Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mutation
Uploaded by
Reymark Novecio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesMutation
Uploaded by
Reymark Novecion
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
3. Chromosomal mutations.
These mutations involve changes
to the structure or number of chromosomes. Examples include
Topics: deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations.
● Introduction to mutations
● Types of mutations Causes of mutations
● Effects of mutations Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
● Mutagens
● Human genetic disorders 1. Spontaneous errors during DNA replication. The DNA
● Evolution and mutations replication process is not perfect, and errors can occur
● Biotechnology and mutations spontaneously. These errors can result in a change in the DNA
sequence, leading to a mutation.
Introduction to Mutations
2. Environmental factors. Exposure to certain environmental
factors such as radiation, chemicals, and viruses can cause
mutations in DNA. For example, ultraviolet (UV) radiation from
the sun can cause mutations that lead to skin cancer.
3. Inherited mutations. Mutations can also be inherited from
parents. When mutations occur in the germ cells (sperm and egg
cells), they can be passed down to offspring and can cause
genetic disorders.
4. Replication errors during cell division. During cell division,
DNA is replicated and distributed to the daughter cells. Errors
during this process can result in mutations.
5. Mutagenic agents. Some chemicals and substances, known
as mutagens, can cause mutations in DNA. Examples of
mutagens include tobacco smoke, certain pesticides, and
industrial chemicals.
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can occur
6. DNA damage repair errors. Cells have mechanisms to repair
spontaneously or be caused by exposure to certain
damaged DNA, but errors in these mechanisms can lead to
environmental factors known as mutagens. Mutations can occur
mutations.
in any cell of an organism and can be inherited or arise
spontaneously during an individual's lifetime.
7. Insertions and deletions. These mutations involve the
addition or removal of one or more nucleotides in the DNA
A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that makes
sequence, which can alter the reading frame and change the
up a gene. This can result in a change in the amino acid
amino acid sequence of the protein.
sequence of a protein, which can affect the protein's function.
Gene mutations can occur naturally or be caused by
Gene mutations can affect an organism differently depending on
environmental factors such as radiation, chemicals, or viruses.
the specific mutation and its location within the genome. Some
mutations may have no effect, while others can lead to genetic
Types of mutations disorders or an increased risk of developing certain diseases.
1. Point mutations. These are the most common type of
mutation, and they involve a change in a single nucleotide (A, T,
C, or G) in the DNA sequence.
Point mutations are divided into three categories:
● Silent mutations. These mutations do not change the
amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the
DNA because of the redundancy of the genetic code.
● Missense mutations. These mutations change one
amino acid in the protein sequence. Depending on the
location of the mutation, this may or may not affect the
protein's function. Effects of mutations
Mutations can affect an organism's phenotype differently, from
● Nonsense mutations. These mutations change a neutral to beneficial or harmful.
codon that normally encodes an amino acid into a stop
codon, leading to premature termination of protein ● Neutral mutations. These mutations have no effect on
synthesis. an organism's phenotype or health. For example, a
change in the DNA sequence that does not alter the
2. Frameshift mutations. These mutations occur when amino acid sequence of a protein.
nucleotides are inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence,
causing a shift in the reading frame of the codons. Frameshift ● Beneficial mutations. These mutations can provide
mutations can have significant effects on the resulting protein's an advantage to an organism, such as resistance to a
function. disease or an increased ability to survive in a particular
environment.
● Harmful mutations. These mutations can cause harm
to an organism, such as a genetic disorder or an
increased risk of developing cancer.
MUTAGENS
Mutagens are chemical or physical agents that can cause
changes or mutations in the DNA sequence of an organism.
These mutations can have a variety of effects, including
changes in the organism's traits, genetic disorders, and cancer.
Examples of chemical mutagens include: 2. Huntington's disease. It is a genetic disorder caused by
● Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) found in mutations in the HTT gene, which codes for a protein called
tobacco smoke and charred meat huntingtin. Mutations in HTT can cause the accumulation of
● Nitrosamines found in processed meats and tobacco abnormal proteins in the brain, leading to the progressive
smoke degeneration of nerve cells and cognitive decline.
● Benzene, a common industrial chemical
● Aflatoxins produced by fungi in food crops like
peanuts and corn
● Vinyl chloride, a chemical used in plastic production
Examples of physical mutagens include:
● Ionizing radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays
● Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial
sources like tanning beds
● Electromagnetic radiation, such as radio waves and
microwaves
● High-energy particles, such as those found in cosmic
radiation and nuclear fallout 3. Sickle cell anemia. It is a genetic disorder caused by
mutations in the HBB gene, which codes for the beta-globin
Mutagens can cause cancer by inducing mutations in genes that subunit of hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen in red blood
control cell growth and division, leading to uncontrolled cell cells. Mutations in HBB can cause the formation of abnormal
growth and the formation of tumors. For example, a mutation in hemoglobin molecules, leading to the characteristic sickle shape
the tumor suppressor gene TP53 can prevent cells from properly of red blood cells and anemia.
regulating their own growth, leading to the development of
cancer. Some mutagens can also damage DNA directly, leading 4. Cri du chat Syndrome. It is a genetic disorder caused by a
to the formation of abnormal or damaged proteins that can deletion of a portion of chromosome 5 causes it. This deletion
interfere with normal cellular functions. can affect gene expression in brain development, leading to
intellectual disability and delayed development. It can also affect
the development of the larynx, resulting in a high-pitched cry that
HUMAN GENETIC DISORDERS
sounds like a cat.
Human genetic disorders are caused by mutations in the DNA
sequence that can affect the function of genes and proteins.
5. Down syndrome. It is a genetic disorder caused by an extra
These mutations can be inherited from parents or arise
copy of chromosome 21. This extra chromosome can lead to
spontaneously during development.
overexpression of genes on chromosome 21, affecting the
development of the brain, heart, and other organs. The
characteristic facial features of Down syndrome may be due to
altered gene expression during facial development.
6. Edward syndrome. It is a genetic disorder (Trisomy 18)
caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 18.
This extra chromosome can disrupt normal development,
leading to severe intellectual disability and physical
abnormalities. Many of the features of Edward syndrome are
thought to be due to the dysregulation of genes on chromosome
18.
7. Jacobsen syndrome. It is a genetic disorder caused by
deleting a portion of chromosome 11. This deletion can affect
1. Cystic fibrosis. It is a genetic disorder caused by mutations
gene expression in brain development, leading to intellectual
in the CFTR gene, which codes for a protein that regulates the
disability and delayed development. It can also affect the heart's
movement of salt and water in and out of cells. Mutations in
and other organs' development, resulting in physical
CFTR can lead to the buildup of thick mucus in the lungs and
abnormalities.
other organs, causing respiratory and digestive problems.
8. Klinefelter syndrome. It is a genetic disorder caused by the
presence of an extra X chromosome in males. This extra
chromosome can affect the production of testosterone, leading
to reduced levels of this hormone and infertility. The physical
and developmental features of Klinefelter syndrome may be due
to altered gene expression resulting from the extra X Human karyotyping is the process of analyzing the number,
chromosome. size, and shape of chromosomes in a person's cells.
Chromosomes are structures that contain an individual's genetic
9. Turner syndrome. It is a genetic disorder caused by the material in the form of DNA. Humans have 23 pairs of
absence of all or part of one X chromosome in females. This chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes
missing chromosome can affect the development of the ovaries
and other organs, leading to infertility and physical abnormalities
such as short stature. The characteristic features of Turner
syndrome may be due to altered gene expression resulting from
the missing X chromosome.
Genetic testing and counseling can help individuals and
families understand their risk of developing or passing on
genetic disorders. Genetic testing involves analyzing a person's
DNA to detect mutations or other genetic variations that may
increase the risk of a particular disorder.
EVOLUTION AND MUTATION
Karyotyping is typically done using cells from a blood sample,
although other types of cells, such as skin cells or amniotic fluid
cells, may also be used. The cells are first treated with a
chemical that stops them in the dividing stage of the cell cycle.
Then, the cells are stained with a dye that highlights the
chromosomes and allows them to be visualized under a
microscope.
