Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry Theory
Uploaded by
Shanmugam Udhaya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageOriginal Title
topic_12_exercise_1_-__bronsted-lowry_theory.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry Theory
Uploaded by
Shanmugam UdhayaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
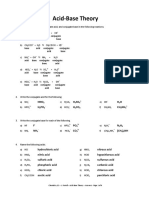
Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry theory
1. State whether the following species can behave as an acid, as a base, or both:
a) NH4+
b) NH3
c) H3O+
d) HClO4
e) CO32-
f) NO3-
g) CH3CH2OH
h) CH3COOH
i) HSO4-
j) HNO3
k) HCl
2. In each of the following reactants, one of the reactants acts as an acid. Identify it:
a) H2O(l) + NH3(aq) == NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
b) CH3COOH(aq) + HClO4(aq) == CH3COOH2+(aq) + ClO4-(aq)
c) HCO3-(aq) + HSO4-(aq) == H2O(l) + CO2(g) + SO42-(aq)
d) H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) == 2H2O(l)
3. Identify the acid-base conjugate pairs in the following reactions:
a) HCO3-(aq) + H2O(l) == CO32-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
b) HCO3-(aq) + H3O+(aq) == CO2(g) + H2O(l) + H2O(l)
c) H2SO4(aq) + HNO3(aq) == HSO4-(aq) + NO2+(aq) + H2O(l)
d) HSO4-(aq) + OH-(aq) == SO42-(aq) + H2O(l)
You might also like
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01Document1 pageBronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01Peshala NishadiNo ratings yet
- ATAR Chemistry Year 12 Asc 2017 Sols (WA)Document12 pagesATAR Chemistry Year 12 Asc 2017 Sols (WA)Raghav GanaNo ratings yet
- Methodist College Kuala Lumpur Assignment 1 Unit 4: Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument1 pageMethodist College Kuala Lumpur Assignment 1 Unit 4: Acid-Base EquilibriaskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Review QuestionsDocument59 pagesChapter 14 Review QuestionsKaiJie HanNo ratings yet
- Ques1 67abe1mcDocument8 pagesQues1 67abe1mcKerimberdiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet - Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet - Redox Reactionsaryaaayush2006No ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Review W KeyDocument19 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Review W KeyJosephine Charles HoNo ratings yet
- 2 Co (G) 2 CO (G) + O (G) H 514 Kj/molDocument3 pages2 Co (G) 2 CO (G) + O (G) H 514 Kj/molShenna Mae Bumanlag DecoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document51 pagesChapter 14Jenny Derne100% (1)
- Acid-Base Theory Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesAcid-Base Theory Key ConceptsPasha TanNo ratings yet
- SAT ABS Bronsted LowryDocument7 pagesSAT ABS Bronsted LowryCatherine Galano PradoNo ratings yet
- Worksheets RRDocument4 pagesWorksheets RRHrithik JerathNo ratings yet
- WORK SHEET - Ionic & Acid-Base ReactionsDocument5 pagesWORK SHEET - Ionic & Acid-Base ReactionsAndrej ZafirovikjNo ratings yet
- 12e1 PDFDocument5 pages12e1 PDFwastequestNo ratings yet
- Assessing Acids, Bases, Salts and Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesAssessing Acids, Bases, Salts and Chemical EquilibriumJuju ZenemijNo ratings yet
- AP Ch. 14-15 Acids & Bases Review AnswersDocument44 pagesAP Ch. 14-15 Acids & Bases Review AnswershksonnganNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument6 pagesChembighneshrath1No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Acids and Bases v2Document42 pagesLecture 6 Acids and Bases v2Yahmeela SernaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Theory AnswersDocument3 pagesAcid Base Theory Answersvinaybharadwajbs0% (1)
- CHEM2-LEC4 Acid Base EquilibriaDocument40 pagesCHEM2-LEC4 Acid Base EquilibriaAlphonse SambranoNo ratings yet
- Obținerea Substanțelor Organice: 1. AlcaniDocument9 pagesObținerea Substanțelor Organice: 1. AlcaniAna-Maria GîlcaNo ratings yet
- Chemactivity 42 KeyDocument1 pageChemactivity 42 KeyQueenQiNo ratings yet
- Analytic Chem Mitdterm QDocument14 pagesAnalytic Chem Mitdterm Qayshhaa.kNo ratings yet
- Conjugate PairsDocument2 pagesConjugate Pairssaowanee toonchueNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry - Chapter11-20Document29 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry - Chapter11-20saowanee toonchueNo ratings yet
- 2015 BiotechDocument74 pages2015 BiotechRosa DemlieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Acids and Bases HWDocument9 pagesChapter 17 Acids and Bases HWAlejo CardoNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- 16.E__Acid___Base_Equilibria__Exercises____Chemistry_LibreTexts.pdfDocument2 pages16.E__Acid___Base_Equilibria__Exercises____Chemistry_LibreTexts.pdfgarciacLoNo ratings yet
- Bronsted Lowery Acid and Base Q&aDocument2 pagesBronsted Lowery Acid and Base Q&asapphireNo ratings yet
- 1c Worksheet Acids Bases With AnswersDocument4 pages1c Worksheet Acids Bases With Answersapi-369690183100% (1)
- NS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesDocument5 pagesNS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesWindere Marie NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria and pH CalculationsDocument124 pagesIonic Equilibria and pH CalculationsTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Acids - Bases (AP MC)Document7 pagesAcids - Bases (AP MC)Habiba AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibrium Slides - StudentDocument74 pagesAcid-Base Equilibrium Slides - StudenteiwkNo ratings yet
- Balancing Redox Reactions by Ion-Electron MethodDocument2 pagesBalancing Redox Reactions by Ion-Electron Methodpeter_br3adNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Key Theories and ConceptsDocument120 pagesAcids and Bases: Key Theories and ConceptsAishaizlNo ratings yet
- Acidicity Basicity & H - Bonding Tautomerism (Q.B.) 12thDocument16 pagesAcidicity Basicity & H - Bonding Tautomerism (Q.B.) 12thAritra Lahiri100% (1)
- Silberberg 3 e ISMChapter 18Document35 pagesSilberberg 3 e ISMChapter 18henry aguilaNo ratings yet
- 51 HMW Solutions Ch14Document43 pages51 HMW Solutions Ch14Cbn NoonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Problems SolutionsDocument20 pagesAcid Base Problems SolutionsldfwykbhnuklerNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Week 4Document2 pagesExtra Practice Week 4ShawnNo ratings yet
- The Arrhenius Theory (Section 9.1) 9.1: Solutions To Selected Problems in Chap. 9 & 10Document20 pagesThe Arrhenius Theory (Section 9.1) 9.1: Solutions To Selected Problems in Chap. 9 & 10Riaz LourencoNo ratings yet
- IONIC EQUATIONS AnswersDocument1 pageIONIC EQUATIONS AnswersAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquationsDocument3 pagesChemical EquationskiranNo ratings yet
- APChemDocument8 pagesAPChemMacie CareyNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and Basessmdali14No ratings yet
- Acid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Document24 pagesAcid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Sara MolinaroNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Pairs Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesConjugate Pairs Practice QuestionsTutor AcademyNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Significant Figures and LogarithmsDocument15 pagesExercises: Significant Figures and LogarithmsSarah ChoiNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry QuizDocument4 pagesHonors Chemistry QuizmariaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesAcids and Bases: Multiple ChoiceDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - Chapter 4Document6 pagesSample Questions - Chapter 4Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesAssignment ElectrochemistryAnas AhmadNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: CHEM 025, Section X, Fall 201X - Anthony DutoiDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: CHEM 025, Section X, Fall 201X - Anthony DutoiJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bukit Timah Nature ReserveDocument1 pageBukit Timah Nature ReserveShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Treaty of Versailles and Policy of AppeasementDocument4 pagesTreaty of Versailles and Policy of AppeasementShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 4 - Titrations and IndicatorsDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 4 - Titrations and IndicatorsShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Fortnite - WeaponsDocument6 pagesFortnite - WeaponsShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- High Success AdvancedDocument4 pagesHigh Success AdvancedShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- High Success AdvancedDocument4 pagesHigh Success AdvancedShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- High Success AdvancedDocument4 pagesHigh Success AdvancedShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- High Success AdvancedDocument4 pagesHigh Success AdvancedShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Exercise 3 - Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageTopic 2 Exercise 3 - Ideal Gas EquationShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Exercise 3 - Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageTopic 2 Exercise 3 - Ideal Gas EquationShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet