Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mutations
Uploaded by
api-2769156810 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views1 pageOriginal Title
mutations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views1 pageMutations
Uploaded by
api-276915681Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
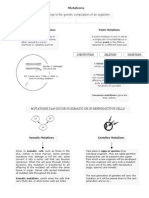
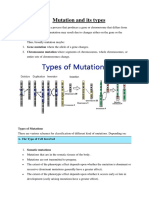
Mutation - Another Cause of Genetic Variation
● A mutation is a permanent change in the base sequence of DNA.
● Some mutations are random occuring during cell division and others are caused by a
mutagen. Examples of mutagens are chemicals, UV light or radiation.
● Mutations can occur in either body (somatic) cells that undergo mitosis or during
meiosis when the gametes are made. To create variation in a population, the mutation
must be passed onto offspring so only mutations which occur in the gametes will be
passed onto the next generation.
● Mutations introduce new alleles into a population and can be:
Beneficial mutation = A mutation that gives an organism a survival advantage.
Harmful mutation = A mutation that effects the survival of the organism.
Silent mutation = a mutation which has no observable effect on the organism.
You might also like
- Mutations ClassificationDocument25 pagesMutations ClassificationEdessa G. FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Spontanious MutationDocument10 pagesSpontanious MutationSachin RachagolNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MutationDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Mutation469t6qctdfNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument5 pagesMutationDrRajkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument4 pagesMutationReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument20 pagesMutationsShelalyn RodimoNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument1 pageMutationsapi-240193026No ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Genetics: Understanding MutationsDocument23 pagesGene Expression and Genetics: Understanding Mutationsprimal100% (1)
- Mutation Breeding BenefitsDocument13 pagesMutation Breeding BenefitsUPASI TRF VandiperiyarNo ratings yet
- Mutation Reporting W3Document17 pagesMutation Reporting W3Marize TerrenalNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument28 pagesMutationdr_47839666No ratings yet
- Introduction To MutationsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Mutationsjarellelozada21No ratings yet
- Presentacion de MutationDocument12 pagesPresentacion de MutationMario Alberto Madrigal MartinezNo ratings yet
- Assessment 13.3: Describe The Two Main Types of Mutation?Document1 pageAssessment 13.3: Describe The Two Main Types of Mutation?Pablo Cesar Velasquez BaquedanoNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations: Causes, Types and EffectsDocument6 pagesDNA Mutations: Causes, Types and EffectsSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Change and Mutation TypesDocument12 pagesGenetic Change and Mutation TypesHSC CoachNo ratings yet
- Mutation and Its TypesDocument7 pagesMutation and Its TypesJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: Types of MutationsDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: Types of MutationsKeara RaleighNo ratings yet
- 13 3 PowerPointDocument17 pages13 3 PowerPointDeena SriyazzNo ratings yet
- Mutations 1Document21 pagesMutations 1James GalvezNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology A-Level: Topic 8: The Control of Gene ExpressionDocument9 pagesAQA Biology A-Level: Topic 8: The Control of Gene ExpressionsamNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations - GCSE BiologyDocument5 pagesGenetic Mutations - GCSE BiologynNo ratings yet
- Utation: Big PictureDocument2 pagesUtation: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Mutations: A sudden heritable changeDocument29 pagesMutations: A sudden heritable changeiariajay100% (1)
- Biotech. (Muleta Germa)Document10 pagesBiotech. (Muleta Germa)Aman aman AbeyeNo ratings yet
- G-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsDocument5 pagesG-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Answers Part 2Document64 pagesAnswers Part 2Rynjeff Lui-Pio100% (1)
- Mutation PDFDocument11 pagesMutation PDFARCHANA BHARTI100% (1)
- AL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationDocument18 pagesAL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationJyoti BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Summarised NotesDocument13 pagesModule 6 Summarised NotesAman TomarNo ratings yet
- Genetic MutationDocument33 pagesGenetic MutationSammy S. Sapalaran100% (1)
- CH 13 Sec 3 NotesDocument24 pagesCH 13 Sec 3 NotesJanet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- Variations Within SpeciesDocument1 pageVariations Within SpeciesEmblemXNo ratings yet
- Gomez - Sauza - Week 3 - The Effects of MutationsDocument17 pagesGomez - Sauza - Week 3 - The Effects of MutationsJuan Nathaniel SauzaNo ratings yet
- DNA MutationsDocument11 pagesDNA MutationsbethNo ratings yet
- MB 402 Microbial GeneticsDocument5 pagesMB 402 Microbial GeneticsAzka FatimaNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Neeraj Kumar Maurya Environmental BiotechnologyDocument24 pagesMutation: Neeraj Kumar Maurya Environmental BiotechnologyNeeraj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Somatic Mutations: Genetic Changes Acquired During Cell DivisionDocument1 pageSomatic Mutations: Genetic Changes Acquired During Cell DivisionZeljko LekovicNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentmuhammadtaofeek55No ratings yet
- 4-10 Gene MutationDocument5 pages4-10 Gene MutationAhmad KarimNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument1 pageMutationtomatorNo ratings yet
- Mutation 3Document30 pagesMutation 3Laiyee ChanNo ratings yet
- 1 MutationsDocument7 pages1 Mutationschurikovalexandr97No ratings yet
- GeneticmutationDocument6 pagesGeneticmutationapi-286256787No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: MutationsDocument8 pagesChapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: Mutationssudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- Variation and Population DynamicsDocument13 pagesVariation and Population DynamicsRM MontemayorNo ratings yet
- D1.3 Mutations and Gene EditingDocument17 pagesD1.3 Mutations and Gene Editingatasay2024No ratings yet
- MutationsDocument1 pageMutationstomatorNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Evolution pptDocument26 pagesMechanism of Evolution pptk15014998No ratings yet
- Detailed Notes On Module 6 643fd17912a86 PDFDocument16 pagesDetailed Notes On Module 6 643fd17912a86 PDFTanisha PatelNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationDocument28 pagesMolecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationJannifer Andrew100% (2)
- Continuous and Discontinuous Variation 2021Document8 pagesContinuous and Discontinuous Variation 2021nigel lawsonNo ratings yet
- Mutation PDFDocument21 pagesMutation PDFatuakiluNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaDocument24 pagesMutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- Genetic MutationDocument8 pagesGenetic MutationLil-Matt JasonNo ratings yet
- Onco, TSG & CancerDocument8 pagesOnco, TSG & Cancersumera120488No ratings yet
- 18.1 VariationDocument14 pages18.1 Variationmi9gx5No ratings yet
- Meaning, Types & Detection of DNA MutationsDocument12 pagesMeaning, Types & Detection of DNA MutationsSamuelNo ratings yet
- Mutation HandoutsDocument3 pagesMutation HandoutsReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- nb2s Organic Survival SheetDocument3 pagesnb2s Organic Survival Sheetapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Yr 12 Phy Mechanics Los 2018Document1 pageYr 12 Phy Mechanics Los 2018api-276915681No ratings yet
- Phys 91168 GuidelinesDocument8 pagesPhys 91168 Guidelinesapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Student Info 2018Document2 pagesStudent Info 2018api-276915681No ratings yet
- Student Info 2018Document2 pagesStudent Info 2018api-276915681No ratings yet
- Science Dept Assessment Procedures StudDocument2 pagesScience Dept Assessment Procedures Studapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Physics Dept Assessment Procedures StudDocument1 pagePhysics Dept Assessment Procedures Studapi-276915681No ratings yet
- SCP Course OutlineDocument1 pageSCP Course Outlineapi-276915681No ratings yet
- 2015 Assessment Specifications NzqaDocument2 pages2015 Assessment Specifications Nzqaapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Yr12 Physics Course Outline 2016Document2 pagesYr12 Physics Course Outline 2016api-276915681No ratings yet
- Phys 90255 Equation TestDocument1 pagePhys 90255 Equation Testapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Phys 90255 Equation Test AnswersDocument2 pagesPhys 90255 Equation Test Answersapi-276915681No ratings yet
- Phys 90255 Fcard FormDocument2 pagesPhys 90255 Fcard Formapi-276915681No ratings yet