Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HO1 Anion Cation List PDF
HO1 Anion Cation List PDF
Uploaded by
Bhakta KishorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HO1 Anion Cation List PDF
HO1 Anion Cation List PDF
Uploaded by
Bhakta KishorCopyright:
Available Formats
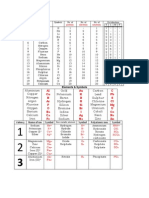
Symbols and Charges for Monoatomic Ions
Symbol Name Symbol Name
H+ hydrogen ion H¯ hydride
Li+ lithium ion F¯ fluoride Note that the
Na+ sodium ion Cl¯ chloride letters in an ion’s
K+ potassium ion Br¯ bromide name before the
Rb+ rubidium ion I¯ iodide -ide ending is
Cs+ cesium ion 2
O ¯ oxide the stem. For
Be2+ beryllium ion 2
S ¯ sulfide example, the stem
Mg2+ magnesium ion Se2¯ selenide for bromide is
Ca2+ calcium ion Te2¯ telluride brom-.
Sr2+ strontium ion
Ba2+ barium ion Ag + silver ion N 3¯ nitride
Ra2+ radium ion Ni2+ nickel ion P 3¯ phosphide
Zn2+ zinc ion Al 3+ aluminum ion 3
As ¯ arsenide
Systematic name Common Systematic name Common
Symbol (Stock system) name Symbol (Stock system) name
Cu+ copper(I) cuprous Hg22+ mercury(I) mercurous
Cu2+ copper(II) cupric Hg2+ mercury(II) mercuric
Fe2+ iron(II) ferrous Pb2+ lead(II) plumbous
Fe3+ iron(III) ferric Pb4+ lead(IV) plumbic
Sn2+ tin(II) stannous Co2+ cobalt(II) cobaltous
Sn4+ tin(IV) stannic Co3+ cobalt(III) cobaltic
Cr2+ chromium(II) chromous Au + gold(I) aurous
Cr3+ chromium(III) chromic Au 3+ gold(III) auric
Mn2+ manganese(II) manganous
Mn3+ manganese(III) manganic
Symbols and Charges for Polyatomic Ions
Formula Name Formula Name
NO3¯ nitrate ClO4¯ perchlorate
NO2¯ nitrite ClO3¯ chlorate
CrO42¯ chromate ClO2¯ chlorite
Cr2O72¯ dichromate ClO¯ hypochlorite
CN¯ cyanide IO 4¯ periodate
MnO 4¯ permanganate IO 3¯ iodate
OH¯ hydroxide IO¯ hypoiodite
O22¯ peroxide BrO3¯ bromate
NH2¯ amide BrO¯ hypobromite
CO32¯ carbonate HCO3¯ hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate)
SO42¯ sulfate HSO4¯ hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate)
SO32¯ sulfite HSO3¯ hydrogen sulfite (bisulfite)
C2O42¯ oxalate HC2O4¯ hydrogen oxalate (binoxalate)
PO43¯ phosphate HPO42¯ hydrogen phosphate
PO33¯ phosphite H2PO4¯ dihydrogen phosphate
More Symbols and Charges for Polyatomic Ions
S2O32¯ thiosulfate HS¯ hydrogen sulfide
AsO43¯ arsenate BO33¯ borate
SeO42¯ selenate 2
B4O7 ¯ tetraborate
SiO32¯ silicate SiF62¯ hexafluorosilicate
C4H4O62¯ tartrate SCN¯ thiocyanate
C2H3O2¯ acetate (an alternate way to write acetate is CH3COO¯)
There is one positive polyatomic ion. It is NH4+ and is called the ammonium ion.
Prefixes Used to Indicate Number in a Name Involving Two Non-Metals
mono– 1 hexa– 6
di– 2 hepta– 7
tri– 3 octa– 8
tetra– 4 nona– 9
penta– 5 deca– 10
These prefixes are used in naming binary compounds involving two non–metals. Example
include P2O5, Cl2O, NO, N2O, NO2, N2O5, PCl3, PCl5, SO2, SO3, SiO2. Sometimes metal ions are
involved in a Greek prefix name, but these are less common. Examples include UF6, SbCl3,
SbCl5, OsO4, BiCl3.
There is a preferred order of the nonmetals when writing them in a formula. It is:
Rn, Xe, Kr, B, Si, C, Sb, As, P, N, H, Te, Se, S, I, Br, Cl, O, F.
CO is carbon monoxide, NOT carbon monooxide. As4O6 is tetrarsenic hexoxide, NOT
tetraarsenic hexaoxide.
Acid Names – add the word acid to each name when saying or writing.
