Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each Side
Uploaded by
Dr santosh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Lateral Ventricle
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views4 pagesLateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each Side
Uploaded by
Dr santoshCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
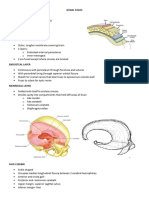
Lateral ventricle
These are irregular cavities with in the lower
& medial part of cerebral hemisphere
Number - two in number one on each side
of median plane & are separated from each
other by a septum pellucidum
Communication -
1. With 3rd ventricle through
interventricular foramen or foramen of
monro ( situated in front of anterior
end of thalamus )
2. Indirectly with opposite lateral ventricle
via 3rd ventricle
Contents – CSF
Lining membrane - ependyma
Different parts -
1. central part
2. three horns
a) anterior
b) posterior
c) inferior
Anterior horn – it lies in front of foramen
monro & it extends in to frontal lobe
Boundaries -
Roof - trunk of corpus callosum
Floor – rostrum of corpus callosum
Medial wall - septum pellucidum & columns
of fornix
Anterior wall - by genu of corpus callosum
Central horn - it is second largest part of
lateral ventricle it lies in parietal lobe it
extends from foramen monro to splenium of
corpus callosum
Boundaries -
Roof - trunk of corpus callosum
Floor - body of caudate nucleus, thalamus,
stria terminalis, thalamostriate vein
Medial wall - septum pellucidum, body of
fornix –it is bundle of fibres connecting RT &
Lt hippocampus
Posterior horn - it is small horn which
extend in to occipital lobe lies behind
Splenium of corpus callosum it may be
absent
Boundaries -
Roof - superior longitudinal fasciculus,
teptum optic radiation
Floor – bulb of posterior horn, due to
forceps major, calcar avis –it is elevation due
calcarine sulcus
Inferior horn - it is largest horn of lateral
ventricle present in temporal lobe
Boundaries -
Roof - tail of caudate nucleus, teptum, and
stria terminalis
Floor - collateral eminence it is due to
collateral sulcus hippocampus gyrus
Applied anatomy -
1. obstruction of foramen monro leads to
hydrocephalous it is due to brain tumor
SOL
2. Ventriculography – X-ray for
visualization of ventricle
3. lateral ventricle can reach by passing
needle oblique from pterion
4. shunt operation done to drainage of
CSF
You might also like
- Brain VentriclesDocument23 pagesBrain VentriclesAndrei Scripcaru100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDeshini Balasubramaniam83% (6)
- 72-HR ChickDocument16 pages72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- Third VentricleDocument4 pagesThird VentricleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour ChickDocument13 pages48 Hour ChickJowi SalNo ratings yet
- Cranial FossaDocument9 pagesCranial FossaDr santoshNo ratings yet
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFDocument3 pages48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachNo ratings yet
- 48hr ChickDocument2 pages48hr ChickYeonruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Eartac_tic_tus100% (1)
- Epitympanic Anatomy Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2013 MarchioniDocument14 pagesEpitympanic Anatomy Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2013 MarchioniAbdiaziz WalhadNo ratings yet
- Ant 325materialDocument13 pagesAnt 325materialDestiny BlissNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pagesMiddle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Dr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord 1Document8 pagesSpinal Cord 1Alina PetreNo ratings yet
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDocument12 pagesDevelopment of The Pig EmbryoKarmina SantosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - GhonemyDocument46 pagesAnatomy of The Ear: Prof. Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - Ghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Author 'S Accepted ManuscriptDocument46 pagesAuthor 'S Accepted ManuscriptRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- Dura Mater & Cranial SinusDocument30 pagesDura Mater & Cranial SinusSadiq Wadood SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Dura Mater & Cranial SinusDocument30 pagesDura Mater & Cranial SinusSadiq Wadood Siddiqui100% (1)
- Pituitary GlandDocument2 pagesPituitary GlandBnB UsmleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cranial CavityDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Cranial CavityexoNo ratings yet
- Cavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumDocument79 pagesCavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumSchönberger AlbertNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The EarBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- The Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دDocument20 pagesThe Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دStevanovic StojaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of External EarDocument49 pagesAnatomy of External EarInderdeep AroraNo ratings yet
- Third Ventricular TumoursDocument4 pagesThird Ventricular Tumourspedrixon123No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy 11: Brain Ventricles: The Anterior HornDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomy 11: Brain Ventricles: The Anterior HornstuffNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone AnatomyDocument39 pagesTemporal Bone AnatomymizmuzNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument63 pagesHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- Middle Ear Anatomy and Physiology of HearingDocument58 pagesMiddle Ear Anatomy and Physiology of HearingGokul Krishnan VadakkeveeduNo ratings yet
- 28 Temporal Bone (Done)Document7 pages28 Temporal Bone (Done)Ayah HyasatNo ratings yet
- Brain Ventricles: (Rabbia Yousaf) Pharm-D Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument29 pagesBrain Ventricles: (Rabbia Yousaf) Pharm-D Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- The Ventricular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Ventricular SystemM Arsalan TariqNo ratings yet
- Posterior Triangle of The Neck: Maribel G. Castro-Enano, M.D. CPU College of MedicineDocument28 pagesPosterior Triangle of The Neck: Maribel G. Castro-Enano, M.D. CPU College of MedicineAlexandru GusacinschiNo ratings yet
- Anterior Skull Base Resection External ApproachesDocument15 pagesAnterior Skull Base Resection External ApproachesDANDYNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3RD Semester by Apostle JohnDocument28 pagesAnatomy 3RD Semester by Apostle JohnOROKE JOHN EJENo ratings yet
- 3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)Document28 pages3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Development of The ForebrainDocument11 pagesDevelopment of The ForebrainShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - Anatomy of The NoseDocument4 pagesLecture - 1 - Anatomy of The NoseDeepBhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Mikey 1stshift ClinicalanatomyDocument1 pageMikey 1stshift ClinicalanatomyMichael Jeffrey M. MillaresNo ratings yet
- Adhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanDocument51 pagesAdhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanErwin DiprajaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PharynxDocument27 pagesAnatomy of PharynxParul Gupta100% (2)
- Pathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. JamesDocument15 pagesPathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. Jameshzol83No ratings yet
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocument22 pagesB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364No ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinuses AnatomyDocument55 pagesParanasal Sinuses AnatomyVictor EnachiNo ratings yet
- Interior of SkullDocument11 pagesInterior of SkullUnaiza Siraj100% (1)
- The Fourth VentricleDocument16 pagesThe Fourth VentricleHiraNo ratings yet
- Dural FoldsDocument3 pagesDural FoldsHello VintunnaraNo ratings yet
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDocument28 pages48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Regional Anatomy Question - MidtermDocument6 pagesRegional Anatomy Question - MidtermManju ShreeNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR - Mohamed Talaat ElghonemyDocument49 pagesProf. DR - Mohamed Talaat Elghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- VTH CNDocument59 pagesVTH CNdoktergigikoeNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument13 pagesThe EarOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Forebrain or Prosencephalon: The DiencephalonDocument6 pagesForebrain or Prosencephalon: The DiencephalonMarcoNo ratings yet
- 1 Pituitary GlandDocument25 pages1 Pituitary Glandali msheikNo ratings yet
- 25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pages25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Potongan CSOM Part 2Document12 pagesPotongan CSOM Part 2Athanasius WrinNo ratings yet
- Correlative AnatomyDocument19 pagesCorrelative AnatomyLicensed to HealNo ratings yet
- Interior of The SkulDocument14 pagesInterior of The SkulArshad hussainNo ratings yet
- MediastinumDocument4 pagesMediastinumDr santosh100% (1)
- Inlet of ThoraxDocument1 pageInlet of ThoraxDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Thoracic DuctDocument2 pagesThoracic DuctDr santosh100% (1)
- LungsDocument7 pagesLungsDr santosh100% (1)
- PericardiumDocument2 pagesPericardiumDr santoshNo ratings yet
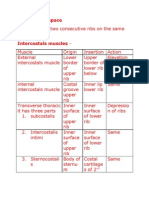
- Intercostals SpaceDocument3 pagesIntercostals SpaceDr santoshNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument12 pagesHeartDr santosh100% (1)
- Introduction To ThoraxDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ThoraxDr santosh100% (2)
- Angle of Louis or Sterna AngleDocument1 pageAngle of Louis or Sterna AngleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument6 pagesBreastDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata 1Document5 pagesMedulla Oblongata 1Dr santoshNo ratings yet
- AxillaDocument3 pagesAxillaDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Thalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDocument8 pagesThalamus-: Disposition - It Lies Obliquely With Its Long AxisDr santoshNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument5 pagesHypothalamusDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Azygos VeinDocument2 pagesAzygos VeinDr santoshNo ratings yet
- White Fibers of CerebrumDocument2 pagesWhite Fibers of CerebrumDr santosh100% (1)
- CerebellumDocument5 pagesCerebellumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument12 pagesCerebrumDr santoshNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument29 pagesCardioDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous SystemDr santoshNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument3 pagesMusclesDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply To Long BonesDocument1 pageBlood Supply To Long BonesDr santoshNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument4 pagesBoneDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Muscles of HandDocument11 pagesMuscles of HandDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Muscles of FaceDocument5 pagesMuscles of FaceDr santosh100% (1)
- Muscles of SoleDocument5 pagesMuscles of SoleDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Muscles of MasticationDocument2 pagesMuscles of MasticationDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Muscles of PharynxDocument3 pagesMuscles of PharynxDr santoshNo ratings yet