Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urinary System: Kidney and Urinary System Parts and Their Functions
Urinary System: Kidney and Urinary System Parts and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Clari Valente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
URINARY SYSTEM GUION.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesUrinary System: Kidney and Urinary System Parts and Their Functions
Urinary System: Kidney and Urinary System Parts and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Clari ValenteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
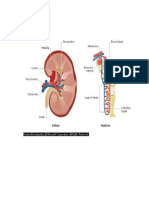
URINARY SYSTEM
Urinary system consisting of the organs that produce,
collect and eliminate urine, include the kidneys,
ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.
¿How do the kidneys and urinary system work?
The body takes nutrients from food and converts them
to energy. After the body has taken the food
components that it needs, waste products are left
behind in the bowel and in the blood.
The kidney and urinary systems help the body to
eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep
chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water
in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and
certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to
the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.
: Other important functions of the kidneys include blood pressure regulation and the
production of erythropoietin, which controls red blood cell production in the bone
marrow. Kidneys also regulate the acid-base balance and conserve fluids.
Kidney and urinary system parts and their functions:
Two kidneys. This pair of purplish-brown organs is
located below the ribs toward the middle of the back.
Their function is to remove liquid waste from the blood
in the form of urine; keep a stable balance of salts and
other substances in the blood; and produce
erythropoietin, a hormone that aids the formation of red
blood cells. The kidneys remove urea from the blood
through tiny filtering units called nephrons.
Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood
capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called
a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other
waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through
the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney.
Two ureters. These narrow tubes carry urine from the
kidneys to the bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls
continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward,
away from the kidneys.
If urine backs up, or is allowed to stand still, a kidney
infection can develop. About every 10 to 15 seconds,
small amounts of urine are emptied into the bladder from
the ureters.
Bladder. This triangle-shaped, hollow organ is located in
the lower abdomen. It is held in place by ligaments that
are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The
bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and
contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra. The typical healthy adult
bladder can store up to two cups of urine for two to five hours.
Two sphincter muscles. These circular muscles help keep urine from leaking by closing
tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder.
: Nerves in the bladder. The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty
the bladder.
Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder
muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain
signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra.
When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
You might also like
- DR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Anatomy of ESRDDocument3 pagesAnatomy of ESRDJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary SystemDonnabell DayudayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SysteDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Urinary SysteCatherine MetraNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyNevoj AnGela NunezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary System-BahanDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System-BahanNurSalimahSuhaimiNo ratings yet
- 1.6 What Do The Kidneys DoDocument3 pages1.6 What Do The Kidneys DoNilar SanNo ratings yet
- Home Based Activity 3Document10 pagesHome Based Activity 3Corpus, Irene Zen P.No ratings yet
- URINARY-SYSTEM XDocument3 pagesURINARY-SYSTEM XRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument5 pagesKidneyecijakaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemCarlos Cardona CanalesNo ratings yet
- KidneysDocument2 pagesKidneysJessan Tapang HernandezNo ratings yet
- Function of The Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesFunction of The Urinary SystemMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Explorer: Click To Read More BelowDocument10 pagesAnatomy Explorer: Click To Read More Belowzahwa dhiyanaNo ratings yet
- Biology THE RENAL SYSTEM OutputDocument7 pagesBiology THE RENAL SYSTEM OutputRhea CabillaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesThe Urinary SystemArl PasolNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Renal SystemDocument5 pagesTutorial Renal SystemManesa ManeshaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Systemmarkerrolbartolome520No ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Urinary Excretory System: AnatomyDocument3 pagesBlood Supply of The Urinary Excretory System: AnatomyJhe CaselNo ratings yet
- Urinary System-WPS OfficeDocument21 pagesUrinary System-WPS OfficeMario Sr. SumpoNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesThe Urinary SystemJoemar TomaquinNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument11 pagesThe Urinary SystemwaplNo ratings yet
- Urinary System ReadingDocument4 pagesUrinary System ReadingpoonamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6John ErickNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: by Marie Cris AmerilaDocument22 pagesUrinary System: by Marie Cris AmerilaZilocke Gelera AmerilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The KidneyDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The KidneyArgie Arguson IINo ratings yet
- Urinary System - Presentation With AudioDocument10 pagesUrinary System - Presentation With AudioSol AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Urinary System: Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra NephronsDocument3 pagesFunctions of The Urinary System: Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra NephronsYahiko YamatoNo ratings yet
- Renal /urinary SystemDocument2 pagesRenal /urinary SystemJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary Systemgaylmm100% (2)
- The Urinary SystemDocument19 pagesThe Urinary SystemCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDianne Dulay VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyrawatanandNo ratings yet
- Name: Nandang, Renaida SDocument6 pagesName: Nandang, Renaida SshakesNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument14 pagesUrinary SystemCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesThe Urinary Systemade100% (1)
- Draft Slide Presentation Human SystemDocument5 pagesDraft Slide Presentation Human SystemNUR AZIERA SYAZWIN MOHAMAD AZMINo ratings yet
- Kidney SystemDocument21 pagesKidney SystemMuntasirNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Kidneys Function 1Document5 pagesKidney and Kidneys Function 1nogakojasmrdiNo ratings yet
- ExcretoryDocument31 pagesExcretoryJevin IndaNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument3 pagesScriptAnghelNo ratings yet
- Definition of Excretory SystemDocument10 pagesDefinition of Excretory SystemTamkeen sheraniNo ratings yet
- Excretory System NotesDocument10 pagesExcretory System Noteswama ojha100% (1)
- The Excretory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Excretory SystemJ’Kell WhyteNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemRosalie EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Functions of Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of Urinary SystemElaiza IcazaNo ratings yet
- An ADocument2 pagesAn Acrazy0214No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Urinary System orDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Urinary System orFatima Dacalos FuerzasNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesUrinary SystemCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- Genitp Urinary SystemDocument200 pagesGenitp Urinary SystemQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary of Urinary System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 6Document6 pagesVocabulary of Urinary System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 6Agustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemCh'an Rak KhunNo ratings yet
- Tabayoyong AnaphysioDocument3 pagesTabayoyong AnaphysioRic VelascoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument22 pagesUrinary Systemapi-288754676No ratings yet
- EXCRETORYDocument2 pagesEXCRETORYdavid beniNo ratings yet
- The Excretory System (Test Paper 1)Document2 pagesThe Excretory System (Test Paper 1)divya manikNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesActivity 10 Urinary SystemKristine Claire GalaceteNo ratings yet
- Pe Excretory SystemDocument19 pagesPe Excretory SystemJelo ClavelNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PCP in A Box - Module 2Document49 pagesPCP in A Box - Module 2shaheershayanqaziNo ratings yet
- Koding Icd 10 & Icd 9 NewwDocument30 pagesKoding Icd 10 & Icd 9 NewwJar Jar79% (14)
- RNL - 2020 - Haramati - PSW Assessment of Tubular HandoutDocument3 pagesRNL - 2020 - Haramati - PSW Assessment of Tubular HandoutSal PaNo ratings yet
- Normal Kidney Anatomy PhysiologyDocument6 pagesNormal Kidney Anatomy PhysiologyAnita CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Course SyllabusDocument9 pagesCourse SyllabusGee RidadNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument6 pagesUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenRahmah Gadis Wartania PutriNo ratings yet
- Adani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Document44 pagesAdani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Siddharth SouravNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Common Drugs PDFDocument221 pagesChapter 18 Common Drugs PDFlalallalaNo ratings yet
- HematuriaDocument51 pagesHematuriaRam ManoharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: The Urinary System: Page 19 of 25Document1 pageChapter 25: The Urinary System: Page 19 of 25JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithotomy To Nephrectomy: A Rare Case in The Field of Philippine-Based SurgeriesDocument58 pagesNephrolithotomy To Nephrectomy: A Rare Case in The Field of Philippine-Based SurgeriesGiuseppe Carlo LaranangNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Anatomi 4 (Sistem Urogenitalia) - 225160100111030 - Almira Carissa Puspita Wijaya (3) - CompressedDocument16 pagesPraktikum Anatomi 4 (Sistem Urogenitalia) - 225160100111030 - Almira Carissa Puspita Wijaya (3) - CompressedAlmira WijayaNo ratings yet
- Notes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - IiiDocument88 pagesNotes 22 - Orientation in para Clinical Science Unit - Iiiswapneelshirsat.ssNo ratings yet
- 101 Homeopathic Remedies FormattedDocument36 pages101 Homeopathic Remedies Formattedapi-26938624100% (12)
- 757 - Penyakit Ginjal KronikDocument30 pages757 - Penyakit Ginjal KronikPujhi Meisya SoniaNo ratings yet
- SN Vs SNADocument26 pagesSN Vs SNAChofi QolbiNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Test Essentials HandbookDocument66 pagesKidney Function Test Essentials HandbookVesna Danity100% (1)
- Urinary Catheterization PPT LectureDocument43 pagesUrinary Catheterization PPT LectureSusan MaglaquiNo ratings yet
- Gagal Ginjal Akut Pada AnakDocument37 pagesGagal Ginjal Akut Pada AnakNycoNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Renal DisordersDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Renal DisordersokaciaNo ratings yet
- Evoluºia I Tratamentul În Sindromul Hemolitic-Uremic La CopilDocument6 pagesEvoluºia I Tratamentul În Sindromul Hemolitic-Uremic La CopilAntonia GenesNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Renal and Urinary Tract FunctionDocument40 pagesAssessment of Renal and Urinary Tract FunctionBjorn Francisco100% (1)
- TURPDocument39 pagesTURPanon_727764033100% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Exam Guidlines 2024Document18 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Exam Guidlines 2024preciousrebotile133No ratings yet
- B SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFDocument183 pagesB SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFsohini bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan UTIDocument5 pagesLesson Plan UTITopeshwar Tpk0% (1)
- Hema, Gut Take Home TestDocument6 pagesHema, Gut Take Home TestNom NomNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument19 pagesRenal SystemAml Sayed Elbadwie KotbNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury DR Moses KazevuDocument52 pagesAcute Kidney Injury DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet