - BiologyDocument15 pagesMCAT - BiologyEmily Teo100% (1)
- SB Notes Master Version 2.0Document156 pagesSB Notes Master Version 2.0anamargarita1962388No ratings yet
- How To Destroy The MCAT With Minimal Study TimeDocument11 pagesHow To Destroy The MCAT With Minimal Study TimeKristin SmithNo ratings yet
- MCAT SecretsDocument32 pagesMCAT SecretsTunde Ipaye100% (2)
- MCAT Crash CourseDocument15 pagesMCAT Crash CourseDe ShepNo ratings yet
- (The Berkeley Review) The Berkeley Review MCAT GenDocument324 pages(The Berkeley Review) The Berkeley Review MCAT GenSara El100% (3)
- MCAT CoverageDocument10 pagesMCAT Coveragecapt_zoe100% (1)
- MCAT Full Length4Document77 pagesMCAT Full Length4Ali100% (1)
- MCAT Review SheetsDocument92 pagesMCAT Review SheetsShafia Batool100% (1)
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsFrom EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNo ratings yet
- MCAT Full Length3Document75 pagesMCAT Full Length3AliNo ratings yet
- Complete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFDocument172 pagesComplete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFWollo NeftegnawNo ratings yet
- MCAT Organic Summary SheetDocument6 pagesMCAT Organic Summary SheetSpencer Thomas100% (2)
- MCAT Biology Complete OutlinesDocument34 pagesMCAT Biology Complete OutlinesJacob Mikhail90% (10)
- MCAT Math PortionMCATDocument22 pagesMCAT Math PortionMCATwbowen92888100% (1)
- McatDocument6 pagesMcatapi-383289428100% (1)
- MCATPrep Practice MCAT Test 2-Mcat2Document39 pagesMCATPrep Practice MCAT Test 2-Mcat2anc2061100% (4)
- MCAT Full Length 1Document77 pagesMCAT Full Length 1GIlgamesh417100% (2)
- MCAT Biology Review 2024-2025: Online + BookFrom EverandMCAT Biology Review 2024-2025: Online + BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideFrom EverandMCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideNo ratings yet
- MCAT Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills Review 2024-2025: Online + BookFrom EverandMCAT Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills Review 2024-2025: Online + BookNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics and Math Review 2024-2025: Online + BookFrom EverandMCAT Physics and Math Review 2024-2025: Online + BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 101 Ways to Score Higher on Your MCAT: What You Need to Know About the Medical College Admission Test Explained SimplyFrom Everand101 Ways to Score Higher on Your MCAT: What You Need to Know About the Medical College Admission Test Explained SimplyNo ratings yet
- MCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideFrom EverandMCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Getting Into Medical School: The Ultimate Guide for the Anxious PremedFrom EverandGetting Into Medical School: The Ultimate Guide for the Anxious PremedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Modern PhysicsDocument88 pagesChapter - 3 Modern PhysicsMehedi Hasan FoysalNo ratings yet
- The Mechanism of The Adsorption of Gold Cyanide On Activated CarbonDocument13 pagesThe Mechanism of The Adsorption of Gold Cyanide On Activated Carbonpakde jongko50% (2)
- Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Revision NotesDocument16 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Revision NotesSamay RanjanNo ratings yet
- Pre Notes 6th Semcode CH 604Document42 pagesPre Notes 6th Semcode CH 604SurajPandeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35 PDFDocument20 pagesLecture 35 PDFRachit ShahNo ratings yet
- Construccion de Turbo ExpanderDocument175 pagesConstruccion de Turbo ExpanderJonatan MamaniNo ratings yet
- At Sample Paper 2018 19 C Xii Pass Paper 2Document23 pagesAt Sample Paper 2018 19 C Xii Pass Paper 2Anurag BhattnagarNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Weebly FileDocument5 pagesAcids and Bases Weebly Fileapi-240469044No ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument71 pagesSpectrosAshraf MambalamNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat MeasurementDocument237 pagesFundamentals of Heat MeasurementJae-Pil ChungNo ratings yet
- Filtro CsPVADocument8 pagesFiltro CsPVASeras VictoriaNo ratings yet
- ENGR 2213 ThermodynamicsDocument25 pagesENGR 2213 ThermodynamicsIgor MatosNo ratings yet
- PH and The Solubility of Antimicrobials in Drinking WaterDocument4 pagesPH and The Solubility of Antimicrobials in Drinking WaterJosé Alberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Lean Oil Absorption 02Document14 pagesLean Oil Absorption 02Shri JrNo ratings yet
- Stripping VoltammetryDocument12 pagesStripping Voltammetry20tamilselvi-ugche100% (1)
- ChE Reviewer 2014 (PART I)Document7 pagesChE Reviewer 2014 (PART I)jantskieNo ratings yet
- GEA Messo BrochureDocument16 pagesGEA Messo Brochuredow2008100% (1)
- Introduction of Air CoolerDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Air CoolerHarshal Madgulkar (Harsh)100% (1)
- Ijertv2is80230 6Document13 pagesIjertv2is80230 6emad hayekNo ratings yet
- Amie Section A Materials Science Mutiple Choice QuestionsDocument0 pagesAmie Section A Materials Science Mutiple Choice QuestionsAkeel Aijaz MalikNo ratings yet
- Working With Non-Ideal Gases PDFDocument3 pagesWorking With Non-Ideal Gases PDFpolaris44No ratings yet
- Tegladza 2021Document21 pagesTegladza 2021Brett Gonzalez CardenasNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12th Ncert Chemistry Solutions-Chapter-11 e BookDocument36 pagesCbse Class 12th Ncert Chemistry Solutions-Chapter-11 e BookMadhuri GajulaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Les Differents Voix Du SynthéseDocument312 pages02 - Les Differents Voix Du SynthéseChërchěf DjămiīlåNo ratings yet
- Tinuvin P - BASFDocument2 pagesTinuvin P - BASFsriNo ratings yet
- Testing and Evaluating Glycol SampleDocument3 pagesTesting and Evaluating Glycol Samplefoobar2016No ratings yet