Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Article (Dragged) 8
Uploaded by
OIJAsdiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Article (Dragged) 8
Uploaded by
OIJAsdiaCopyright:
Available Formats
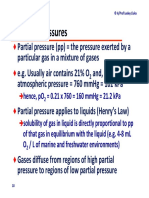
ONLINE METHODS aversion for either acetophenone or propanol as the concentration increased.
Mice. All experiments on adult offspring were conducted with 2-month-old male Independent mice were used in the acetophenone and propanol experiments
mice. When F0 males and F0 females were fear conditioned with odor, 2-month- (F1-Ace-C57, n = 16; F1-Prop-C57, n = 16).
old sexually inexperienced and odor-inexperienced mice were used. C57Bl/6J
mice (parents) were procured from Jackson Laboratory. M71-IRES-tauLacZ mice IVF. IVF was carried out by the Emory Transgenic Mouse Facility (TMF) located
(parents) maintained in mixed 129/Sv × C57Bl/6J background were bred in the in a different building from our colony (http://med.emory.edu/research/core_
Yerkes Neuroscience animal facility. Mice were housed on a 12-h light/dark cycle labs/transgenic_mouse/) across the Emory Campus. Briefly, F0-M71 males were
in standard groups cages (a5/cage) with ad libitum access to food and water, fear conditioned either to acetophenone or propanol as outlined above. 10 d
with all experiments conducted during the light half of the cycle. All procedures after fear conditioning, sperm was collected from the caudal epididymis and vas
were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Emory deferens of these males in our facility, and then transported to the TMF wherein
University, and followed guidelines set by the US National Institutes of Health. IVF was conducted by TMF personnel blinded to the experimental conditions
of the sperm samples according to protocols followed by Jackson Laboratory51.
Behavior. All behavior was performed in a double-blind manner and data In vitro fertilization culture medium, Mouse Vitro Fert (MVF, Cook Medical),
acquired using automated computer software programs. We are grateful to was used for sperm isolation, IVF and zygote culture. Superovulated C57BL/6
S. Banerjee, R. Andero-Gali, D. Choi, J. Goodman and F. Morrison for help with female mice were used as oocyte donors. Sperm were co-incubated with oocytes
ensuring double-blindness of data acquisition and analysis. in MVF for 4 h in a 5% CO2 incubator, the presumptive zygotes were washed, and
were cultured overnight in a 150-Ml MVF drop in the incubator. In the second
Elevated plus maze. The elevated-plus maze consists of an elevated platform morning, two-cell embryos were scored and washed in MVF drop; pseudopreg-
with two walled, closed arms and two non-walled, open arms connected by an nant CD-1 female mice of 9–13 weeks of age were used as embryo recipients.
open center. The mice were placed onto the center between the plus maze arms 15–20 embryos were transferred into one oviduct of each female. Pups were
and were recorded exploring the plus maze for 5 min. The amount of time spent born after 19 d and weaned from their foster moms at 3.5 weeks of age, they were
in the closed and open arms is viewed as a measure of anxiety. reared to 2 months of age and then tissue was collected in the TMF facility for
B-galactosidase staining on the MOE and olfactory bulb.
© 201 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
Olfactory fear conditioning of parents. Mice were trained to associate ace-
tophenone or propanol presentation with mild foot shocks. For this purpose, b-galactosidase staining, quantitation of MOE OSN number and glomerular
the Startle-Response system (SR-LAB, San Diego Instruments) was modified to area in bulb. The MOE and olfactory bulbs of 2-month-old M71-LacZ mice
deliver discrete odor stimuli as previously described19. The mice were trained on were processed for B-galactosidase staining, and then M71 OSN number and
3 consecutive days, with each training day consisting of 5 trials of odor presen- glomerular area were quantitated using previously published protocols19. Briefly,
tation for 10-s co-terminating with a 0.25-s 0.4-mA foot shock with an average lateral whole-mount MOE and brains were rapidly dissected and placed into 4%
inter-trial interval of 120 s. Both acetophenone and propanol (from Sigma) were paraformaldehyde (wt/vol) for 10 min at ~23 °C, after which they were washed
used at a 10% concentration diluted with propylene glycol. three times in 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 5 min. M71-LacZ was
stained for B-galactosidase using 45 mg of X-gal (1 mg ml−1) dissolved in 600 Ml of
OPS of adult offspring. Mice were habituated to the startle chambers for 5–10 min DMSO and 45 ml of a solution of 5 mM potassium ferricyanide, 5 mM potassium
on three separate days. On the day of testing, mice were first exposed to 15 startle- ferrocyanide and 2 mM MgCl in 1× PBS, and incubated at 37 °C for 3 h.
