Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connecting: Making Connections With HSS Members Is Easier Than You Might Think!
Uploaded by
PauloAndresSepulvedaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Connecting: Making Connections With HSS Members Is Easier Than You Might Think!
Uploaded by
PauloAndresSepulvedaCopyright:
Available Formats
Connecting HSS
By Donald R. Sherman
Making connections with HSS members is easier than you might think!
A
frequent comment in the not- ➜ Single angle the HSS Connections Manual) except
so-distant past was, “Tubes ➜ Unstiffened seat for limit states involving the HSS wall.
would make good structural ➜ Double angle These limit states are shear in the HSS
members, but how can good ➜ WT wall adjacent to the weld and punch-
connections be made?” The ➜ Stiffened seat ing shear in the case of single plate
AISC Hollow Structural Sections (HSS) ➜ Through-plate connections.
Connections Manual addressed this ques- These are listed roughly in order of 4. The single plate, through-plate, and
tion in 1997. The HSS Connections Manual cost; however, this may vary depending stiffened seats are the only shear con-
shows a variety of connections and con- on the fabricator’s equipment and expe- nections that can be used with round
tains numerous examples on how they rience. The through-plate would have a HSS columns. In the case of the stiff-
can be designed, along with aids to facili- less expensive placement if similar beams ened seat, the seat plate must be cut to
tate the design. However, there are sev- are framing into opposite sides of the col- conform to the radius of the column.
eral nuances regarding HSS connections umn. Generally, through-plates are not 5. The double angle connection is the
that should be of interest to designers recommended unless there are axial forc- only one that requires coping of the
and detailers. es that have to be transferred through the beam so that the web can be knifed
There are four basic categories of HSS support. Orthogonal through-plates are between the outstanding angle legs
connections, with several types within to be avoided in all cases. during erection. In all the other con-
each category. Some important aspects of 2. In order to maintain rotational flex- nections, the beam is swung into posi-
detailing must be considered in selecting ibility in the connection, transverse tion for bolting, which facilitates time
an appropriate type of HSS connection. welds across the face of the HSS are and safety during erection.
used only in the stiffened seat and 6. For double angle and single angle
Simple Shear Connections across the bottom of the single angle. connections, the HSS column width
1. Shear connections in typical framing The other connections use only verti- should be 12” or greater. This is neces-
systems are made by shop-welding a cal welds with small return. However, sary to accommodate the thickness of
connecting element to an HSS column for single and through-plates, AISC the beam web, the size of the typical 4
or girder and field-bolting to a W- recommends no weld across the thick- or 3.5” angle leg, the size of the fillet
shape beam. If there are HSS beams, ness of the plate. welds, and the corner radii of the HSS.
gussets or end tees can be used to pro- 3. The through-plate is the only connec- Single plate and through-plate con-
vide a field-bolted connection similar tion that is unique to HSS columns. nections can be used with any width
to the web of a W-shape. The types of All others are also used with W-shape of HSS column. The width of the con-
connections are: columns, and design assumptions nection and HSS for the other types
➜ Single plate (shear tab) and criteria are the same (as noted in of connections are determined by the
Simple Shear Connections for HSS
MOST ECONOMICAL MORE EXPENSIVE MOST EXPENSIVE
Single plate connection (shear tab) Double angle shear connection Through-plate shear connection
July 2005 • Modern Steel Construction
Bolted Moment Connections for HSS
End plate moment connection Tee-stub moment connection with shear plate
Through-Plate Moment Connection for HSS
Through-plate moment connection, with a column splice
flange width of the beam. However, varies with the length of the connec- The beam-over-column is the only
allowance must be made to permit tion and will be outside the bolt line one that is efficient and economical.
a fillet weld on the flat of the HSS. If for long connections. The others are expensive, as is the case
flare bevel welds are required for tees 9. The stabilizing angles at the top of with most moment connections.
with flanges that are wider than the seated connections will probably re- Four factors that dictate the critical
HSS, the cost of the connection in- quire field welding since bolting to limit states are important in selecting
creases dramatically. the HSS to accommodate the tilt in the the type of connection:
7. Single plate connections can be used flanges of the W-shape beam permit- a. The magnitude of moment that
in place of through-plate connections ted by mill tolerances is impossible or must be transferred to the HSS.
