Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expetiment 1 AIC (KTU)
Uploaded by
Kirti ArunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expetiment 1 AIC (KTU)
Uploaded by
Kirti ArunCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment: 1 Date:
Familiarization of operational amplifier - Inverting amplifier, Non inverting
amplifier, Adder, Integrator, Comparator.
Aim:
1. To design and set up inverting amplifier, non inverting amplifier, adder, integrator and
comparator circuits using IC 741.
2. To plot the frequency response of integrator circuit.
Components required:
IC 741, Resistors, Capacitors
Theory:
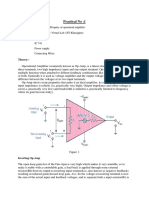
INVERTING AMPLIFIER
This is the most widely used circuit of all the Op-amp circuits. The output V0 is fed back to
the inverting input through the Rf – Rin network as shown in figure where Rf is the feedback
resistor. The input signal Vi is applied to the inverting input terminal through Rin and non-
inverting input terminal of Op-amp is grounded.The output V0 is given by
Where, the gain of amplifier is
The negative sign indicates a phase-shift of 180 degrees between Vi and V0. The effective
input impedance is Ri. An inverting amplifier uses negative feedback to invert and amplify a
voltage. The Rin,Rf resistor network allows some of the output signal to be returned to the
input. Since the output is 180° out of phase, this amount is effectively subtracted from the
input, thereby reducing the input into the operational amplifier. This reduces the overall gain
of the amplifier and is dubbed negative feedback
Circuit Diagram: (left side)
Pin Configuration: (left side)
Tabulation: (left side)
Vi=2Vpp
Rin= 1K
Input and output Waveforms: (left side)
NON-INVERTING AMPLIFIER
The circuit diagram of non inverting amplifier is shown in figure. Here , the signal is applied to the
non inverting input terminal and feedback is given to inverting terminal. The circuit amplifies the
input signal without inverting it. The output Vout is given by
The voltage gain is given by
A=
Compared to the inverting amplifier, input resistance of non inverting amplifier is extremely large
Circuit Diagram: (left side)
Tabulation: (left side)
Vi=2Vpp
Ri= 1K
Input and output Waveforms: (left side)
ADDER
This is one of the liner applications of the Op-Amp. A circuit whose output is the sum of several
input signals is called a summer. Shown in fig.1 is an inverting summer. The output is
Where Rf = R1 =R2, then
V0 = - (V1+V2)
That is, the output is an inverted sum of the inputs.
Circuit Diagram: (left side)
R1=R2=Rf=1K
Tabulation: (left side)
Input and output Waveforms: (left side)
INTEGRATOR
In an integrator circuit, the output voltage is integral of the input signal. The output voltage of an
integrator is given by
At low frequencies the gain becomes infinite, so the capacitor is fully charged and behaves like
an open circuit. The gain of an integrator at low frequency can be limited by connecting a
resistor in shunt with capacitor.
Circuit Diagram: (left side)
Design (left side)
Choose
Where T= time period of the input signal
Assume and find
Select =10
Input and Output Waveforms (left side)
Tabulation: (left side)
frequency Output Voltage Gain(Vo/Vin)
COMPARATOR
The circuit diagram shows an op-amp used as a comparator. A fixed reference voltage
Vref is applied to the (-) input, and the other time – varying signal voltage Vin is applied to the (+)
input; Because of this arrangement, the circuit is called the non-inverting comparator. Depending
upon the levels of Vin and Vref, the circuit produces output. In short, the comparator is a type of
analog-to-digital converter. At any given time the output waveform shows whether Vin is greater
or less than Vref. The comparator is sometimes also called a voltage-level detector because, for a
desired value of Vref, the voltage level of the input Vin can be detected.
Circuit Diagram: (left side)
Tabulation: (left side)
Vin pp=10V
Vref=0V, -2V, +2V
Procedure:
1. Collect and check the components.
2. Connect the circuits as shown in figure.
3. Apply the corresponding input signal and observe the output signal.
4. For frequency response vary the input frequency and note the corresponding output
voltage to find the gain.
