Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 4 Gases 2015
Tutorial 4 Gases 2015
Uploaded by
AthinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 4 Gases 2015
Tutorial 4 Gases 2015
Uploaded by
AthinaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHY2018 Gases Tutorial 4
1. A sample of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) occupies 210 L at 27oC at 1200 T. What volume would it
occupy at STP?
2. What is the density of a gas that has a molar mass of 44.01 g/mol at STP?
3. What is the volume of a balloon filled with 32.02 grams of Helium when the atmospheric pressure
is 722 torr and the temperature is 40o C?
4. The Goodyear blimp must be inflated with Helium prior to a football game. Its volume is 7601 ft 3.
How many grams of He are needed for a pressure of 740 torr at 22o C? (1 ft3 = 28.3 L)
5. A 0.723 g sample of a gas occupies 176 mL at 100.o C and 750. torr. What is its molar mass?
6. A 20.5 L bulb contains 0.200 moles of methane, 0.300 moles of hydrogen, and 0.400 moles of
nitrogen at 20.0 o C. It is stinky and explosive. What is the pressure inside the bulb? How much
pressure does each of the three gases contribute?
7. One tank of gas contains 5.00 L of N 2 at 32.0 atm. A second tank contains 3.00 L of O 2 at 24.0
atm. What pressure is attained when the valve between the tanks is opened?
8. Calculate the (a) pressure exerted by 5.00 moles of NH 3 in a 1.00 L vessel at 25.0oC assuming
ideal and non-ideal behavior. ( a = 4.22 L2 atm mol-2 and b = 3.707 x 10 -2 L-1 mol)
9. Could 25g of Argon gas in vessel of volume 1 dm 3 exert a pressure of 2.0 bar at 30 oC if it behaved
as a perfect gas? If not, what pressure would it exert? What pressure would it exert if it behaved as
a van der waal gas?
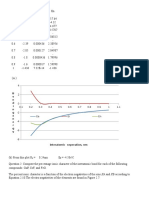
10. The following data have been obtained for oxygen gas at 273.15 K.
11. A gas mixture consists of 320 mg of methane, 175 mg of argon and 225 mg of neon. The partial
pressure of neon at 300 K is 66.5 Torr. Calculate (a) the volume and (b) the total pressure of the
mixture.
12. At 300 K and 20 atm, the compression factor of a gas is 0.86. Calculate (a) the volume occupied
by 8.2 mmol of the gas under these conditions.
13. A vessel of volume 22.4 dm 3 contains 1.5 mol H2 and 2.5 mol N2 at 273.15 K. Calculate a) the
mole fraction of each component, b) their partial pressures, and c) their total pressure.
14. Using a suitable diagram, discuss how compression factor varies with temperature and pressure.
15. What is the root mean square velocity of Cl2 molecules at room T, 50.0oC?
16. Calculate the ratio of the rate of effusion of NH 3 to that of SO3, at the same temperature and
pressure.
17. A sample of F2, was found to effuse through a pinhole 10. 2 times as rapidly as the same volume
of unknown gas (at the same temperature and pressure). What is the molecular weight of the
unknown gas?
18. When silver carbonate (Ag2CO3) is dissolved in pure deionized water at room temperature, the
concentration of Ag+ was found to be 2.3 10-4 mol/L.