without impairing the strength of the difficult. b. The magnitude of the moment that
column due to distortion of the wall must be transferred through the
as long as the HSS section is not thin- Moment Connections HSS.
walled (b/t ≤ 238/√√
Fy or D/t ≤ 3300/Fy). 1. There are no standard types of moment c. The magnitude of the axial load in
Through-plates cannot be used in connections between W-shape beams the HSS.
both planes for orthogonal shear con- and HSS columns, and there is little d. The requirements of orthogonal
nections. information in published literature. framing.
8. All of the connections produce a mo- However, the HSS Connections Manual 2. Due to the unique requirements of a
ment on the column that must be describes several possibilities along particular job, a relative cost evalua-
considered in its design. In addition with suggested design procedures. tion is not possible. However, the need
to the eccentricity from the face of the ➜ Beam-over-column for single story for stiffeners and the degree of shop
column to its centroid, there is an ec- construction welding make moment connections
centricity of the shear force assumed ➜ Beam through a column expensive. They can all be detailed to
in the design criteria for each of the ➜ Flange splice plate through the avoid field welding.
types of connections, as noted in the column 3. For W-shape beam-over-column con-
HSS Connections Manual. Usually the ➜ Flange splice plate around the struction, with lateral bracing at the
shear is assumed to act at the weld or column top of the beam, there are column sta-
the bolt line. For single and through- ➜ Direct beam to column connec- bility concerns due to the out-of-plane
plate connections, the eccentricity tions flexibility of the beam web. This pro-
July 2005 • Modern Steel Construction
End Connections for HSS
Welded-tee end connection Slotted HSS/gusset plate end connection
duces a weakness between the brace to make and inspect and are almost spreadsheets are useful design tools.
point and the top of the HSS and al- never needed to develop the required 3. Design rules for K-connections con-
lows sidesway in the column buck- strength. sider some eccentricity where the
ling mode. This must be resisted by 3. Due to shear lag, gussets and end tees intersection of the branch centerlines
stiffening the web or providing lateral cannot efficiently develop more than does not lie on the centerline of the
bracing at the top of the HSS. 50% of the tensile strength of the HSS. main member. If the intersection is
4. When the beam passes through the 4. The bolt layout for end plates should within these limits, secondary mo-
HSS column, web stiffening must be not use corner bolts that lie outside ments in the connection do not have
provided to transfer the column axial the projections of two sides of the HSS. to be considered.
load through the column. When flange Close length tolerances are required for 4. Gapped K-connections are preferred
splice plates pass through the column, fit-up and bolt tightening at both ends. to overlapped connections in order
a column stub is required between the Only fillet or PJP welds should be used to avoid profiling of the overlapping
plates to provide column continuity. to attach the end plate to the HSS. branch, which is especially complex
Flange splice plates around the col- for round HSS.
umn permit the column to be continu- Direct Connections 5. The weld between a sloping branch
ous through the connection. 1. Welded HSS-to-HSS connections are and main member may vary from a
5. Mill tolerances permit variations in typically used in trusses to connect fillet weld to PJP weld depending on
beam depth and flange tilt, which branch members to main members the position in the joint. CJP welds
must be recognized and provided for with welds around the perimeter of should not be specified.
in the details for flange splice plates the branch. The types of connections 6. CJP welds may be necessary in tension
and beams through the column. This are: butt splices, but PJP welds should be
can be accomplished with field shims ➜ T or Y with a single branch perpen- used in compression splices. If CJP
between the splice plates and beam dicular or at an angle to the main welds use backing, it cannot be re-
flanges. member. moved. Without backing, prequalified
6. When flange splice plates are used, ➜ K with two or three branches in a procedures, careful fit-up, and quali-
single plate shear connections should single plane; gapped or overlapping. fied welders must be used to ensure
be used to carry the shear force be- ➜ Cross where the load is transferred adequate root passes.
tween the beam and column and to through the main member to the 7. When rectangular HSS have a branch
facilitate field erection. branch(es). and main member with the same
7. In direct connections, the beam flang- ➜ Butt splices. width, there is a problem making the
es and web are welded directly to the ➜ Other types such as multiplanar side welds due to the gap resulting
HSS wall. The limit states in the HSS and offset branches. from the corner radius of the main
wall will determine the magnitude The new 2005 AISC Specification gives member. This requires either:
of moment that can be transferred, design criteria for rectangular and round ➜ Profiling the transverse wall of the
which will generally be less than the HSS in T, Y, and K connections with axial branch to the contour of the main
full moment capacity of the beam. loads or moments in the branches. T, Y, and member.
gapped K-connections are discussed in the ➜ Using a backing which cannot be
End Connections HSS Connections Manual. AISC does not removed.
1. End connections are primarily used in consider multiplanar connections or offset ➜ Placing a weld bead on the corner
bracing members. They can be made branches. AWS D1.1 should be used. of the main member to act as a
by using gussets, end tees, end plates, 2. The design criteria specify the maxi- backing.
or welding around the perimeter. mum load in the branch based on local 8. Visual inspection is the best way to
2. Welding around the perimeter can de- limit states in the main member, which ensure sound welds, since no access
velop the full strength of the member, are obtained empirically through ex- to the inside and continually changing
but only fillet or PJP welds should tensive testing. Member and connec- angles make radiographic and ultra-
be specified. CJP welds are difficult tion design cannot be separated and sonic inspection difficult and unreli-
July 2005 • Modern Steel Construction
able. Visual inspection should include blind bolt products on page 63 of
the fit-up before welding and compli- this month’s issue.)
ance with the weld procedure, as well ➜ Welded threaded studs.
as examination of the final weld. ➜ Self-tapping screws with thin HSS.
➜ Flow-drilled and cold tapped holes,
Direct Bolting to HSS suitable for repetitive shop operations.
1. It is possible to use mechanical fasten- 2. Fasteners can be used for unusual ap-
ers to make attachments to HSS. plications or atypical field repairs.
➜ Through-bolts, which cannot be
fully tightened due to HSS wall Donald R. Sherman is a Professor Emeritus
flexibility. of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Univer-
➜ Side access holes, which will weak- sity of Wisconsin-Milwaukee.
en the HSS if not reinforced.
➜ Commercially available expanding
blind bolts, which are molly bolts
for steel. (Read about available
Limit States in K-Connections for HSS
July 2005 • Modern Steel Construction
You might also like
- Civil Am Practice Exam: For More Problems Visit Follow Us On FacebookDocument14 pagesCivil Am Practice Exam: For More Problems Visit Follow Us On Facebooknarjis bano67% (3)
- Designing HSS ConnectionsDocument8 pagesDesigning HSS Connectionsjarneberg100% (1)
- Composite Construction Design (ULS Only)Document93 pagesComposite Construction Design (ULS Only)CawanNeroMiranio100% (1)
- BIA - Steel Lintel DesignDocument7 pagesBIA - Steel Lintel Designgpax42No ratings yet
- HSS Connection ManualDocument34 pagesHSS Connection Manualtylerlhsmith100% (15)
- Flexibility Matrix MethodDocument36 pagesFlexibility Matrix MethodAnuja Jape100% (6)
- Aci 211Document38 pagesAci 211Fabian MartnezNo ratings yet
- Steel Design ThesisDocument5 pagesSteel Design Thesiszuhemad0g0n3100% (2)
- Home PlansDocument5 pagesHome PlansRoberto Herrera100% (1)
- WF To HSS Moment Connections R1 - FINAL PDFDocument7 pagesWF To HSS Moment Connections R1 - FINAL PDFrene_angel1No ratings yet
- Article: Wide-Flange Beam To Hss Column Moment ConnectionsDocument3 pagesArticle: Wide-Flange Beam To Hss Column Moment ConnectionsBudi SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Bolted Beam Column ConnectionsDocument16 pagesBolted Beam Column Connectionslael00No ratings yet
- HHS Connection DesignDocument3 pagesHHS Connection Designwii2001No ratings yet
- Simple Steel ConnectionsDocument7 pagesSimple Steel ConnectionsShams Abbas NaqviNo ratings yet
- CHH LVL Portal Frame Design Example - Sept 2008Document92 pagesCHH LVL Portal Frame Design Example - Sept 2008podderickNo ratings yet
- ASDIP Steel - Composite Beam Verification ExampleDocument6 pagesASDIP Steel - Composite Beam Verification ExampleEdwin VizueteNo ratings yet
- Large Moment ExampleDocument5 pagesLarge Moment ExampleAmro Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Condeck HP Composite Decking Product Technical ManualDocument48 pagesCondeck HP Composite Decking Product Technical ManualTamara KnoxNo ratings yet
- Wide-Flange Beam To HSS Column Moment Connections PDFDocument7 pagesWide-Flange Beam To HSS Column Moment Connections PDFing_fernandogalvez2015No ratings yet
- Seismic Behavior & Design of Gusset PlatesDocument41 pagesSeismic Behavior & Design of Gusset PlateswilfredNo ratings yet
- Sherman - Extended Shear TabsDocument148 pagesSherman - Extended Shear TabsRohan KarandeNo ratings yet
- Built Up ColumnsDocument22 pagesBuilt Up Columnsfinn.crown100% (1)
- Peb Division ManualDocument8 pagesPeb Division ManualGeorgeEdwardNo ratings yet
- Design Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Document60 pagesDesign Guide Joist Girder Rev4 Final 11sep06Тодор ИлиескиNo ratings yet
- CFSD - Paper - 2013 AISI CFS Design Manual - 11-05-2014 PDFDocument13 pagesCFSD - Paper - 2013 AISI CFS Design Manual - 11-05-2014 PDFBONDHON-2 APARTMENTNo ratings yet
- Industrial ConstDocument34 pagesIndustrial Constkirti0% (1)
- SD Column Design 2Document8 pagesSD Column Design 2egozenovieNo ratings yet
- Design of Aluminum StructureDocument29 pagesDesign of Aluminum StructurerobcfuNo ratings yet
- SteelDesign PlateGirder Fu NewDocument32 pagesSteelDesign PlateGirder Fu NewFhatony Silvershadows BondanNo ratings yet
- SP6 - 5 - Cold Formed Light Gauge Steel Structures PDFDocument128 pagesSP6 - 5 - Cold Formed Light Gauge Steel Structures PDFAnkur JainNo ratings yet
- 2way Slab & FootingDocument52 pages2way Slab & FootingMuhammad Saqib Abrar0% (1)
- Connections in Steel Structures PDFDocument54 pagesConnections in Steel Structures PDFsmmsajediNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Steel Frame ConstructionDocument24 pagesUnit 5: Steel Frame ConstructionNeeraj Gupta100% (1)
- Truss DesignDocument16 pagesTruss DesignRabindraUpretiNo ratings yet
- Cold Formed Steel Framing System CatalogDocument32 pagesCold Formed Steel Framing System CatalogMujjo SahbNo ratings yet
- Moment Connection HSS Top Plate 9-27-2014Document36 pagesMoment Connection HSS Top Plate 9-27-2014Jesus Rafael Curiel PensoNo ratings yet
- Tech Brochures Truss Facts AusDocument28 pagesTech Brochures Truss Facts AusDee Reyes100% (1)
- C & Zed Purlins Design Manual and Catalogue BC783d01Document31 pagesC & Zed Purlins Design Manual and Catalogue BC783d01GnabBangNo ratings yet
- Light Gauge Steel Profiles Case StudyDocument2 pagesLight Gauge Steel Profiles Case StudyDeepum HalloomanNo ratings yet
