Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COLUMN BASES 5 Design Examples
Uploaded by
Gaddam Padmaja ReddyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COLUMN BASES 5 Design Examples
Uploaded by
Gaddam Padmaja ReddyCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.
Santha Kumar
8.5 Design Examples
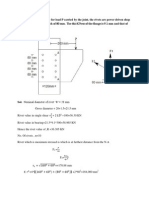
8.5.1 Design example (slab base)
A built-up steel column comprising two ISWB 400 RSJ sections with their
webs spaced at 325mm and connected by 10 mm thick battens transmits an
axial load of 2000 kN. SBC of boil at site=300kN/m2. The safe permissible stress
on the concrete bed= 4N/mm2. Design a suitable foundation for the column
adopting a slab base, and sketch the details of the foundation.
1. Data
Axial load on column = 2000kN
Permissible compressive stress on concrete = 4N/mm2
Column built up of two ISWB 400 RSJ sections connected by 10 mm thick
battens.
2. Column base
Area of base plate = (2000 / 4000) = 0.5 m2
using a square base plate,
Side length of base plate = = 0.706 m
Adopt a base plate of size 750mm x 750mm.
Referring to figure 8.10, the projection of the base plate from the edge of the
column is obtained as
a = greater projection
= 0.5(750 - 420) = 165 mm
b = smaller projection
= 0.5(750 - 525) = 112.5 mm
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Intensity of pressure on base plate
= 3.56 N/mm2
Permissible bearing stress in base plate sbs = 185N/mm2
The thickness of the base plate is obtained from the relation
3w ⎛ 2 b2 ⎞
t= ⎜⎜ a − ⎟
σbs ⎝ 4 ⎟⎠
Aiming the thickness of base plate
(
t s = 2.5w a 2 − 0.3b 2 ) γ m0 f y > t f
Figure 8.10 Column base plate
3 x 3.56 ⎛ 2 112.5
2 ⎞
⎜⎜165 − ⎟⎟ = 37mm
185 ⎝ 4 ⎠
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Adopt a base plate of size 750mm x 750mm x 40mm.
3. Cleat angle
For connecting the column section to the base plate, adopt ISA 100 x 100
x 10 mm angles with four 22mm diameter rivets on flange side and ISA 75 x 75 x
8 mm with three 22mm diameter rivets in the webs.
8.5.2 Design example (gusseted base)
For the built-up column of design example 8.5.1, design a suitable
foundation adopting a gusseted base.
1. Size of base plate
Area of base plate = (2000 / 4000) = 0.5 m2
Adopt ISA 150 x 100 x 12 mm gusset angles on the flange side with
100mm leg horizontal, gusset plate 12mm thick, 10 mm batten, and cover plates.
Minimum length required allowing 30mm projection on either side in the direction
parallel to the webs
= (400 + 20 + 24 + 200 + 60) = 704mm
Length of base plate parallel to the flanges = 750mm.
Adopt a base plate of size 750mm x 750mm as shown in Fig 5.2a
2. Thickness of base plate
Intensity of pressure below the plate
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
w = (2000 x 103 / 750 x 750) = 3.55 Nmm2
Referring to Fig 5.2b, cantilever projection of plate from the face of the
gusset angle = 141 mm.
⎛ wL2 ⎞ ⎛ 3.55 x 1412 ⎞
Bending moment M = ⎜ ⎟⎟ = ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ = 35288 N / mm
⎜ 2 2
⎝ ⎠ ⎝ ⎠
If t = thickness of plate required,
⎛ σbs bt 2 ⎞
M=⎜ ⎟
⎜ 6 ⎟
⎝ ⎠
6M 6 x 35288
t= = = 33.8 mm
σ bs b 185 x 1
In LSD, No allowable being stress,
In WSD σb allow =0.75 fy
Thickness of base plate = (t - thickness of angle leg) = (33.8 - 12) = 21.8mm
Adopt 750 x 750 x 22 mm base plate.
