Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air and Combustion: 1. Oxygen
Uploaded by
omarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air and Combustion: 1. Oxygen
Uploaded by
omarCopyright:
Available Formats
Air and combustion
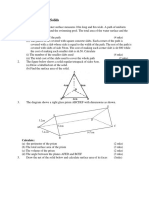
1.
Oxygen
Water
2. a) 3 Mg + N2 g ________ Mg 3 N2 g
b) Argon
- It is inert
3. a) Rust is hydrated iron (III) Oxide
b) - Electroplating
- Painting
- Oiling
- Galvanization
c) - Salts
- Acids
4. a) Dust particles
b) They readily solidify hence may block the pipes
c) Argon
6. - Water rose up the test-tube to occupy the space of active air √½ which has been
used in resting. √½
- Iron wool turned reddish – brown √½ due formation of red-oxide of iron √½ which is
rust.
7. a )i)rusting occurred√ ½
ii) No rusting√ ½
b) In (i) iron is more reactive than copper hence undergoes corrosion√1
in (ii) zinc is more reactive than iron hence undergoes corrosion in place of iron√1
8. a) To remove any magnesium oxide coating from the surface of magnesium// To
remove any oxide film on it
b) White solid which is magnesium oxide
c) Increase in mass was due to oxygen which combined with magnesium
d) 2Mg(s) + O2(g) _______ 2MgO(s)
e) The filtrate is magnesium hydroxide which is an alkaline
Red litmus paper changed blue, but blue litmus paper remained blue
9. (a) So that they may stick to the gas Jar to prevent them from falling into water when
the gas jar is inverted
(b) Iron filings turned to reddish brown because they reacted with oxygen in presence
of moisture to form rust.
- The level of water inside the gas jar rise so as to occupy the volume initially
occupied by part of air used up for rusting
(c) - Air is made up of two parts; - the active part that is necessary for rusting and the
inactive part that is not used for rusting
- oxygen is the active part of air
Water
(d) Oxygen
Sodium
Peroxide
- Neat diagram-
- correct method of collection
(e) - For cutting and welding metals
- Rocket fuel
- Mountain climbing
- Sea diving
11. (i) Oxygen
(ii) Sodium hydroxide is a strong base
(iii) Slightly soluble in water
12. (i) White fumes form in the gas jar which disappear after sometime.
- The level of water rises in the gas jar.
(ii) P4(s) + 5O2(g) P4O10(s)
P4O10(s) + 3H2O(l) 2H3PO4(aq)
(iii) Magnesium react with oxygen and nitrogen hence greater of fraction of air is
used.
(iv) (a) Blue litmus changed to red as remained red. The solution was acid due to
phosphoric
(b) Red litmus changed to blue as blue remained blue due to formation of basic
magnesium
hydroxide ammonia solution.
(v) – Pass air over conc. KOH / NaOH to absorb CO2
- Pass the remaining gases over hot copper solid which reacts with oxygen.
- Collect the remaining gas over water. The gas is mainly nitrogen.
13. a) i) 3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) √1
ii) Gas with√1 choking irritating smell.
Mg3N2 reacts with water to form ammonia √1 gas.
iii) It remains blue. √½ Ammonia gas is alkaline. √½
14. (a) (i) Phosphorous
(ii) - Do not react with water when being inserted into the tube
- reacts with oxygen when exposed to air.
(b) 4P(s) + 3O2(g) 2P2O3(s)
or 4P(s) + SO2(g) 2P2O5(s)
(c) (i) Y – X x 100
y
(ii) – Wrong reading of volume
- Phosphorous can go off before complete combustion
(d) (i) – Red litmus paper no effect
- Blue litmus paper turns red due to formation of phosphoric acid/phosphorous (V)
Oxide whish is an acidic oxide
(ii) – Oxygen
(iii) – Burning of candle
- Use of pyrogallol
- Rusting of iron fillings
15. i) P4(g) + 5O2(g) ______________ 2P2O5(s)
// P4(s) + 3O2(g) ____________ 2P2O3(g) Anyone 1 mark
ii) Phosphorous (v) or (iii) oxide formed is an acidic Oxide which dissolves in
water to
form a strong acidic solution of phosphoric acid whose PH is 2
16. (a) – Iron nails turns brown.
½
- Water rises up the delivery tube/water level drops in the trough ( any ½mk)
Explanation: Oxygen has been used up in rusting of iron nails hence water rises up
to take 1
the place of oxygen
(b) 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) + 2H2O(l) 2Fe2O3.2H2O(s)1
(accept a balanced chemical equation)
17. a) FeCO3 (s) Fe O(s) + CO2(g)
Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g) Fe O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Or
2 Fe(s) + 202(g) Fe3 O4(s)
b) Fe3O4(s) + 8H+ (aq) 4H2O (l) + 2 Fe3+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
18. a) N2O 1 (Nitrogen (I) oxide) – Denitrogen Oxide.
b) K2O 1 (Potassium oxide)
c) Al2O3 (Aluminium oxide)
19. a) water √1
b) 2Na2O2(S) + 2H2o (L) 4NaOH (aq) + O2(g) √1 mk
Penalize ½ - wrong missing state symbols
You might also like
- CLASS-10TH - CHAPTER - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument3 pagesCLASS-10TH - CHAPTER - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsTanmay LahaNo ratings yet
- Transiton metal chemistryDocument15 pagesTransiton metal chemistryazabokennedy09No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Jan 1996 Unit-1Document10 pagesMark Scheme Jan 1996 Unit-1Samira MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ores and Metallurgy-03-Assignments (New)Document13 pagesOres and Metallurgy-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- FORM 3 Nitrogen and It's CompoudsDocument14 pagesFORM 3 Nitrogen and It's CompoudsKevinNo ratings yet
- CARBON: AN IMPORTANT ELEMENTDocument33 pagesCARBON: AN IMPORTANT ELEMENTDavyieNo ratings yet
- FORM 3 Nitrogen and It's CompoudsDocument18 pagesFORM 3 Nitrogen and It's CompoudsKevinNo ratings yet
- HASBUL RIZUAN B ISMAIL'S CHEMICAL SUBSTANCESDocument63 pagesHASBUL RIZUAN B ISMAIL'S CHEMICAL SUBSTANCEShasbulrNo ratings yet
- YCT General Principles and Process NEET JEE Questions PracticeDocument43 pagesYCT General Principles and Process NEET JEE Questions Practicenaughtydeadpool007No ratings yet
- JEE - Chemistry - MetallurgyDocument20 pagesJEE - Chemistry - Metallurgyofficial.archit234No ratings yet
- Electronic Configuration and Properties of Group 14 ElementsDocument7 pagesElectronic Configuration and Properties of Group 14 ElementsAman9692No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbon - Chem - f3 - v1 1Document25 pagesChemistry of Carbon - Chem - f3 - v1 1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- s.4 Chem Self Study WorkDocument44 pagess.4 Chem Self Study Workmusisi ahmedNo ratings yet
- Abhimnyu Metal and Non Metal - AsignmentDocument3 pagesAbhimnyu Metal and Non Metal - Asignmentaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Ch-1 - CLASS XDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 Ch-1 - CLASS XPRVLNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form Three Q&a1Document110 pagesChemistry Form Three Q&a1MajaningumbaoNo ratings yet
- Study of Hydrogen as the First ElementDocument10 pagesStudy of Hydrogen as the First ElementAyush DasNo ratings yet
- 5 A 9 e 8700 e 4 B 07 Ae 4 B 60 BD 59 DDocument36 pages5 A 9 e 8700 e 4 B 07 Ae 4 B 60 BD 59 DVKNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Metals and S - Block ElementsDocument5 pagesExtraction of Metals and S - Block ElementsAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- Part 3 MetalsDocument8 pagesPart 3 Metals劉曉晴No ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2009Document11 pagesICSE Paper 2009CGPSC - P&P TutorialNo ratings yet
- Cha 10newDocument14 pagesCha 10newTun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Freelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFDocument13 pagesFreelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFKodati Durga Prasad KodatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 Manufacture Substances in IndustryDocument18 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 Manufacture Substances in Industrychulan93100% (15)