Non–oxygen containing Oxygen containing (oxyacids)
Name when dis- Name when a pure
Formula solved in water compound Formula Name
HF hydrofluoric acid hydrogen fluoride HNO3 nitric acid
HCl hydrochloric acid hydrogen chloride HNO2 nitrous acid
HBr hydrobromic acid hydrogen bromide H2SO4 sulfuric acid
HI hydroiodic acid hydrogen iodide H2SO3 sulfurous acid
HCN hydrocyanic acid hydrogen cyanide H3PO4 phosphoric acid
H2S hydrosulfuic acid hydrogen sulfide H2CO3 carbonic acid
HC2H3O2 acetic acid
(Note that it is hydrogen sulfide, NOT hydrogen sulfuride.) (also written CH3COOH)
You might also like
- A2 NMR Spectroscopy Mini Mock PDFDocument22 pagesA2 NMR Spectroscopy Mini Mock PDFkasimNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Gas Worksheet 3 Molar Volume and Gas Stoichiometry 2010Document1 pageUnit 11 Gas Worksheet 3 Molar Volume and Gas Stoichiometry 2010GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet Redox and Reactivity of MetalsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet Redox and Reactivity of MetalshahaNo ratings yet
- IB Chem 1 Assess Cws1aDocument3 pagesIB Chem 1 Assess Cws1aEmi JiHyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 Topic 1Document61 pagesBooklet 2 Topic 1Sarah Al ObaidanNo ratings yet
- Redox WorksheetDocument4 pagesRedox WorksheetAzain CardenasNo ratings yet
- 2021 Grade 11 End of Term 1 Science Paper 2 TestDocument3 pages2021 Grade 11 End of Term 1 Science Paper 2 TestDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Balancing Stoich Worksheet and KeyDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Balancing Stoich Worksheet and KeypolickNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Valencies and Atomic Nos.Document1 pageChemistry Valencies and Atomic Nos.kskkingNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Document79 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Phillip TranNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Document28 pagesTopic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Blood - GCSE-Questions - 1.Rtf - Biology 1Document6 pagesBlood - GCSE-Questions - 1.Rtf - Biology 1RekaNo ratings yet
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- WS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESDocument4 pagesWS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Preparing Common Salts G8Document21 pagesPreparing Common Salts G8shanaayaa kunder100% (1)
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- SNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data BookDocument17 pagesSNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data Bookapi-125934329No ratings yet
- CHM096-Tutorial 1 (Alkanes & Alkenes)Document4 pagesCHM096-Tutorial 1 (Alkanes & Alkenes)Anonymous RD1CrAINo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-01: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and EquationsGMSUNDARINo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations: Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesBalancing Equations: Practice ProblemsAnagha VSNo ratings yet
- Shapes of Molecules Ions (Further Practice) QPDocument10 pagesShapes of Molecules Ions (Further Practice) QPAli EslamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SaltsDocument23 pagesChapter 8: SaltsWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument300 pagesChem NotesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Metals and Non Metals WorksheetDocument2 pagesMetals and Non Metals WorksheetKamaljeet Singh100% (1)
- Acids and Bases Unit Test 2011Document8 pagesAcids and Bases Unit Test 2011jkdfal1No ratings yet
- Precipitation ReactionsDocument3 pagesPrecipitation ReactionsborgiamatriceNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDocument149 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsFaria TahsinNo ratings yet
- Answers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryDocument13 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryJulia AgustianaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument29 pagesRedox ReactionsSoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry BioChem WS 1Document8 pagesIB Chemistry BioChem WS 1whalerfishNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Chemistry Annual Term Revision WorksheetsDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Chemistry Annual Term Revision WorksheetsAbhayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDocument63 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/11afyNo ratings yet
- SL Topic 2: Atomic Structure: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDocument8 pagesSL Topic 2: Atomic Structure: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingCarlos Moreno BorralloNo ratings yet
- Acid Base WorksheetDocument5 pagesAcid Base WorksheetOmar IjazNo ratings yet
- Redox ChemistryDocument20 pagesRedox ChemistryNisidini JasingheNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis ExerciseDocument1 pageElectrolysis ExerciseSeptina R Nurhalimah100% (1)
- SP4 HigherDocument8 pagesSP4 HigherMalika MamajonovaNo ratings yet
- Chem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionDocument24 pagesChem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionKarim WaelNo ratings yet
- Topic 7-17 Practice Questions Key 1 2Document8 pagesTopic 7-17 Practice Questions Key 1 2Isaline GurneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 2Document8 pagesChemistry Worksheet 2Marie BozemanNo ratings yet
- Metals Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMetals Worksheet 1Sharizah Bte Md Amin100% (1)