a. What is the solubility product (Ksp) of Ag2CO3? [3]
b. If Ag2CO3 is dissolved in an aqueous solution containing sodium carbonate (Na 2CO3), at
the same temperature, would the solubility product be different? Briefly explain. [3]
19. Given a titration of a strong acid – weak base,
(i) draw a suitable titration curve. [3]
(ii) and suggest an indicator that can be used to determine the equivalence point. Explain
your choice. [3]
a. What is the solubility product and common ion effect? [4]
b. What is the molar solubility of the PbCl2 in water, given that the Ksp for PbCl2 is 1.6
× 10-5? [4]
c. What would be the molar solubility of PbCl2 in a 0.10 M Pb(NO3)2 solution . [3]
20. Discuss Raoult's Law and how it applies to solutions in which the solute is non-volatile. (8)
L . atm / mol . K 0.08206
J / mol . K 8.314
m3 . Pa / mol . K 8.314
21. Describe with the aid of a diagram, the distillation of ethanol. (6)
L . atm / mol . K 0.08206
J / mol . K 8.314
m3 . Pa / mol . K 8.314
You might also like
- The Rotary Cement KilnDocument388 pagesThe Rotary Cement KilnDubistWhite100% (5)
- ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistryJoniele Angelo Anin100% (1)
- TUTORIAL 4B StudentDocument7 pagesTUTORIAL 4B StudentvNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter-05 Questions and AnswerDocument68 pagesChemistry Chapter-05 Questions and Answerrnp2007123No ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 5Document3 pagesWorksheet Chapter 5أخبار المشاهيرNo ratings yet
- Set 7 AnsDocument4 pagesSet 7 AnsArturo Hernández MoralesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Document2 pagesTutorial 9 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Hai AwakNo ratings yet
- AP Gases WorksheetDocument4 pagesAP Gases Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument6 pagesStates of MatterSiddhant KarmarkarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Gaseous State CHM131Document2 pagesTutorial Gaseous State CHM131asyhqnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 StudyGuideDocument3 pagesChapter 5 StudyGuideadfNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 6Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 6ayuni nadhirahNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State Iit NumericalsDocument5 pagesGaseous State Iit NumericalssamareshcmondalNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5Document8 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5haha_le12No ratings yet
- Physical, Inorganic & Organic Chem QnsDocument45 pagesPhysical, Inorganic & Organic Chem QnsMarvin NdashimyeNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Chapter 5Document7 pagesExtra Exercise Chapter 5Veshal RameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Gasesnicole.lippolisNo ratings yet
- Class XI Assignment States of MatterDocument2 pagesClass XI Assignment States of MatterCheryl ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Review ProblemsDocument4 pagesGas Law Review Problemsemma dailNo ratings yet
- Garg Study Centre: Gaseous StateDocument2 pagesGarg Study Centre: Gaseous StateveerlocusNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bootcamp10collaborativegaslawsgasstoichiometryfa18 1Document5 pagesQuiz Bootcamp10collaborativegaslawsgasstoichiometryfa18 1api-233552637No ratings yet
- Gas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Document2 pagesGas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Kurt Bidua0% (1)
- HW 2 - ChemDocument14 pagesHW 2 - ChemStephanieNo ratings yet
- Gases Practice Quest 2013 AnswersDocument5 pagesGases Practice Quest 2013 Answersethanwong3412No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 1 Prob SetDocument8 pagesPhysical Chemistry 1 Prob SetArrianne Jaye MataNo ratings yet
- E. Gaseoso Tutorial 1Document3 pagesE. Gaseoso Tutorial 1Jaime PoloNo ratings yet
- Homework Questions For Writing PracticeDocument8 pagesHomework Questions For Writing Practicenirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- Chemistry 105, Chapter 5 Exercises: Final and Initial StateDocument4 pagesChemistry 105, Chapter 5 Exercises: Final and Initial StateAdLuqueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Eq. R C MukarjeeDocument48 pagesChemical Eq. R C MukarjeevaibhavNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry PP Ch1 Some Basic Concepts Chemistry 1Document6 pages11 Chemistry PP Ch1 Some Basic Concepts Chemistry 1Jwalant0% (1)
- AGC 311 Exam of 2020Document2 pagesAGC 311 Exam of 2020Chileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven PDFDocument29 pagesChapter Seven PDFTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- POPDocument16 pagesPOPzaneNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 2 (Gas Laws, Density, Molar Mass)Document4 pagesWorksheet - 2 (Gas Laws, Density, Molar Mass)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 QuestionsDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Questions06-087No ratings yet
- Gen Chem Revision 2013 PDFDocument2 pagesGen Chem Revision 2013 PDFPSCNo ratings yet
- Academy For Foun Dation Education in Math & Scien CeDocument5 pagesAcademy For Foun Dation Education in Math & Scien CeprabhakarmetNo ratings yet
- Numericals of Chemical CalculationDocument4 pagesNumericals of Chemical CalculationSaswata Sundar LagaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Gases Due After Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesProblem Set Gases Due After Midterm ExamMorsid LipolesNo ratings yet
- SCES1094 Tutorial 2Document21 pagesSCES1094 Tutorial 2SN2-0622 NURUL ADLYNA BINTI LOKMANNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario de QuimicaDocument3 pagesCuestionario de QuimicaPablo Andres GambaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 20024 General Chemistry Practice Exam #2Document7 pagesCHEM 20024 General Chemistry Practice Exam #2Yhana Ruth PajitaNo ratings yet
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDocument20 pagesGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - 101117Document1 pageTutorial 1 - 101117Yap Khai Ming OscarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial+5-+States of Matter 2022-23Document2 pagesTutorial+5-+States of Matter 2022-23Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- CHEM 015 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet 4 6Document7 pagesCHEM 015 Chemistry For Engineers Worksheet 4 6Ranah Pauolynne LintanNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet IIDocument4 pagesGas Laws Worksheet IIJensen Ryan LimNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDocument2 pagesCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Questions - Structure of Atom + States of Matter +some Basic Concepts of Chemistry, EquilibriumDocument6 pagesNumerical Questions - Structure of Atom + States of Matter +some Basic Concepts of Chemistry, EquilibriummohammedNo ratings yet
- Gas Stoichiometry练习Document2 pagesGas Stoichiometry练习Mary JewelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Exercises See Appendix B For More Exercises On The Gas Laws. 1. 11. A) B) C) 12Document3 pagesChapter 7 Exercises See Appendix B For More Exercises On The Gas Laws. 1. 11. A) B) C) 12Mark Kenneth BaldoqueNo ratings yet
- Pressure Temperature Moles GramsDocument2 pagesPressure Temperature Moles GramsFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 2 (Applications of Ideal Gas Law)Document3 pagesPractice Problems 2 (Applications of Ideal Gas Law)Jose Ruben SortoNo ratings yet
- 04.05 Mole Concept & Stoichiometry CHEM XDocument3 pages04.05 Mole Concept & Stoichiometry CHEM XMohammad Zafrul HasanNo ratings yet
- HW Ch5 (Gases) 2023 2024Document6 pagesHW Ch5 (Gases) 2023 2024hamadaturkman10No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument1 pageChem ReviewerKiki_Amamanglon_3115No ratings yet
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawDocument5 pagesKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsDocument14 pages1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsShyamal DlrNo ratings yet
- 14 - Raw MixDocument31 pages14 - Raw MixDubistWhite100% (1)
- Crushing Principles and Equipment: by Evgueni Porokhovoi. 2019Document53 pagesCrushing Principles and Equipment: by Evgueni Porokhovoi. 2019DubistWhite100% (1)
- 9 - Quarry RehabilitationDocument36 pages9 - Quarry RehabilitationDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Frigate Flyer Air LiftDocument1 pageFrigate Flyer Air LiftDubistWhite100% (1)
- 1 - General GeologyDocument60 pages1 - General GeologyDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- 5 BlastingDocument75 pages5 BlastingDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cement Raw MaterialsDocument32 pages2 - Cement Raw MaterialsDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Rossin RammbllerDocument15 pagesRossin RammbllerDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Engineering PaperDocument15 pagesEngineering PaperDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- M Aking An Impact at Kohat CementDocument4 pagesM Aking An Impact at Kohat CementDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Experiment Molarity (Mol DM) Rates (Mol DM / Min) : Chy2018 Tutorial 3 (Kinetics)Document2 pagesExperiment Molarity (Mol DM) Rates (Mol DM / Min) : Chy2018 Tutorial 3 (Kinetics)DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Transport CoefficientsDocument3 pagesTransport Phenomena Transport CoefficientsDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Tut 2008Document3 pagesElectrochemistry Tut 2008DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- Hach K - C D: ITS Arbon IoxideDocument2 pagesHach K - C D: ITS Arbon IoxideDubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- MAT3004 Work Sheet 2 201314Document3 pagesMAT3004 Work Sheet 2 201314DubistWhiteNo ratings yet