3. Connections
Outstand on each side = (750 - 400)/2 = 175 mm
Load on each connection = (175 x 750 x 3.55)/1000 = 466 kN
Using 22mm diameter rivets,
⎛ π x 23.52 x 100 ⎞
Rivet value in single shear = ⎜
⎜ ⎟⎟ = 43.4 kN
⎝ 4 x 1000 ⎠
⎛ 23.5 x12 x 300 ⎞
Rivet value in bearing = ⎜ ⎟ = 84.6 kN
⎝ 1000 ⎠
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Therefore least value of rivet = 43.4kN
Number of rivets = (466/43.4) = 11
Adopt 16 rivets connecting gusset angles with plate and the same number of
rivets to connect the gusset plate with the column. The arrangement of rivets and
the details of the gusseted base are shown in Fig 8.12
8.12 (a) Details of base plate
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
(b) Cantillever projection
Fig 8.12 Gusset and base plate details
8.5.3 Design example (grillage foundation)
Design a suitable grillage foundation for the gusseted column of design
example 8.5.2 which supports an axial load of 2000kN. Assuming SBC of soil at
site = 300 kN/m2, draw the elevation and plan of the grillage foundation.
1. Area of grillage
Using gusseted base for the column,
Total load on foundation
= (2000kN + 10% for self weight of foundation)
= 2200 kN
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Two tiers of girders will be used.
Bottom-tier area = (2200/300) = 7.33 m2
Using a square grillage, side length = 7.33 = 2.72 m
Adopt a grillage of size 2.75m x 2.75m.
Allowing 125mm concrete cover on all the sides, the overall size of the grillage
block = (3.0m x 3.0m)
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Fig 8.13 Arrangement of rivets and details of gusseted base
2. Design of top-tier girders
The bending moment is obtained as M = W/8 (L - L1)
Where W = axial load on column = 2000kN
L = length of grillage = 2.75m
L1 = length of base plate = 0.75m
M = 2000/8 (2.75 - 0.75) = 500kNm
Allowable stress can be increased by 33.33% since the beams are encased
in concrete.
Therefore σbt = (165 x 1.33) = 220 N/mm2
⎛ M ⎞ ⎛ 500 x106 ⎞
Z=⎜ ⎟ = ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ = 227 x10 mm
4 3
⎝ σbt ⎠ ⎝ 220 ⎠
Section modulus
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Using three beams in top tier,
Z for each beam = (227 x 104 / 3) = 756600mm3
Use ISBM 350 having the section properties
Zxx = 778900 mm3
tf = 14.2 mm
tw = 8.1 mm
⎛W⎞
The maximum shear force is given by V = ⎜ ⎟ ( L − L1 )
⎝ 2L ⎠
V = (2000 / 2 x 2.75) (2.75 - 0.75) = 730 kN
Shear force per beam = (730 / 3) = 243.33 kN
Average shear stress τv = (243.33 x 103 / 8.1 x 350)
= 78 N/mm2 < 100 N/mm2
minimum gap between two beams = 75mm
3. Design of bottom-tier girders
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
BM is obtained as
W
M= ( L − L2 )
8
⎛ 2000 ⎞
=⎜ ⎟ ( 2.75 − 0.75 )
⎝ 8 ⎠
⎛ M ⎞ ⎛ 500 x106 ⎞
Z=⎜ ⎟ = ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ = 227 x10 mm
4 3
σ
⎝ bt ⎠ ⎝ 165 x1.33 ⎠
Using eight beams in the bottom tier,
Z for each beam = (239 x 104 / 8) = 298 x 103
Use ISLB 250, Zxx = 297 x 103mm3
Spacing of beams = 1 / 7(2.75 - 0.125) = 0.375 m
Use eight beams of ISLB 250 spaced at 375 mm c/c.
Maximum shear force is given by
W ⎛ 2000 ⎞
V= ( L − L2 ) = ⎜ ⎟ ( 2.75 − 0.75 ) = 730kN
2L ⎝ 2 x 2.75 ⎠
Shear force per beam = (730 / 8) = 91.25 kN
Shear stress = τv = (91.25 x 103 / 6.1 x 250 ) = 60 N/mm2 < 100N/mm2
Adopt separators made up of angles ISA 50 x 50 x 6mm and 2.75 m long,
welded or bolted with 12mm diameter bolts to the flanges of the lower-tier girders
at two ends to prevent displacement of girders.