alone (105-dB noise burst) trials (leaders), before being presented with ten odor +
startle trials randomly intermingled with ten startle-alone trials. The odor + Quantitation of MOE M71-positive OSN number. The lateral whole mount
startle trials consisted of a 10-s odor presentation co-terminating with a 50-ms, MOE was imaged using a microscope-mounted digital camera. B-galactosidase–
105-dB noise burst. For each mouse, an OPS score was computed by subtracting stained blue OSNs were manually counted by an experimenter blinded to the
the startle response in the first odor + startle trial from the startle response in the experimental groups.
last startle-alone leader. This OPS score was then divided by the last startle-alone
leader and multiplied by 100 to yield the percent OPS score (% OPS) reported in Measurement of glomerular area in the olfactory bulb. A microscope-mounted
the results. Mice were exposed to the acetophenone-potentiated startle (acetophe- digital camera was used to capture high-resolution images of the B-galactosidase–
npg
none + startle) and propanol-potentiated startle (propanol + startle) procedures stained M71 glomeruli at 40× magnification. Images were converted to grayscale
on independent days in a counter-balanced fashion. and equalized for background brightness. The distribution of pixel brightness was
exported in ImageJ as gray levels from 0 = black to 255 = white. X-gal–labeled
Auditory fear conditioning. Mice were pre-exposed to sound attenuated glomerular area was quantified as pixels, less than a set threshold gray level of
conditioning chambers (San Diego Instruments) for three consecutive days 150 (optimized for axon versus background). Each glomerulus was traced using
before training. On the day of auditory fear conditioning, mice received five the lasso tool in Photoshop and the area was recorded from the histogram tool.
conditioned-unconditioned stimulus pairings (conditioned stimulus: 30-s, 6- This quantitation was conducted by two experimenters both blinded to the
kHz, 75-dB tone; unconditioned stimulus: 500-ms, 0.6-mA foot shock) with a experimental groups.
5-min inter-trial interval. The percentage of time spent freezing to the tones was
measured by SR-LAB software (San Diego Instruments). The consolidation of fear N-ChIP on sperm. N-ChIP was conducted on sperm chromatin using previously
memory was tested 24 h after fear conditioning in a novel context (modular test described procedures52. Briefly, the cauda epidydymis was dissected into 1 ml of
chambers, Med Associates) when mice were exposed to 15 conditioned stimulus M2 medium (Sigma), and sperm were allowed to swim into the medium for 1 h
tones with a 1.5-min inter-trial interval. Freezing during the tone presentations at 37 °C. Five epidydymis were used per sample, and each experimental group
was measured with FreezeView software (Coulbourn Instruments). The extinc- had three samples. At least 3 × 106 sperm were used for each ChIP. Sperm were
tion retention test occurred 24 h after extinction training and consisted of 30 then collected by centrifugation at 4 °C for 10 min at 500g, and resuspended in
conditioned stimulus tone presentations to the mice. 1× PBS, 1 mM PMSF. Sperm were then lysed on ice for 10 min in 1× PBS, 1 mM
PMSF, 0.5% Triton X-100 (vol/vol). Nuclei were pelleted by centrifugation at
Odor sensitivity. Mice were placed in a three-chambered box and allowed to 4 °C for 10 min at 371g. The pellet was then suspended in 1× PBS, 1 mM PMSF,
explore between all three chambers for 10 min. A particular concentration of 10 mM DTT, and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min, before the addition of 0.6 mM
odor (Fig. 2, either acetophenone or propanol) contained in a 1.5-ml Eppendorf CaCl2 and MNase (Sigma) to yield mono-, di- and tri-nucleosomal chroma-
tube was placed in one of the chambers with the middle chamber empty and an tin. Immunoprecipitation was then carried out as described for the MOE and
empty Eppendorf tube in the farthest chamber. Association time with either the followed the previously established protocol52. The antibodies were used at
odor or the empty chamber was recorded. An aversion index was computed by 1:1,000 and were specific to H3 trimethyl lysine-27 (07-449) and acetyl histone H3
subtracting the amount of time spent in the open chamber from the time spent in (06-599) from Upstate. Immunoprecipitated DNA was isolated by phenol-
the odor chamber. Pilot experiments on independent mice revealed an increasing chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation and used in quantitative PCR
