Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internet Electronics Internet Connectivity Sensors
Internet Electronics Internet Connectivity Sensors
Uploaded by
Engr Raheel SindhiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet Electronics Internet Connectivity Sensors
Internet Electronics Internet Connectivity Sensors
Uploaded by
Engr Raheel SindhiCopyright:
Available Formats
The Internet of things (IoT) is the extension of Internet connectivity into physical devices and
everyday objects. Embedded with electronics, Internet connectivity, and other forms of hardware
(such as sensors), these devices can communicate and interact with others over the Internet,
and they can be remotely monitored and controlled.[1][2][3][4]
The definition of the Internet of things has evolved due to convergence of multiple technologies,
real-time analytics, machine learning, commodity sensors, and embedded systems.[5] Traditional
fields of embedded systems, wireless sensor networks, control
systems, automation (including home and building automation), and others all contribute to
enabling the Internet of things. In the consumer market, IoT technology is most synonymous with
products pertaining to the concept of the "smart home", covering devices and appliances (such
as lighting fixtures, thermostats, home security systems and cameras, and other home
appliances) that support one or more common ecosystems, and can be controlled via devices
associated with that ecosystem, such as smartphones and smart speakers.
The IoT concept has faced prominent criticism, especially in regards
to privacy and security concerns related to these devices and their intention of pervasive
presence.
You might also like
- Internet of Things - WikipediaDocument208 pagesInternet of Things - WikipediaDebajyoti DattaNo ratings yet
- EmgTech Chapter 4Document30 pagesEmgTech Chapter 4kevin 11No ratings yet
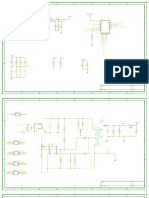
- Sonoff 4ch Pro-SchedmaticDocument4 pagesSonoff 4ch Pro-SchedmaticEngr Raheel Sindhi100% (2)
- Cyber and Physical Security VulnerabilityDocument17 pagesCyber and Physical Security VulnerabilityِAl TuraihiNo ratings yet
- A Survey On IoT Architectures, Protocols, Applications, Security, Privacy, Real-World Implementation and Future TrendsDocument6 pagesA Survey On IoT Architectures, Protocols, Applications, Security, Privacy, Real-World Implementation and Future TrendsirvanNo ratings yet
- Home Automation System Using Internet of Things: AbstractDocument9 pagesHome Automation System Using Internet of Things: AbstractPartha Parida0% (1)
- Updated Notes Unit-1Document23 pagesUpdated Notes Unit-1Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Synopsis IOT and EdgeDocument25 pagesSynopsis IOT and EdgeMandeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text Documentsmartautosystem307No ratings yet
- Vyshnavi NewDocument5 pagesVyshnavi NewUCET GUNTURNo ratings yet
- IotDocument6 pagesIotBhavanthi KarthikNo ratings yet
- Security Testing Methodology of IoTDocument5 pagesSecurity Testing Methodology of IoTHa NhNo ratings yet
- History: Ieee SpectrumDocument3 pagesHistory: Ieee SpectrumShubham ThoratNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Iot Based Home Security System 1.1Document1 pageIntroduction To Iot Based Home Security System 1.1Kyaw Yair LwinNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Security Requirements For The Internet of Things: A Systematic ApproachDocument35 pagesSensors: Security Requirements For The Internet of Things: A Systematic ApproachGeorges karamNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things - WikipediaDocument68 pagesInternet of Things - WikipediaAbdulrasheed Ibrahim OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- IEEE SpectrumDocument5 pagesIEEE SpectrumafroxxxNo ratings yet
- Iot NotesDocument47 pagesIot NotesArnold del surNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument51 pagesInternet of ThingsamanNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument34 pagesInternet of ThingsEd Cornejo MaytaNo ratings yet
- IOTDAVIDNINADocument2 pagesIOTDAVIDNINAdavidgg0165No ratings yet
- Final VersionDocument11 pagesFinal Versionapo panagNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument7 pagesInternet of ThingsKushal ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Emerging AssignmentDocument2 pagesEmerging AssignmentAmanuel MarkosNo ratings yet
- Multilingual Home AutomationDocument10 pagesMultilingual Home AutomationRaghavendra TalekarNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things (Iot) : Definitions, Challenges and Future ApplicationsDocument7 pagesInternet of Things (Iot) : Definitions, Challenges and Future ApplicationsKHUSHAL CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Better Source NeededDocument1 pageBetter Source NeededsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument68 pagesInternet of Thingsgilvantalosig0618No ratings yet
- IOT AssignmentDocument8 pagesIOT Assignmentsoftware khanNo ratings yet
