Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SSLC MATHS Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Muruga Vel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views3 pagesSSLC MATHS chapter 6
Original Title
SSLC MATHS chapter 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSSLC MATHS chapter 6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views3 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Muruga VelSSLC MATHS chapter 6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
6.
GEOMETRY
Two Marks:
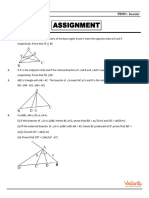
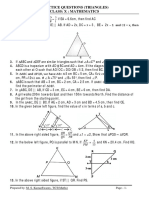
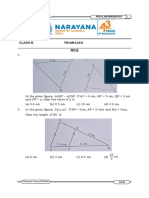
1. In ∆ABC, DE|| BC and DB = 3 If AE = 3.7 cm, find EC.
AD 2
2. In a ∆ABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE|| BC
(i) If AD = 6 cm, DB = 9 cm and AE = 8 cm, then find AC.
(ii) If AD = 8 cm, AB = 12 cm and AE = 12 cm, then find CE
3. In ∆ABC, AE is the external bisector of A, meeting BC produced at E. If AB = 10 cm, AC = 6 cm and BC
= 12 cm, then find CE.
4. In a ∆ABC, AD is the internal bisector of A, meeting BC at D.
(i) If BD = 2 cm, AB = 5 cm, DC = 3 cm find AC.
(ii) If AB = 5.6 cm, AC = 6 cm and DC = 3 cm find BC.
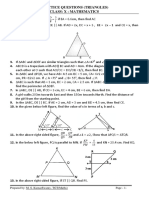
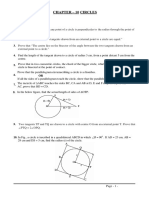
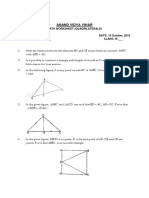
5. AB and CD are two chords of a circle which intersect each other internally at P.
(i) If CP = 4 cm, AP = 8 cm, PB = 2 cm, then find PD.
(ii) If AP = 12 cm, AB = 15 cm, CP = PD, then find CD
6. AB and CD are two chords of a circle which intersect each other externally at P
(i) If AB = 4 cm BP = 5 cm and PD = 3 cm, then find CD.
(ii) If BP = 3 cm, CP = 6 cm and CD = 2 cm, then find AB
5. Let PQ be a tangent to a circle at A and AB be a chord. Let C be a point on the circle such that
BAC = 54● and BAQ = 62●Find ABC.
Five Marks:
1. State and prove Basic Proportionality theorem.
2. State and prove Angle bisector theorem.
3. State and Prove Pythagoras theorem.
Prepared by
S.MURUGAVEL M.Sc., B.Ed.,
Email: murugavel213@gmail.com
Website: www.jobs-edn.blogspot.com
You might also like
- SSLC Maths Chapter-6Document1 pageSSLC Maths Chapter-6Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TrianglesDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Trianglesmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- Traingle Class 10thDocument6 pagesTraingle Class 10thAarthiKalyanNo ratings yet
- Geometry II AssignmentDocument102 pagesGeometry II Assignmentkoushik reddyNo ratings yet
- 6.triangles MCQsDocument7 pages6.triangles MCQsAnubhav KattnaNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: Grade 9 Mathematic WorksheetDocument22 pagesQuadrilaterals: Grade 9 Mathematic Worksheethuang pok manNo ratings yet
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocument20 pagesGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- PRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsDocument4 pagesPRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsAnshika MishraNo ratings yet
- 10th Maths Cbse Test Paper Chapter - Similar Triangle Class 10thDocument1 page10th Maths Cbse Test Paper Chapter - Similar Triangle Class 10thTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SSC Maths RevisionDocument11 pagesSSC Maths RevisionAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument3 pagesTrianglesmohammedrehan94905No ratings yet
- Build-Up Your Understanding 1Document16 pagesBuild-Up Your Understanding 1NadiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Triangles Class XDocument2 pagesPractice Questions Triangles Class XAnonymous La3xzbvxyWNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Triangles Class XDocument2 pagesPractice Questions Triangles Class XSHRIJAL SAHUNo ratings yet
- 9th Triangle Test Paper-3Document1 page9th Triangle Test Paper-3vishal_bokaroNo ratings yet
- MC Geometry PDFDocument4 pagesMC Geometry PDFสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Triangles 10 DavDocument2 pagesTriangles 10 DavHarpreet Singh SainiNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Sample Question 1Document9 pagesTriangles: Sample Question 1soumikbhNo ratings yet
- AfrykaDocument12 pagesAfrykaryszard_lubicz100% (1)
- Extra Questions CH 8 QuadrilateralsDocument2 pagesExtra Questions CH 8 Quadrilateralspjqkj6rhdfNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions CH 8 QuadrilateralsDocument2 pagesExtra Questions CH 8 Quadrilateralspjqkj6rhdfNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADocument14 pagesChapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADuong QuangNo ratings yet
- Prmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14Document19 pagesPrmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 14sudhir singh100% (3)
- G-9 Chapter 10 CirclesDocument5 pagesG-9 Chapter 10 CirclesChetanNo ratings yet
- Prmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 12Document16 pagesPrmo Daily Practice Problems: Sub.: Mathematics DPP: 12Sai Gokul100% (3)
- TrianglesDocument13 pagesTrianglessudhir_kumar_33100% (1)
- Ps As Icse STD 10 Math LocusDocument5 pagesPs As Icse STD 10 Math Locuspravingosavi1011_578No ratings yet
- Geometry I AssignmentDocument114 pagesGeometry I AssignmentSAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties of Circles (Q)Document30 pagesBasic Properties of Circles (Q)Daniel LeungNo ratings yet