The plan and elevation of the grillage foundation is shown in figure 8.14.
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Design of Steel Structures Prof. S.R.Satish Kumar and Prof. A.R.Santha Kumar
Fig 8.14 Plan and elevation of grillage foundation
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
You might also like
- Dome Design in ExcelDocument2 pagesDome Design in Excelجميل عبد الله الحماطي100% (2)
- TOS 3 Unit 1 Fixed Beams & Continuous Beams and TorsionDocument19 pagesTOS 3 Unit 1 Fixed Beams & Continuous Beams and TorsionKrushna100% (1)
- New PPT Presentation (13-4-20)Document28 pagesNew PPT Presentation (13-4-20)sanket pawar100% (1)
- Column SplicingDocument31 pagesColumn Splicingprabhu8150% (4)
- Industrial BuildingDocument37 pagesIndustrial Buildingrexdindigul70% (10)
- Civil Pile FoundationDocument14 pagesCivil Pile FoundationDipesh Kumar83% (6)
- Design of Multistorey Steel BuildingDocument77 pagesDesign of Multistorey Steel BuildinggopinathNo ratings yet
- Design of Columns As Per IS 456-2000Document68 pagesDesign of Columns As Per IS 456-2000S Praveenkumar87% (93)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sloping Slab - Analysis and Design of Sloping SlabDocument5 pagesSloping Slab - Analysis and Design of Sloping SlabAbuturab SharikmaslatNo ratings yet
- Grillage FoundationDocument3 pagesGrillage FoundationShraddha Pawar100% (4)
- A 7 C 1Document2 pagesA 7 C 1FAUJINo ratings yet
- TOS 4 Unit 3 Design of R.C.C Slabs ContinuedDocument24 pagesTOS 4 Unit 3 Design of R.C.C Slabs ContinuedSporty GameNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall PDFDocument18 pagesShear Wall PDFRubina Hannure100% (1)
- Case ProjectDocument47 pagesCase ProjectAshish LoyaNo ratings yet
- Long Span TrussesDocument12 pagesLong Span TrussesPrashant PalNo ratings yet
- Column Design 1. Guideline For Fixing The Position and Orientation of Columns in The LayoutDocument14 pagesColumn Design 1. Guideline For Fixing The Position and Orientation of Columns in The LayoutV.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Howe Roof TrussDocument6 pagesModeling of Howe Roof TrussChetan B ArkasaliNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument43 pagesTrussTanuj Bhardwaj75% (4)
- Analysis Design of Strong Column Weak Beam Sni 0328472002Document16 pagesAnalysis Design of Strong Column Weak Beam Sni 0328472002hemalcmistryNo ratings yet
- PEBDocument27 pagesPEBMadan YadavNo ratings yet
- TOS 4 Unit 3 Design of R.C.C Slabs Continued-1Document24 pagesTOS 4 Unit 3 Design of R.C.C Slabs Continued-1Psedit 2020100% (1)
- Properties of Structure Steel As Per Limit State Method IS 800:2007, Mechanical Properties of SteelDocument19 pagesProperties of Structure Steel As Per Limit State Method IS 800:2007, Mechanical Properties of SteelRaju Sharma75% (4)
- Slpoed Footing With PedestalDocument11 pagesSlpoed Footing With PedestalD.V.Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Design Parameters - Concrete Is 456Document5 pagesDesign Parameters - Concrete Is 456Uttam Kumar GhoshNo ratings yet
- Built Up ColumnsDocument28 pagesBuilt Up ColumnsSuneesh PNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design PDFDocument45 pagesIsolated Footing Design PDFChau Suktana Enling0% (1)
- Steel Design Project: Laterally Supported and Unsupported Beams, Columns, Column Base Plate, ConnectionsDocument24 pagesSteel Design Project: Laterally Supported and Unsupported Beams, Columns, Column Base Plate, Connectionsozzieastro96% (24)
- Parameters For Steel Design (Is 800-2007)Document7 pagesParameters For Steel Design (Is 800-2007)Richa100% (1)
- Design of Two Way SlabDocument64 pagesDesign of Two Way SlabVINOTHINI100% (1)
- III Design of Steel Structures Unit 1Document76 pagesIII Design of Steel Structures Unit 1laiju p bNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Assignment 5 Solution Full Marks: 20: W + W - T 75 + 40 - 10 105 MMDocument2 pagesWeek 5 Assignment 5 Solution Full Marks: 20: W + W - T 75 + 40 - 10 105 MMamin alzuraikiNo ratings yet
