Professional Documents
Culture Documents
28 Waves-Wave Basics
Uploaded by
eltytanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
28 Waves-Wave Basics
Uploaded by
eltytanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Basics
1. Which type of wave requires a material medium 7. A ringing bell is located in a chamber. When the air
through which to travel? is removed from the chamber, why can the bell be
1. sound seen vibrating but not be heard?
2. television 1. Light waves can travel through a vacuum, but
3. radio sound waves cannot.
4. x ray 2. Sound waves have greater amplitude than light
waves.
2. A single vibratory disturbance moving through a 3. Light waves travel slower than sound waves.
medium is called 4. Sound waves have higher frequencies than light
1. a node waves.
2. an antinode
3. a standing wave 8. Which statement correctly describes one characteris-
4. a pulse tic of a sound wave?
1. A sound wave can travel through a vacuum
3. The diagram below represents a transverse wave 2. A sound wave is a transverse wave
traveling to the right through a medium. Point A 3. The amount of energy a sound wave transmits is
represents a particle of the medium. directly related to the wave’s amplitude.
4. The amount of energy a sound wave transmits is
inversely related to the wave’s frequency
9. A television remote control is used to direct pulses of
electromagnetic radiation to a receiver on a televi-
sion. This communication from the remote control
In which direction will particle A move in the next to the television illustrates that electromagnetic
instant of time? radiation
1. up 1. is a longitudinal wave
2. down 2. possesses energy inversely proportional to its
3. left frequency
4. right 3. diffracts and accelerates in air
4. transfers energy without transferring mass
4. As a transverse wave travels through a medium, the
individual particles of the medium move 10. The diagram below represents a transverse wa-
1. perpendicular to the direction of wave travel ter wave propagating toward the left. A cork
2. parallel to the direction of wave travel is floating on the water’s surface at point P.
3. in circles
4. in ellipses
5. A periodic wave transfers
1. energy, only
2. mass, only
3. both energy and mass In which direction will the cork move as the wave
4. neither energy nor mass passes point P?
1. up, then down, then up
6. Which type of wave requires a material medium 2. down, then up, then down
through which to travel? 3. left, then right, then left
1. radio wave 4. right, then left, then right
2. microwave
3. light wave
4. mechanical wave
Page 156 WAV.A1 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Basics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Basics
11. A pulse traveled the length of a stretched spring. 14. Which form(s) of energy can be transmitted through
The pulse transferred a vacuum?
1. energy, only 1. light, only
2. mass, only 2. sound, only
3. both energy and mass 3. both light and sound
4. neither energy nor mass 4. neither light nor sound
12. A transverse wave passes through a uniform material 15. How are electromagnetic waves that are produced by
medium from left to right, as shown in the diagram oscillating charges and sound waves that are pro-
below. duced by oscillating tuning forks similar?
1. Both have the same frequency as their respective
sources.
2. Both require a matter medium for propagation.
3. Both are longitudinal waves.
4. Both are transverse waves.
16. A student strikes the top rope of a volleyball net,
Which diagram best represents the direction
sending a single vibratory disturbance along the
of vibration of the particles of the medium?
length of the net, as shown in the diagram below.
13. A tuning fork vibrating in air produces sound waves.
These waves are best classified as
1. transverse, because the air molecules are vibrat-
ing parallel to the direction of wave motion
2. transverse, because the air molecules are vibrat-
ing perpendicular to the direction of wave mo-
tion
3. longitudinal, because the air molecules are vi-
brating parallel to the direction of wave motion
4. longitudinal, because the air molecules are This disturbance is best described as
vibrating perpendicular to the direction of wave 1. a pulse
motion 2. a periodic wave
3. a longitudinal wave
4. an electromagnetic wave
17. Which diagram below does not represent a periodic wave?
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Basics WAV.A1 Page 157
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Basics
18. An earthquake wave is traveling from west to east 20. A tuning fork oscillates with a frequency of 256
through rock. If the particles of the rock are vibrat- hertz after being struck by a rubber hammer. Which
ing in a north-south direction, the wave must be phrase best describes the sound waves produced by
classified as this oscillating tuning fork?
