Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cannizzaro Reaction: Mechanism
Cannizzaro Reaction: Mechanism
Uploaded by
RAAHEELOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cannizzaro Reaction: Mechanism
Cannizzaro Reaction: Mechanism
Uploaded by
RAAHEELCopyright:
Available Formats
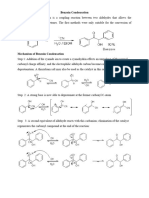
Cannizzaro reaction
The Cannizzaro reaction is a redox reaction in which two molecules of an aldehyde are reacted to
produce a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid using a hydroxide base. The reaction begins
with hydroxide attack on the carbonyl carbon followed by deprotonation to give a dianion. This
unstable intermediate releases a hydride anion which attacks another molecule of aldehyde. In
this process the dianion converts to a carboxylate anion and the aldehyde to an alkoxide. The
alkoxide then picks up a proton from water to provide the alcohol final product, while the
caboxylate is converted to the carboxylic acid product after acid work-up.[1]
Mechanism
References:
1. Cannizzaro, S. Ann. Chem. Pharm. 1853, 88, 129–130.
You might also like
- CHEM35.1 E7 Cannizzaro ReactionDocument4 pagesCHEM35.1 E7 Cannizzaro ReactionGlenn Vincent Tumimbang100% (7)
- 9-Cannizzaro's Reaction: Reduced (Giving Primary Alcohol)Document5 pages9-Cannizzaro's Reaction: Reduced (Giving Primary Alcohol)maheen aurangzaibNo ratings yet
- Cannizzaro reac-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesCannizzaro reac-WPS Officenharnahquophi8080No ratings yet
- Cannizzaro ReactionDocument16 pagesCannizzaro ReactionEm NaNo ratings yet
- Cannizzaro Reaction - Mechanism, Examples With IllustrationsDocument2 pagesCannizzaro Reaction - Mechanism, Examples With IllustrationsHanin Latpi0% (1)
- Applied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismDocument5 pagesApplied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismHammad Raza 362-FET/BTECHME/F18No ratings yet
- 306 Cannizzaro ReactionDocument9 pages306 Cannizzaro Reactionayesha sanaNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismDocument5 pagesApplied Chemistry (MS-133) : Cannizzaro Reaction With Complete MechanismHammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Hints)Document2 pagesHydrocarbons (Hints)hchawla421No ratings yet
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument117 pages1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds TVVDocument13 pagesCarbonyl Compounds TVVjyothi sai sriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationTiya KapoorNo ratings yet
- Cannizaro ReactionDocument13 pagesCannizaro Reactionhussein alnasryNo ratings yet
- Presentation (1) SKDocument8 pagesPresentation (1) SKsalman khanNo ratings yet
- ReactionDocument54 pagesReactionAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions 1Document81 pagesName Reactions 1Anjish PatelNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Phenol 2Document18 pagesAlcohol and Phenol 2Nayem Uddin ToukirNo ratings yet
- Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Top ConceptsDocument15 pagesClass XII: Chemistry Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Top ConceptsAshaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsDocument55 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsMaria AGNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesnvmohankumar85No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsDocument39 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsashathtNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocument45 pagesAldehyde and KetonesShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument22 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Document16 pages3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Vergil HashimotoNo ratings yet
- CHEM35 1 E7 Cannizzaro Reaction PDFDocument4 pagesCHEM35 1 E7 Cannizzaro Reaction PDFSherlHolmesNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalDocument32 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalSaeed UrrehmanNo ratings yet
- Namedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Document11 pagesNamedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Vishant SinghNo ratings yet
- Akash & Priyanshu XIIDocument24 pagesAkash & Priyanshu XIIAnindya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument5 pagesAldehydes and KetonesEl NastyNo ratings yet
- Alkene 6Document5 pagesAlkene 6Prazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of MonosaccharideDocument13 pagesReactions of MonosaccharideKate Lyle ParfanNo ratings yet
- AlkynesDocument16 pagesAlkynesMichael AttehNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 242 Adipic Acid.09Document5 pagesChemistry 242 Adipic Acid.09khaledegy10No ratings yet
- AlkaneDocument14 pagesAlkanebijansharma019No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument22 pagesOrganic ChemistryjhoyvanNo ratings yet
- Poc - Benzoin CondensationDocument1 pagePoc - Benzoin Condensationkavi bharathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Hydro CarbonDocument22 pagesChapter - 13 Hydro CarbonManan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Updated Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativesDocument44 pagesChapter 4 Updated Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives- Maiyasa -No ratings yet
- Addition To AlkenesDocument25 pagesAddition To AlkenesHeba AkbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document38 pagesChapter 20Amir ZaxxNo ratings yet
- 32 DR Zhou Lecture 32 PDFDocument23 pages32 DR Zhou Lecture 32 PDFBUCH203No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesLecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsSHUBHAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document52 pagesChapter 21Seung Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Emmanuel SyNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6C The Chemistry of Alkenes and Alkynes CME 2023Document37 pagesLECTURE 6C The Chemistry of Alkenes and Alkynes CME 2023LinearNo ratings yet
- Adipic Acid PreparationDocument9 pagesAdipic Acid PreparationSmaeUB100% (1)
- Catalytic Hydrogenations: Birch ReductionDocument9 pagesCatalytic Hydrogenations: Birch ReductionAnamikaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsAnthony KwofieNo ratings yet
- The Reactions of Adipic AcidDocument3 pagesThe Reactions of Adipic AcidmeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument31 pagesHydrocarbonstannie2512No ratings yet
- Chem-12. Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument17 pagesChem-12. Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsJitendra kumarNo ratings yet
- AlkeneDocument14 pagesAlkenebijansharma019No ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument120 pagesAlkenesVidhan PatniNo ratings yet
- Alkene ReactionsDocument34 pagesAlkene ReactionsIamKasiraporn MahanilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHDocument23 pagesChemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alkane FunctionalizationFrom EverandAlkane FunctionalizationArmando J. L. PombeiroNo ratings yet