doi:10.1038/nn.3594 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
You might also like
- The Molecular and Hormonal Basis of Plant-Growth RegulationFrom EverandThe Molecular and Hormonal Basis of Plant-Growth RegulationNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki 1997Document6 pagesKawasaki 1997AmatystNo ratings yet
- Total Prostatectomy in Papillary Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in DogDocument84 pagesTotal Prostatectomy in Papillary Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in DoglendalindaNo ratings yet
- Development and Imprinted Gene Expression in Uniparental Preimplantation Mouse Embryos in VitroDocument9 pagesDevelopment and Imprinted Gene Expression in Uniparental Preimplantation Mouse Embryos in VitroTlad AljazeraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0143400411005339 Main PDFDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0143400411005339 Main PDFMarco Antonio AspronNo ratings yet
- 582 Full1Document7 pages582 Full1Sayda DhaouadiNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Electrophysiological Characterization of GFP-Expressing CA1 Interneurons in GAD65-GFP MiceDocument11 pagesMolecular and Electrophysiological Characterization of GFP-Expressing CA1 Interneurons in GAD65-GFP MiceFrontiersNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Enro Oxacin On Sperm Quality in Male Mice: Faruk Aral, Fu Sun Karac Al, Fu Sun BabaDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Enro Oxacin On Sperm Quality in Male Mice: Faruk Aral, Fu Sun Karac Al, Fu Sun BabaSueNo ratings yet
- Methods of StudyDocument27 pagesMethods of StudyMary Eunice Elizabeth YraNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism in Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK-21/C13) Cells Treated With Karnozin EXTRA®Document7 pagesMitochondrial Energy Metabolism in Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK-21/C13) Cells Treated With Karnozin EXTRA®Garbuz ElenaNo ratings yet
- Pheromone-Induced Odor Associative Fear Learning in RatsDocument10 pagesPheromone-Induced Odor Associative Fear Learning in RatsArntransNo ratings yet
- 259 Full PDFDocument12 pages259 Full PDFNehaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Infection of A Cat Kidney Cell Line With The Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus1Document7 pagesExperimental Infection of A Cat Kidney Cell Line With The Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus1Mardha TillahNo ratings yet
- The Onset of Germ Cell Migration in The Mouse EmbryoDocument8 pagesThe Onset of Germ Cell Migration in The Mouse EmbryoLin Zahir González GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Assaying β-amyloid Toxicity using a Transgenic C. elegans ModelDocument4 pagesAssaying β-amyloid Toxicity using a Transgenic C. elegans ModelAle GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Identification and Localization of Estrogen Receptor A-And B-Positive Cells in Adult Male and Female Mouse Intestine at Various Estrogen LevelsDocument7 pagesIdentification and Localization of Estrogen Receptor A-And B-Positive Cells in Adult Male and Female Mouse Intestine at Various Estrogen LevelsChyntia D. RahadiaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Pathogenic Leptospira From Selected Environment in Kelantan and Terengganu, MalaysiaDocument7 pagesDetection of Pathogenic Leptospira From Selected Environment in Kelantan and Terengganu, MalaysiaSiti Shairah MnrNo ratings yet
- Collection and Cryopreservation of Preimplantation Embryos of Cavia PorcellusDocument6 pagesCollection and Cryopreservation of Preimplantation Embryos of Cavia PorcellusEveAriNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Immunological Sexing of Sperm Blecher 1999Document13 pagesA New Approach To Immunological Sexing of Sperm Blecher 1999Sergio L.No ratings yet
- Nature 723Document1 pageNature 723Gmo AnraNo ratings yet
- Rat Adult Stem Cells (Marrow Stromal Cells) Engraft and Differentiate in Chick Embryos Without Evidence of Cell FusionDocument4 pagesRat Adult Stem Cells (Marrow Stromal Cells) Engraft and Differentiate in Chick Embryos Without Evidence of Cell Fusion1alfredo12100% (1)
- Tingkat Fertilisasi Oosit Sapi Silangan Simmental Peranakan Ongole Dan Limousin Peranakan Ongole Secara in VitroDocument5 pagesTingkat Fertilisasi Oosit Sapi Silangan Simmental Peranakan Ongole Dan Limousin Peranakan Ongole Secara in VitroNanaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0093691X9090575E MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 0093691X9090575E MainPâmela FreitasNo ratings yet