1. transverse 1. electromagnetic waves that require no medium
2. longitudinal for transmission
3. a microwave 2. electromagnetic waves that require a medium for
4. a radio wave transmission
3. mechanical waves that require no medium for
19. As a transverse wave travels through a medium, the transmission
individual particles of the medium move 4. mechanical waves that require a medium for
1. perpendicular to the direction of wave travel transmission
2. parallel to the direction of wave travel
3. in circles
4. in ellipses
A longitudinal wave moves to the right through a uniform medium, as shown below. Points A, B, C, D, and E repre-
sent the positions of particles of the medium.
21. Which diagram best represents the motion of the particle at position C as the wave moves to the right?
22. The wavelength of this wave is equal to the distance between points
1. A and B
2. A and C
3. B and C
4. B and E
23. The energy of this wave is related to its
1. amplitude
2. period
3. speed
4. wavelength
Page 158 WAV.A1 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Basics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Basics
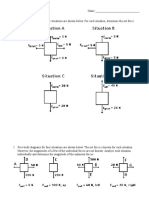
Base your answers to questions 24 and 25 on the diagram at right,
which shows a wave in a rope.
24. Determine the wavelength of the wave.
25. Determine the amplitude of the wave.
26. The energy of a sound wave is most closely related to 29. Transverse waves are to radio waves as longitudinal
the wave’s waves are to
1. frequency 1. light waves
2. amplitude 2. microwaves
3. wavelength 3. ultraviolet waves
4. speed 4. sound waves
27. Which statement describes a characteristic common 30. The diagram below shows a periodic wave.
to all electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves?
1. Both types of waves travel at the same speed.
2. Both types of waves require a material medium
for propagation.
3. Both types of waves propagate in a vacuum.
4. Both types of waves transfer energy.
Which two points on the wave are 180° out of
28. The diagram below represents a periodic wave mov- phase?
ing along a rope. 1. A and C
2. B and E
3. F and G
4. D and H
31. The diagram below shows a mechanical transverse
wave traveling to the right in a medium. Point
A represents a particle in the medium. Draw an
On the grid below, draw at least one full wave with arrow originating at point A to indicate the initial
the same amplitude and half the wavelength of the direction that the particle will move as the wave
given wave. continues to travel to the right in the medium.
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Basics WAV.A1 Page 159
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Basics
32. The amplitude of a sound wave is most closely re-
lated to the sound’s
1. speed
2. wavelength
3. loudness
4. pitch
33. As a longitudinal wave moves through a medium,
the particles of the medium
1. vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave’s
propagation
2. vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the
wave’s propagation
3. are transferred in the direction of the wave’s mo-
tion, only
4. are stationary
Page 160 WAV.A1 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Basics
You might also like
- Bixby MaxFire and UBB Service ManualDocument71 pagesBixby MaxFire and UBB Service ManualAl Malley92% (13)
- Pogil Describing MotionDocument2 pagesPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- Active Reading: Answer KeyDocument3 pagesActive Reading: Answer KeyJonas Montero100% (2)
- Accuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabDocument6 pagesAccuracy Precision Mini POGIL, LabAlistair Morgan100% (1)
- Spectrum WebquestDocument3 pagesSpectrum Webquestjanet_tran0% (1)
- Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesWaves Worksheettownsenr94100% (14)
- Unit TestBDocument7 pagesUnit TestBdanahansenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable EcosystemsDocument5 pagesSustainable EcosystemsbobNo ratings yet
- 6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-SDocument5 pages6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-Sapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Light Sound Wave Simulations AnswersDocument9 pagesLight Sound Wave Simulations Answersapi-233194737No ratings yet
- Unit 1 TestDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Testapi-485795043No ratings yet
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocument27 pages7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy WebquestDocument3 pagesRenewable Energy Webquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramDocument3 pagesFree Body DiagramMani MalNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23Document12 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23shkjsdhfskjd60% (5)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheeteltytanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Physics-MC/Electromagnetism/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesElectromagnetism: Physics-MC/Electromagnetism/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3eltytanNo ratings yet
