Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Me2252 MT1 Unit1 PDF
Uploaded by
Kamalakkannan KrishnanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Me2252 MT1 Unit1 PDF
Uploaded by
Kamalakkannan KrishnanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.Vidyarthiplus.
com
QUESTION BANK
DEPARTMENT: MECH SEMESTER: IV
SUBJECT CODE / NAME: ME 2252 / MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY – II
UNIT I – THEORY OF METAL CUTTING
Part A
1. List the various metal removal processes? ( AU Apr 2011,Dec12)
a. Non cutting process or chipless process.
b. Cutting process or Chip process
2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? ( AU Apr 2011, Dec11)
The material of the work piece is stressed beyond its yield point under
compressive force .This cause the material to deform plastically and
shear off.
3. What is tool wear? ( AU Apr 2011)
During machining the toll is subjected to three important factors such as forces,
temperature and sliding action due to relative motion between tool and work piece. Due
to these factors tool will undergo wear.
4. Mention the cutting fluids? ( AU Apr 2012)
Two basic types are
(i) Water based cutting fluids
(ii) Straight or heat oil based cutting fluids
5. Draw the nomenclature of cutting tool geometry? ( AU Apr 2013,Dec 11)
6. Compare orthogonal and oblique cutting? ( AU Dec 2012, Apr 2010)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 1
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
7. Define tool life. www.Vidyarthiplus.com( AU Dec 2010) ( AU Apr 2013)
Tool life is defined as the time elapsed between two consecutive tool resharpening.
During this period the toll serves effectively and efficiently.
8. What are the objectives and functions of cutting fluids?( AU Dec 2010,Apr 13)
(i) It is used to cool the cutting tool and work piece
(ii) It improves surface finish
(iii) It protects finished surface from corrosion
(iv) It washes away chips from tool
9. Briefly explain the effect of rake angle during cutting? (AU Dec 2010,Apr 09)
Effect of back rack angle:
For softer material greater angle should be given
For harder material smaller angle is enough
Effect of Side rack angle:
Curling of chip depends on this angle.
10. What are the factors responsible for builtup edge in cutting tools?( AU Dec
2009,Apr 13)
(i) Low cutting speed
(ii) Small rake angle
(iii)Coarse feed
(iv) Strong adhesion between chip and tool face.
11. List out the essential characteristics of a cutting fluid. ( AU Dec 2009,Apr 12)
(i) It should have good lubricating properties
(ii)High heat absorbing capacity
(iii) High flash point
(iv) It should be odorless
12. Name the various cutting tool materials. ( AU Dec 2008,Apr 09).
(i) Carbon tool steel
(ii) High speed steel
(iii) Cemented carbides
(iv) Ceramics
(v) Diamonds
13. Give two examples of orthogonal cutting. ( AU Dec 2007)
(i) Turning (ii) Facing (iii) Thread cutting (iv) Parting off
14. What are the four important characteristics of materials used for
cutting tools? ( AU Dec 2007)
(i)Hot hardness (ii) Wear resistance (iii High thermal conductivity
(iv) Easy to grind and sharpen (v) Resistance to thermal shock
15. What is the function of chip breakers? ( AU Dec 2006)
The chip breakers are used to break the chips into small pieces for removal , safety and
to prevent both the machine and work damage
16. Name the factors that contribute to poor surface finish in cutting.( AU Dec 2006)
(i) Cutting speed
(ii) Feed
(iii) Depth of cut
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 2
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Part B
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
1. Explain various cutting tool materials? ( AU Apr 2011,Dec 12)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 3
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 4
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
2. In an orthogonal cutting operation on a workpiece of width 2.5mm, the uncut chip
thickness was 0.25mm and the tool rake angle was zero degree. It was observed that
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
the chip thickness was 1.25mm.The cutting force was measured to be 900N and the
thrust force was found to be 810 N. ( AU Dec 2013,Apr 12)
(a) Find the shear angle.
(b) If the coefficient of friction between the chip and the tool, was 0.5, what is the
machining constant Cm
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 5
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
3. What is a chip Describe the different types of chips produced during metal machining
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
with neat sketches. ( AU Dec 2010) ( AU Apr 2010) ( AU Dec 2006)
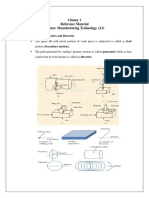
TYPES OF CHIPS
In a metal cutting operation is carried out in machine shop. Chips are separated from
the workpiece to impart the required size and shape to the workpiece. The type of chips
edge formed is basically a function of the work material and cutting conditions. The
chips that are formed during metal cutting operations can be classified into four types:
1. Discontinuous or segmental chips
2. Continuous chips
3. Continuous chips with built-up edge.
4. Non homogenous chips
The above three common types of chips are shown in
Continuous chips: It shows continuous chips coming out during machining in machine
shop. These types of chips are obtained while machining ductile material such as mild
steel and copper. A continuous chip comes from the cutting edge of a cutting tool as a
single one piece, and it will remain as one piece unless purposely broken for safety or
for convenience in handling. Formation of very lengthy chip is hazardous to the
machining process and the machine operators. It may wrap up on the cutting tool, work
piece and interrupt in the cutting operation. Thus, it becomes necessary to deform or
break long continuous chips into small pieces. It is done by using chip breakers. Chip
breaker can be an integral part of the tool design or a separate device.
Discontinuous chips: It shows discontinuous chips coming out during machining in
machine shop. In this type, the chip is produced in the form of small pieces. These types
of chips are obtained while machining brittle material like cast iron, brass and bronze.
Fairly good surface finish is obtained and tool life is increased with this type of chips.
Chips With Built up edge: It shows continuous chip with built-up edge. During cutting
operation, the temperature rises and as the hot chip passes over s the face of the tool,
alloying and welding action may take place due to high pressure, which results in the
formation of weak bonds in microstructure and weakened particles might pullout.
Owing to high heat and pressure generated, these particles get welded to the cutting tip
of the tool and form a false cutting edge. This is known as built-up edge Non
homogenous chips are developed during machining highly hard alloys like titanium
which suffers a marked decrease in yield strength with increase in temperature
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 6
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
4. Mention the functions of cutting fluids. ( AU Dec 2010,Apr 11)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
During any machining or metal cutting process, enough heat is evolved in cutting zone.
To remove this heat from cutting zone, soluble oils are used as cutting fluid during
machining. Emulsions (also known as soluble oil) cool the work-piece and tool and thus
relieved them from overheat. Air circulation is required so as to remove the heat by
evaporation. The remaining oil forms a protecting layer over the machined work piece
and save it from rust and corrosion. Such coolants decrease adhesion between chip and
tool, provides lower friction and wear and a smaller built up edge. They remove chips
and hence help in keeping freshly machined surface bright. They also protect the surface
from corrosion. They decrease wear and tear of tool and hence increase tool life. They
improve machinability and reduce machining forces.
Chemical cutting fluids possess a good flushing action and are non-corrosive
and nonclogging. Since they are non-clogging, they are widely used for grinding and
sawing. The most efficient method of applying cutting fluids is to use a pump, tray and
reservoir, to give a slow continuous stream over the cutting action. Chemical cutting
fluids are replacing straight and emulsifiable cutting oils for many applications. If
chemical concentrates are mixed in correct proportion with deionized water, chemical
cutting fluids provide longer life at less cost than oil base cutting fluids. Other coolants
and cutting fluids are cutting wax and kerosene. Cutting fluids may also be used on
aluminium, aluminium alloys and brass for machining operations of low severity. It may
be used as a coolant and for removing chips when machining cast iron.
Some commonly used machining materials require following cutting fluids:
Steel Soluble oil Straight, Water base mainly grinding
Aluminium and alloys Paraffin Dry
Cast iron Dry
Brass, Copper and Bronze Dry
Functions or Uses of Coolants or Cutting Fluids
The important functions of cutting fluids are given as under.
(i) Cutting fluid washes away the chips and hence keeps the cutting region free.
(ii) It helps in keeping freshly machined surface bright by giving a protective coating
against atmospheric, oxygen and thus protects the finished surface from corrosion.
(iii) It decreases wear and tear of cutting tool and hence increases tool life.
(iv) It improves machinability and reduce power requirements
(v) It prevents expansion of work pieces.
(vi) It cools the tool and work piece and remove the generated heat from the cutting
zone.
(vii) It decreases adhesion between chip and tool; provide lower friction and wear, and
a smaller built-up edge.
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 7
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
5. Describe the mechanism of metal cutting? ( AU Dec 2010,Apr 13)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 8
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
6. List the various tool materials used in industry. State the optimum temperature of each of
the tool materials. www.Vidyarthiplus.com ( AU Dec 2010)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 9
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
7. The Taylor tool life equation for machining C-40 steel with a HSS cutting tool at a feed of
0.2mm/min and a depth of cut of 2mm is given by VTn= C, Where n and C are constants.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
The following V and T observations have been noted( AU Dec 2010) ( AU Dec 2006)
V , m/min 25 35
T , min 90 20
Calculate
(1) n and C
(2) Hence recommend the cutting speed for a desired tool life of 60min.
8. State the parameters that influence the life of tool and discuss?( AU Apr 2010)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 10
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 11
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 12
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
9. What is meant by orthogonal cutting and oblique cutting? ( AU Apr 2010)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 13
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
10. Explain “merchant force circle” along with assumptions.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com ( AU Apr 2010)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 14
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 15
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
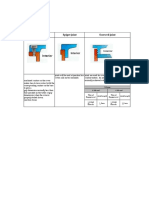
11. Explain the geometry of a single point cutting tool with suitable sketches? ( AU
Dec 2009)( AU Dec 2010) www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 16
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 17
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
12. Explain the basic actions of cutting fluids ( AU Dec 2009 , Apr 10)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 18
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 19
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
13. Describe an expression for the determination of shear angle in
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Orthogonal metal cutting . ( AU Dec 2007)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 20
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 21
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
14. What are the standard angles of cutting tool? Illustrate with an example.( AU Dec
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
2007)
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 22
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
M.P.KEDARNATH / Asst Prof - Mechanical 23
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
You might also like
- Unit III - MachiningDocument141 pagesUnit III - MachiningmonaNo ratings yet
- MFT-2 .Two Marks With KeyDocument13 pagesMFT-2 .Two Marks With KeySujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Key 2Document22 pagesKey 2Jury.rahulNo ratings yet
- Me8451 QB2Document32 pagesMe8451 QB2Jayaram R S [MECH]No ratings yet
- Unit 4 New MPDocument31 pagesUnit 4 New MPPriya DharshniNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractPyae PhyoaungNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Single Point Cutting ToolDocument46 pagesDesign and Analysis of Single Point Cutting ToolkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- ME6023 Manufacturing Technology - I Part - A Unit I: 1. State Any Four Types of Patterns. (May 2006)Document12 pagesME6023 Manufacturing Technology - I Part - A Unit I: 1. State Any Four Types of Patterns. (May 2006)Karthik SubramaniNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Forging Processes With Their Defects: Mahendra G. Rathi, Nilesh A. JakhadeDocument7 pagesAn Overview of Forging Processes With Their Defects: Mahendra G. Rathi, Nilesh A. JakhadeNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- III Sem Me6302 TMDocument13 pagesIII Sem Me6302 TMKalkidan DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document45 pagesChapter 1idris_ali_7No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TO 5Document49 pagesChapter 1 TO 5nagisafurukawa122333No ratings yet
- Development of A High Speed Abrasive Cutting Machine: Journal of Engineering Research January 2010Document9 pagesDevelopment of A High Speed Abrasive Cutting Machine: Journal of Engineering Research January 2010Basavaraj G LNo ratings yet
- CAT II - EMMU 7241 - Machine Tool Vibrations and Cutting Dynamics-Marking SchemeDocument14 pagesCAT II - EMMU 7241 - Machine Tool Vibrations and Cutting Dynamics-Marking SchemeCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 7Document4 pagesWorksheet No. 7Ben Jericho T. BayatônNo ratings yet
- Abebe BeyeneDocument21 pagesAbebe Beyenedawit solomonNo ratings yet
- ToolbitDocument7 pagesToolbitVon Allen DayoNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Four Way Hacksaw MachineDocument22 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Four Way Hacksaw MachineDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Sience Laboratory Technology (Assignment)Document3 pagesDepartment of Sience Laboratory Technology (Assignment)abdulmajeedabdussalam09No ratings yet
- Cap 1Document9 pagesCap 1irinuca12No ratings yet
- Ucmp 2 Mark With AnswerDocument17 pagesUcmp 2 Mark With AnsweranithayesurajNo ratings yet
- StudyoncuttingtoollifeDocument8 pagesStudyoncuttingtoollifeArun NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Sheet Production TechnologyDocument23 pagesSheet Production TechnologyOmar AlyNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Variation in Cutting Speed On Wear Rate of Uncoated and Coated Carbide Cutting ToolsDocument8 pagesThe Influence of Variation in Cutting Speed On Wear Rate of Uncoated and Coated Carbide Cutting ToolsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 10.short Questions and AnswersDocument41 pages10.short Questions and Answersananda narayanan100% (1)
- Research Paper On Metal Cutting PDFDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Metal Cutting PDFcan3z5gx100% (1)
- Me6402 2M Rejinpaul ViDocument30 pagesMe6402 2M Rejinpaul ViBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Study On Cutting Tool Life: August 2013Document8 pagesStudy On Cutting Tool Life: August 2013Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology I 2 MarksDocument69 pagesManufacturing Technology I 2 MarksVenkatesh VenkatNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 - MAE 3344 - Fall 2017Document4 pagesExam 2 - MAE 3344 - Fall 2017Eseosa MusaNo ratings yet
- Production Technology SyllabusDocument9 pagesProduction Technology SyllabusPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Sheet Metal Cutting MachineDocument21 pagesPneumatic Sheet Metal Cutting MachineMAHAMMADRAFEEQ MANVINo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal CuttingDocument3 pagesTheory of Metal CuttingGeorge Oliver100% (1)
- MT II - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument40 pagesMT II - 2 Marks With AnswersArulNo ratings yet
- D.E.I. Faculty of Engineering MEM-103: M P - IDocument6 pagesD.E.I. Faculty of Engineering MEM-103: M P - Ikapil sharmaNo ratings yet
- Austenite Stainless SteelDocument13 pagesAustenite Stainless SteelYuvaraj RajuNo ratings yet
- Machining by CuttingDocument4 pagesMachining by CuttingSiddhi JainNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis of Micro Drill BitDocument4 pagesModelling and Analysis of Micro Drill BitMr. S. Thiyagu Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument48 pagesQuestion Banksanjai kumarNo ratings yet
- Dawit SolomonDocument24 pagesDawit Solomondawit solomonNo ratings yet
- Pnuematic Riveting MachineDocument49 pagesPnuematic Riveting MachineMAHAMMADRAFEEQ MANVINo ratings yet
- Module-3: Cutting Tool Materials, Geometry and Surface FinishDocument18 pagesModule-3: Cutting Tool Materials, Geometry and Surface FinishYashas KattemaneNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process - Module4.0Document18 pagesManufacturing Process - Module4.0Fiza KamaNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting TechnologyDocument22 pagesMetal Cutting Technologydema_diasNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigations and Multi-Objective Optimization of Friction Drilling Process On AISI 1015Document14 pagesExperimental Investigations and Multi-Objective Optimization of Friction Drilling Process On AISI 1015Raghav RaoNo ratings yet
- Reference Material Cluster 1 2 3Document40 pagesReference Material Cluster 1 2 3VENKATA RAGHAVENDRA SAI KUMAR SAMBHARANo ratings yet
- IPE-4102-Machine Tool SessionalDocument29 pagesIPE-4102-Machine Tool SessionalNafiz AlamNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument2 pagesMaterialsPebo GreenNo ratings yet
- 171226-An Overview of Forging Processes With Their DefectsDocument8 pages171226-An Overview of Forging Processes With Their DefectsNguyen Hoang DungNo ratings yet
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument10 pagesMapúa Institute of Technology: School of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringJoseph ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology NotesDocument97 pagesManufacturing Technology Notesswap1983No ratings yet
- WORKSHOP REPORT Sheet MetalworkingDocument10 pagesWORKSHOP REPORT Sheet MetalworkingYuthinee100% (1)
- MFT 2 TWO Marks With AnswersDocument28 pagesMFT 2 TWO Marks With AnswersThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Metal Swarf: Definition of ChippsDocument10 pagesMetal Swarf: Definition of ChippsabenezerNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cutting ToolsDocument36 pagesTheory of Cutting ToolsimranNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Sheet Metal Cutting Machine Final (PDF - Io)Document15 pagesPneumatic Sheet Metal Cutting Machine Final (PDF - Io)sukhdeep0% (1)
- Me1008 Unit 3 Theory of Metal CuttingDocument39 pagesMe1008 Unit 3 Theory of Metal CuttingPruthviraj rathodNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding of 2XXX Aluminum Alloys including Al-Li AlloysFrom EverandFriction Stir Welding of 2XXX Aluminum Alloys including Al-Li AlloysNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Notes On Production CycleDocument2 pages5.2 Notes On Production CyclesaisenthNo ratings yet
- Application of Low Cost Inhibitors To Reduce Rate of Corrosion in Rail Passenger CoachesDocument9 pagesApplication of Low Cost Inhibitors To Reduce Rate of Corrosion in Rail Passenger CoachessaisenthNo ratings yet
- 5.6 Notes On Material Requirements PlanningDocument2 pages5.6 Notes On Material Requirements PlanningsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Vision Mission UniversityDocument2 pagesVision Mission UniversitysaisenthNo ratings yet
- 12 WorkstationdesignDocument31 pages12 WorkstationdesignsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Lean SylDocument2 pagesLean SylsaisenthNo ratings yet
- 12 WorkstationdesignDocument31 pages12 WorkstationdesignsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellDocument12 pagesFuel CellsaisenthNo ratings yet
- 2010 Reg Automobile SylDocument112 pages2010 Reg Automobile SylsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Asper School of Business 9.613 Using Information Technology Part-Time MBA, December 2001 Instructor: Bob TravicaDocument13 pagesAsper School of Business 9.613 Using Information Technology Part-Time MBA, December 2001 Instructor: Bob TravicasaisenthNo ratings yet
- Electrical Notes - PvsDocument84 pagesElectrical Notes - PvssaisenthNo ratings yet
- Cellular Manufacturing Systems - Lecture Series 8: Ie 3265 Pom R. R. Lindeke, PHD Spring 2005Document42 pagesCellular Manufacturing Systems - Lecture Series 8: Ie 3265 Pom R. R. Lindeke, PHD Spring 2005saisenthNo ratings yet
- GasoholDocument11 pagesGasoholsaisenthNo ratings yet
- CABINS: A Framework of Knowledge Acquisition and Iterative Revision For Schedule Improvement and Reactive RepairDocument31 pagesCABINS: A Framework of Knowledge Acquisition and Iterative Revision For Schedule Improvement and Reactive RepairsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines: By, Mohammad Arish Lodi Shashank ZodapeDocument10 pagesHydraulic Machines: By, Mohammad Arish Lodi Shashank ZodapesaisenthNo ratings yet
- Boiler ManufacturingDocument18 pagesBoiler ManufacturingsaisenthNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing A&B: B.E./ B.Tech Degree Examination, Sep - 2013Document2 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing A&B: B.E./ B.Tech Degree Examination, Sep - 2013saisenthNo ratings yet
- Capp 2Document56 pagesCapp 2Sikander GirgoukarNo ratings yet
- Broaching Production ProcessDocument18 pagesBroaching Production ProcessRogério Dogliotti de CamposNo ratings yet
- Index: Lathe MachineDocument33 pagesIndex: Lathe MachinedakshNo ratings yet
- Mil DTL 1222jDocument51 pagesMil DTL 1222jPAOLO GIANNELLINo ratings yet
- P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya: San Engineering and Locomotive Co & Ltd. MysoreDocument28 pagesP.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya: San Engineering and Locomotive Co & Ltd. Mysoreabdulzubair100% (1)
- Woodworking Plans - Workbench - Popular Mechanics - Hard MapleDocument7 pagesWoodworking Plans - Workbench - Popular Mechanics - Hard Maplepandearroz100% (2)
- Shaper Mechanism Its One of The Applications of The Quick Return Mechanism Its Converts The Rotating Motion (Input) To Reciprocating Motion (Out Put)Document4 pagesShaper Mechanism Its One of The Applications of The Quick Return Mechanism Its Converts The Rotating Motion (Input) To Reciprocating Motion (Out Put)Shady YehiaNo ratings yet
- Gestamp-Experience of VANADIS 4Document38 pagesGestamp-Experience of VANADIS 4k4r0_oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Bench LatheDocument55 pagesOperation Manual: Bench LatheJhon SantosNo ratings yet
- End Mill Basic TrainingDocument22 pagesEnd Mill Basic TrainingChiao YunNo ratings yet
- Axminster Lathe ManualDocument24 pagesAxminster Lathe ManualGary SmithNo ratings yet
- YCM500AW Operatin Manual - InglésDocument107 pagesYCM500AW Operatin Manual - InglésConociendoANuestraGenteNo ratings yet
- Ball Mill: Experiment No.-5Document2 pagesBall Mill: Experiment No.-5SagarNo ratings yet
- Flanged Joint Spigot Joint Screwed Joint: Junction BoxesDocument2 pagesFlanged Joint Spigot Joint Screwed Joint: Junction BoxesAdel FawziNo ratings yet
- PSL-3 Seal KitDocument12 pagesPSL-3 Seal KitbrunosamaeianNo ratings yet
- Insert MoldingDocument27 pagesInsert MoldingYuvaraj Yuvaraj100% (1)
- Lesson Plan DJFPTDocument5 pagesLesson Plan DJFPTarumugam_rNo ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixtures DesignDocument9 pagesJigs and Fixtures Designazizmaarof100% (4)
- Specification For Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts For Bolts For High-Pressure or High-Temperature Service, or BothDocument18 pagesSpecification For Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts For Bolts For High-Pressure or High-Temperature Service, or BothPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Gording ConnectionDocument9 pagesGording ConnectionRicho MSNo ratings yet
- 8th To Jib Interface On Hiab 1055Document9 pages8th To Jib Interface On Hiab 1055Matt SmithNo ratings yet
- 2012 Rcs C Spec Com MinutesDocument53 pages2012 Rcs C Spec Com MinutesMo ZeroNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir WeldingDocument4 pagesFriction Stir WeldingarianaseriNo ratings yet
- WPS PQR As Per IsDocument3 pagesWPS PQR As Per Istarun kaushalNo ratings yet
- Air Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Document310 pagesAir Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Michael SmallNo ratings yet
- Mr. A. Panchariya Dept. of Mech. Engg. MNIT JaipurDocument143 pagesMr. A. Panchariya Dept. of Mech. Engg. MNIT JaipurAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Austlift Catalogue EYE BOLTDocument10 pagesAustlift Catalogue EYE BOLTdoshi78No ratings yet
- Brother BAS-311H PDFDocument80 pagesBrother BAS-311H PDFaliahad84No ratings yet
- Elements of Jigs and FixturesDocument9 pagesElements of Jigs and FixtureskhuljascribdNo ratings yet
- RB A225 Approval Rev 1 - 12 12Document1 pageRB A225 Approval Rev 1 - 12 12TariqMahmoodNo ratings yet
- System of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and Gauging PDFDocument32 pagesSystem of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and Gauging PDFPraveen MohapatraNo ratings yet