- PS 22 - Akhilesh 2022Document18 pagesPS 22 - Akhilesh 2022einstein.ortiz27No ratings yet
- Better Source NeededDocument1 pageBetter Source NeededSaikumarVavilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesLecture Notesgiordan24aNo ratings yet
- Touqeer2021 Article SmartHomeSecurityChallengesIss 2Document37 pagesTouqeer2021 Article SmartHomeSecurityChallengesIss 2negin mNo ratings yet
- CCS Unit V Notes 2Document24 pagesCCS Unit V Notes 2Vasantha Kumar VNo ratings yet
- IoT Unit IDocument72 pagesIoT Unit Iaakaankshaagupta20No ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument14 pagesInternet of Thingssol therese cairelNo ratings yet
- Internet of The Things-IOTDocument13 pagesInternet of The Things-IOTmaniNo ratings yet
- Lu y Xu - 2019 - Internet of Things (IoT) Cybersecurity Research ADocument13 pagesLu y Xu - 2019 - Internet of Things (IoT) Cybersecurity Research AW. Eduardo Castellanos H.No ratings yet
- Security Threats in Iot: Vision, Technologies & Research ChallengesDocument10 pagesSecurity Threats in Iot: Vision, Technologies & Research ChallengesSujatha KNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 OrganizedDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1 OrganizedJayanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Interne TOF Things: Group 3: Do Hoang Phong Tran Hong Phuc Doan Trung Quyen Do Khanh Toan Teacher: Ngo Thi Mai LoanDocument12 pagesInterne TOF Things: Group 3: Do Hoang Phong Tran Hong Phuc Doan Trung Quyen Do Khanh Toan Teacher: Ngo Thi Mai LoanToàn Đỗ KhánhNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things (IoT) Taxonomy of SecurityDocument6 pagesInternet of Things (IoT) Taxonomy of SecurityKISHORE C100% (1)
- IOT Smart City Ignou PDFDocument19 pagesIOT Smart City Ignou PDFVikram PatelNo ratings yet
- Internet of Thing1Document5 pagesInternet of Thing1ehoxha22No ratings yet
- Internet of Things: Security Vulnerabilities and Challenges: George HadjichristofiDocument8 pagesInternet of Things: Security Vulnerabilities and Challenges: George Hadjichristofimadhu manjuNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things Security, Device Authentication and Access Control A ReviewDocument11 pagesInternet of Things Security, Device Authentication and Access Control A Reviewfalconinayat0% (1)
- Chapter Four Internet of Things (Iot) : Iot Services+ Data+ Networks + SensorsDocument14 pagesChapter Four Internet of Things (Iot) : Iot Services+ Data+ Networks + SensorsAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Smart Home: Security and PrivacyDocument18 pagesAssessment of Smart Home: Security and Privacybez plagijataNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Smart Home: Security and PrivacyDocument18 pagesAssessment of Smart Home: Security and PrivacyFidojahfal PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Iot PDFDocument13 pagesIot PDF20230036No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4nuri mohammedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Iot Chapter 2 NotesDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Iot Chapter 2 NoteskpadmajaNo ratings yet
- Convenience and Security Implications of IoT in Smart AppliancesDocument12 pagesConvenience and Security Implications of IoT in Smart ApplianceswilberNo ratings yet
- Iot Model Exam AnswerDocument5 pagesIot Model Exam AnswerJoshua . SNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Report M BochenkovaDocument16 pagesSmart Home Report M BochenkovaMarina BochenkovaNo ratings yet
- Societal Change and Transformation by Internet of Things (IoT)Document7 pagesSocietal Change and Transformation by Internet of Things (IoT)AI Coordinator - CSC JournalsNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.4 - Internet of Things and Data Science PDFDocument11 pagesTopic 4.4 - Internet of Things and Data Science PDFNight WolfNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Iot ("Internet of Things")Document50 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To Iot ("Internet of Things")krishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document109 pagesUnit 1Rithik BarsalNo ratings yet
- Lal Shahbaz Motel WhatsappDocument2 pagesLal Shahbaz Motel WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Shahjahan Restaurant Rest House WhatsappDocument2 pagesShahjahan Restaurant Rest House WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Ranikot Resort WhatsappDocument2 pagesRanikot Resort WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Sambara Inn WhatsappDocument2 pagesSambara Inn WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Keenjhar Lake WhatsappDocument2 pagesKeenjhar Lake WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Laki Rest House WhatsappDocument2 pagesLaki Rest House WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Kai Rest House WhatsappDocument2 pagesKai Rest House WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet
- Haleji Lake Resort WhatsappDocument2 pagesHaleji Lake Resort WhatsappEngr Raheel SindhiNo ratings yet