- 6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTDocument7 pages6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTOm KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSESohail Ahmed0% (1)
- Key Neutron Proton: A2 The Diagram Shows The Nuclei of Five Different AtomsDocument20 pagesKey Neutron Proton: A2 The Diagram Shows The Nuclei of Five Different AtomsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryArya VermaNo ratings yet
- 6 Organic Chemistry IDocument27 pages6 Organic Chemistry IAwil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Symbol Equations You Need To Be Familiar WithDocument3 pagesSymbol Equations You Need To Be Familiar WithKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- 2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)Document21 pages2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)JohnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 21 - Experimental Design and Separation TechniquesDocument11 pagesChemistry-Ch 21 - Experimental Design and Separation TechniquesHassan Riaz100% (1)
- Chemical Properties of Period 3 Elements WorkSheetDocument1 pageChemical Properties of Period 3 Elements WorkSheetNishchay BhattNo ratings yet
- Organic reactive intermediatesFrom EverandOrganic reactive intermediatesSamuel McManusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectMayank SinhaNo ratings yet
- Baguette With Poolish Recipe Bruno AlbouzeDocument5 pagesBaguette With Poolish Recipe Bruno Albouzeidr823No ratings yet
- Diacetylenic Isobutylamides of Echinacea: Synthesis and Natural DistributionDocument8 pagesDiacetylenic Isobutylamides of Echinacea: Synthesis and Natural Distributionaji gumelarNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument11 pagesPolymersdovoo lolNo ratings yet
- Applications and Opportunities For Ultrasound Assisted ExtractionDocument9 pagesApplications and Opportunities For Ultrasound Assisted ExtractionSinisa CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Directory of Chemical Units (Large and Medium Scale Units) - 2017-18Document32 pagesDirectory of Chemical Units (Large and Medium Scale Units) - 2017-18Bhrugu DhokaiNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms: Splendid Gifts For The Cosmetic IndustryDocument27 pagesMushrooms: Splendid Gifts For The Cosmetic IndustrymNo ratings yet
- K L Mittal Silanes and Other Coupling Agents, Volume 3Document265 pagesK L Mittal Silanes and Other Coupling Agents, Volume 3Raka Satria DewanggaNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Fish Culture PDFHanumant JagtapNo ratings yet
- Mechster 5310FR: Commitment To Quality and ConsistencyDocument1 pageMechster 5310FR: Commitment To Quality and ConsistencyreinpolyNo ratings yet
- FAQs About Chia and MilaDocument2 pagesFAQs About Chia and MilaAzam AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4. Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Carbonyl CompoundsDocument30 pagesLesson 4. Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Carbonyl Compoundsann wamburaNo ratings yet
- Study of The Chemical Structure of Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose Produced by Periodate Oxidation Under Different ConditionsDocument8 pagesStudy of The Chemical Structure of Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose Produced by Periodate Oxidation Under Different ConditionsCamelia TincuNo ratings yet
- Ncracs 2016 PDFDocument133 pagesNcracs 2016 PDFncracsNo ratings yet
- Globular Proteins: Myoglobin/HemoglobinDocument26 pagesGlobular Proteins: Myoglobin/HemoglobinMoheb GhobrialNo ratings yet
- MX Org Input List 9.3.20Document240 pagesMX Org Input List 9.3.20Efren HuertaNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document9 pagesChem 2Gajendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Sodium Chloride Equivalent of A SubstanceDocument8 pagesCalculating The Sodium Chloride Equivalent of A SubstanceLorenzOrminitaNo ratings yet
- Production of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionDocument11 pagesProduction of MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) From Methanol and Butylene by Catalytic ConversionAsim RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDocument5 pagesBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724No ratings yet
- Bacteriological Assessment of CommerciallyDocument48 pagesBacteriological Assessment of CommerciallyESECHIE CEPHASNo ratings yet
- 2.5.2 LipidsDocument10 pages2.5.2 Lipidscamille chuaNo ratings yet
- 2020-09-16 - Intertek Webinar - Compliance Strategy of Japan New Food Contact Regulations and Positive ListsDocument48 pages2020-09-16 - Intertek Webinar - Compliance Strategy of Japan New Food Contact Regulations and Positive ListsBasvanLeeuwenNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black ProcessDocument4 pagesCarbon Black ProcessAnonymous azD9vQD100% (1)
- N The V: Organometallic CompoundsDocument12 pagesN The V: Organometallic CompoundslaythNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Mixed Waste Processing FacilitiesDocument62 pagesThe Evolution of Mixed Waste Processing FacilitiesmmmeuropeNo ratings yet
- Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 2011, 64, 688-698 PDFDocument12 pagesJournal of Coordination Chemistry, 2011, 64, 688-698 PDFBhavesh PansuriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction and ReviewDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Introduction and ReviewWorld JohnNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersKaren OngNo ratings yet