Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Denis QosjaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Denis QosjaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 9
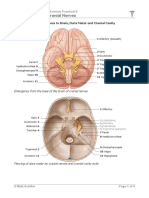
Neuroanatomy – Cranial Nerves
Relations of Cranial Nerves to Brain,
Brain Dura Mater and Cranial Cavity
1 Olfactory (beneath)
2 Optic
3 Oculomotor
culomotor
4 Trochlear
Facial 7
5 Trigeminal (sensory)
Vestibulocochlear 8
5 Trigeminal (motor)
Glossopharyngeal 9
6 Abducens
Vagus 10
12 Hypoglossal
Accessory 11
Emergence from the base of the brain of cranial nerves
1 Olfactory
Optic 2
51 Ophthalmic
Oculomotor 3
52 Maxillary
Abducens 6 53 Mandibular
5 Trigeminal (ganglion)
Trochlear 4
7 Facial
8 Vestibulocochlear
9 Glossopharyngeal
Trigeminal 5
10 Vagus
Accessory 11 12 Hypoglossal
Piercing of dura mater by cranial nerves and cranial cavity exits
© Matt Schiller Page 1 of 4
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 9
Neuroanatomy – Cranial Nerves
Components of Craniall Nerves
GSA GVA SVA SSA GSE GVE SVE
Special
Somatic Visceral Special Somatic
visceral Visceral motor Branchiomotor
sensory sensory sensory motor
sensory Major effects
Sensory Sensory
Somatosensory
from from ear
Tongue
Preganglionic Muscles derived of lesion
from skin, muscles and
viscera of Taste – balance autonomic from branchial
bone, muscle, extraocular
thorax and and neurons arches
and joints muscles
abdomen hearing
S Extraocular Ciliary muscle; Inferolateral deviation
muscles sphincter of eye and diplopia;
(not LR and pupillae muscle ptosis; dilated pupil
SO); levator and loss of pulillary
III palperbrae reflex; myhydriasis
superioris
muscle
C - Ciliary ganglion
S Superior Inability to depress
oblique adducted eye and
IV muscle diplopia
C -
S Face and head Muscles of Sensory loss to upper
mastication and (1), middle (2) or
tensor tympani lower (3) part of face;
C Trigeminal - loss of corneal reflex
V ganglion (1); jaw weakness
(except and ipsilateral
proprioception) deviation (3);
hyperacusia (3)
S Lateral Medial deviation of
rectus eye, inability to
VI muscle abduct eye, and
C - diplopia
S External ear Anterior Glands of orbit Muscles of facial Facial weakness or
(posterior 2/3 of and nasal cavity; expression; paralysis; dry eye; dry
auricular area) tongue submandibular stapedius muscle mouth; loss of
and sublingual corneal reflex;
VII salivary glands hyperacusia; loss of
C Geniculate Geniculate Submandibular - taste from anterior
ganglion ganglion and 2/3 tongue
pterygopalatine
ganglia
S Hair cells Loss of hearing; loss
of cochlea of balance/equilibrium
and
VIII vestibule
C Spiral and
vestibular
ganglia
S Posterior 1/3 Carotid Posterior Parotid gland Stylopharyngeus Loss of gag reflex;
tongue; walls body and 1/3 muscle dysphgagia; loss of
of pharynx sinus tongue carotid sinus reflex
IX C Superior Inferior ganglion of CNIX Otic ganglion - (bilateral only)
ganglion of
CNIX
S External ear GIT and Palate Viscera Muscles of Dysphagia; weak and
respiratory pharynx, larynx hoarse voice;
tract and upper respiratory stridor
X oesophagus
C Superior vagal Inferior vagal ganglion Ganglia in/near -
ganglion walls of targets
S Sternomastoid Weakness in turning
and trapezius head toward opposite
XI muscles side and shrugging
C - shoulder
S Intrinsic Ipsilateral atrophy
muscles of and deviation of
XII tongue tongue; impaired
C - speech
(S = structures supplied; C = location
l of external cell bodies, if any)
© Matt Schiller Page 2 of 4
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 9
Neuroanatomy – Cranial Nerves
Distribution of Cranial Nerves
Emergence from Course inside cranial Exit from
Course outside cranial cavity
brainstem cavity cranial cavity
III Interpeduncular fossa • Passes between PCA Superior orbital • Further divides into branches to supply each
and SCeA fissure (common extraoccular muscle supplied and levator
• Pierces dura and tendinous ring) palpedbae superior muscle
passes
asses anteriorly in • Parasympathetic fibres leave inferior rectus
cavernous sinus, where branch to synapse in on postganglionic cells
it divides into superior in ciliary ganglion, which eye to supply
and inferior divisions at sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
anterior end
IV Dorsal surface of • Passes around side of Superior orbital Travels to superior oblique muscle
midbrain, caudal to cerebral peduncle fissure (common
inferior colliculus • Pierces dura and tendinous ring)
passes
asses anteriorly in
cavernous sinus
V 1 Lateral side of base Pierces dura Passes Superior orbital Divides into branches to supply cornea, upper
