Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab #3, Ch. 20 Heart
Uploaded by
CCP0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageHeart Lab
Original Title
Lab #3 ,Ch. 20 Heart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeart Lab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageLab #3, Ch. 20 Heart
Uploaded by
CCPHeart Lab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Lab outlines for A & P II
Lab #3, (Ch. 20): Heart
I. Identify tissues from models (or figures):
1. Four chambers:
A. Right atrium (R. A.): or R. auricle
B. Right ventricle (R. V.)
C. Left atrium (L. A.): or L. auricle
D. Left ventricle (L. V.)
2. Interventricular septum:
3. Four valves:
A. Tricuspid valve: R.A. R.V.
B. Pulmonary valve: R.V. pulmonary trunk (& arteries)
C. Bicuspid (= mitral) valve: L.A. L.V.
D. Aortic valve: L.V. Aorta
4. Chordae tendineae:
5. Papillary muscles:
6. Three layers of heart wall:
a. Epicardium: ( or visceral pericardium): outer layer
b. Myocardium: muscular wall , thickest layer
c. Endocardium: inner surfaces (including valves)
7. Base & Apex of heart; moderator band; model of coronary bypasses
8. Superior vena cava
9. Inferior vena cava
10. Coronary sinus, great cardiac vein, R. & L. coronary arteries, circumflex art.,
Anterior & posterior interventricular arteries; 2R & 2L pulmonary veins
11. Fossa ovalis: a remnant site of foramen ovale in fetus (a hole between RA & LA)
12. Aorta; Pulmonary trunk: branches into 2 R & 2 L pulmonary arteries.
13. Ligamentum arteriosum: remnant of ductus arteriosus in fetus.
14. Pericardium: (serous membranes that cover the heart):
a. Parietal pericardium: close to chest wall.
b. Visceral pericardium (= Epicardium): Surface membrane of the heart
15. Coronary sulcus, anterior interventricular sulcus, posterior interventricular sulcus.
16. (Slide): Intercalated discs of cardiac muscles:
II. Know the following terms:
1. Cardiac cycle: systole, diastole
2. EKG: P wave, QRS complex, T wave
3. First and second heart sound
III. Using stethoscope to listen the heart sounds
IV. Using sphygmomanometer & stethoscope to measure blood pressure.
You might also like
- In Lab, What Nerve Will You Find Adhered To The Fibrous Pericardium?Document4 pagesIn Lab, What Nerve Will You Find Adhered To The Fibrous Pericardium?Amar AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - The HeartDocument53 pagesLecture 18 - The HeartkiranNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLab 9 - Circulatory SystemClobelle Marie SiachuaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System QuizDocument4 pagesCardiovascular System QuizIrams KitchenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ConditionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular System ConditionsNinjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartNina Anne ParacadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemkaz92100% (6)
- Medical Investigations PDFDocument136 pagesMedical Investigations PDFFathy ElsheshtawyNo ratings yet
- Heart OutlineDocument7 pagesHeart OutlinepattynurseNo ratings yet
- Week 9 CVS WorkbookDocument24 pagesWeek 9 CVS Workbooksupriyakunwar2019No ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy & Physiology: Cardiovascular Heart AnatomyDocument16 pagesBasic Anatomy & Physiology: Cardiovascular Heart AnatomyLalu Ahmad AsmayadiNo ratings yet
- 23Document11 pages23monicaNo ratings yet
- 01 HeartDocument39 pages01 HeartFahvy tvNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by AehlertDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by AehlertWoodrow Fleming100% (31)
- The Heart TransDocument15 pagesThe Heart TransAmelie Sta RomanaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardio XIIDocument15 pagesAnaphy Cardio XIIRue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- Structure List - Thorax - Tentative-2020Document6 pagesStructure List - Thorax - Tentative-2020Ori BelsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 (Blood and Circulation)Document10 pagesChapter-6 (Blood and Circulation)ProdeepNo ratings yet
- Name: Cristina Silva Period: 3rd Heart Worksheet (Put Answers in Color)Document3 pagesName: Cristina Silva Period: 3rd Heart Worksheet (Put Answers in Color)api-334907221No ratings yet
- Cardiac Ultrasound Imaging ProtocolDocument152 pagesCardiac Ultrasound Imaging Protocolbashir019No ratings yet
- Lab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument4 pagesLab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To BetweenDocument6 pagesChapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To Betweentomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Vascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaDocument47 pagesVascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaJose PerezNo ratings yet
- 1 Cardiovascular System (FINAL) PDFDocument11 pages1 Cardiovascular System (FINAL) PDFJohn Juan TwanNo ratings yet
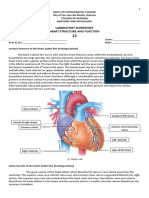
- Laboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- 45 Pericardium and HeartDocument10 pages45 Pericardium and HeartkiranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 6, Pericardium and The Heart (Slides)Document22 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 6, Pericardium and The Heart (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- Chapter 20 Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesChapter 20 Heart and Neck Vesselsannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- L6 7 CVS (2022) PDFDocument51 pagesL6 7 CVS (2022) PDFFung Shan CheungNo ratings yet
- Tutor c2 Bio310Document5 pagesTutor c2 Bio310Syaiful Ashraf Mohd AshriNo ratings yet
- Guide For Practical ExamDocument13 pagesGuide For Practical ExamAnastasija ArsicNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test ReviewDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Test Reviewobuob3940No ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory System: Structure and FunctionsDocument19 pagesCardiorespiratory System: Structure and FunctionsKasam ANo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Document12 pagesClass 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Shlok JaiswalNo ratings yet
- NPTE CArdio NotesDocument27 pagesNPTE CArdio NotesAubrey Vale SagunNo ratings yet
- Circulatory LabDocument4 pagesCirculatory LabKyla NicoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Pig Heart Dissection Manual STEMDocument8 pagesPig Heart Dissection Manual STEMSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Cardio PDFDocument8 pagesCardio PDFRica Mae TingcoNo ratings yet
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocument55 pagesMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyMarileth CoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlertgrinting.creation4qlo100% (41)
- Full Download Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert PDF Full Chapteradrianblackiadxetkrqm100% (14)
- PMLS2 LEC - Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesPMLS2 LEC - Circulatory SystemCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pages8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0No ratings yet
- CVS 217 QaDocument125 pagesCVS 217 QaDoaa Zakaria AliNo ratings yet
- Angiology: (Circulatory System)Document40 pagesAngiology: (Circulatory System)api-19641337100% (1)
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 4th Edition Barbara J AehlertDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 4th Edition Barbara J AehlertauroradaisynztNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition AehlertauroradaisynztNo ratings yet
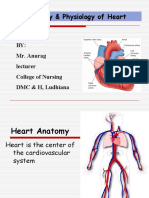
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Heart Lab 2015Document10 pagesHeart Lab 2015Ammanuel YohannesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemitsmesuvekshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document9 pagesChapter 12Charlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumShreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Anatomy Circulatory SystemDocument131 pagesAnatomy Circulatory Systemanduamlakmolalgn332No ratings yet
- Circulatory SDocument110 pagesCirculatory SMohammed HabibNo ratings yet
- 4CFB Cardiology 1 CVS SummaryDocument64 pages4CFB Cardiology 1 CVS SummaryHoang Nhu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Heart (2) + Superior & Inferior MediastinaDocument58 pagesHeart (2) + Superior & Inferior MediastinaAli Al-QudsiNo ratings yet