The chromosomes are then arranged in pairs according to their
size, shape, and banding patterns, numbered from 1 to 22 based
Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, which on their size (with chromosome 1 being the largest) and labeled
is the raw material for evolution. Mutations can lead to evolution X and Y for the sex chromosomes. Normal human karyotype
by introducing new genetic traits into a population. Over time, should show 23 pairs of chromosomes, with the sex
natural selection can act on these traits, leading to changes in chromosomes being either XX (female) or XY (male).
the genetic makeup of the population.
Karyotyping can be used to detect chromosomal
When a mutation occurs, it can create a new allele (a variant abnormalities, such as aneuploidy (an abnormal number of
form of a gene) that was not previously present in the population. chromosomes), or structural abnormalities, like translocations,
This can increase genetic variation within the population. If this deletions, or duplications. This can be helpful in diagnosing
new allele confers a beneficial trait, individuals carrying that genetic disorders like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, or
allele may be more likely to survive and reproduce, passing Klinefelter syndrome.
the beneficial trait to their offspring. This process is called
natural selection, and it can lead to the spread of the ● Translocations occur when a piece of one
advantageous allele in the population. chromosome breaks off and attaches to another
chromosome. This can result in a change in the
On the other hand, if a mutation creates a harmful allele, position of certain genes, which can affect their
individuals carrying that allele may be less likely to survive and expression and potentially lead to genetic disorders.
reproduce. This can lead to the removal of the deleterious
allele from the population over time through a process called ● Deletions occur when a portion of a chromosome is
negative selection. missing, either due to a break in the chromosome or
failure of a chromosome to separate properly during
Genetic variation is important for evolution because it provides cell division. Deletions can range in size from small to
the raw material for natural selection to act upon. Without very large and can lead to a variety of genetic
genetic variation, natural selection would not be able to favor disorders, depending on which genes are affected.
certain traits over others, and evolution would not occur.
● Duplications occur when a section of a chromosome
A dominant gene is a gene that expresses its phenotype is duplicated, resulting in an extra copy of that
(observable trait) when present in either one or both copies of segment. Duplications can be inherited from a parent
the gene. A recessive gene is a gene that expresses its or can occur spontaneously during cell division. Like
phenotype only when present in both copies of the gene. deletions, duplications can range in size and can have
varying effects on gene expression and development.
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND MUTATION
GENETIC ENGINEERING
Biotechnology is the application of technology to study,
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating the genetic
manipulate and modify biological systems, including living
material of an organism, often by introducing or modifying
organisms, cells, and molecules. One of the major areas of
specific genes. This process can involve introducing new
biotechnology is genetic engineering, which involves modifying
genetic material from a different organism or modifying an
the genetic material of living organisms to produce new products
organism's existing DNA to produce a desired trait or
or improve existing ones.
characteristic.
HUMAN KARYOTYPING
For example, scientists can use gene editing technologies like 3. A DNA strand that originally reads 5’-GATATC-3’ undergoes
CRISPR-Cas9 to precisely target and modify specific genes in a mutation that changes it to 5’- GATCATC-3’. This is an
an organism's DNA, introducing or removing mutations in the example of what type of mutation?
A. Deletion
process. This can be used to create new crop varieties that are
B. Insertion
more resistant to pests or environmental stresses or to develop C. Nonsense mutation
new treatments for genetic diseases by correcting specific D. Point mutation
mutations that cause the disease.
4. What type of point mutation results in a frameshift mutation?
Genetic engineering relies on the ability to manipulate DNA, A. Deletion
which can be achieved through a number of techniques, B. Insertion
C. Substitution
including CRISPR-Cas9 technology, gene therapy, and
D. Both A and B
others. CRISPR-Cas9 technology is a powerful tool that
enables scientists to precisely target and edit specific genes 5. Which is NOT a type of substitution mutation?
within an organism's DNA, allowing for the creation of A. Conservation
genetically modified organisms with desirable traits or the B. Missense
correction of genetic disorders. C. Nonsense
D. Silent
Gene therapy is another form of genetic engineering that
6. Which is an example of a stop codon in RNA?
involves the delivery of functional copies of genes into cells A. UAG
to correct genetic defects or diseases. This technology is still in B. UAA
its early stages, but it holds promise for treating a variety of C. UGA
genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, D. All of the above
and sickle cell anemia.
7. Which type of mutations can result in a frameshift?
A. Nonsense and missense
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) is a type of DNA that is artificially B. Nonsense and insertions
created by combining DNA molecules from different sources. C. Insertions and deletions
This technology involves the use of enzymes called restriction D. Missense and deletions
endonucleases to cut DNA molecules at specific locations,
allowing for the insertion of new DNA sequences from other 8. Which type of mutation does NOT change the overall function
sources helps them understand the concept of gene mutation of the protein?
A. Insertion
and its implications.
B. Missense
C. Nonsense
D. Silent
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING:
9. Which type of mutation results in the replacement of one
Name: __________________________ nucleotide by another?
Grade and Section: _______________ A. Insertion
B. Missense
C. Nonsense
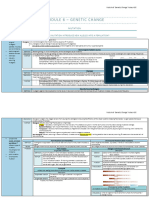
Test 1. Complete the following table: D. Silent
DNA ACT CTG AAT TAA CTA ATG GGT
coding
DNA 10. Which of the following is not an example of a point mutation?
template A. Frameshift mutation
mRNA B. Missense mutation
tRNA C. Nonsense mutation
Amino D. Silent mutation
Acid
TEST 3. Match the following
DNA CTG CGA ATA TCA CAA ATC GGT
coding
DNA
template
mRNA
tRNA
Amino
Acid
TEST 2. Encircle the letter of the correct answer
1. Frameshift Mutations are generally much more serious and
often more deadly than point mutations.
A. True
B. False
C. Depends upon the condition of the DNA
D. It is much more serious but not deadly
2. Frameshift mutations are the result of what occurrence?
A. Insertions or deletions that are not a multiple of three.
B. A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to a stop codon
C. A mutation that changes one amino acid to another.
D. A nucleotide-pair substitution
You might also like
- Mutation HandoutsDocument3 pagesMutation HandoutsReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MutationsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Mutationsjarellelozada21No ratings yet
- Introduction To Mutation 2Document5 pagesIntroduction To Mutation 2jarellelozada21No ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Genetics: Understanding MutationsDocument23 pagesGene Expression and Genetics: Understanding Mutationsprimal100% (1)
- D1.3 Mutations and Gene EditingDocument17 pagesD1.3 Mutations and Gene Editingatasay2024No ratings yet
- DNA Mutations: Causes, Types and EffectsDocument6 pagesDNA Mutations: Causes, Types and EffectsSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology A-Level: Topic 8: The Control of Gene ExpressionDocument9 pagesAQA Biology A-Level: Topic 8: The Control of Gene ExpressionsamNo ratings yet
- Mutation 3Document30 pagesMutation 3Laiyee ChanNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Sec 3 NotesDocument24 pagesCH 13 Sec 3 NotesJanet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations: Types, Causes and EffectsDocument28 pagesDNA Mutations: Types, Causes and EffectsCaroline Nguyen100% (1)
- DNA and MutationsDocument13 pagesDNA and MutationspiaNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument28 pagesMutationdr_47839666No ratings yet
- 13 3 PowerPointDocument17 pages13 3 PowerPointDeena SriyazzNo ratings yet
- Gene mutations presentation insightsDocument6 pagesGene mutations presentation insightsDeep PatelNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensDocument9 pagesX Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensNi Wayan SuliartiniNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentmuhammadtaofeek55No ratings yet
- d1.3 MutationsDocument20 pagesd1.3 Mutationselena farahNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor of Molecular GeneticsDocument32 pagesHuman Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor of Molecular GeneticsBarrak AldosaryNo ratings yet
- Essay Question Mutations-1Document1 pageEssay Question Mutations-1InactiveAccount100% (1)
- Bio Mutations Show 2019Document21 pagesBio Mutations Show 2019Ashish SethyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes On Module 6 643fd17912a86 PDFDocument16 pagesDetailed Notes On Module 6 643fd17912a86 PDFTanisha PatelNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationDocument28 pagesMolecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationJannifer Andrew100% (2)
- Biochemistry MutationDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Mutation469t6qctdfNo ratings yet
- MB 402 Microbial GeneticsDocument5 pagesMB 402 Microbial GeneticsAzka FatimaNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Physical Sciences Dept. College of Science de La Salle University-Dasmariñas Cavite March 15, 2010Document5 pagesMutation: Physical Sciences Dept. College of Science de La Salle University-Dasmariñas Cavite March 15, 2010Aki OtaniNo ratings yet
- Genetic MutationDocument33 pagesGenetic MutationSammy S. Sapalaran100% (1)
- Genetic Change and Mutation TypesDocument12 pagesGenetic Change and Mutation TypesHSC CoachNo ratings yet
- DNA MutationsDocument44 pagesDNA MutationsYashika A.No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Genetic Mutations and Applied GeneticsDocument9 pagesLecture Notes Genetic Mutations and Applied GeneticsRia Gale AsiloNo ratings yet
- Organism Mutation Mutagens: MutagenesisDocument19 pagesOrganism Mutation Mutagens: Mutagenesissobia faryadaliNo ratings yet
- Mutation PDFDocument11 pagesMutation PDFARCHANA BHARTI100% (1)
- Gene and Chromosomal Mutation PDFDocument2 pagesGene and Chromosomal Mutation PDFesgrid1No ratings yet
- Spontanious MutationDocument10 pagesSpontanious MutationSachin RachagolNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Summarised NotesDocument13 pagesModule 6 Summarised NotesAman TomarNo ratings yet
- What Is Mutation2Document21 pagesWhat Is Mutation2Deepsnehil Dubey100% (2)
- Genotoxicity Project 1Document46 pagesGenotoxicity Project 1Vivek DNo ratings yet
- Biotech. (Muleta Germa)Document10 pagesBiotech. (Muleta Germa)Aman aman AbeyeNo ratings yet
- Mutations FinalDocument13 pagesMutations FinalMuhammad Tazeem MunawarNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Solutions Manualstacyperezbrstzpmgif100% (30)
- Ch450 and Ch451: Biochemistry - Defining Life at The Molecular LevelDocument19 pagesCh450 and Ch451: Biochemistry - Defining Life at The Molecular LevelHasan AnandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: MutationsDocument8 pagesChapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: Mutationssudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- ReportingDocument9 pagesReportingJorell lapatingNo ratings yet
- Biology Mod 6 Notes - TableDocument18 pagesBiology Mod 6 Notes - Tablekatelinj2942No ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: Types of MutationsDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: Types of MutationsKeara RaleighNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument2 pagesBiotechnologyBhertson RamosNo ratings yet
- AL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationDocument18 pagesAL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationJyoti BarnwalNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument5 pagesMutationDrRajkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson OverviewDocument32 pagesLesson OverviewvnappenNo ratings yet
- Presentacion de MutationDocument12 pagesPresentacion de MutationMario Alberto Madrigal MartinezNo ratings yet
- Utation: Big PictureDocument2 pagesUtation: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to DNA Mutations: Causes and TypesDocument7 pagesAn Introduction to DNA Mutations: Causes and TypesHASHIRANo ratings yet
- DNA MutationsDocument11 pagesDNA MutationsbethNo ratings yet
- G-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsDocument5 pagesG-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Muta GenesisDocument8 pagesMuta GenesisOphy FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Genetic Change Study NotesDocument38 pagesGenetic Change Study NotesPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Ch+08 7+mutationsDocument3 pagesCh+08 7+mutationsdavisguerrero194No ratings yet
- Aakaash BiologyDocument23 pagesAakaash BiologyHASHIRANo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument20 pagesMutationsShelalyn RodimoNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument7 pagesDepartment of EducationShania Joan LopezNo ratings yet
- Beyond DNA: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchFrom EverandBeyond DNA: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Science - First Preliminary Examination - MS - Set ADocument5 pagesClass - X - Science - First Preliminary Examination - MS - Set ALaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Acute appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other medical quiz diagnosesDocument23 pagesAcute appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other medical quiz diagnoses182 ROHIL HNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 9th Edition Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Shawn o Farrellowen M McdougalDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 9th Edition Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Shawn o Farrellowen M McdougalNathan Cook94% (36)
- JRF 2015 Group-D Entomology and Nematology ExamDocument10 pagesJRF 2015 Group-D Entomology and Nematology ExamDada PeerNo ratings yet
- Effects of Quinine Quinidine and Chloroquine On A9Document8 pagesEffects of Quinine Quinidine and Chloroquine On A9Arun BharathiNo ratings yet
- 02 Gene Aid Isolation KitDocument16 pages02 Gene Aid Isolation KitLusi OktavianaNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life LESSONDocument104 pagesCell - The Fundamental Unit of Life LESSONGrade 4 B TeacherNo ratings yet
- Science 8: 4 QUARTER Module 4Document10 pagesScience 8: 4 QUARTER Module 4katt100% (1)
- Step Forward in Plant Taxonomy Book (Final)Document113 pagesStep Forward in Plant Taxonomy Book (Final)DoctorQariNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Pharmacology of Neuropeptides - Oxytocin (PDFDrive)Document586 pagesBehavioral Pharmacology of Neuropeptides - Oxytocin (PDFDrive)Emine Mamuti100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Chapter 9: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument30 pagesGrade 8 Science Chapter 9: Reproduction in AnimalsManimala ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Issues in Bioprospecting: Lessons From The Field: P. PushpangadanDocument35 pagesIssues in Bioprospecting: Lessons From The Field: P. PushpangadanKhoirun NisyakNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Coin Toss LabDocument2 pagesMendelian Genetics Coin Toss LabJoy PanesNo ratings yet
- The Key Difference Between Essential and NonDocument2 pagesThe Key Difference Between Essential and NonRafael CurtesNo ratings yet
- PhanerogamsDocument3 pagesPhanerogamsKrishna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Prospects of Microbial Cell Factories Developed Through Systems Metabolic EngineeringDocument8 pagesProspects of Microbial Cell Factories Developed Through Systems Metabolic Engineeringjessi jamNo ratings yet
- LIFE CYCLE AND PATHOGENECITY OF Plasmodium Vivax and Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument7 pagesLIFE CYCLE AND PATHOGENECITY OF Plasmodium Vivax and Entamoeba Histolyticaarifsheikh4025No ratings yet
- Folding of The EmbryoDocument22 pagesFolding of The EmbryoConstance EphraimNo ratings yet
- Hemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesDocument15 pagesHemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Move Over, CRISPR - RNA-editing Therapies Pick Up SteamDocument2 pagesMove Over, CRISPR - RNA-editing Therapies Pick Up SteamHuaxia ShiNo ratings yet
- Application of Innovative Technologies For Improved Food Quality and SafetyDocument83 pagesApplication of Innovative Technologies For Improved Food Quality and SafetyIsha GargNo ratings yet
- Ed190357 PDFDocument156 pagesEd190357 PDFM A R C ONo ratings yet
- CHP 7 Class 10Document13 pagesCHP 7 Class 10sourabh nuwalNo ratings yet
- Semester VI course detailsDocument7 pagesSemester VI course detailsHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Full download book Biophysical Characterization Of Proteins In Developing Biopharmaceuticals 2 pdfDocument41 pagesFull download book Biophysical Characterization Of Proteins In Developing Biopharmaceuticals 2 pdfjerome.ruiz660100% (12)
- Full Download Genetics Analysis and Principles 6th Edition Brooker Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Genetics Analysis and Principles 6th Edition Brooker Test Bankbeliechopper05srz100% (40)
- Bio 10 Master Study Guide Part 1Document9 pagesBio 10 Master Study Guide Part 1leonor.estimaNo ratings yet
- Practice - DNA, RNA, Gene Expression (Solutions)Document4 pagesPractice - DNA, RNA, Gene Expression (Solutions)SophieNo ratings yet
- Cycloheximide: For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic ProceduresDocument1 pageCycloheximide: For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic ProceduresRochnald PigaiNo ratings yet
- Diagram 4.1 MAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTSDocument2 pagesDiagram 4.1 MAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTSalma bruno garciaNo ratings yet