of pons (smaller and forms anteriorly in fissure nasal mucosa, and skin of upper eyelid and
motor root more trigeminal cavernous forehead
2 medially and larger ganglion sinus Foramen Divides into branchess to supply nasal cavity
sensory root more rotundum mucosa, upper jaw and teeth, maxillary sinuses,
laterally) and skin of lower eyelid, nose,
nose upper lip and
cheek
3 Passes a Foramen ovale Divides into branches to supply muscles of
short mastication, mucosa of cheek, mucosa and teeth
distance of lower jaw, and skin of temporal region and chin
antero-
laterally
VI Pontomedullary Pierces dura and passes Superior orbital Travels to superior oblique muscle
junction (most anteriorly in cavernous sinus fissure (common
medial) tendinous ring)
VII Pontomedullary Passes a short distance Internal acoustic • Travels to inner ear, where parasympathetic
pa
junction anterolaterally meatus / Facial fibres branch off to synapse on
canal/ pteregopalatine ganglion, from which
Stylomastoid postganglionic fibres supply glands of nose
foramen and orbit
• Passes behind ear in facial canal, where it
gives off a branch to supply tongue and
salivary glands (chorda tympani), and a
branch to supply stapedius muscle
• Passes through stylomastoid foramen to
enter parotid gland, where it divides into
branches to supply muscles of facial
expression
VIII Pontomedullary Passes a short distance Internal acoustic Travels to hair cells of vestibule and cochlea in
junction anterolaterally meatus inner ear
IX Pontomedullary Passes a short distance Jugular foramen (Not covered in this course)
junction (most anterolaterally
lateral) / Lateral side
of olive
X Lateral side of olive Passes a short distance Jugular foramen • Passes through neck in carotid sheath
(rootlets) anterolaterally as rootlets • Gives off branches to pharynx and larynx
collect • Enters thorax
XI Lateral side of caudal Spinal fibres pass in through Jugular foramen • Gives off branches to supply sternomastoid
medulla and C1-5 foramen magnum to unite muscle
(rootlets) with medullary fibres • Crosses side of neck to supply trapezius
muscle
XII Between olive and Passes a short distance Hypo-glossal • Runs down behind ICA for a short distance
pyramid (rootlets) anterolaterally as rootlets canal • Turns forward, crossing lateral surface of
collect ECA to reach side of tongue, where it gives
off branches to supply tongue muscles
© Matt Schiller Page 3 of 4
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 9
Neuroanatomy – Cranial Nerves
Cavernous Sinus
Cavernous sinus
Dura mater
3 Occulomotor
4 Trochlear
51 Ophthalmic
52 Maxillary
6 Abducens
Internal carotid artery
Cranial nerves within the cavernous sinus (transverse section)
Openings of Cranial Cavity
Cranial nerves Other major structures
Optic canal 2 -
Superior orbital fissure 3, 4, 6, 51 -
Foramen rotundum 52 -
Foramen ovale 53 -
Foramen spinosum - Middle meningeal artery
Foramen lacerum - (Cartilage-filled)
Carotid canal - Internal carotid artery
Internal acoustic meatus 7, 8 -
Jugular foramen 9, 10, 11 Internal jugular vein
Hypoglossal canal 12 -
Foramen magnum 11 (spinal root) • Medulla
• Vertebral arteries
Structures passing through openings of cranial cavity
© Matt Schiller Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- Vertigo Physiology and Clinical AssessmentDocument63 pagesVertigo Physiology and Clinical AssessmentdraseemmishraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesDigestive SystemDanesa MadoNo ratings yet
- Fight or Flight Response En-UsDocument1 pageFight or Flight Response En-Ussusie cabrillanaNo ratings yet
- Bone Marking Table KpattonDocument4 pagesBone Marking Table Kpattonapi-255334265No ratings yet
- Vertigo and Its Management PDFDocument21 pagesVertigo and Its Management PDFNitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54Document74 pagesLect. 1 Organization of The Nervous System 54nopporn2520No ratings yet
- Leaflet BPPVDocument3 pagesLeaflet BPPVJemsner IrothNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument6 pagesBasal Ganglia381a53c99bNo ratings yet
- Brainstem StrokesDocument4 pagesBrainstem StrokesChandniNo ratings yet
- I 2x Get Laid On FridaysDocument3 pagesI 2x Get Laid On FridaysRoma Fe MabanagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimNo ratings yet
- Embryo EyeDocument25 pagesEmbryo EyeMarera DomnicNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument39 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandGish KioiNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument21 pagesHypothalamusMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Mineral MetabolismDocument24 pagesMineral Metabolismyasarc365No ratings yet
