Professional Documents
Culture Documents
121IB Ws w2 Digestion
121IB Ws w2 Digestion
Uploaded by
tuncaseda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesThe document provides information about the digestive system, including the organs involved and their functions. It includes a matching exercise that pairs digestive organs with their functions. There is also a diagram of the digestive system to label with the organ names and the stage of digestion each is involved in - mechanical, chemical, absorption, or elimination.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about the digestive system, including the organs involved and their functions. It includes a matching exercise that pairs digestive organs with their functions. There is also a diagram of the digestive system to label with the organ names and the stage of digestion each is involved in - mechanical, chemical, absorption, or elimination.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pages121IB Ws w2 Digestion
121IB Ws w2 Digestion
Uploaded by
tuncasedaThe document provides information about the digestive system, including the organs involved and their functions. It includes a matching exercise that pairs digestive organs with their functions. There is also a diagram of the digestive system to label with the organ names and the stage of digestion each is involved in - mechanical, chemical, absorption, or elimination.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
LESSON, TOPIC: Biology, Digestion DATE:20.09.
2010
SOYADI, ADI:
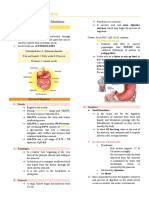
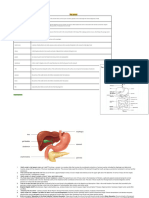
1) Match one box from the left column with one box from the right column
DIGESTIVE ORGAN FUNCTION
Produces an alkaline substance which is secreted into
the duodenum to neutralise the stomach acid.
a.SMALL INTESTINE
b. MOUTH Storage area for feces at the end of the large
intestine
There is a sphincter surrounding the anus, the hole
through which faeces passes on defaecation.
c.LARGE INTESTINE Thicker in diameter than the small intestine
Water is absorbed from the remains of undigested
food to make feces
Bacteria produce Vitamin B
d.STOMACH Production of Bile – It produces bile which is stored
temporarily in the gall bladder, and then is secreted
into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine)
for the emulsification of lipids. Bile is also alkaline and
aids in the neutralisation of stomach acid in the small
intestine.
Sugar Conversion - After a meal, excess simple sugars
in the bloodstream pass to the liver and are converted
and stored as glycogen. However, between meals, the
glycogen is converted back to simple sugars and
released into the bloodstream. In this way, the blood
sugar remains constant.
e.PHARYNX Tube between mouth and stomach
A flap called the epiglottis closes over the top of the
windpipe or trachea when swallowing, so that food does
not enter the respiratory tract
f.OESOPHAGUS Ingests food
Teeth physically break down food by chewing
Saliva lubricates food
The enzyme, salivary amylase also called ptyalin, breaks
down starch into simple sugar, glucose
g. LIVER and Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and has a pH
GALL BLADDER of 1 without food, and 3 with food.
(accessory organs) Hydrochloric acid helps to kill bacteria, and works in
association with the enzyme, pepsin, to partially break
down proteins.
h. RECTUM Long tube that is about 7 metres long and 2.5 cm in
diameter
Most of digestion occurs here
Bile emulsifies lipids. Amylase breaks starch into
simple sugars. Lipase breaks lipids into fatty acids and
glycerol. Proteases break down proteins into amino
acids.
After the food into broken into smaller particles, it is
absorbed through finger-like projections called villi
into blood capillaries.
i. PANCREAS At the back of the mouth cavity
(accessory organ) Both food and air pass through here
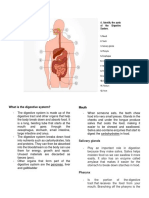
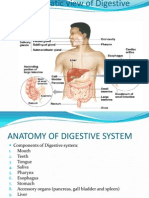
2) Label the diagram below. Next to each letter, write both the name of structure and
the abbreviation of which of the four stages it is involved in (use this key: M=mechanical,
C=chemical, A=absorption, E=elimination).
Show the path of food through the digestive system, indicate this with an arrow.
What structure is show below?