- SP6 (6) 1972Document220 pagesSP6 (6) 1972SourabhAdike100% (1)
- Design of Nailed N Glued Plywd GussetsDocument36 pagesDesign of Nailed N Glued Plywd Gussetsboon1961No ratings yet
- 24 Tips For Simplifying Braced Frame ConnectionsDocument2 pages24 Tips For Simplifying Braced Frame Connectionsgpax42100% (1)
- Vulcraft Steel DeckDocument116 pagesVulcraft Steel DeckLuis Adrian SigchaNo ratings yet
- Portal Frame Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesPortal Frame Practice ProblemsBoyzz ChinNo ratings yet
- Steel Ramp Pedestrian Bridge - BOQ A. Steel DeckDocument2 pagesSteel Ramp Pedestrian Bridge - BOQ A. Steel Decksatyanarayana mukkuNo ratings yet
- Strength of Screw Connections Subject To Shear ForceDocument34 pagesStrength of Screw Connections Subject To Shear ForceGuillermo Agustín Yáñez QuezadaNo ratings yet
- AISC-Connections in SteelDocument42 pagesAISC-Connections in SteelAlan PeterNo ratings yet
- Base PlateDocument27 pagesBase PlateSabih Hashim AlzuhairyNo ratings yet
- WF To HSS Moment Connections R1 - FINAL PDFDocument1 pageWF To HSS Moment Connections R1 - FINAL PDFcecastaNo ratings yet
- Bolted Beam Splice: (A) Conventional SpliceDocument11 pagesBolted Beam Splice: (A) Conventional SpliceKimberly Binay-anNo ratings yet
- HSS Column Splice Enews v5Document6 pagesHSS Column Splice Enews v5lavignenoeNo ratings yet
- Beam To HSS Column Moment Connections Using Laser Cut Col 1709090950Document5 pagesBeam To HSS Column Moment Connections Using Laser Cut Col 1709090950kika1614No ratings yet
- Connections-I Bolted ConnectionsDocument21 pagesConnections-I Bolted ConnectionsA.k.MandalNo ratings yet
- HSS Blind Structural Fasteners - May 2021Document7 pagesHSS Blind Structural Fasteners - May 2021David ArndtNo ratings yet
- Top Things To Know About HSS Connections: Seaak On-Line Presentation Wednesday, September 23, 2020 Brad Fletcher, S.EDocument41 pagesTop Things To Know About HSS Connections: Seaak On-Line Presentation Wednesday, September 23, 2020 Brad Fletcher, S.Ehlopez861No ratings yet
- Splicing Bar Resources: Additional Information On Lap Splices Can Be Found HereDocument5 pagesSplicing Bar Resources: Additional Information On Lap Splices Can Be Found HereLiyakhat aliNo ratings yet
- Steel DetailerDocument3 pagesSteel DetailerKooroshNo ratings yet
- Basic ConnectionsDocument116 pagesBasic Connectionsnavin jollyNo ratings yet
- Galvanized Slip-Critical ConnectionsDocument2 pagesGalvanized Slip-Critical Connectionsaams_sNo ratings yet
- PDF Branded HSS SplicesDocument4 pagesPDF Branded HSS SpliceshungNo ratings yet
- Proceeding of 13th Nordic Steel 2015 Construction Conference PDFDocument254 pagesProceeding of 13th Nordic Steel 2015 Construction Conference PDFPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of High Rise Irregular Shape Building With Shear Wall at Different LocationsDocument7 pagesAnalysis of High Rise Irregular Shape Building With Shear Wall at Different LocationsPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Performance-Based Design of RC Coupled Wall High-Rise Buildings With Viscoelastic Coupling DampersDocument235 pagesPerformance-Based Design of RC Coupled Wall High-Rise Buildings With Viscoelastic Coupling DampersPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Dsi Suspa Systems Eta 03 0036 Monostrandsystem enDocument42 pagesDsi Suspa Systems Eta 03 0036 Monostrandsystem enPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Dsi Usa Dywidag Bonded Post Tensioning Systems Us PDFDocument32 pagesDsi Usa Dywidag Bonded Post Tensioning Systems Us PDFPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Design of Neoprene Bearing Pads Dupont PDFDocument25 pagesDesign of Neoprene Bearing Pads Dupont PDFPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Neoprene Bridge Bearings Dupont 1984 PDFDocument16 pagesNeoprene Bridge Bearings Dupont 1984 PDFPauloAndresSepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Parking Shed Quotation RV00Document2 pagesParking Shed Quotation RV00venky 934No ratings yet