- Eye HistologyDocument9 pagesEye HistologyGrace Shan BernusNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument55 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaNo ratings yet
- Anat 6.5 Basal Ganglia - QuijanoDocument6 pagesAnat 6.5 Basal Ganglia - Quijanolovelots1234No ratings yet
- Pathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. JamesDocument15 pagesPathways For Neuroanatomy SCT: R. Heaslip M. Jameshzol83No ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument36 pagesNeurologic AssessmentJune Regina Mae DublasNo ratings yet
- Ascending Tracts Spinal CordDocument1 pageAscending Tracts Spinal CordChristopher Samuel0% (1)
- 2 Af 5 VERTIGODocument35 pages2 Af 5 VERTIGOmuneceNo ratings yet
- Nerves in Lower LimbDocument21 pagesNerves in Lower LimbTom WuNo ratings yet
- Board Questions by Category - GoodDocument33 pagesBoard Questions by Category - GoodNitin Nanda50% (2)
- Case 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusDocument7 pagesCase 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusCharlie WalkerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Limbic SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy of The Limbic SystemMohammed ShaikNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument51 pagesCerebellumLiya ThaaraNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Cerebellum: Anatomy, Functions and Clinical LocalizationDocument70 pagesUnderstanding the Cerebellum: Anatomy, Functions and Clinical Localizationmandeep axonNo ratings yet
- ALL Clinicals of Upper LimbDocument28 pagesALL Clinicals of Upper LimbБайден ТрампNo ratings yet
- I. Walls: Walls Muscles/Comp. Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Actions DiseaseDocument8 pagesI. Walls: Walls Muscles/Comp. Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Actions DiseaseAustin CabreraNo ratings yet
- Comparsion of Lipid Profile in Diabetic Hypertensives VS Diabetic NormotensivesDocument8 pagesComparsion of Lipid Profile in Diabetic Hypertensives VS Diabetic NormotensivesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Anatomy of Vestibular SystemDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Vestibular SystemFranciscus BuwanaNo ratings yet
- 15 PharynxDocument9 pages15 Pharynxapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Respiratory System HistologyDocument32 pagesRespiratory System HistologyMohib HassanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologygirlwithbrowneyesNo ratings yet
- Nerve Components, Location, Exits, ActionsDocument3 pagesNerve Components, Location, Exits, ActionsTan En YingNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves and BranchesDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves and Branchesballer0417No ratings yet
- Visual-Procedural Memory Consolidation During Sleep Blocked by Glutamatergic Receptor AntagonistsDocument6 pagesVisual-Procedural Memory Consolidation During Sleep Blocked by Glutamatergic Receptor Antagonistsdrfaruqui2551No ratings yet
- Temporal LobeDocument68 pagesTemporal LobeRupinder GillNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument14 pagesCerebellumapi-508474347No ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocument71 pagesCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Document89 pages3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Sheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- PONS: NeuroanatomyDocument20 pagesPONS: NeuroanatomyHassan IlyasNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument2 pagesMuscles of The BackavrilaNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument22 pagesCerebellumSalman XahirNo ratings yet
- Eye MovementsDocument17 pagesEye MovementsbcchingangbamNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Central Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesUnderstanding the Central Nervous SystemHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Head and neck anatomy trianglesDocument15 pagesHead and neck anatomy trianglesANDRE MANo ratings yet
- Disorders of Cho MetabolismDocument4 pagesDisorders of Cho MetabolismJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Gluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaDocument4 pagesGluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaSteph SantosNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Neck PDFDocument1 pageMuscles of The Neck PDFEdreyn DellosaNo ratings yet
- D. Brainstem: PONS (Ventral Metencephalon) 1. External Consideration A. Ventral ViewDocument39 pagesD. Brainstem: PONS (Ventral Metencephalon) 1. External Consideration A. Ventral ViewMarvic SueltoNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument11 pagesBlood Supply of The Brainneleh grayNo ratings yet
