Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3WireSensors SLI pdf1 PDF
3WireSensors SLI pdf1 PDF
Uploaded by
Khaleel Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views48 pagesOriginal Title
167989981-3WireSensors-SLI-pdf1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views48 pages3WireSensors SLI pdf1 PDF
3WireSensors SLI pdf1 PDF
Uploaded by
Khaleel KhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 48
Operation and Diagnosis of 3-Wire
Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Overview
• Correct Operation of Analog Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Overview
• Correct Operation of Analog Sensors
• Correct Operation of Digital Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Overview
• Correct Operation of Analog Sensors
• Correct Operation of Digital Sensors
• Diagnosis of Typical Sensor in a Circuit
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Correct Operation of Analog Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Internal Components of an Analog Sensor
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Correct Operation of Digital Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Internal Components of a Digital Sensor
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Diagnosing Pressure and Temperature Sensors
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Symptoms Leading to Diagnosing Sensors
• Active and/or logged faults
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Symptoms Leading to Diagnosing Sensors
• Active and/or logged faults
• Action lamp or other alert indicators on
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Symptoms Leading to Diagnosing Sensors
• Active and/or logged faults
• Action lamp or other alert indicators on
• Other performance indicators (cranks
but will not start, low power, etc.)
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Inspect Electrical Connectors and
Wiring
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Determine What Condition is Present
• Monitor Active Diagnostic Codes
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Troubleshooting With Diagnostic Codes
• Always start at suspect sensor
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Troubleshooting With Diagnostic Codes
• Always start at suspect sensor
• If the code indicates a “voltage high”, or
open, short the signal circuit to ground
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Troubleshooting With Diagnostic Codes
• Always start at suspect sensor
• If the code indicates a “voltage high”, or
open, check supply voltage, then short
the signal circuit to ground
• If the code indicates a “voltage low”, or
short, check supply voltage, then open
the signal circuit
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Diagnosing “Voltage Low” or Short
• Check for power; If OK then
• Disconnect suspect sensor
• Check for an active “voltage high”
(open) diagnostic code. Allow 15
seconds for any codes to activate.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK – A “voltage low” code was active before
disconnecting the sensor. A “voltage high” code
became active after disconnecting the sensor.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK – A “voltage low” code was active before
disconnecting the sensor. A “voltage high” code
became active after disconnecting the sensor.
• Repair: Temporarily connect a new sensor. Check
for active diagnostic codes. If the new sensor fixes
the problem, reconnect the suspect sensor. If the
problem returns, permanently install the new sensor.
Verify that the repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – There is a short in the
harness between the sensor and the
ECM or the ECM is faulty.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – There is a short between the
sensor and the ECM or the ECM is
faulty.
• Repair: Leave the suspect sensor
disconnected
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – There is a short between the
sensor and the ECM or the ECM is
faulty.
• Repair: Leave the suspect sensor
disconnected
• Create an open circuit at the ECM
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Create an Open Circuit at the ECM
• Remove signal wire of the suspect sensor from the
ECM
• Check for active diagnostic codes
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK – A “voltage high” code (open circuit) became
active after disconnecting the signal wire.
• There is a short in the wiring between the ECM and
the sensor
• Repair: Inspect the wiring between the ECM and the
sensor. Repair or replace the faulty harness. Verify
that the repair eliminates the problem
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – There is still a “voltage low”
diagnostic code (short)
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – There is still a “voltage low” diagnostic code
(short)
• Repair: Connect a test ECM. If the test ECM fixes
the problem, reconnect the suspect ECM. If the
problem returns, permanently install the new ECM.
Verify that the repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Diagnosing “Voltage High” or Open
• Check for power; If OK then
• Disconnect suspect sensor
• Create a short circuit at the harness side of the
sensor
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
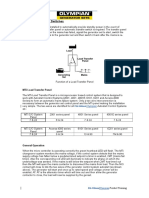
Create a Short Circuit at the Sensor
• Monitor active diagnostic code screen
• Install a jumper wire between terminal “C” (signal)
and terminal “B” (sensor common) on the harness
side of the sensor connector. Wait 15 seconds for
activation of “voltage low” code.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK – A “voltage low” diagnostic code (short)
is active when the jumper is installed. The
engine harness and the ECM are OK.
• Repair: Temporarily connect a new sensor.
If the new sensor fixes the problem,
reconnect the suspect sensor. If the problem
returns, permanently install the new sensor.
Verify that the repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – The “voltage high” diagnostic
code (open) remains active when the
jumper wire is installed.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – The “voltage high” diagnostic
code (open) remains active when the
jumper wire is installed.
• Repair: Remove the jumper wire.
Create a short at the ECM
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Creating a Short at the ECM
• Install a jumper wire between the terminal for the
signal of the suspect sensor and the sensor common
at the ECM
• Monitor the active code screen. Wait 15 seconds for
activation of any code.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK – The ECM is operating properly. There is an
open in the wiring between the ECM and the sensor.
• Repair: Inspect the wiring and connectors between
the ECM and the sensor. Repair or replace faulty
harness components. Verify that the repair
eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – The “voltage high” code (open) is still active
when the jumper wire is installed.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• Not OK – The “voltage high” code (open) is still active
when the jumper wire is installed.
• Repair: Temporarily connect a test ECM. If the test
ECM fixes the problem, reconnect the suspect ECM.
If the problem returns, permanently install a new
ECM. Verify that the repair eliminates the problem
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Invalid Signal Codes
Codes that do not indicate open or shorted state
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Monitor Supply Voltage at
Sensor
• Install breakout “T” or test probes (spoons)
• Measure voltage between terminals “A” and “B”
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Measured supply voltage is supply voltage +/-
.5 volt. Proceed to measure signal at harness side of
connector.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Measured supply voltage is supply voltage +/-
.5 volt. Proceed to measure signal at harness side of
connector.
• Not OK: Sensor is not receiving correct voltage.
Measure voltage at ECM using breakout “T” or
spoons. Inspect electrical connectors and wires.
Repair or replace faulty components. Verify repair
eliminates problem
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Measure Signal at Harness Side
of Sensor
• With breakout installed, disconnect “C” terminal from
harness side of connector
• Using a DMM, measure the duty cycle between “B”
and “C” at the breakout while depressing and
releasing accelerator pedal
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Duty cycle is between 10 and 22 percent
while fully released. Duty cycle is between 75
and 90 percent while fully depressed.
Reconnect “C” wire. Proceed to measure
signal at ECM.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Duty cycle is between 10 and 22 percent
while fully released. Duty cycle is between 75
and 90 percent while fully depressed.
Reconnect “C” wire. Proceed to measure
signal at ECM.
• Not OK: Duty cycle is not present or out of
range. Temporarily install a new sensor. If
the new sensor eliminates the problem,
reconnect the suspect sensor. If problem
returns, permanently install a new sensor.
Verify repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Measure Duty Cycle at Harness
Side of ECM
• Use appropriate ECM breakout or
spoons at ECM connector
• Using a DMM, measure duty cycle
between signal and sensor return pins
while depressing and releasing pedal
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Duty cycle is between 10 and 22 percent
while fully released. Duty cycle is between 75
and 90 percent while fully depressed.
Temporarily connect a test ECM. If problem
is resolved with the test ECM, reconnect
suspect ECM. If problem returns,
permanently install new ECM. Verify that the
repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Results
• OK: Duty cycle is between 10 and 22 percent while
fully released. Duty cycle is between 75 and 90
percent while fully depressed. Temporarily connect a
test ECM. If problem is resolved with the test ECM,
reconnect suspect ECM. If problem returns,
permanently install new ECM. Verify that the repair
eliminates the problem.
• Not OK: Duty cycle is not present or out of range.
There is a problem with the pedal position sensor
signal wire. Repair or replace faulty wiring. Verify
that the repair eliminates the problem.
