Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistor Electron Hole Field-Effect Transistors Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Amplifiers
Transistor Electron Hole Field-Effect Transistors Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Amplifiers
Uploaded by
AlemKomićOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor Electron Hole Field-Effect Transistors Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Amplifiers
Transistor Electron Hole Field-Effect Transistors Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Amplifiers
Uploaded by
AlemKomićCopyright:
Available Formats
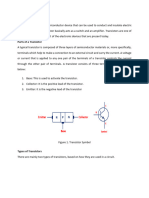
A bipolar junction transistor (bipolar transistor or BJT) is a type of transistor that
uses both electron and hole charge carriers. In contrast, unipolar transistors, such
as field-effect transistors, only use one kind of charge carrier. For their operation,
BJTs use two junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type.
BJTs are manufactured in two types, NPN and PNP, and are available as individual
components, or fabricated in integrated circuits, often in large numbers. The basic
function of a BJT is to amplify current. This allows BJTs to be used as amplifiers or
switches, giving them wide applicability in electronic equipment, including computers,
televisions, mobile phones, audio amplifiers, industrial control, and radio transmitters.
You might also like
- Bi-Polar TransistorDocument10 pagesBi-Polar Transistorddwerer0% (1)
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorTêrrã MäûttNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument1 pageBipolar Junction TransistorAyan ButtNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument2 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorJason BreguilesNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesBipolar TransistorAndrei Josef NizaNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument4 pagesTransistorSanthosh KingNo ratings yet
- English (Transistor) : Jurusan Teknik Elektro Program Studi D-Iv Teknik Elektronika Politeknik Negeri Malang 2019Document5 pagesEnglish (Transistor) : Jurusan Teknik Elektro Program Studi D-Iv Teknik Elektronika Politeknik Negeri Malang 2019Zulfikar Iannur AwwalNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument1 pageBipolar Junction TransistorAshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Construction, Types & Its ApplicationsDocument1 pageBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Construction, Types & Its ApplicationszigijuNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument4 pagesTransistorcomputer tricksNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETDocument6 pagesAssignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unijunction Transistor - WikipediaDocument8 pagesUnijunction Transistor - WikipedialorenianbertolanoNo ratings yet
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- Types of Transistors - Junction Transistors and FETsDocument16 pagesTypes of Transistors - Junction Transistors and FETsKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument19 pagesTransistorsEunice NuñezNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarDocument6 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarJade JoseNo ratings yet
- 3 TransistorDocument7 pages3 TransistorrameshNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument2 pagesTransistorSOR SOTYNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaDocument12 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaWisamAkramNo ratings yet
- Transistor2 TypesDocument5 pagesTransistor2 TypesidanzbhNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaDocument21 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - WikipediaFABIAN NATANAEL MURRIETA RICONo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Classification and Different Types of Transistors 2Document15 pagesClassification and Different Types of Transistors 2Abrham CherinetNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric4Document4 pagesBasic Electric4Ravi SankarNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument5 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendsupNo ratings yet
- The Best Example of Rectifier That Is Used in Our Daily Life Is in The Mobile Phone Charger andDocument3 pagesThe Best Example of Rectifier That Is Used in Our Daily Life Is in The Mobile Phone Charger andENTERTAINMENT TUBENo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- Transistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkDocument7 pagesTransistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkmonalisaNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument1 pageNothingJyothula VenkateshNo ratings yet
- LM II TransistorDocument53 pagesLM II TransistorMa. Fe TabbuNo ratings yet
- Vasquez - Junction TransistorDocument1 pageVasquez - Junction TransistorJonarc Joseph VasquezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationDocument23 pagesElectronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationRonald ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument35 pagesSemiconductor DevicesRacknarockNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentBethelhem AshenafiNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument3 pagesTransistorsSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mosfet and BJT DiffDocument2 pagesMosfet and BJT DiffKancharana SarathchandraNo ratings yet
- Electronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orDocument13 pagesElectronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 111 MergedDocument47 pages111 MergedIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1Document32 pagesUnit 2 Part 1Harsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Transistors ReportDocument41 pagesTransistors ReportHannah Grace Almine Pag-iwayan100% (1)
- Know The Major Difference Between BJT and FETDocument11 pagesKnow The Major Difference Between BJT and FETabraham kaseyaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- Impedence Is High Compared Then BJT - Jfet Is Voltage Driven DeviceDocument1 pageImpedence Is High Compared Then BJT - Jfet Is Voltage Driven Devicemshweta_44944984No ratings yet
- Power Amplifier Project ReportDocument27 pagesPower Amplifier Project ReportAhsan Ijaz100% (2)
- TransistorsDocument44 pagesTransistorsramil.bocaNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument11 pagesTransistorEllaine P. De ClaroNo ratings yet
- BJT IntroductionDocument4 pagesBJT IntroductionMr KNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1: de La Salle University - DasmarinasDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 1: de La Salle University - DasmarinasFatimaNo ratings yet
- Transistors and Logic GatesDocument17 pagesTransistors and Logic GatesJef SotisNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument2 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorAravind VinasNo ratings yet
- Ensayo en-USDocument2 pagesEnsayo en-USgeancarlo rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4:ujt: Uni-Junction Transistor G.Venkatasubbaiah Asst., Professor Dept., of ECE VrsecDocument8 pagesChapter 4:ujt: Uni-Junction Transistor G.Venkatasubbaiah Asst., Professor Dept., of ECE VrsecSai RohithNo ratings yet
- Eeeb273 n01 - Review BJT x6Document7 pagesEeeb273 n01 - Review BJT x6ANazz SzNo ratings yet
- Electronic EngeeniringDocument11 pagesElectronic EngeeniringMuataz ZyadaNo ratings yet
- Jamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Document3 pagesJamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Koji OdoNo ratings yet
- Operating System Real-Time: JitterDocument1 pageOperating System Real-Time: JitterWrathchild_No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics or Digital (Electronic) Circuits AreDocument1 pageDigital Electronics or Digital (Electronic) Circuits AreWrathchild_No ratings yet
- Amplifier (Often Op-Amp or Opamp)Document1 pageAmplifier (Often Op-Amp or Opamp)Wrathchild_No ratings yet
- Control Loop Feedback Mechanism Controller Industrial Control Systems Setpoint Process Variable Proportional Integral DerivativeDocument1 pageControl Loop Feedback Mechanism Controller Industrial Control Systems Setpoint Process Variable Proportional Integral DerivativeWrathchild_No ratings yet
- Feedback Control System Plant Control Signal: Thermostat Industrial Control SystemsDocument1 pageFeedback Control System Plant Control Signal: Thermostat Industrial Control SystemsWrathchild_No ratings yet
- Transactions On Signal Processing States That The Term "Signal" Includes Audio, Video, Speech, ImageDocument1 pageTransactions On Signal Processing States That The Term "Signal" Includes Audio, Video, Speech, ImageWrathchild_No ratings yet
- James BondDocument1 pageJames BondWrathchild_No ratings yet
- Hamid AlgarDocument1 pageHamid AlgarWrathchild_No ratings yet