You might also like
- Life Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2023 EngDocument18 pagesLife Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2023 Engtendanim23No ratings yet
- CSEC Bio 2022 June P2 SolutionsDocument19 pagesCSEC Bio 2022 June P2 SolutionsAshe Kennedy100% (17)
- CELTA. Assignment 3Document7 pagesCELTA. Assignment 3Mehdi RoostapourNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Prelims ReviewerDocument28 pagesNCM 116 Prelims ReviewerMary Cruz100% (2)
- Digestive SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive SystemNyasha RumhezaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesLecture 1 Digestive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Week 17 BIO LEARN - Digestion and Energy in FoodDocument27 pagesWeek 17 BIO LEARN - Digestion and Energy in FoodArt SoupzNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: by DR Vipan GoyalDocument18 pagesDigestive System: by DR Vipan GoyalAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument44 pagesDigestive SystemRey Mark Bagalacsa LagdaanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - Study NotesDocument8 pagesDigestive System - Study NotesMayank ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - The Digestive SystemDocument21 pages3.1 - The Digestive SystemJavierNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BODY Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesHUMAN BODY Digestive SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandDocument25 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Final 1Document34 pagesThe Digestive System Final 1Jam DabalosNo ratings yet
- Life Processes QuestionsDocument58 pagesLife Processes QuestionsAnonymousNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesThe Digestive Systemofurumchinyere9No ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 - Human Digestive SystemDocument31 pagesTopic 2.1 - Human Digestive Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaDocument37 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- The Alimentary SystemDocument34 pagesThe Alimentary SystemAhnaf Muttaqi Spondan 1716No ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumansDocument33 pagesDigestive System in Humansstewart pelingonNo ratings yet
- Tled13 PPTDocument15 pagesTled13 PPTjoyceannserra8No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesDigestive SystemAngelyn AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumanDocument20 pagesDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document15 pagesChapter 9NG SHER WYNN MoeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-ADocument40 pagesNutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-AWaqas TahirNo ratings yet
- Science8 Lasq4 Week-1Document11 pagesScience8 Lasq4 Week-1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemjustharitssNo ratings yet
- Name - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsDocument5 pagesName - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsRJ CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Human Digestion PresentationDocument35 pagesHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNo ratings yet
- 182 Anatomy Digestive SystemDocument15 pages182 Anatomy Digestive SystemFrencee Rein Caleo100% (1)
- Digestive System Notes in ScienceDocument7 pagesDigestive System Notes in ScienceAllyson CadalzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Digestion - Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Digestion - Lecture Notesapi-372850882% (11)
- Animal Physiology: Human NutritionDocument30 pagesAnimal Physiology: Human NutritionHtet Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Nutrition in HumansDocument47 pagesChapter 6: Nutrition in HumansorangeslimeNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument45 pagesThe Digestive SystemgwormtalaveraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SysDocument36 pagesDigestive SysMubashir KhanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SysDocument36 pagesDigestive SysMubashir KhanNo ratings yet
- Gastro highlightCHAPTER1Document12 pagesGastro highlightCHAPTER1Lovely CruzxNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal PhysiologySamuel BordohNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption NotesDocument2 pagesDigestion and Absorption NotesHyazen E. DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)Document5 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Alimentary Canal and Human Digestion 2015Document7 pagesAlimentary Canal and Human Digestion 2015Tharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Digestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadDocument11 pagesDigestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadShan RomioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document47 pagesChapter 06gayathmipereraNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 (3.3 Human Digestive System)Document10 pagesScience Form 2 (3.3 Human Digestive System)sivanesshniNo ratings yet
- Updated Draft of Circulatory SystemDocument55 pagesUpdated Draft of Circulatory SystemKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DigestionDocument8 pagesNutrition and DigestionjeffchegzodNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument17 pages1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. DigestionDocument23 pagesChapter 3. DigestionNoviNo ratings yet
- Digestion WiwiDocument23 pagesDigestion WiwiSCE1-0622 Amni Insyirah Binti Mohd NasarudinNo ratings yet
- Glossary Key PointsDocument3 pagesGlossary Key PointsbxyrtbgyxcNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science8Document60 pagesQ4 Science8AILEEN LUZON100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- 3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemDocument36 pages3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemValery GvNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System BrochureDocument2 pagesThe Digestive System BrochureWasna Osama Al SaifNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument72 pagesDigestive System NotesQueen SarrahNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument117 pagesDigestive SystemKBDNo ratings yet
- Digestive System FINALDocument43 pagesDigestive System FINALSean Lorenzo TumacderNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ContinuationDocument38 pagesDigestive System ContinuationLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyFrom EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Bio Heterotrophic Nutrition in Plants Part B New 1624717471Document5 pagesClass 7 Bio Heterotrophic Nutrition in Plants Part B New 1624717471Darshan PadmapriyaNo ratings yet
- LettuceDocument2 pagesLettuceAyanda SimelaneNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Thesis TopicsDocument8 pagesFood and Nutrition Thesis TopicsStacy Vasquez100% (2)
- 2.3 Ingredients Used in Processing of Meat ProductsDocument4 pages2.3 Ingredients Used in Processing of Meat ProductsDrYogesh SomvanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To NutritionDocument55 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Nutritionikmal hazimNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension 4TH LevelDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension 4TH LevelJuan Muñoz0% (2)
- ch11Document27 pagesch11tintfenNo ratings yet
- Parenteralnutrition: Indications, Access, and ComplicationsDocument21 pagesParenteralnutrition: Indications, Access, and ComplicationsJair Alexander Quintero PanucoNo ratings yet
- © Maple Leaf International School Online 2021 Page 1 of 2Document2 pages© Maple Leaf International School Online 2021 Page 1 of 2Maasrur NeehonNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION BUDGET AUSTIN 2022 DraftDocument4 pagesINTRODUCTION BUDGET AUSTIN 2022 DraftRukundo Austin100% (1)
- AgricultureandFood-ENewsLetterDocument336 pagesAgricultureandFood-ENewsLetterPinky Perez Durango100% (1)
- Ampm Salessheet Us English 2Document2 pagesAmpm Salessheet Us English 2mirna kalashNo ratings yet
- Info Sheet 6.1-1 MEAT COMPOSITION AND STRUCTUREDocument18 pagesInfo Sheet 6.1-1 MEAT COMPOSITION AND STRUCTUREOubli BonheurNo ratings yet
- Product Description - PD 45000-7en Material No. 104414 Natamax®Document2 pagesProduct Description - PD 45000-7en Material No. 104414 Natamax®Mohamed BayomyNo ratings yet
- Comm Skills Past QuestionsDocument16 pagesComm Skills Past QuestionsGeorge AsanteNo ratings yet
- Test 1 I. Circle The Word (A, B, C or D) Which Has A Different Underlined SoundDocument4 pagesTest 1 I. Circle The Word (A, B, C or D) Which Has A Different Underlined SoundTham CaoNo ratings yet
- Lusaka Basic Needs Basket - April 2010Document2 pagesLusaka Basic Needs Basket - April 2010Chola MukangaNo ratings yet
- Smart Snacks at HomeDocument1 pageSmart Snacks at Homeapi-536242116No ratings yet
- Pigments in Fruits and Vegetables - Genomics and Dietetics (PDFDrive)Document280 pagesPigments in Fruits and Vegetables - Genomics and Dietetics (PDFDrive)abinaya100% (1)
- Food Insecurity Has Economic Root Causes: CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesFood Insecurity Has Economic Root Causes: CorrespondenceNazia AmjadNo ratings yet
- DNI PPT (Autosaved)Document8 pagesDNI PPT (Autosaved)Mamo SisayNo ratings yet
- Bakery General KnowledgeDocument2 pagesBakery General KnowledgeYisel Perez OrtizNo ratings yet
- Summative Evaluation - Meat and Poultry Test KeyDocument3 pagesSummative Evaluation - Meat and Poultry Test Keyjennifer bajoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Urban GardeningDocument10 pagesWeek 1 - Urban GardeningMariane Joy SantosNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Caries and Rampant CariesDocument24 pagesEarly Childhood Caries and Rampant CariesAmit GaurNo ratings yet
- 21 22CSAT Test5 KEYDocument37 pages21 22CSAT Test5 KEYAJNo ratings yet
- Rizal Medical Center: Vicinity MapDocument1 pageRizal Medical Center: Vicinity MapPeifixy CaraanNo ratings yet