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
Open “A” Pin
Global Service Learning & Performance Division
You might also like
- 3406-40 Pin - ECM Diagramas PDFDocument2 pages3406-40 Pin - ECM Diagramas PDFDavid Fuentes79% (29)
- 1078 3Document5 pages1078 3Marco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- 3512 Sensor TestDocument14 pages3512 Sensor TestSayed Younis Sadaat100% (1)
- Caterpillar ADEM II 3176C 3406E C10 C12 Completo PDFDocument2 pagesCaterpillar ADEM II 3176C 3406E C10 C12 Completo PDFOmar Garcia Cazares100% (3)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- 1079 3Document5 pages1079 3Marco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- No Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023From EverandNo Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Motor DiagnosticsDocument5 pagesMotor DiagnosticssabrahimaNo ratings yet
- Engine Speed Circuit FaultDocument7 pagesEngine Speed Circuit Faultyasser eljabaliNo ratings yet
- Baker D1200 Troubleshoot GuideDocument29 pagesBaker D1200 Troubleshoot GuideChristian LefroitNo ratings yet
- 5 Volt Engine Pressure Sensor Supply Circuit - TestDocument8 pages5 Volt Engine Pressure Sensor Supply Circuit - TestGustavo GarzaNo ratings yet
- Mxs Fault Codes EngDocument31 pagesMxs Fault Codes EngKristofer OyervidesNo ratings yet
- C15 E-Oil PressureDocument11 pagesC15 E-Oil PressureAndiNo ratings yet
- Digital Clamp-On Meter: Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesDigital Clamp-On Meter: Instruction ManualIBjsc VietnamNo ratings yet
- Falla D8T Mando de DireccionDocument5 pagesFalla D8T Mando de Direccionalonso fernanezNo ratings yet
- D6R Track-Type Tractor 2YN00001-UP (MACHINE) POللببWERED BY 3306 Engine (SEBP2615 - 58) - Document StructureDocument5 pagesD6R Track-Type Tractor 2YN00001-UP (MACHINE) POللببWERED BY 3306 Engine (SEBP2615 - 58) - Document StructureBasem ElhosanyNo ratings yet
- Illustration 1 g01374861 Connections of The Tilt Lever Position SensorDocument3 pagesIllustration 1 g01374861 Connections of The Tilt Lever Position SensorNofy SNo ratings yet
- 4bz 3412 Gensets PeecDocument7 pages4bz 3412 Gensets PeecSameh Rashad Ahmed67% (3)
- Capacitación MidtronicsDocument44 pagesCapacitación MidtronicsYolian Andres Aricapa CastañoNo ratings yet
- Ali Endris - 230502 - 204733Document22 pagesAli Endris - 230502 - 204733Ali EndrisNo ratings yet
- Manual IDEAL Series 700Document17 pagesManual IDEAL Series 700Enrique Matus RecabalNo ratings yet
- 700 Series: 200 Amp Clamp MetersDocument12 pages700 Series: 200 Amp Clamp MetersTom BeanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting: D3G, D4G and D5G Track-Type Tractors ElectrohydraulicDocument5 pagesTroubleshooting: D3G, D4G and D5G Track-Type Tractors ElectrohydraulicX'mix ĐreamerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document107 pagesLecture 8sampath bandaraNo ratings yet
- P0713Document6 pagesP0713SenaMecánicaElectrónicaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Transducer (YOKOGAWA)Document8 pagesPressure Transducer (YOKOGAWA)Yogaditya ModukuriNo ratings yet
- Testing Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterDocument17 pagesTesting Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterIra CervoNo ratings yet
- How To Completely Check The High Voltage Circuit in CRT Monitor/TelevisionDocument12 pagesHow To Completely Check The High Voltage Circuit in CRT Monitor/TelevisionspencerNo ratings yet
- Illustration 1 g01374755 Connections of The Blade Lift Lever Position SensorDocument3 pagesIllustration 1 g01374755 Connections of The Blade Lift Lever Position SensorNofy SNo ratings yet
- Not Ok (Digital) : Test Step Result Diagnosis/ActionDocument24 pagesNot Ok (Digital) : Test Step Result Diagnosis/ActionDaniel LopezNo ratings yet
- 1505 1018 000 CRCDocument4 pages1505 1018 000 CRCtomNo ratings yet
- FC Change DiagnosticsDocument37 pagesFC Change DiagnosticsMustofa TofaNo ratings yet
- Digital Product TestingDocument43 pagesDigital Product TestingecehemnathNo ratings yet
- Analog InstrumentsDocument58 pagesAnalog Instrumentsrajkumar.gNo ratings yet
- ENG CS 13C9138 Verification Diagnosis AppNote 0613 13C9138 - Verification and Diagnosis of Suspected Relay FailuresDocument4 pagesENG CS 13C9138 Verification Diagnosis AppNote 0613 13C9138 - Verification and Diagnosis of Suspected Relay FailuresZorbanfrNo ratings yet