- Peb Foundation DesignDocument24 pagesPeb Foundation DesignDevendra HolkarNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument42 pagesBeamlavyNo ratings yet
- DSS AssignmentDocument29 pagesDSS AssignmentRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- TOS 5 Unit 2a Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocument7 pagesTOS 5 Unit 2a Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsKshitija100% (1)
- 3 Tier Grillage Design CalculationDocument5 pages3 Tier Grillage Design CalculationDebesh KuanrNo ratings yet
- Slab Design As Per IS 456Document7 pagesSlab Design As Per IS 456RitaBiswas100% (1)
- 10 - Multi Storey BuildingDocument33 pages10 - Multi Storey Buildinghari1008108100% (1)
- Peb Seminar 1Document78 pagesPeb Seminar 1MuraliKrishna NaiduNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Design For Tension MemberDocument14 pagesChapter-2 Design For Tension Memberzakai zakiNo ratings yet
- TOS 5 Unit 2d Coffered SlabDocument5 pagesTOS 5 Unit 2d Coffered SlabKshitijaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotessatydevsinghnegiNo ratings yet
- Design PhilosophyDocument49 pagesDesign PhilosophyAnuj ChandiwalaNo ratings yet
- Web Buckling and CripplingDocument3 pagesWeb Buckling and CripplingManoj Nagarkond100% (2)
- Long Span StructureDocument94 pagesLong Span StructureMicron Macron100% (5)
- Tension MemberDocument58 pagesTension MemberD SRINIVASNo ratings yet
- Grillage FoundationsDocument10 pagesGrillage FoundationsAbhish RajNo ratings yet
- 13.B Design The Interior Panel of A Flat Slab 6 M × 8 M in Size For A Super Imposed Load of 5 kN/m2. Use M20 Grade Concrete and Fe415 SteelDocument6 pages13.B Design The Interior Panel of A Flat Slab 6 M × 8 M in Size For A Super Imposed Load of 5 kN/m2. Use M20 Grade Concrete and Fe415 SteelSaran T SNo ratings yet
- Substitute Frame AnalysisDocument5 pagesSubstitute Frame Analysissiniann7100% (1)
- Steel StaircaseDocument24 pagesSteel StaircaseKanak Yadav100% (1)
- Stepped FootingDocument12 pagesStepped FootingV.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- Limit State MethodDocument4 pagesLimit State Methodrajanciviltneb67% (3)
- 8.5 Design Examples: 8.5.1 Design Example (Slab Base)Document11 pages8.5 Design Examples: 8.5.1 Design Example (Slab Base)Gheorghe IonicaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual: Exercise 6.1 (Design of Vertical Stirrups)Document10 pagesSolution Manual: Exercise 6.1 (Design of Vertical Stirrups)Arun GoyalNo ratings yet
- 150 KLD NirmalpurDocument19 pages150 KLD NirmalpurHirak BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Column BasesDocument6 pagesColumn BasesPrantik MitraNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Design of ColumnsDocument74 pagesUnit 6 Design of ColumnsManoj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Punching Shear Check For SlabDocument2 pagesPunching Shear Check For SlabArnab Sur50% (2)
- Compression Members ProblemsDocument23 pagesCompression Members ProblemsReyNo ratings yet
- Gou 2016-Robust Hybrid Simulation With PDFDocument326 pagesGou 2016-Robust Hybrid Simulation With PDFutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 94 024 0867 6 PDFDocument735 pages10.1007@978 94 024 0867 6 PDFutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Conv Gaetanomiraglia Xxxi Assembled PHD Thesis v2 PDFDocument214 pagesConv Gaetanomiraglia Xxxi Assembled PHD Thesis v2 PDFutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Seismic Performance Evaluation of Building-Damper System Under Near-Fault EarthquakeDocument21 pagesResearch Article: Seismic Performance Evaluation of Building-Damper System Under Near-Fault Earthquakeutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- A New Approach in Fatigue Testing and Evaluation of Hot Mix Asphalt Using A Dynamic Shear