- The Sites of Early Viral Replication in FelineDocument13 pagesThe Sites of Early Viral Replication in FelineMinaduki KashouNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Facial Diversity ArisesDocument9 pagesUnderstanding How Facial Diversity Arisesadri steveNo ratings yet
- Drosophila: 4 BIO-8 (Group 5)Document98 pagesDrosophila: 4 BIO-8 (Group 5)AudreyNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic Arousal Regions Are Activated During Modafinil-Induced WakefulnessDocument9 pagesHypothalamic Arousal Regions Are Activated During Modafinil-Induced WakefulnessYorka OlavarriaNo ratings yet
- AcidoDocument6 pagesAcidoDark WolfNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Adult Olfactory Shock Learning: James - Hodge@bristol - Ac.uk Doi:10.3791/50107Document5 pagesDrosophila Adult Olfactory Shock Learning: James - Hodge@bristol - Ac.uk Doi:10.3791/50107David RolNo ratings yet
- Muller Cell Expression of Gliol Fibrillory Acidic Protein Offer Genetic and Experimental Photoreceptor Degeneration in The Rat RetinaDocument8 pagesMuller Cell Expression of Gliol Fibrillory Acidic Protein Offer Genetic and Experimental Photoreceptor Degeneration in The Rat Retinaosvaldo2494No ratings yet
- Mouse Parthenogenetic EmbryosDocument7 pagesMouse Parthenogenetic EmbryosIvan SBNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Tetraploid Mice Show Apparently Normal Morphological, Physiological, and Neurological CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesHybrid Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Tetraploid Mice Show Apparently Normal Morphological, Physiological, and Neurological CharacteristicsGmewop30mNo ratings yet
- Caracteres y Proteinas en A. PisumDocument16 pagesCaracteres y Proteinas en A. PisumJhonny Andre Blas PonceNo ratings yet
- Cell Transfer CatDocument5 pagesCell Transfer CatGmo AnraNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Animals: Hoza, A.S BLS 209 LectureDocument34 pagesTransgenic Animals: Hoza, A.S BLS 209 LectureGaurav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Adharm Ka Naash 2007Document10 pagesAdharm Ka Naash 2007Rahul AmbawataNo ratings yet
- Duncan H L Robertson Molecular Heterogeneity ofDocument5 pagesDuncan H L Robertson Molecular Heterogeneity of9hvgfzdqhbNo ratings yet
- Human Sperm Chemotaxis: Both The Oocyte and Its Surrounding Cumulus Cells Secrete Sperm ChemoattractantsDocument7 pagesHuman Sperm Chemotaxis: Both The Oocyte and Its Surrounding Cumulus Cells Secrete Sperm Chemoattractantsapi-3844475No ratings yet
- Autocrine IL-1 Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis in Thymoma CellsDocument6 pagesAutocrine IL-1 Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis in Thymoma CellsMauricio LinaresNo ratings yet
- WRR 114Document8 pagesWRR 1141alfredo12No ratings yet
- Module 704Document22 pagesModule 704Riza Joy PalomarNo ratings yet
- Myelination and Demyelination of Schwann Cells and Neuron CellsDocument4 pagesMyelination and Demyelination of Schwann Cells and Neuron Cellsdayoon hong메롱No ratings yet
- Dmba Alfredo 2004Document5 pagesDmba Alfredo 2004EN Ka ERNo ratings yet
- TMP 5 CCDocument13 pagesTMP 5 CCFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells - overview: Embryonic stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury faces delaysDocument39 pagesStem Cells - overview: Embryonic stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury faces delaysubaidu dikkoNo ratings yet
- Part I A. Basic Experiment in Embryology & SCB LabDocument75 pagesPart I A. Basic Experiment in Embryology & SCB LabNhư Quỳnh Vương ThịNo ratings yet
- Baba T.1984. Cell-Mediated Immune Protection in Chickens Against P MultocidaDocument6 pagesBaba T.1984. Cell-Mediated Immune Protection in Chickens Against P MultocidakrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Organotypic Cultures of Adult Mouse Retina: Morphologic Changes and Gene ExpressionDocument11 pagesOrganotypic Cultures of Adult Mouse Retina: Morphologic Changes and Gene ExpressionErick MartinezNo ratings yet
- Memantine Improves Cognition and Reduces AnxietyDocument7 pagesMemantine Improves Cognition and Reduces AnxietyDian GbligNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Internal Medicne - 2013 - Sharp - Endothelin 1 Concentrations in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Cats WithDocument3 pagesVeterinary Internal Medicne - 2013 - Sharp - Endothelin 1 Concentrations in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Cats WithGuillaume Penning-ReefNo ratings yet
- Eur Grosveld 9086Document4 pagesEur Grosveld 9086carlitoseverectNo ratings yet
- 4.development of Leptospiral Outer Membrane Protein-Based dot-ELISA - Turkish Journal - 2017Document9 pages4.development of Leptospiral Outer Membrane Protein-Based dot-ELISA - Turkish Journal - 2017SHIVA JYOTHINo ratings yet
- Ann Clin Transl Neurol - 2019 - Suzuki - de Novo NSF Mutations Cause Early Infantile Epileptic EncephalopathyDocument6 pagesAnn Clin Transl Neurol - 2019 - Suzuki - de Novo NSF Mutations Cause Early Infantile Epileptic Encephalopathyee wwNo ratings yet
- Enzyme-Linked Fluorescence: Assay: Ultrasensitive Solid-Phase Assay For Detection of Human RotavirusDocument5 pagesEnzyme-Linked Fluorescence: Assay: Ultrasensitive Solid-Phase Assay For Detection of Human RotavirusAngela WijayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Transgenic AnimalsDocument25 pagesLecture On Transgenic AnimalsMuhammad Ikram Anwar100% (3)
- Continuous Somatic Embryogenesis in Japanese MapleDocument7 pagesContinuous Somatic Embryogenesis in Japanese MapleSteve SardinaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Transformation Purified: of Mouse Embryos by Microinjection of DNADocument5 pagesGenetic Transformation Purified: of Mouse Embryos by Microinjection of DNAChepard14No ratings yet
- 2010 Harriet Fetal-Adult CognitionDocument7 pages2010 Harriet Fetal-Adult CognitionJoanna Riera MNo ratings yet
- Mouse Epidermal Development - Effects of Retinoic Acid Exposure in Utero (Pages 36-44)Document9 pagesMouse Epidermal Development - Effects of Retinoic Acid Exposure in Utero (Pages 36-44)jenNo ratings yet
- Genomic Equivalence: DefinitionDocument5 pagesGenomic Equivalence: Definitionjgfjhf arwtrNo ratings yet
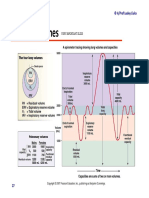
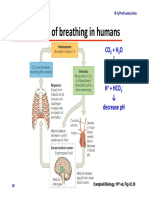
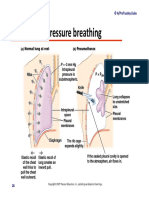
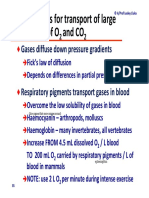
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 17Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 17OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 18Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 18OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 2Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 2OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 16Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 16OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 20Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 20OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 14Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 14OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 11Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 11OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 13Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 13OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 15Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 15OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 7Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 7OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 14Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 14OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 13 PDFDocument1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 13 PDFOIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 4Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 4OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 2Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 2OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 9Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 9OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Insect respiratory systems and tracheal air sacsDocument1 pageInsect respiratory systems and tracheal air sacsOIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 10Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 10OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 2Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 2OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 4 PDFDocument1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 4 PDFOIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 3Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 3OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 6Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 6OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Article (Dragged) 10Document1 page1.1 Article (Dragged) 10OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 5Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 5OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Article (Dragged) 8Document1 page1.1 Article (Dragged) 8OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 1Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 1OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Module 5.2 (Dragged) 1Document1 pageModule 5.2 (Dragged) 1OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Article (Dragged) 7Document1 page1.1 Article (Dragged) 7OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- NGS Analysis of Bisulfite PCR Amplicons From Sperm and MOE DNA. F0-C57Document1 pageNGS Analysis of Bisulfite PCR Amplicons From Sperm and MOE DNA. F0-C57OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Article (Dragged) 8Document1 page1.1 Article (Dragged) 8OIJAsdiaNo ratings yet
- Steps of The Scientific MethodDocument3 pagesSteps of The Scientific MethodnestorNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Professional EducationDocument15 pagesPart 4 Professional EducationMerry Cris Honculada MalalisNo ratings yet
- Faculty Lab Video Presentation EvaluationDocument3 pagesFaculty Lab Video Presentation EvaluationArics ChiengNo ratings yet
- Conclusion and RecommendationDocument1 pageConclusion and RecommendationJudy Ann BoseNo ratings yet
- Crowd Classification Problem PDFDocument29 pagesCrowd Classification Problem PDFLee QinghuaNo ratings yet
- Application of Statistics to Agriculture Using Graeco-Latin Square DesignDocument8 pagesApplication of Statistics to Agriculture Using Graeco-Latin Square Designee4ehigieNo ratings yet
- DISS - Mod1 - Introduction To Social Sciences With Natural Sciences and HumanitiesDocument28 pagesDISS - Mod1 - Introduction To Social Sciences With Natural Sciences and HumanitiesChristopher Celis73% (22)
- Edexcel GCE Art and Design SpecsDocument120 pagesEdexcel GCE Art and Design SpecsSarazeen Saif AhanaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics FundamentalsDocument34 pagesProbability and Statistics FundamentalsMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Measuring the Metric SystemDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 1: Measuring the Metric SystemVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data 2018Document321 pagesUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect Data 2018gin black100% (2)
- Experiment# 3 Projectile MotionDocument18 pagesExperiment# 3 Projectile MotionHafiz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Research Aptitude TestDocument14 pagesResearch Aptitude TestMaths CTNo ratings yet
- Critical Chloride Content in ConcreteDocument8 pagesCritical Chloride Content in ConcreteChatchai ManathamsombatNo ratings yet
- Cefr Intermediate 2021Document32 pagesCefr Intermediate 2021Z. LiliNo ratings yet
- Professional Adjustment and ResearchDocument26 pagesProfessional Adjustment and ResearchjeshemaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 TOSDocument1 pageMathematics 8 TOSAldrin BagasinaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Politics: Nature and Major ApproachesDocument19 pagesComparative Politics: Nature and Major ApproachesPhyoben S OdyuoNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Conducting Surveys, Experiments or ObservationsDocument28 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Conducting Surveys, Experiments or ObservationsJames Russell Abellar88% (16)
- Investigating Plant Systems: Unit ProjectDocument5 pagesInvestigating Plant Systems: Unit ProjectKathleen DennisNo ratings yet
- Proposal GuidelinesDocument7 pagesProposal GuidelinesNoraimi AainaaNo ratings yet
- Current Issues Fangirling Research111Document14 pagesCurrent Issues Fangirling Research111Diane Sairah PerezNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Modeling and SimulationDocument29 pagesLec 1 Modeling and SimulationlitrakhanNo ratings yet
- CAR Full PaperDocument10 pagesCAR Full PaperMarilou KimayongNo ratings yet
- Alvar Aalto's Paimio Sanatorium and the Development of Evidence-Based DesignDocument15 pagesAlvar Aalto's Paimio Sanatorium and the Development of Evidence-Based DesignomarNo ratings yet
- Presumed Consent for AnesthesiaDocument171 pagesPresumed Consent for AnesthesiaEunice RiveraNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 (Quantitative Research)Document5 pagesPractical Research 2 (Quantitative Research)Jerahmeel Madrigal Laderas89% (244)
- Writing Lab ReportsDocument31 pagesWriting Lab ReportschaciNo ratings yet
- SSS's Experiment: Choosing An Appropriate Research Design: Ref. No.: BRM0016Document3 pagesSSS's Experiment: Choosing An Appropriate Research Design: Ref. No.: BRM0016rishi rajNo ratings yet
- E-Learning in The Teaching of MathematicsDocument16 pagesE-Learning in The Teaching of MathematicsHB ChutorialNo ratings yet