- Planning For Project Layout ReportDocument11 pagesPlanning For Project Layout ReportAko C Rence100% (2)
- Bird On Fire Lessons From The World's Least Sustainable CityDocument310 pagesBird On Fire Lessons From The World's Least Sustainable CityDavidNo ratings yet
- 30 Waves-Wave BehaviorsDocument10 pages30 Waves-Wave BehaviorseltytanNo ratings yet
- General Wave PropertiesDocument8 pagesGeneral Wave PropertiesHunterNo ratings yet
- Waves Page 1 2013Document1 pageWaves Page 1 2013api-222503660No ratings yet
- 21 Evolution and Selection-SDocument6 pages21 Evolution and Selection-SSSSSSSSSSS100% (1)
- 16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFDocument7 pages16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- Types of Natural SelectionDocument2 pagesTypes of Natural SelectionRichard MohammedNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- POGIL Scientific MethodDocument4 pagesPOGIL Scientific MethodKavita SadanaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations POGILDocument7 pagesBalancing Equations POGILSharmet SolarzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On RefractionDocument1 pageWorksheet On RefractionMariam SturgessNo ratings yet
- Biome Poster RubricDocument1 pageBiome Poster Rubricapi-359626316No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 AQA Physics GCSEDocument7 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 AQA Physics GCSEsolzorNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet (Unit # 11) - Class VIIIDocument7 pagesRevision Worksheet (Unit # 11) - Class VIIISitwat BatoolNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Document21 pagesWork Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Liam ReillyNo ratings yet
- Study Guide WavesDocument2 pagesStudy Guide Wavesapi-259781257No ratings yet
- Genetics Study GuideDocument4 pagesGenetics Study Guidegmanb5100% (2)
- Waves Worksheet #2: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesWaves Worksheet #2: Name: - Dateapi-260547045No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Webquest 3Document5 pagesChemical Reactions Webquest 3api-262586446No ratings yet
- Waves LabDocument6 pagesWaves Labsamarghai0% (1)
- Elasticity BoardworksDocument27 pagesElasticity BoardworksMurugan.SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetDocument2 pagesLesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetJep Val0% (1)
- Year 11 Genetics Revision TestDocument10 pagesYear 11 Genetics Revision Testapi-338606774No ratings yet
- Trends in Period 3Document34 pagesTrends in Period 3Fildzah AdanyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument81 pagesChemical BondingkhushiNo ratings yet
- Punnett SQ Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPunnett SQ Cheat SheetMark Anthony Nelvida VirayNo ratings yet
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 pagesVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of PopulationsDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of PopulationsAnn Marilette100% (2)
- The Atomic ModelDocument22 pagesThe Atomic ModelIntan CahyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Problem SetDocument5 pagesHardy Weinberg Problem SetNur Syakira IsmailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Review PacketDocument17 pagesChapter 11 Review PacketLalisampt.20% (1)
- A Level PhysicsDocument25 pagesA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Quiz, Quiz, Trade Atom and Periodic TableDocument5 pagesQuiz, Quiz, Trade Atom and Periodic TablefatraxiiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: The Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument7 pagesChemistry: The Periodic Table and PeriodicityAiden100% (1)
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelDocument6 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- Incomplete and Codominance Review Worksheet 2012Document3 pagesIncomplete and Codominance Review Worksheet 2012Brasa Y. de Almira0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Mendelian InheritDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Mendelian InheritDiego Garcia67% (3)
- BondingDocument24 pagesBondingapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Sound PDFDocument23 pagesSound PDFOmer KaleemNo ratings yet
- Genotype Phenotype WorksheetDocument3 pagesGenotype Phenotype WorksheetJohn G Villar100% (1)
- Coastal ProcessesDocument15 pagesCoastal Processesapi-258813608No ratings yet
- Ch5.1 Types of WaveDocument13 pagesCh5.1 Types of WaveAmaresh SivakumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ From Sound & WaveDocument3 pagesMCQ From Sound & WaveRaktimNo ratings yet