RheometerDocument10 pagesA New Approach in Fatigue Testing and Evaluation of Hot Mix Asphalt Using A Dynamic Shear Rheometerutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Analysis of MR Dampers: Manuel T. Braz-César, Rui C. BarrosDocument19 pagesExperimental and Numerical Analysis of MR Dampers: Manuel T. Braz-César, Rui C. Barrosutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- SeismoStruct 2021 User Manual - ENG PDFDocument562 pagesSeismoStruct 2021 User Manual - ENG PDFutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- V. Nonlinear Regression by Modified Gauss-Newton Method: TheoryDocument39 pagesV. Nonlinear Regression by Modified Gauss-Newton Method: Theoryutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Parameter Estimation of Bouc-Wen Hysteretic Systems by Sawtooth Genetic AlgorithmDocument18 pagesParameter Estimation of Bouc-Wen Hysteretic Systems by Sawtooth Genetic Algorithmutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument6 pagesResearch Articleutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Random Vibration Analysis of Sdof Systems With Asymmetric HysteresisDocument12 pagesModeling and Random Vibration Analysis of Sdof Systems With Asymmetric Hysteresisutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of A Hybrid Damping System Composed of A Buckling Restrained Brace With A Magneto Rheological DamperDocument8 pagesNumerical Study of A Hybrid Damping System Composed of A Buckling Restrained Brace With A Magneto Rheological Damperutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis For Random Vibration of Hysteretic FramesDocument19 pagesModal Analysis For Random Vibration of Hysteretic Framesutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- RCC - Civil Engineering Objective QuestionsDocument9 pagesRCC - Civil Engineering Objective Questionsutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Objective Civil EngineeringDocument59 pagesObjective Civil Engineeringutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Development of Small Scale Models For K 12 and Undergraduate Students To Demonstrate Earthquake Effects On Building Structures and Aseismic Design ProceduresDocument23 pagesDevelopment of Small Scale Models For K 12 and Undergraduate Students To Demonstrate Earthquake Effects On Building Structures and Aseismic Design Proceduresutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Amp13us UgDocument7 pagesAmp13us Ugutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Flexural Strengthening of Structural Steel Angle Sections Using CFRP: Experimental InvestigationDocument10 pagesFlexural Strengthening of Structural Steel Angle Sections Using CFRP: Experimental Investigationutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- TMFMN1 de 1Document110 pagesTMFMN1 de 1utsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis MAS500 MR Damper Hysteresis Characterization For The Semi-Active Suspension SystemDocument65 pagesMaster Thesis MAS500 MR Damper Hysteresis Characterization For The Semi-Active Suspension Systemutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Nist GCR 15-917-34 TB 11 FinalDocument34 pagesNist GCR 15-917-34 TB 11 Finalhyungo kwonNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Non-Linear Parameters On The Modeling of Multi-Storey Seismically Isolated BuildingsDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Non-Linear Parameters On The Modeling of Multi-Storey Seismically Isolated Buildingsutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Ffiwwwwww: I Reduction I ! L) LayoutDocument1 pageFfiwwwwww: I Reduction I ! L) Layoututsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- MosDocument20 pagesMosutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Firstname LASTNAME, Firstname LASTNAME, Firstname Last NameDocument7 pagesFirstname LASTNAME, Firstname LASTNAME, Firstname Last Nameutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet