Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roads and highways: A vital urban infrastructure
Uploaded by
Josiah Antonino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views3 pagesDifferent types of roads and highways
Original Title
Roads and Highways
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDifferent types of roads and highways
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views3 pagesRoads and highways: A vital urban infrastructure
Uploaded by
Josiah AntoninoDifferent types of roads and highways
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ROADS AND HIGHWAYS such, it has an important role to play in the urban
environment to facilitate mobility. It furthermore
Roads and highways, traveled way on which people, determines the accessibility of an urban area
animals, or wheeled vehicles move. In modern together with public transport options.
usage the term road describes a rural, lesser
ADVANTAGES OF DEVELOPING GOOD ROAD
traveled way, while the word street denotes an
NETWORKS
urban roadway. Highway refers to a major rural
traveled way; more recently it has been used for a 1. Stimulating the development of certain
road, in either a rural or urban area, where points of areas in terms of commercial activities,
entrance and exit for traffic are limited and urban development, and creating jobs.
controlled. 2. Security, good accessibility by the road
network is also important, for example for
good accessibility in case of incidents
HISTORY
FACTORS AFFECTING THE SELECTION OF LOCATION
The first roads were paths made by animals and OF ROADS AND HIGHWAYS
later adapted by humans. The earliest records of
such paths have been found around some springs 1. TRAFFIC
near Jericho and date from about 6000 BC. The first Traffic planner from various studies can
indications of constructed roads date from about predict the effect of travel patterns of
4000 BC and consist of stone-paved streets at Ur in alternative location proposed highway. Also
modern-day Iraq and timber roads preserved in a they analyze the probable effect of new links
swamp in Glastonbury, England. During the Bronze in highway network. This permits the
Age, the availability of metal tools made the location engineer to determine how well
construction of stone paving more feasible; at the alternative locations will fit with the existing
same time, demand for paved roads rose with the network.
use of wheeled vehicles, which were well
established by 2000 BC. 2. LAND USE
It is a major factor affecting the pattern of
traffic generation is an urban areas. For
IMPORTANCE OF ROADS AND HIGHWAYS IN urban highway the commercial, residential
URBAN AREAS and industrial areas are too considered.
SOCIAL - The road network facilitates the Although the highway should be designed
movement of people allowing for social interaction. for peak hour volume and the travel patterns
A high quality road network is essential not only for vary with time of day, day of weak. Season of
connecting key urban centers but for improving the year also has effect in other ways.
connectivity. 3. PARKING FACILITY FOR VEHICLES
For highway location in an urban area the
ECONOMIC - By connecting geographic
locations, road networks facilitate the transport and existing parking facility should be
movement of people, goods, and services, creating considered. Ideally the location should be
welfare. Road networks played a crucial role in the close to existing and potential parking areas
economic development of the 20th century, to avoiding the amount of travel on existing
enabling relatively fast individual transportation for street.
the masses from the second part of the 20th
century. Road transport still plays a crucial role in
the national and local transportation networks.
MOBILITY - The function of a road network is
to facilitate movement from one area to another. As
4. ALREADY EXISTING TRANSPORTATION and horses. Urban footpaths are usually paved, may
SYSTEM have steps, and can be called alleys, lanes, steps,
To increase the overall level of service of etc.
transportation in an urban area interference TYPES OF ROAD PATTERNS
and interaction with other transportation
system should be considered. Rectangular/ Block/ Grid Pattern
5. TOPOGRAPHY AND GEOLOGY The rectangular/ block/ grid pattern is a plan
Same importance as in rural area. Due to where the streets and roads are in the form
high cost of right of way are certain areas of grids or blocks running perpendicularly
from where the road should not pass. into each other thus forming a grid or block.
Radial Pattern
6. SOCIOLOGICAL, HISTORICAL AND
In this type of pattern the network of roads
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
is in the form of circles emanating from the
Proposed location should not serve
residential neighbourhoods or create center of the area.
barriers between residential and other Radial and Block Pattern
community service. This type of network is a combination
Open public land should be retained as far as of radial and block pattern. A radial
possible. network of roads radiate from the
Park an residential land should be used only center outwardly with block pattern
if there is no alternate location can serve as network of roads in between the
stabilizing force by screening the traffic from radial main streets.
residential communities. Radial and Circular Pattern
In this type of road pattern the main
ROAD NETWORKS
roads radiate from the central point
Intersections
and are connected together by
Roundabouts
concentric roads that are also
Motorways
radiating outwardly.
Urban roads
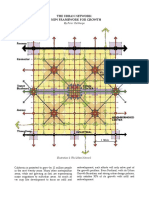
Radial and Grid Pattern
Footpaths
It is a combination of radial and grid
Intersections – ……………………………………………. pattern. A radial network of roads
Roundabouts – …………………………………………….. radiate from the center outwardly.
Motorways – a main road for fast-moving traffic, The main radial streets are then
having limited access, separate carriageways for interconnected by providing grid
vehicles travelling in opposite directions, and pattern in between the main streets.
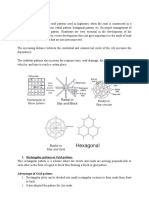
usually a total of four or six lanes. Hexagonal Patterns
This pattern is a network of roads that grow
Bicycle lanes – defined as a portion of the roadway
in such a manner in various directions
that has been designated by striping, signage, and
forming hexagons.
pavement markings for the preferential or exclusive
Linear Patterns
use of bicyclists. Bike lanes enable bicyclists to ride In this type of pattern the roads grow linearly in
at their preferred speed without interference from one direction possibly due to the presence of
prevailing traffic conditions. some natural forces such as sea or ocean at one
side of the city.
Footpaths – footpath is a type of thoroughfare that
is intended for use only by pedestrians and no other
forms of traffic such as motorized vehicles, cycles,
HIGHWAYS
Other District Roads (O.D.R)
Freeways - A freeway is a major road with
several lanes that has been The roads serving rural areas of production and
specially built for fast travel over long distances. connecting them with outlet to market centers,
taluk headquarters, block headquarters or other
Primary Streets - These provide for main roads are called Other District Roads.
major traffic movement between centers of
population and economic activity on a national
Village Roads
and regional level. The roads connecting villages or groups of villages
with each other or with the nearest road of higher
Primary Streets - Within urban boundaries these
category are known as village roads.
link traffic from
strategic roads to residential streets or
industrial roads.
Classification of Urban Roads
Service roads - A frontage road (also known as an
access road, service road or parallel road) is a local Express ways
The portion of road way of an urban road reserved
road running parallel to a higher-speed, limited-
for use only by high speed or power driven vehicles
access road. A frontage road is often used to provide
is called Express way or motor way or super
access to private driveways, shops, houses,
highway.
industries or farms.
NON-URBAN VS. URBAN ROADS Arterial Roads
These are streets primarily for the high traffic on a
Classification of Non-urban Roads continuous route. Arterial's have a higher level of
traffic mobility,
National Highway (N.H)
National highway are main roads running through
the length and breadth of the country. They connect Sub-arterial Roads
capitals of states, ports, large towns, industrial These roads serve same purposes as arterial road,
centers and foreign highways but have lower level of traffic than the arterial
roads.
State Highways (S.H)
These roads are the main arteries of traffic within a Collector Streets
state. They connect important cities and district Collector Streets provide access to arterial streets
headquarters within the state. They are also known and they collect & distribute from and to local
as Provincial Highways. streets.
Major District Roads (M.D.R)
The important roads within a district serving areas Local Streets
of production and markets and connecting those Local Streets provide access to adjoining property.
with each other or with main highways are known
as Major District Roads.
You might also like
- Ceng55-Lectures (1-3)Document9 pagesCeng55-Lectures (1-3)Lorcie CruzNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 HighwayDocument12 pagesGROUP 2 Highway201240290No ratings yet
- Urban Roads Road Sections PDFDocument26 pagesUrban Roads Road Sections PDFtejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Group 2 HighwayDocument51 pagesGroup 2 Highway201240290No ratings yet
- Different Types of RoadsDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of RoadsJosiah AntoninoNo ratings yet
- History of Road1Document10 pagesHistory of Road1Heart HackerNo ratings yet
- Mixed-Use Development: Additional RequirementsDocument15 pagesMixed-Use Development: Additional RequirementsaldreinNo ratings yet
- 23 - Anuja Jadhav - Electives - ReportDocument8 pages23 - Anuja Jadhav - Electives - ReportAnuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Urban Street Pattern: ARCH 305: Architecture and Town PlanningDocument34 pagesUrban Street Pattern: ARCH 305: Architecture and Town PlanningHabib Ullah100% (1)
- 2.0 Highway Development and PlanningDocument35 pages2.0 Highway Development and PlanningPearl Mae AngusNo ratings yet
- Link Aspect of Street Design Group - 2Document8 pagesLink Aspect of Street Design Group - 2Yosef BekeleNo ratings yet
- Urban Street Patterns Explained: Types, Benefits and EvolutionDocument33 pagesUrban Street Patterns Explained: Types, Benefits and EvolutionAhsan HameedNo ratings yet
- 5 Inter-City & Intracity CirculationDocument30 pages5 Inter-City & Intracity Circulationtanie100% (11)
- 1 180118145355 PDFDocument16 pages1 180118145355 PDFprachiNo ratings yet
- Human Settlement: Case StudyDocument17 pagesHuman Settlement: Case StudyaparnaNo ratings yet
- Residential Street PatternDocument8 pagesResidential Street PatternsakitkaplaxNo ratings yet
- Transportation Planning As Effective MeaDocument7 pagesTransportation Planning As Effective MeaRwitika TarafderNo ratings yet
- Trans Principle 1Document6 pagesTrans Principle 1Vena CavaNo ratings yet
- Residential Street Pattern Design: Fanis Grammenos Sevag Pogharian Julie Tasker-BrownDocument11 pagesResidential Street Pattern Design: Fanis Grammenos Sevag Pogharian Julie Tasker-BrownNazifa SubhaNo ratings yet
- Design Case StudyDocument42 pagesDesign Case StudyJiya RobertNo ratings yet
- Highway Development and PlanningDocument62 pagesHighway Development and PlanningEstephany BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Street & Lot LayoutDocument29 pagesStreet & Lot LayoutChelsea MakilingNo ratings yet
- Planning 04Document21 pagesPlanning 04Architecture DocumentsNo ratings yet
- Urban Roads & Road SectionsDocument26 pagesUrban Roads & Road SectionsKandarp RajyaguruNo ratings yet
- Arch 315 QF - 5Document3 pagesArch 315 QF - 5MARRIAH ELIZZA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- RADIAL-ROAD-NETWORK-PATTERNDocument12 pagesRADIAL-ROAD-NETWORK-PATTERNAlefher Buendia PatriaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Highway Development and PlanningDocument10 pagesWeek 2 - Highway Development and PlanningADRIAN FRAGATANo ratings yet
- Highway 06.Document32 pagesHighway 06.Marshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Residential Street Pattern DesignDocument5 pagesResidential Street Pattern DesignReem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Roads and StreetsDocument47 pagesRoads and StreetsCHERUKURI YUVA RAJU 20981A0107No ratings yet
- The Urban Network: A New Framework For Growth: by Peter CalthorpeDocument6 pagesThe Urban Network: A New Framework For Growth: by Peter CalthorpeDave LicerioNo ratings yet
- 23 - Anuja Jadhav - Electives - HypothesisDocument8 pages23 - Anuja Jadhav - Electives - HypothesisAnuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Cities Afoot-Pedestrians Walkability and Urban DesDocument5 pagesCities Afoot-Pedestrians Walkability and Urban DesBADR HAMDAN ALATEBENo ratings yet
- CE 312 Activity 4 - Classification of Roads and Road PatternsDocument9 pagesCE 312 Activity 4 - Classification of Roads and Road PatternsANCHETA, ANA MARIE P.No ratings yet
- ARC-3080 TOWN PLANNING: Types of Streets and Road SystemsDocument17 pagesARC-3080 TOWN PLANNING: Types of Streets and Road SystemsTARIQ TANSEEFNo ratings yet
- CE315ec3 Group 2Document40 pagesCE315ec3 Group 2Renaizel MalcredoNo ratings yet
- Journal of Urban DesignDocument4 pagesJournal of Urban DesignDagim FikaduNo ratings yet
- Understanding Urban Patterns: Radial, Grid, Irregular and Models of GrowthDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Urban Patterns: Radial, Grid, Irregular and Models of GrowthEncinas, Mary Joyce M.No ratings yet
- Group 2 Highways 1Document40 pagesGroup 2 Highways 1Melian RebamontanNo ratings yet
- C4C Design Guidelines 2.0Document38 pagesC4C Design Guidelines 2.0ITDP IndiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PDFDocument32 pagesUnit 5 PDFmoni_john_1No ratings yet
- Topic 1. Road Classification DesignDocument39 pagesTopic 1. Road Classification DesignRoopen FearkyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Legibility: Ar 512 HousingDocument12 pagesGuidelines On Legibility: Ar 512 HousingCamille Anne Madriaga NajorraNo ratings yet
- Activity MT - 02 - SimCity DevelopmentDocument5 pagesActivity MT - 02 - SimCity DevelopmentHARLAND GHODFREY YABESNo ratings yet
- Highway Development and PlanningDocument9 pagesHighway Development and PlanningRenaizel MalcredoNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Urban DesignDocument28 pagesCirculation and Urban Designjagat100% (2)
- Civil V Transportation Engineering 1 U2Document11 pagesCivil V Transportation Engineering 1 U2Abhishek nNo ratings yet
- High-density apartment road networkDocument32 pagesHigh-density apartment road networkSheeren Sitara Chelladurai100% (1)
- Udc1 Section 4 - Making The ConnectionsDocument16 pagesUdc1 Section 4 - Making The ConnectionsHotel ObrenovacNo ratings yet
- Part Iii: Prototype DesignDocument15 pagesPart Iii: Prototype DesignAmir HamzahNo ratings yet
- Highway and Street Classification SystemsDocument39 pagesHighway and Street Classification SystemsAmirul ZolkhairiNo ratings yet
- Urban Design Guidelines: For The Germantown Employment Area Sector PlanDocument55 pagesUrban Design Guidelines: For The Germantown Employment Area Sector PlanM-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- RCP C6 PP13 - Road HierarchyDocument4 pagesRCP C6 PP13 - Road HierarchyHiskia SimaNo ratings yet
- Road PatternsDocument3 pagesRoad PatternsMubasheer KNo ratings yet
- Morphological Dimension Summary by ArnavDocument7 pagesMorphological Dimension Summary by Arnavarnav saikiaNo ratings yet
- Street Design Guidelines October 2012Document85 pagesStreet Design Guidelines October 2012shishirkrNo ratings yet
- Highway and Raildroad EngineeringDocument10 pagesHighway and Raildroad EngineeringJannila PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Road PatternsDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Road Patterns198W1A0591-SEC-B KOTHAPALLI CHAKRADHARNo ratings yet
- Urban: DesignDocument32 pagesUrban: DesignBurud MeghanaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Qualification and Evaluation ReportDocument76 pagesPre-Qualification and Evaluation ReportSyed Mohsan Abbas Naqvi100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction PDFDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Introduction PDFRUSLAN SALAEHNo ratings yet
- DMS MasterplanDocument71 pagesDMS MasterplanacabadingNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (HE)Document25 pagesUnit 2 (HE)PAVITHRA H SNo ratings yet
- SHC 301 FinalDocument556 pagesSHC 301 FinalAmr HassanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat: Gets GoingDocument28 pagesGujarat: Gets GoingShashank Verma100% (1)
- Highway Engineering GuideDocument198 pagesHighway Engineering GuideMae Laspa100% (1)
- 2 Tcds IntroductionDocument9 pages2 Tcds Introductionmczen_associatesNo ratings yet
- Data Collection Survey On The Trunk RoadDocument18 pagesData Collection Survey On The Trunk RoadJay ChenNo ratings yet
- The Urban Network: A New Framework For Growth: by Peter CalthorpeDocument6 pagesThe Urban Network: A New Framework For Growth: by Peter CalthorpeDave LicerioNo ratings yet
- Caltrans Encroachment Permitting and Highway Right-of-Way UseDocument8 pagesCaltrans Encroachment Permitting and Highway Right-of-Way UseAlbyNo ratings yet
- 15th Ward Traffic Study Full VersionDocument122 pages15th Ward Traffic Study Full VersionMegan-Ellyia GreenNo ratings yet
- HIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of HighwaysDocument75 pagesHIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of Highwaysabubakar100% (1)
- Spatial Temporal Visualization: Insights and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesSpatial Temporal Visualization: Insights and ApplicationsYana AliNo ratings yet
- Ceres 2012Document319 pagesCeres 2012mohammed_fathelbabNo ratings yet
- Street Lighting Design - Electrical DesignDocument13 pagesStreet Lighting Design - Electrical DesignHerman DamanikNo ratings yet
- Whitemud Freeway Speed Limit ChangesDocument2 pagesWhitemud Freeway Speed Limit ChangespkGlobalNo ratings yet
- YonasMinalu Mscthesis PDFDocument84 pagesYonasMinalu Mscthesis PDFAnonymous modfBhExS100% (1)
- Highway Link Design - 2002Document70 pagesHighway Link Design - 2002Welly Pradipta bin MaryulisNo ratings yet
- Nota Kursus Lampu JalanDocument142 pagesNota Kursus Lampu JalanMohammad Rafnie Arif100% (1)
- Difference Between British English and American EnglishDocument7 pagesDifference Between British English and American EnglishIchraf KhechineNo ratings yet
- Highway Development and PlanningDocument10 pagesHighway Development and PlanningRufa May Auingan YbiasNo ratings yet
- Traffic and Revenue Forecasting For The Dhaka-Chittagong Expressway: Distributed Values of Time and Vehicle-Specific Volume-Delay FunctionsDocument19 pagesTraffic and Revenue Forecasting For The Dhaka-Chittagong Expressway: Distributed Values of Time and Vehicle-Specific Volume-Delay FunctionsRichard Di BonaNo ratings yet
- Drivers TestDocument100 pagesDrivers TestcrashtestdummyX2100% (1)
- Project ManaggementDocument5 pagesProject ManaggementOwais KadiriNo ratings yet
- Project Reference Catalogue: Balanced Cantilever BridgesDocument26 pagesProject Reference Catalogue: Balanced Cantilever BridgesRaymond Sent75% (4)
- 34 - Robatsch ROAD SAFETY IN TUNNELS WITH Uni-And Bidirectional TrafficDocument7 pages34 - Robatsch ROAD SAFETY IN TUNNELS WITH Uni-And Bidirectional TrafficPJNo ratings yet
- Cdin 4Document15 pagesCdin 4Alma EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Highway Geometric Design (CE 532) Handout Part 1Document18 pagesHighway Geometric Design (CE 532) Handout Part 1Jeewana MeegahageNo ratings yet
- Functional Classification of RoadsDocument6 pagesFunctional Classification of RoadsOshada AttygalleNo ratings yet