- AortaDocument1 pageAortadankirsh100% (1)
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderDocument10 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusDocument5 pagesParasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusChristine NathaliaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in HADocument3 pagesReviewer in HAjulia.caballero0107No ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic FeverDocument3 pagesHemorrhagic FeverDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- 4 2 Vitamin D Guidance Feb 2016 CCG v1 Id 589240Document2 pages4 2 Vitamin D Guidance Feb 2016 CCG v1 Id 589240Suzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Suicidal Attempts-Data BaseDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of Suicidal Attempts-Data BaseDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- Internal Capsule and Horizontal Slices of ForebrainDocument5 pagesInternal Capsule and Horizontal Slices of ForebrainDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Wellbeing TestsDocument22 pagesFetal Wellbeing TestsNurulrezki Atika100% (3)
- FTP Booster Training Plan OverviewDocument1 pageFTP Booster Training Plan Overviewwiligton oswaldo uribe rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Effects of Pollution Sample EssayDocument2 pagesEffects of Pollution Sample EssaybeNo ratings yet
- Simpsons Forensic Page 67-68Document3 pagesSimpsons Forensic Page 67-68anggarayudha89No ratings yet
- 1 Rep MassDocument97 pages1 Rep MassIt's Just Me100% (3)
- Pancreatic Hormones Regulate Blood GlucoseDocument10 pagesPancreatic Hormones Regulate Blood Glucosekrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument81 pagesTransport in AnimalsIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Sudden Death SyndromeDocument34 pagesSudden Death SyndromeDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi UrgensiDocument26 pagesHipertensi UrgensidiegoNo ratings yet
- Onion and Human Cheek CellDocument3 pagesOnion and Human Cheek CellAnjehyn Elle100% (1)
- Screening ShortDocument30 pagesScreening Shortjignesh100% (1)
- Muscle Tone Exam UsmleDocument49 pagesMuscle Tone Exam UsmleFlowerNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in Pregnancy-HmDocument58 pagesAnaemia in Pregnancy-HmMazlina MaidinNo ratings yet
- Nose AnatomyDocument113 pagesNose AnatomyPratiksha PatilNo ratings yet
- Motor Unit Number Index (Munix) - Principle, Method, and Findings in Healthy Subjects and in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease PDFDocument10 pagesMotor Unit Number Index (Munix) - Principle, Method, and Findings in Healthy Subjects and in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease PDFMauricio ZambrottaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of a 12-Channel ECG DeviceDocument74 pagesDesign and Implementation of a 12-Channel ECG DeviceMcSudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D. Clinical Biochemistry HucomDocument7 pagesMinerals: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D. Clinical Biochemistry HucomHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Fish Shape and ScalesDocument14 pagesFish Shape and ScalesFantôme ErrantNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument16 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumBabi PanggangNo ratings yet
- ResearchpaperDocument11 pagesResearchpaperapi-339290387No ratings yet
- Fisilogi Anal KanalDocument45 pagesFisilogi Anal KanalMargarethaNo ratings yet
- Glucose InfusionDocument5 pagesGlucose InfusionPudyo KriswhardaniNo ratings yet
- PSY101 Final Term Solved Paper by Ali Raza TawaryDocument73 pagesPSY101 Final Term Solved Paper by Ali Raza TawaryTayybaNo ratings yet
- Method Recommendations 4Document108 pagesMethod Recommendations 4Сухоставець Наталія ПетрівнаNo ratings yet
- Weebly CTLDocument14 pagesWeebly CTLapi-531838839No ratings yet
- A Comparison of Sterofundin & RL On Intraoperative Acid Base & Electrolytes Status in Children (ACCM Journal)Document8 pagesA Comparison of Sterofundin & RL On Intraoperative Acid Base & Electrolytes Status in Children (ACCM Journal)TedyJaswadiNo ratings yet
- Soal Penyisihan Gis SMP 2022Document18 pagesSoal Penyisihan Gis SMP 2022Aqidatul izzaNo ratings yet
- Pedh 112 Week 11 19Document11 pagesPedh 112 Week 11 19April Puncia67% (3)
- Amino Acids - Biochemistry Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument1 pageAmino Acids - Biochemistry Questions and Answers - SanfoundryAli HassanNo ratings yet