- Engine Pressure Sensor Open or Short Circuit - TestDocument10 pagesEngine Pressure Sensor Open or Short Circuit - TestGustavo GarzaNo ratings yet
- KT62 ManualDocument30 pagesKT62 ManualandyjwatsonNo ratings yet
- Saturn GC-MS TroubleshootingDocument32 pagesSaturn GC-MS Troubleshootingrenatomiani100% (1)
- 2688 DerechoDocument4 pages2688 DerechoDiego CatariNo ratings yet
- Digital Clamp-On Meter: Instruction ManualDocument40 pagesDigital Clamp-On Meter: Instruction ManualIBjsc VietnamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Equipment Troubleshooting ProcessDocument277 pagesElectronic Equipment Troubleshooting Processznim04No ratings yet
- Codigo 1079 - 3Document4 pagesCodigo 1079 - 3ericNo ratings yet
- Tea Sensor de Velocidade 2Document7 pagesTea Sensor de Velocidade 2Valmaq Prestação Serviço LdaNo ratings yet
- Challeger Testeo y AjusteDocument304 pagesChalleger Testeo y AjusteCarlos Irabedra100% (1)
- Illustration 1 g01375618 Connections of The Forward/reverse Position SensorDocument3 pagesIllustration 1 g01375618 Connections of The Forward/reverse Position SensorNofy SNo ratings yet
- Core Skills TrainingDocument6 pagesCore Skills TraininggentoaliNo ratings yet
- 5 Volt Engine Pressure Sensor Supply Circuit - Test: TroubleshootingDocument7 pages5 Volt Engine Pressure Sensor Supply Circuit - Test: TroubleshootingsyahrilNo ratings yet
- Injection Actuation Pressure Control Valve - Test: TroubleshootingDocument10 pagesInjection Actuation Pressure Control Valve - Test: TroubleshootingsatyaNo ratings yet
- Fnirsi-S1: Digital Multimeter Instruction ManualDocument64 pagesFnirsi-S1: Digital Multimeter Instruction ManualJose Maria Silva PimentaNo ratings yet
- Sensor Signal (PWM) - Test: TroubleshootingDocument9 pagesSensor Signal (PWM) - Test: TroubleshootingOsvaldo UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Q4 - Week 1 - V2 - 084059Document4 pagesQ4 - Week 1 - V2 - 084059Vina TomeNo ratings yet
- Cirris 1100H+: Performance Verification ManualDocument33 pagesCirris 1100H+: Performance Verification ManualJosé MLNo ratings yet
- Report Multimeter and OsiloskopDocument13 pagesReport Multimeter and OsiloskopFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- 33XR ManualDocument20 pages33XR ManualAbubacker SiddiqNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsFrom EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNo ratings yet
- CDVR CommisioningDocument47 pagesCDVR CommisioningCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- Conexiune Serie SteaDocument1 pageConexiune Serie SteaCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- High Voltage: Shutdown SISDocument6 pagesHigh Voltage: Shutdown SISCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- PPL035268 - Alternator: Catalogue ID: OLY - v2019Document2 pagesPPL035268 - Alternator: Catalogue ID: OLY - v2019Candiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- Installation CDVRDocument12 pagesInstallation CDVRCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- USB CANmodul SeriesDocument2 pagesUSB CANmodul SeriesCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- Sentinel 150 / UL150: Automatic Switch Mode Battery ChargersDocument4 pagesSentinel 150 / UL150: Automatic Switch Mode Battery ChargersCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- 227 242 211 228 227 237 209 228 227 244 210 227 610 618 0 519 608 614 0 517 604 610 0 513 Mains Freq (1) (HZ) 49.9 53.7 41.2 49.9Document1 page227 242 211 228 227 237 209 228 227 244 210 227 610 618 0 519 608 614 0 517 604 610 0 513 Mains Freq (1) (HZ) 49.9 53.7 41.2 49.9Candiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- EST-OLYMPIAN 2010B v1.0 ECM Replacement 02/03/2012 16:45Document65 pagesEST-OLYMPIAN 2010B v1.0 ECM Replacement 02/03/2012 16:45Candiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- Oly Changeover SystemsDocument5 pagesOly Changeover SystemsCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet
- LG 32LD650 - 32LD651 - 32LD680 - 32LD690 LCD TV SM PDFDocument40 pagesLG 32LD650 - 32LD651 - 32LD680 - 32LD690 LCD TV SM PDFQDownload4575No ratings yet
- Oly Changeover SystemsDocument5 pagesOly Changeover SystemsCandiano PopescuNo ratings yet