- 03+G7 WavesDocument26 pages03+G7 WavesRose Ann YamcoNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument2 pagesWAVESJustus D ZatkalikNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceeltytanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: © 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: © 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights ReservedeltytanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Comparing Various Types of CollisionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Comparing Various Types of CollisionseltytanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Units and DimensionsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Units and Dimensionseltytan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationeltytanNo ratings yet
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Document7 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanNo ratings yet
- Phy Graphical Method P2Document1 pagePhy Graphical Method P2eltytanNo ratings yet
- Phy Electronics P2Document5 pagesPhy Electronics P2eltytanNo ratings yet
- AL Applied Mathematics 1987 Paper1+2 (E)Document6 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1987 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanNo ratings yet
- Phy Radioactivity P2Document2 pagesPhy Radioactivity P2eltytanNo ratings yet
- Phy Radioactivity P22Document5 pagesPhy Radioactivity P22eltytanNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Physics-MC/Electronics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 11Document11 pagesElectronics: Physics-MC/Electronics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 11eltytanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Physics-MC/Electrostatics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesElectrostatics: Physics-MC/Electrostatics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3eltytanNo ratings yet
- Physics - Reflection & Refraction: Sahil KhandareDocument11 pagesPhysics - Reflection & Refraction: Sahil KhandaressskNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Performance Analysis of Francis HydDocument9 pagesA Study On The Performance Analysis of Francis HydAru Mithayatri RamlanNo ratings yet
- A User S Guide To Electrical Ppe Based On Nfpa 70 e Ray A. Jones and Jae G. Jones PDFDocument88 pagesA User S Guide To Electrical Ppe Based On Nfpa 70 e Ray A. Jones and Jae G. Jones PDFJairo FlechasNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: LC320EM81Document69 pagesService Manual: LC320EM81wilfredo falconNo ratings yet
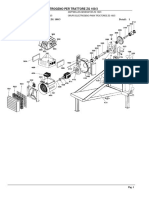
- 1 Detail: Gr. Elettrogeno Per Trattore ZG 100/3Document3 pages1 Detail: Gr. Elettrogeno Per Trattore ZG 100/3npNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document43 pagesLecture 12salem bahsan100% (1)
- The Starting SystemDocument20 pagesThe Starting SystemRuth MwendaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Test - Flushing - Pickling - Passivation Hyd-Cw-GrDocument12 pagesPressure Test - Flushing - Pickling - Passivation Hyd-Cw-GrVidal Choque N.100% (1)
- Application TGADocument8 pagesApplication TGAMOHD KHAIRY IZZUAN BIN MOHD YUSOFNo ratings yet
- E25b'04 E30h'04 25B'04 30H'04: (69P4) (60B4) (69R4) (69S4)Document61 pagesE25b'04 E30h'04 25B'04 30H'04: (69P4) (60B4) (69R4) (69S4)Mauro SantafeNo ratings yet
- Ghorahi Cement Industry Ltd.Document71 pagesGhorahi Cement Industry Ltd.सुबास अधिकारीNo ratings yet
- LITIX™ Power Flex TLD5190: Voltage Regulator in Buck-Boost TopologyDocument23 pagesLITIX™ Power Flex TLD5190: Voltage Regulator in Buck-Boost TopologyManoel Camargo SampaioNo ratings yet
- 1N4728 - 1N4764 - Z1110 - Z1200 Zener DiodesDocument2 pages1N4728 - 1N4764 - Z1110 - Z1200 Zener DiodesFabian BordaNo ratings yet
- DPS Phy - Set - ADocument3 pagesDPS Phy - Set - AscNo ratings yet
- TSI Job Aid 1Document8 pagesTSI Job Aid 1mumamaduraiNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchange PDFDocument3 pagesHeat Exchange PDFmunhNo ratings yet
- Applications Steel: Plexicoke in The VmezuelanDocument8 pagesApplications Steel: Plexicoke in The VmezuelanJose Marval RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics in Motor DrivesDocument7 pagesPower Electronics in Motor DrivesAlfredo Brumnić Fredo0% (1)
- SUNON DC Brushless Fan & Blower (255-E)Document214 pagesSUNON DC Brushless Fan & Blower (255-E)Carlos X.No ratings yet
- XS49281 4100XPC AC TrifoldDocument2 pagesXS49281 4100XPC AC TrifoldJuan Antonio TovarNo ratings yet
- Why I Must Attack ThriveDocument6 pagesWhy I Must Attack ThriveMatthew EhretNo ratings yet
- Electronics Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectronics Interview QuestionsshyamNo ratings yet
- Pipa Tembaga - Streamline MuellerDocument8 pagesPipa Tembaga - Streamline MuellerAhmad Syaifudin ZNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Invt gd100 PVDocument10 pagesCatalogo Invt gd100 PVSergio RecabarrenNo ratings yet
- 140KDocument63 pages140KRuben Chumacero100% (3)
- Eks Energy PresentationDocument17 pagesEks Energy PresentationFrancisco Javier Marín SuárezNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology of Non-SaccharomycesDocument15 pagesBiotechnology of Non-SaccharomycesIonuț NeaguNo ratings yet