- Mastering Chemistry Topic 3 Metals ReviewDocument9 pagesMastering Chemistry Topic 3 Metals ReviewRaiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY MCQ 10th Ch-1 To 4Document2 pagesCHEMISTRY MCQ 10th Ch-1 To 4akash4624singh89No ratings yet
- Praktikum Anorganik Hydrogen and OxygenDocument25 pagesPraktikum Anorganik Hydrogen and Oxygenqurrota ainynNo ratings yet
- Understand Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid and AmmoniaDocument20 pagesUnderstand Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid and AmmoniaKamal AliqNo ratings yet
- Iron and Its CompoundsDocument5 pagesIron and Its CompoundszakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Corrected Material Unit 12-17Document55 pagesChemistry Corrected Material Unit 12-17Pandu RockingNo ratings yet
- Form 5 AnswerDocument61 pagesForm 5 AnswerLEE YI HAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document61 pagesAnswer 1Crystal 16No ratings yet
- Chap9 StudentDocument22 pagesChap9 StudentIsabel GohNo ratings yet
- Kimia Chapter 9Document35 pagesKimia Chapter 9Mohammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSDocument3 pagesChemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSZeneon82% (17)
- Cordova Class 8 Solution-12-15Document4 pagesCordova Class 8 Solution-12-15Rashmi MuhalNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988039Document5 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988039abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument3 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- DR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryDocument25 pagesDR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryHan Zin OoNo ratings yet
- Folio ChemistryDocument16 pagesFolio Chemistryamirah_dayanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 9 (Manufacture Substances in Industry)Document17 pagesChemistry Form 4: Chapter 9 (Manufacture Substances in Industry)faiz_son96% (73)
- CLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument17 pagesCLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important Questionsvt654009No ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument3 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Ex. Gold (III) Chloride Can Be Formed by Reacting Gold Metal With Chlorine GasDocument2 pagesEx. Gold (III) Chloride Can Be Formed by Reacting Gold Metal With Chlorine GasIvoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Nitric Acid and NitratesDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank Nitric Acid and NitratesGanesh sargarNo ratings yet
- Aluminium and Its CompoundsDocument25 pagesAluminium and Its CompoundsAwatifNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 7 Topic:: Metals and Non-MetalDocument2 pagesAssignment - 7 Topic:: Metals and Non-MetalLeap Up JEE NEETNo ratings yet
- Graphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandGraphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAyrat M. DimievNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry V2From EverandHandbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry V2Georg BrauerNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Structure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsFrom EverandStructure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Copper, Silver and Gold: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Copper, Silver and Gold: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Iron, Cobalt and Nickel: Comprehensive Inorganic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Iron, Cobalt and Nickel: Comprehensive Inorganic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationomarNo ratings yet
- Water and HydrogenDocument4 pagesWater and HydrogenomarNo ratings yet
- 2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1Document8 pages2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1omarNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of SolidsDocument10 pagesSurface Area of SolidsomarNo ratings yet
- AcidsDocument4 pagesAcidsomarNo ratings yet
- 2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1Document8 pages2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1omarNo ratings yet
- AcidsDocument4 pagesAcidsomarNo ratings yet
- Water and HydrogenDocument4 pagesWater and HydrogenomarNo ratings yet
- 2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1 AnswersDocument4 pages2006 Bondo District Chemistry Paper 1 AnswersomarNo ratings yet
- Marshall AttackDocument1 pageMarshall AttackomarNo ratings yet
- Complete Endgame Course Jeremy SilmanDocument543 pagesComplete Endgame Course Jeremy SilmanCarlos Mañez100% (2)
- HelloDocument1 pageHellorusbhaiNo ratings yet
- HelloDocument1 pageHellorusbhaiNo ratings yet
- Acidity of Benzene Toluene Xylenes Solvent Naphthas Astm d847Document3 pagesAcidity of Benzene Toluene Xylenes Solvent Naphthas Astm d847Iraílson MatosNo ratings yet
- Mech - 2010 PDFDocument8 pagesMech - 2010 PDFmurthy gNo ratings yet
- Wall THK Calculation Asme b31.4Document5 pagesWall THK Calculation Asme b31.4Dwi Hermawan100% (2)
- 1233 - Pharmaceutical Products Variation Guidelines 3-2018 - 1st Edition PDFDocument36 pages1233 - Pharmaceutical Products Variation Guidelines 3-2018 - 1st Edition PDFmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Astm A571mDocument5 pagesAstm A571mtingNo ratings yet
- Enduro MG Product Data SheetDocument1 pageEnduro MG Product Data SheetAbu Bilal AbdillahNo ratings yet
- AATCC - Quality Control Catalog - Updated 2021Document36 pagesAATCC - Quality Control Catalog - Updated 2021Naeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Welder Performance Qualification (WPQ)Document1 pageWelder Performance Qualification (WPQ)JBStringerNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Slabs 1Document19 pagesAnalysis and Design of Slabs 1Adil Javed Chaudhary100% (5)
- Bonding EdexcelDocument19 pagesBonding EdexcelahmedNo ratings yet
- Evolast: FFKM - The Ultimate Generation of Perfl UoroelastomersDocument4 pagesEvolast: FFKM - The Ultimate Generation of Perfl UoroelastomersJose Luis Ortiz PerdomoNo ratings yet
- HERFLEX HF-50-180 - EnglishDocument2 pagesHERFLEX HF-50-180 - Englishlaroussi aymenNo ratings yet
- Pa66 GF30 - Ultramid A3wg6Document2 pagesPa66 GF30 - Ultramid A3wg6armandoNo ratings yet
- Types of Steel PDFDocument8 pagesTypes of Steel PDFIyappan MuruganNo ratings yet
- Zerokorr - Method StatementDocument8 pagesZerokorr - Method StatementAshif AkhtarNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Organic3Document72 pagesCHM1 Organic3Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- IonsDocument14 pagesIonsapi-423980580No ratings yet
- Introduction To Dry Etching PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Dry Etching PDFp.designNo ratings yet
- Bride DollDocument32 pagesBride DollApoorva Gowda100% (2)
- Asphalt Concrete Report Final VersionDocument11 pagesAsphalt Concrete Report Final VersionLorraine Custodio100% (1)
- Flower Cardigan (Kids)Document13 pagesFlower Cardigan (Kids)analeilanilunaNo ratings yet
- II.01.A. DRAEGER HPS - 3500 - Technical - Data - Sheet - ENDocument7 pagesII.01.A. DRAEGER HPS - 3500 - Technical - Data - Sheet - ENBayu NawungkridoNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Spur Gear Using Palm Fiber and Aluminum CompositeDocument21 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Spur Gear Using Palm Fiber and Aluminum Compositesabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- Kerbs & Inl SpecDocument4 pagesKerbs & Inl Specabdulrehman731No ratings yet
- Maintenance Painting of Steelwork Manual Provides GuidanceDocument33 pagesMaintenance Painting of Steelwork Manual Provides GuidancerohanZorbaNo ratings yet
- Gasket SWGDocument21 pagesGasket SWGArthur Yerikho100% (1)
- Photo LithographyDocument34 pagesPhoto LithographynidalNo ratings yet
- Dross Inclusions and Galvanized SteelDocument2 pagesDross Inclusions and Galvanized SteelcurtisvaleroNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Report PLCDocument10 pagesInorganic Chemistry Report PLCPablo LópezNo ratings yet
- Air Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionDocument16 pagesAir Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionxL1U BusinessNo ratings yet