5. Plot the input and output waveforms.
Results and Inference:
You might also like
- OP-AMP APPLICATIONS: AMPLIFIERS, FOLLOWER, SUMMER & SUBTRACTORDocument11 pagesOP-AMP APPLICATIONS: AMPLIFIERS, FOLLOWER, SUMMER & SUBTRACTORVijayakumar KNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierDocument116 pagesLinear and Digital Integrated Circuits: Uni T - 1 Operati Onal Ampli FierBOGGULA SURENDAR REDDYNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- OPampDocument16 pagesOPampDarshan Iyer NNo ratings yet
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Opamp PesentationDocument34 pagesOpamp Pesentation2shreedNo ratings yet
- Linear Applications of Op-AmpsDocument94 pagesLinear Applications of Op-AmpsManar HosnyNo ratings yet
- EXP10Document7 pagesEXP10Abhigyan SinghNo ratings yet
- Non Inverting LabDocument6 pagesNon Inverting LabKenzie WalipiNo ratings yet
- ch-3 OpampDocument12 pagesch-3 OpampS KumarNo ratings yet
- EXP7 - Manual Inverting and Non-InvertingDocument4 pagesEXP7 - Manual Inverting and Non-InvertingRaju Punawat RajuNo ratings yet
- Inverting AmplifierDocument9 pagesInverting AmplifierKenzie WalipiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document5 pagesExperiment 6rachit guptaNo ratings yet
- Lic Lab ManualDocument89 pagesLic Lab ManualKALAIMATHI100% (1)
- Acd Lab ManualDocument34 pagesAcd Lab ManualAbhishek PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document32 pagesChapter 4Ram Bahadur KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Op Amp PDFDocument34 pagesOp Amp PDFHamza MazenNo ratings yet
- Djukarna Stkip Surya Serpong, BantenDocument34 pagesDjukarna Stkip Surya Serpong, BantenjainamshahNo ratings yet
- Opaamp NewwwDocument20 pagesOpaamp NewwwArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 02Document12 pagesExperiment No - 02VINITA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Detector Using 741 ICDocument13 pagesZero Crossing Detector Using 741 ICkapil chander100% (1)
- LIC Manual PDFDocument55 pagesLIC Manual PDFmekalajesiNo ratings yet
- Iv - Semester, Ece List of ExperimentsDocument117 pagesIv - Semester, Ece List of ExperimentsvibinmanualNo ratings yet
- Design An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.Document8 pagesDesign An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.Sudeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Analogue controller op-ampDocument36 pagesAnalogue controller op-ampFaissalNo ratings yet
- Aim Lab Used Components: Practical No:1Document12 pagesAim Lab Used Components: Practical No:1Sominath HarneNo ratings yet
- Basic AppsDocument10 pagesBasic AppsajayganeshNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Analog ElexDocument21 pagesUnit-4 Analog ElexAkshat goyalNo ratings yet
- Op Amp and Its Applications2.0Document27 pagesOp Amp and Its Applications2.0Arpita Sharma100% (1)
- Unit-22 Electronic devices AssignmentDocument13 pagesUnit-22 Electronic devices AssignmentChathura RanathungaNo ratings yet
- Lic Unit 1 (1) eDocument114 pagesLic Unit 1 (1) eganeshNo ratings yet
- Plugin-TE0221 - Analog & Digital System LabDocument53 pagesPlugin-TE0221 - Analog & Digital System Labnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- IntegratorDocument38 pagesIntegratorSyed AshmadNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) : Voltages. Symbol For An Op-AmpDocument8 pagesOperational Amplifiers (Op Amps) : Voltages. Symbol For An Op-AmpRaymond ScottNo ratings yet
- Exp No8Document9 pagesExp No8Mohd Syamsul Ramli100% (1)
- Dasar OpampDocument54 pagesDasar OpampMaulana HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp ApplicationsDocument146 pagesOp-Amp ApplicationsPB PrasathNo ratings yet
- Precision Full Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesPrecision Full Wave Rectifiermjns25No ratings yet
- IC741 Op-Amp Lab ManualDocument40 pagesIC741 Op-Amp Lab ManualPreethamReddy100% (1)
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramJm RezanoNo ratings yet
- 1 Study of Basic Properties of Operational Amplifier - TheoryDocument3 pages1 Study of Basic Properties of Operational Amplifier - TheoryVicNo ratings yet
- Dasar OpampDocument54 pagesDasar OpampAdri Muhaimin AfifNo ratings yet
- Open Loop - Closed Loop - Op Amp PDFDocument11 pagesOpen Loop - Closed Loop - Op Amp PDFtanishk jainNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document33 pagesUnit - 1Madhavan SamNo ratings yet
- Op AmpDocument16 pagesOp AmpChandan SasamalNo ratings yet
- Op-amp Integrator and Differentiator CircuitsDocument17 pagesOp-amp Integrator and Differentiator CircuitsnagarajudbpNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Operational Amplifier: Fig.6.1 Symbol of Op-AmpDocument12 pagesUnit - 6 Operational Amplifier: Fig.6.1 Symbol of Op-AmpJovita LasradoNo ratings yet
- Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument13 pagesInverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsBereket TsegayeNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentimalik16No ratings yet
- Epc M3Document13 pagesEpc M3karanphutane2254No ratings yet
- Summer AdderDocument26 pagesSummer AdderAyush Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL ADSlatest PDFDocument62 pagesLAB MANUAL ADSlatest PDFP HAMSA DATTANo ratings yet
- Op Amp 2Document14 pagesOp Amp 2Dhileepan SankarNo ratings yet
- Op AmpsDocument17 pagesOp AmpsshilpaNo ratings yet
- Final Op Amp Lab ReportDocument7 pagesFinal Op Amp Lab Reportmehrin12367% (3)
- Analog Electronics CircuitDocument28 pagesAnalog Electronics CircuitKarishma SharmaNo ratings yet
- Op Amp ReportDocument57 pagesOp Amp ReportvenkateshNo ratings yet
- ASTRO 500: 10 Year LED Array WarrantyDocument2 pagesASTRO 500: 10 Year LED Array WarrantyJerome Cardenas TablacNo ratings yet
- KCP Operation Modes Coordinate SystemsDocument25 pagesKCP Operation Modes Coordinate SystemsNguyễn Duy AnhNo ratings yet
- S6D155-4C S/N 10011-UpDocument179 pagesS6D155-4C S/N 10011-UpHelio100% (1)
- Bubble Chart TimelineDocument7 pagesBubble Chart TimelineNurholisNo ratings yet
- V382 - 20 (00205363) - DecryptDocument27 pagesV382 - 20 (00205363) - Decryptleodias.souzaNo ratings yet
- 1182 - Data Sheet - 26.11.2018.2018Document1 page1182 - Data Sheet - 26.11.2018.2018GG JetTech EPCNo ratings yet
- How To Filter Data by Multiple Colors in ExcelDocument3 pagesHow To Filter Data by Multiple Colors in ExceldarkwolfbrNo ratings yet
- Fluke 27 II and 28 II:: Rugged IP 67 Industrial MultimetersDocument2 pagesFluke 27 II and 28 II:: Rugged IP 67 Industrial MultimetersSuleyman KapucuNo ratings yet
- Turning and Drilling PPT MFG Chapter23 FinalDocument78 pagesTurning and Drilling PPT MFG Chapter23 FinalRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- AnyScan BrochureDocument28 pagesAnyScan BrochureManjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- COS111u Tut 101 - 3 (2009)Document107 pagesCOS111u Tut 101 - 3 (2009)Willemien Du PlessisNo ratings yet
- Fleet Tracking & Ride Management AppsDocument15 pagesFleet Tracking & Ride Management AppsAbnan YazdaniNo ratings yet
- Application of GIS in Management of City Gas Pipeline NetworkDocument6 pagesApplication of GIS in Management of City Gas Pipeline NetworkMileneEsdenkaArnezNo ratings yet
- Berk Sop PDFDocument2 pagesBerk Sop PDFKhadsaar Singh100% (1)
- Uninterrupted DC Power Supply PDFDocument59 pagesUninterrupted DC Power Supply PDFit's DifFerEntNo ratings yet
- SINUMERIK 840D sl ManualsDocument3 pagesSINUMERIK 840D sl ManualsEliane SouzaNo ratings yet
- McGraw-Edison SPI Lighting Monitor Wall Light Series Brochure 1983Document4 pagesMcGraw-Edison SPI Lighting Monitor Wall Light Series Brochure 1983Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Department of Defense: DirectiveDocument11 pagesDepartment of Defense: DirectiveChristopher DorobekNo ratings yet
- OptiX OSN 500 Commissioning Guide (V100R006)Document104 pagesOptiX OSN 500 Commissioning Guide (V100R006)Thunder-Link.comNo ratings yet
- Approved Drawing of Boundary WallDocument1 pageApproved Drawing of Boundary WallAnup Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Carbonite Portal v8.84 - Release NotesDocument14 pagesCarbonite Portal v8.84 - Release NotesAlbertoDanielRodriguezSandovalNo ratings yet
- PT 100 Za TemperaturaDocument21 pagesPT 100 Za Temperaturawarmaster81No ratings yet
- High-Power LED Technical Data SheetDocument7 pagesHigh-Power LED Technical Data Sheetdyaza_1No ratings yet
- The Modern Digital Design FlowDocument6 pagesThe Modern Digital Design FlowSatyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Flyboard 2412723958766647Document3 pagesFlyboard 2412723958766647Christopher Lennon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SMB PRO MULTI BMS Supports LFP, LI Ion, LTO & LIPO CellsDocument6 pagesSMB PRO MULTI BMS Supports LFP, LI Ion, LTO & LIPO CellsGustavo R GorNo ratings yet
- Omron E5 JDocument69 pagesOmron E5 JVoneisisoNo ratings yet
- Advantages of TETRADocument11 pagesAdvantages of TETRAtetraprimigNo ratings yet
- Pressure ControlDocument12 pagesPressure ControlMohamed RashedNo ratings yet
- Purlin DesignDocument30 pagesPurlin DesignRangel Lara BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingFrom EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- ARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)From EverandARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)No ratings yet
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsFrom EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignFrom EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo ratings yet
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesFrom EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsFrom EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinFrom EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)