- Grade 11Document1 pageGrade 11Tr LynnNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument69 pagesSimilarityavinandan chandraNo ratings yet
- Circle QnsDocument4 pagesCircle Qnsaris lensNo ratings yet
- English Class X Maths Chapter08Document40 pagesEnglish Class X Maths Chapter08KhanNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document20 pagesDay 3chaostheoristNo ratings yet
- Circles XDocument5 pagesCircles XbadmashkasimNo ratings yet
- Rmo (India) - 2012 (1) : Pe BP PD ApDocument1 pageRmo (India) - 2012 (1) : Pe BP PD ApdrssagrawalNo ratings yet
- ANGLE BISECTORS - San Jose Math CircleDocument20 pagesANGLE BISECTORS - San Jose Math CircleAltananyNo ratings yet
- Assorted Geometry (J) : 1 StrategyDocument4 pagesAssorted Geometry (J) : 1 StrategyBobNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsMizaZainalNo ratings yet
- 1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math CirclesDocument7 pages1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math Circleskabbur.anushkaNo ratings yet
- 6.triangles Marks BoosterDocument19 pages6.triangles Marks BoosterDROZON GAMING YTNo ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument23 pagesTrianglesШунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- 04 TrianglesDocument9 pages04 TrianglesS PragadeshNo ratings yet
- 6 Triangles PDFDocument5 pages6 Triangles PDFvxvcbcfbcbNo ratings yet
- 278525geometry Practice Sheet - 11 - CrwillDocument6 pages278525geometry Practice Sheet - 11 - Crwillsivejad276No ratings yet
- Euclidean Geometry NotesDocument170 pagesEuclidean Geometry NoteseisatoponNo ratings yet
- Circle 9.3Document12 pagesCircle 9.3ambastreaming913No ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument13 pagesTrianglessudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Abe FG CD Abh Bce Ade Abe: Test GeometryDocument1 pageAbe FG CD Abh Bce Ade Abe: Test GeometryGARNETT HUTAHAEANNo ratings yet
- TrianglesDocument139 pagesTrianglessujaritha sureshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 6 TrianglesDocument4 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 6 TrianglesAJAY KUMAR SAROJNo ratings yet
- Anand Vidya ViharDocument3 pagesAnand Vidya ViharANILA RAMESH PillaiNo ratings yet
- Geometry AssignmentDocument17 pagesGeometry AssignmentDaksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 250% (2)
- Geometry - 3RD Quarter - WorksheetDocument14 pagesGeometry - 3RD Quarter - WorksheetmikiNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- The Solution of the Pyramid Problem or, Pyramide Discoveries with a New Theory as to their Ancient UseFrom EverandThe Solution of the Pyramid Problem or, Pyramide Discoveries with a New Theory as to their Ancient UseNo ratings yet
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsFrom EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- SSLC Maths Important 2 and 5 Marks Question Tamil MediumDocument5 pagesSSLC Maths Important 2 and 5 Marks Question Tamil MediumMuruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 12Document4 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 12Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLCMathschapter 11Document2 pagesSSLCMathschapter 11Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MathsDocument28 pagesSSLC MathsMuruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS 5 Marks CompulsoryDocument6 pagesSSLC MATHS 5 Marks CompulsoryMuruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 8Document5 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 8Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 7Document4 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 7Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 5Document5 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 5Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 4Document4 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 4Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Chapter 2Document4 pagesSSLC Maths Chapter 2Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC MATHS Chapter 3Document5 pagesSSLC MATHS Chapter 3Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- CV ListDocument82 pagesCV ListMuruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Mar 2017 NR Online Uploading InstructionDocument3 pagesSSLC Mar 2017 NR Online Uploading InstructionMuruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Chapter 4Document2 pagesSSLC Maths Chapter 4Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLCMathschapter 12Document2 pagesSSLCMathschapter 12Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Chapter 4Document2 pagesSSLC Maths Chapter 4Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Chapter 4Document2 pagesSSLC Maths Chapter 4Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLCMathsChapter 7Document1 pageSSLCMathsChapter 7Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLCMathschapter 11Document2 pagesSSLCMathschapter 11Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLCMathschapter 8Document3 pagesSSLCMathschapter 8Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Chapter 2Document2 pagesSSLC Chapter 2Muruga VelNo ratings yet
- SSLC Chapter 5Document3 pagesSSLC Chapter 5Muruga VelNo ratings yet