- Tameer Consulting Associates: Design of PurlinDocument8 pagesTameer Consulting Associates: Design of PurlinSabrina ImloulNo ratings yet
- S06 - Pushover Analysis Using Midas Civil - Engr - SumanDocument25 pagesS06 - Pushover Analysis Using Midas Civil - Engr - Sumanomar42170No ratings yet
- Formulario Vigas MATLABDocument29 pagesFormulario Vigas MATLABLeonardo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Bill All Forms - JRG 11th Ward RoadDocument60 pagesBill All Forms - JRG 11th Ward Roadsasidharkatari91572No ratings yet
- Dual Plastic Hinge Design Concept For Reducing Higher Mode Effects On Higher Rise Cantilever Wall BuildingsDocument22 pagesDual Plastic Hinge Design Concept For Reducing Higher Mode Effects On Higher Rise Cantilever Wall BuildingsmyantiNo ratings yet
- Ruh8 2021 M-101 Ground Floor Hvac-M - 1 0 1Document1 pageRuh8 2021 M-101 Ground Floor Hvac-M - 1 0 1Ata AtefNo ratings yet
- Const Estimate Made Easy by Engr CajillaDocument26 pagesConst Estimate Made Easy by Engr CajillaKarl BellezaNo ratings yet
- Hornby High Level EquipmentDocument2 pagesHornby High Level EquipmentJohn GasparNo ratings yet
- Clubhouse Structural NotesDocument17 pagesClubhouse Structural NotesCarlo Doragos100% (1)
- Sheet Piling ExampleDocument12 pagesSheet Piling Exampleshravan38No ratings yet
- Cold Formed Steel Joints and Structures - A ReviewDocument14 pagesCold Formed Steel Joints and Structures - A ReviewGabriel MacedoNo ratings yet
- Example of Shear Wall Design To Ec2: June 2020Document33 pagesExample of Shear Wall Design To Ec2: June 2020laijunNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing Design With Example and Types of Combined FootingDocument2 pagesCombined Footing Design With Example and Types of Combined FootingNick GeneseNo ratings yet
- Extradosed Bridge - Technical AspectsDocument3 pagesExtradosed Bridge - Technical AspectsVenkat Palli100% (1)
- Lopez PrefiDocument5 pagesLopez PrefiCarl Adrienne LopezNo ratings yet
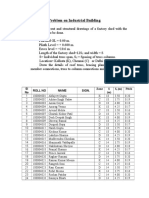
- Problem On Industrial Building: SL No Roll No Name Sign. Zone S (M) S (M) PitchDocument2 pagesProblem On Industrial Building: SL No Roll No Name Sign. Zone S (M) S (M) PitchAnshul KaushikNo ratings yet
- StaircaseDocument21 pagesStaircaseThien MaiNo ratings yet
- Fixed ArchDocument1 pageFixed ArchShah KhanNo ratings yet
- 02 PEIKKO Anchor BoltsDocument16 pages02 PEIKKO Anchor Boltsmixi1978No ratings yet
- Roof and Roofing Materials: Engr. Lito I. MauroDocument32 pagesRoof and Roofing Materials: Engr. Lito I. MauroGerald PrimaveraNo ratings yet
- Seepco-2020-Lpgrc-Cv-Dwg-005 Structural Plan Details of Management Villa-Revision-3 (2ND Part) - 18.08.2023Document18 pagesSeepco-2020-Lpgrc-Cv-Dwg-005 Structural Plan Details of Management Villa-Revision-3 (2ND Part) - 18.08.2023Ajay Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Construction Development Corp: Item Description Unit QTY Unit Cost AmountDocument4 pagesConstruction Development Corp: Item Description Unit QTY Unit Cost AmountMark Nathan Sta MonicaNo ratings yet
- Centenial Bridge, Panama - Medellin 10-18-17 v04Document126 pagesCentenial Bridge, Panama - Medellin 10-18-17 v04Miguel MasmelaNo ratings yet
- PERVIOUS ConcreteDocument5 pagesPERVIOUS Concreteadvin kujurNo ratings yet