Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus PDF
Uploaded by
Prashant JagdaleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus PDF
Uploaded by
Prashant JagdaleCopyright:
Available Formats
w.e.
f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CURRICULUM FOR
ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN
INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
(IT)
(State Government Approved Short Term Diploma Course)
Any Science Graduate / Graduate in Medical Science / BDS /
OT.PT. / Graduate in Veterinary Science or its Equivalent
ELIGIBILITY from a recognized Statutory University / Board or Degree /
Diploma in Engineering / Technology / Diploma in Fire
Service Engineering.
DURATION One Year
SCHEME I
PATTERN Full Time - Yearly
(To be implemented from the Academic Year 2017 – 2018)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL
EDUCATION, MUMBAI
(AUTONOMOUS)
ISO 9001-2008 Certified
49, Kherwadi, Bandra (East), Mumbai – 400 051
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
A. INTRODUCTION OF PROGRAMME
Modern life is dependent on things provided by Industry. The curriculum honours
expectations of the Industry. The Industries employ the successful candidates in the
Management Cadre in Safety, Health and Environment at the level of Safety Professionals as
required under the Environment Protection Act, enlisting Legislation and other Acts in
various capacities like Consultant, Expert Safety Auditor under the Statutes of the
Government of India and Govt. of Maharashtra. supervisory/Inspector cadre, as management
cadre which has respect in the society.
This curriculum is designed to develop professionals who demonstrate not just strong
problem solving acumen and analytical skills but also great interpersonal skills. The student
of this course imbibe in them a sense of ownership towards the business and the society at
large. Curriculum through this course gives insights for managing Safety, Health &
Environment in industries and this helps to develop safe work culture in industries & in
societies.
The aims of this course are:
To induce lifelong learning knowledge skills, attitudes for social & personal development.
1) To provide trained Human Resource.
2) To provide leadership qualities.
3) To create awareness of “The Quality of Life Protection” through Safety, Health and
Environment.
4) To create awareness of hazards & operational hazards.
5) To assist in development of new methods & process of Safety, Health and Environment
skills and analytical techniques.
6) To develop managerial abilities and analytical skills ,training, communicate with the
community and interaction with government and statutory authorities
7) To train the people concerned.
B. APPROACH TO DESIGN OF REVISED CURRICULUM OF MAHARASHTRA
STATE GOVERNMENT APPROVED SHORT TERM DIPLOMA AND
ADVANCE DIPLOMA PROGRAMMES.
The Project is taken up to revise the curriculum which was implemented since 2008-09. The
methodology is to assess the present Industry/Society needs, revisit the earlier curriculum and
make suitable changes.
The programmes are specialized and shall impart essential skills to generate self-employment
or provide industry-ready manpower.
In the present phase, four groups are identified for revision for implementation w.e.f. 2017-
18.
Each Programme shall have Coordinator, Co-coordinator and Subject experts who will work
for developing curriculum with the following objectives.
1. Identify sectors where the students can seek employment.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 1 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
2. Job Profile/ Responsibilities.
3. Skills and Outcome expected.
4. Revisit earlier curriculum for identifying gaps.
5. Revise Eligibility Criteria (if needed).
6. Internship of Six Weeks for courses of 2/3 years duration.
7. Skill based Curriculum shall be a good blend of Theory, Practicals, Case Studies,
Industrial Visits, Mini Projects, Major Projects.
8. Focus shall be on Skill development and outcomes.
9. Thrust should be on Hands-on experience.
10. Changes based on Industry and futuristic needs.
C. SECTORS IDENTIFICATION
Chemical, Petro-chemical, Engineering, Textile, Construction, Pharmaceutical, Food &
Paint Industries in which Safety, Health & Environment (SHE) matters involving and
activity is carried out for raw, intermediate and finished products, designs and processes
including Transportation.
To start own Consultancy / Advisory Services, Auditing of SHE and Co-ordinate with
approval By and MSPCB (Maharashtra State Pollution Control Board) DISH, MOE,
F&CC to carry out Analysis as per the recommended Standards for various products and
as well as for air, water and industrial effluents.
D. JOB PROFILE
Safety Steward
Safety Instructor
Safety Supervisor
Safety Officer
Safety Manager
E. SKILLS and OUTCOME
Will reduce the industrial accidents.
Build Safe Work Culture
Improve the production and efficiency
Motivate the employees
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 2 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
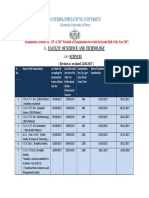
F. LIST OF WORKSHOPS CONDUCTED
WORKSHOP DATE OF WORKSHOP VENUE
NO.
1 21st April 2017 Conference Hall, MSBTE, Mumbai
2 26th April 2017 Conference Hall, Govt. Polytechnic,
Mumbai
27th April 2017 Conference Hall, MSBTE, Mumbai
29th April 2017 V.P.M’s Polytechnic, Thane
3 5th and 6th May 2017 V.P.M’s Polytechnic, Thane
4 11th, 12th and 13th May 2017 V.P.M’s Polytechnic, Thane
5 16th and 17th May 2017 V.P.M’s Polytechnic, Thane
G. LIST OF EXPERTS IDENTIFIED
SR. NAME OF EXPERTS WORKED AS DESIGNATION AND
NO. NAME OF INSTITUTE
1 Prof. D.K. Nayak Chief Coordinator Principal, V.P.M.’s
Polytechnic, Thane
2 Prof. V.R. Jadhav Deputy Secretary, CDC Deputy Secretary, CDC
Section, MSBTE, Mumbai Section, MSBTE, Mumbai
3 Mrs. K.Y. Kale Assistant Secretary, CDC Assistant Secretary, CDC
Section, MSBTE, Mumbai Section, MSBTE, Mumbai
4 Mr. B.B. Dethe Coordinator Chief Manager- Corporate
EHS, Piramal Enterprises
Ltd. Mumbai
5 Mr. A.K. Kulkarni Subject Expert Ex Corporate Head - SHE,
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co.
Ltd. – Vikhroli, Mumbai
6 Mr. H. Vishwanathan Subject Expert Consultant, Meenakshi
Safety Consultancy
Services
7 Mr. A.A. Raichur Subject Expert Technical Advisor,
National Safety Council,
Navi Mumbai
8 Mr. P.S. Sen Subject Expert Ex Maintenance and
Safety Executive, Khatau
Mills Limited, Byculla
9 Mr. A.K. Gupta Subject Expert Consultant, Safeways
Safety Consultant
10 Mr. A.S. Karmarkar Subject Expert Hon. Joint Secretary,
National Safety Council -
Maharashtra Chapter,
Mumbai
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 3 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. NAME OF EXPERTS WORKED AS DESIGNATION AND
NO. NAME OF INSTITUTE
11 Mr. V.V. Wani Subject Expert Dy. General Manager,
Reliance Infra Mumbai
Transmission
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 4 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, MUMBAI
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
DURATION OF COURSE : ONE YEAR DURATION : 32 WEEKS
YEAR : FIRST WITH EFFECT FROM 2017-18
PATTERN : FULL TIME - YEARLY SCHEME : I
TEACHING EXAMINATION SCHEME
SR. SUB SCHEME SW
SUBJECT TITLE PAPER TH PR OR TW TOTAL
NO. CODE ( )
TH TU PR HRS. MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN
1 Industrial Safety Management 02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
2 Safety in Engineering Industries 02 -- 02 03 100 50 -- -- 50# 25 -- -- 150
3 Construction Safety 02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
4 Chemical and Process Safety Management 02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
5 Environmental Management 02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
100
Quality Control in Occupational Safety &
6 Health
02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
Safety, Health and Environmental
7 Legislation
02 01 -- 03 100 50 -- -- -- -- -- -- 100
Industrial Hygiene and Occupational
8 Health
02 -- 02 03 100 50 -- -- 50# 25 -- -- 100
9 Project -- -- 04 -- -- -- -- -- 50# 25 50@ 25 150
TOTAL 16 06 08 -- 800 -- -- -- 150 -- 50 -- 1000 100
STUDENT CONTACT HOURS PER WEEK: 30 HRS.
THEORY AND PRACTICAL PERIODS OF 60 MINUTES EACH.
Total Marks : 1100
@ Internal Assessment, # External Assessment, Ø Common to All Conventional Diploma, #* Online Examination, No Theory Examination.
Abbreviations: TH-Theory, TU- Tutorial, PR-Practical, OR-Oral, TW- Term work, SW- Sessional Work
Conduct two class tests each of 25 marks for each theory subject. Sum of the total test marks of all subject are to be converted out of 100 marks as sessional work.
Progressive evaluation is to be done by subject teacher as per the prevailing curriculum implementation and assessment norms
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 4 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : INDUSTRIAL SAFETY MANAGEMENT
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
To inculcate the Management Principles and Techniques for Good Practices of Safety, Health
and Environment (SHE).
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 5 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
To develop management skills and understand basic functioning of Safety, Health
Application & Environment Management.
Organising, Compilation Application of Development of
Procedures Directing & and Collation Standards Training
Monitoring for SHE Programme
Statutory Analysis and Principles of Training Methods
Principles
Enactments Programming Accident and Strategy
Prevention
Data Theories and C.B.T.
Concepts Strategic Planning Information Models of Competence
System Accident Building
Prevention Techniques
Facts Management Accident, Injury, Education and
Planning Information Unsafe Condition Training
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 6 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Introduction:
Management Principles, Levels of Management-
Lower, Middle and Top, Types of Management –
Line and Staff, Authority, Accountability and
Responsibility of Management. Span of
Management, Delegation and decentralization of
authority.
Role of Management in Industrial Safety:
Planning for Safety- Definition, Purpose, Nature,
Scope and Procedure. Range of planning, Types of
plans, Management By Objectives (MBO), Policy
formulation and implementation
Organising for Safety :
1 20 14
Definition, need, nature and principles. Organising
for Safety, Health and Environment, Organisation
structure, functions and responsibilities.
Directing Safety :
Definition, process, principles and techniques,
Leadership – Styles, Role, functions and attributes of
a good leader.
Communication:
Purpose, process, types and channels of
communication Process. Group-dynamics and Team
building.
National Policy on Safety, Health and
Environment at Workplace.
Safety - Education and Training :
Element of training cycle, Training Need Assessment
(TNA). Techniques of training, design and
development of training programs/module. Training
2 16 10
methods and strategies, Types of training. Evaluation
and review of training programs. Competence
Building Technique (CBT), Role of Multi-Media,
Communication, Applications of Computers.
Employee Participation in Safety :
Purpose, areas of participation, methods. Role of
trade union in Safety Health and Environment
Protection, Safety Committee - Structure and
functions. Tool Box Talks, Safety Kaizen, One Point
3 16 10
Lessons, etc. Safety Promotion and Safety Awards
(National, State Level and unit level) and Suggestion
Schemes, Safety Competitions, Safety Incentives
Publicity Schemes, Audio Visual Publicity, other
Promotional Methods.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 7 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Behavior Based Safety (BBS) :
Human behavior - Individual differences, behavior as
function of self and situation, perception of danger
and acceptance of risk, knowledge, and responsibility
4 vis-a-vis safety performance, theories of motivation
16 10
and their application to safety, role of supervisors and
safety departments in motivation.
Conflict & Frustration :
Identification of situations leading to conflict and
frustration and techniques of management.
Management Information System (MIS):
Sources of information on Safety, Health and
Environment. Compilation and collation of
information, Analysis & use of modern methods of
5 16 10
programming, storing and retrieval of information for
Safety, Health and Environment. Computer
utilization in Safety, Health and Environment (SHE)
and SHE software development.
Accident Prevention :
Principles of Accident Prevention/Program/Plan,
Theories of Accident Causation, Need of Accident
Prevention, Causes of Accident, Accident Prevention
Models - Heinrich Theory, Frank Bird Model,
6 Domino Model. Motivation for Safety, Accident 16 10
Proneness, Accident Cost-Direct & Indirect. Role of
Supervisor in Accident Prevention, Role of
Workmen, Role of Management, Role of Trade
Union, Role of Factory Medical Officer, Role of
Safety Officer.
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 Training Module For Induction Training
2 Training Module for Accident Prevention
3 Preparation of Model Occupational Health & Safety Policy
4 Annual Training Calendar
5 Preparation of MIS Form
6 BBS Observation Form
7 Tool Box Talk on Eye Protection / Head Protection
8 Any one Safety Kaizen
9 One Point Lesson
10 Accident Prevention Programme
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 8 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 Industrial Accident By H.W. Heinrich, Dan McGraw-Hill Book
Prevention Petersen, and Nestor Roos Company,
New York / New Delhi
2 Accident Prevention --- National Safety Council
Manual (Vol. 1 & 2) 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912135- Itasca, Illinois 60143
8) (USA)
3 Accident Prevention --- National Safety Council
Manual for Industrial 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
Operations (ISBN: 978- Itasca, Illinois 60143
08-7-912024-5) (USA)
4 Supervisors’ Safety --- National Safety Council
Manual 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912288- Itasca, Illinois 60143
1) (USA)
5 Loss Control Management By Frank E. Bird, Jr. & Institute Press, Loganville,
Robert G. Loftus Georgia (USA)
(ISBN: 0-8247-8479-0)
6 Management Guide to By Frank E. Bird, Jr. Institute Press, Loganville,
Loss Control Georgia (USA)
7 Techniques of Safety By Dan Petersen (ISBN: McGraw-Hill Book Co.
Management 978-18-8-558139-6) Ltd., New York, N.Y.
(USA)
8 Industrial Safety and By A.K. Gupta Laxmi Publications,
Environment New Delhi
9 Industrial Safety: By K.T. Kulkarni Pune
Concepts and Practices VidyarthiGrihaPrakashan,
1786, Sadashiv Peth, Pune
- 411 030
10 A Course in Industrial By K.U. Mistry NKM Publishers,
Safety Ahmedabad
11 ‘Method for computation --- IS:3786 – 1983
of Frequency and Severity Indian Standards
Rates for Industrial Institution, New Delhi
Injuries and Classification
of Industrial Accidents’
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 9 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : SAFETY IN ENGINEERING INDUSTRIES
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 -- 02 03 100 -- 50# -- 150
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
Acquire the Knowledge, Skill and Mechanism of functioning of machine, tools and safe use
of the same.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 10 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Engineering Techniques being applied to use of machines and materials
Application in safe manner.
Ergonomics
Procedures Proper Work Permit Safe use of
of Machine Application
Design and Tools and
Guarding and
Procedure Gadgets etc.
Enforcement
Operation
and Guarding Centralised
Principles In-built Safety and Personal
Safety System Tool Issue
System
Prevention
Preventive Prevention
Safety and Control
Concepts Maintenance and Handling
of Accidents
Use of Handling of
Working at Hazards Materials
Facts Machines
different sites
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 11 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Machine Operation and Guarding :
Principles in machine guarding. Ergonomics of
machine guarding. Type of guards, their design and
selection. Guarding of different types of machinery
including special
Precautions for wood working, paper, rubber and
printing machinery, machine, tools etc. Built-in-
safety devices, maintenance and repairs of guards,
incidental safety devices and tools. Concept of zero
access guarding.
Safety in the use of Machines :
Safety in the use of power presses (all types),
shearing, bending, rolling, drawing, turning, boring,
1 20 14
milling, shaping, planing, broaching, plating,
grinding, CNCs, robotics, etc.
Safety in the use of Hand Tools and Power Tools :
Main Causes, Prevention and Control of accidents in
the use of hand and power tools. Centralized and
personal tool issues System. Purchase, storage and
supply of tools. Inspection, maintenance and repair of
tools. Portable power tools and their selection,
inspection, maintenance, repair and safe use. Non-
sparking tool.
Hazards at Workplace:
Welding, Gas Cutting, Brazing, Soldering, buffing
and polishing hazards and their preventive measures.
Material Handling and Storage:
Manual: Kinetics of manual handling. Maximum
loads that could be carried. Lifting and carrying of
objects of different shapes, size and weight. Safe use
of accessories for manual handling Storage of
materials. Safety in stacking and un-stacking, floor
loading conditions. Layout condition for safety in
storage, ergonomics of manual handling and storage.
Mechanical: Lifting machinery, lifts and hoists;
2 16 10
design, use and care, signaling, inspection and
maintenance. Safety in design and construction,
operation, inspection and maintenance of industrial
trucks, lifting tackles and loose gears, conveyors.
Safety features, safe locations, testing, inspection and
maintenance of lifting tackles, safe working load for
all mechanical material handling equipment. The
competent persons in relation to safety legislation -
duties and responsibilities.
Plant Layout Design and Housekeeping :
3 Plant layout, design and safe distance. Need for 16 10
planning and follow-up. Safety and good house-
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 12 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
keeping. Typical accidents due to poor house-
keeping. Disposal of scrap and other trade wastes.
Prevention of spillage. Marking of aisles space and
other locations.
Use of colour as an aid for good housekeeping.
Cleaning methods. Benefits of good housekeeping.
‘5S’ system.
Inspections and check-lists. Safety Check list for
buying new machinery for the plant. Role of preventive
maintenance in safety and health. Importance of
standards and codes of practice for plant and
equipment.
Electrical Hazards At Workplace
Hazards of electrical energy. Safe limits of
amperages, voltages. Safe distance from lines.
Capacity and protection of conductor. Joints and
connections. Means of cutting off power. Overload
and short circuit protection. No load protection. Earth
fault protection. Earth insulation and continuity tests.
Earthing Standards. Protection against voltage
fluctuation.
Hazards arising out of 'borrowed' neutrals. Types of
protection for electrical equipment in hazardous
atmosphere. Hazardous area classification. Criteria
4 for selection, installation, maintenance and use of 16 10
equipment in hazardous area.
Static Electricity:
Introduction, Electro-Static charge. Electro Static
dissipaters. Electro Static hazards and their control.
Earthing and bonding. Recommended earthling
resistance.
Lightning Arrestors :
Definition, lightning splash, lightning strokes,
lightning protection systems. Characterization of
health effects of lightening stroke (electrical effects,
side flashers, thermal effects, mechanical effects.
Function of lightning arrestors.
Safety in Engineering Industries :
Engineering Industries, Automobile Manufacturing
activity like pattern making, melting, moulding,
machining, forging, chipping, grinding, Metallurgy:
Ferrous and Non Ferrous Industry Foundry, Steel
5 Plant. Hazards associated with Process of melting 16 10
(furnaces), casting, foundry, forging and hot & cold
rolling operations and their control measures
Hazards at workplace :
Mechanical hazards, Noise/Vibration Hazards, Fire
Hazards, Physical, Toxic and Chemical Handling
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 13 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Hazards
Safety in Textile Industry: Processes and Various
hazards in textile industries and their control
measures.
Safety in Agro-Industry / Sugar Industry :
Processes and Various hazards in agro/sugar
industries and their control measures.
Safety in Docks Operations:
Hazards in Handling of cargo – On Board
Operations, On Shore and along Shore Operations,
Warehouse Operations, Dangerous Goods, Container
operations, Lifting appliance, Loose Gears and wire
ropes, Responsibility of different agencies for safety
and health involved in dock work.
Destructive Testing, Non Destructive Testing and
Heat Treatment :
Break load test, Tensile Stress Load testing, etc.
NDT-testing, significance and limitations. Types of
NDT – Die Penetration Radiography, Ultrasound,
Magnetic Particle Methods, Eddy-Current Method,
Thermography etc
Safety in IT and Electronic Industry and Service
Sector
6 16 10
Various hazards in IT, Electronic, related Service
sectors and their control measures. Ergonomic
hazards / Musculoskeletal Disorder (MSD), electrical
hazards, physical hazards, radiation hazard, fire
hazards, Computer Vision Syndrome (CVS), Carpal
Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), Repetitive Strain Injury
(RSI), Various hazards in Malls, Cinema Halls,
Parking Lots and Commercial Sectors, etc. -
Preventive and Control measures.
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF PRACTICAL ASSIGNMENTS / CASE STUDIES (Minimum 8)
SR. TOPIC
NO.
1 Design of a machine guard
2 Development of a plant Layout
3 Preparation of a safety Inspection Check list for Dock Area
4 Prepare Tool Box on Good Housekeeping
5 List out the Hazards at IT / Electronic Industries
6 Preparation of Housekeeping Checklist
7 List out the Hazards at Engineering Industries
8 Preparation of a safety Inspection Check list for Housekeeping
9 Development of a SOP for any one machine
10 List out the Hazards at Textile Industries
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 14 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 Safety code for Scaffolds -- IS : 3696 , (Part II) - 1966
and Ladders, (Part II) –
Ladders
2 1979 Glossary of terms -- IS 2363
relating to wire ropes
3 1977 Steel wire ropes for -- IS 2266
general engineering
purposes
4 1964 Wire rope slings and -- IS 2762
sling legs
5 1977 Steel wire -- IS 2365
suspension ropes for lifts,
elevators and hoists.
6 1967 Code of practice for -- IS 3973
the selection, installation
and maintenance of wire
ropes
7 Accident Prevention -- National Safety
Manual for Industrial Council444, North
Operations Michigan Avenue,
Chicago, I 11 – 60611
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 15 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
The subject paper is based for various industries for which National classification is
considered to be based for selection of new industries. Since no. of industries under
classification is very large, the scope is limited to only certain industries.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 16 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Engineering Techniques being applied to use of machines and
Application materials in safe manner.
Ergonomics
Procedures Proper Work Permit Safe use of
of Machine Application
Design Tools and
Guarding and
and Gadgets etc.
Procedure Enforcement
Operation In-built Safety Centralised and
Principles and Safety Personal Tool
System
Guarding Issue System
Preventive Prevention Prevention and
Safety and Control of
Concepts Maintenance
Handling Accidents
Handling of
Working at Hazards Materials
Facts Use of different
Machines sites
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 17 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
The industries have been selected keeping in view of degree of risk frequency and severity of
accidents caused in the specific industries and the safety, health & environment measures to
be taken.
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Safety in Construction Industry :
Hazards in Construction Sector and their
preventive measures - Basic philosophy,
peculiarities and parameters governing the safety in
construction - site planning and design layout, safe
access, good housekeeping, safety in the use of
construction machinery and transport equipment,
signs and indication liaison for safety with local
1 authorities, structural soundness. 20 14
Safety in the use of construction machinery.
Heavy/Long Items. Earth Moving equipments,
Railway wagons, motor trucks, Materials Vehicles
etc., Hazardous Materials, Material handling
equipments, Seismic structural soundness and
Structural stability.
Good Safety Practices / Initiatives in Construction
Safety.
Types of Construction Activity:
Working below ground level: Excavation, drilling
and blasting pneumatic, trenching, Excavation
equipment, shoring, strutting, tunneling, piling and
Safety in using and operating machinery and
equipment relating to the above works. Foundations
2 : Plant & Machinery and Structure 16 10
Working at height: Scaffolding, shuttering / form
work, ladders, concrete, cofferdams and special
operation connected with irrigation work. Safety in
use and portion of related machinery and equipments.
Safety on working on fragile roof. Precautions on
Tower Cranes, Temporary installation and structures.
General Safety Measures:
At Ground Level: Housekeeping, Electrical
Hazards, Handling and Storage of construction
material at site.
Safety precautions in storage handling and staking of
3 material. 16 10
Underwater portions: Well sinking, caissons
underwater concreting, cofferdams and special
operations connected with irrigation work. Safety in
use of machinery and equipments related to
underwater portions.
Special Works: High rise buildings, bridges and
4 tunnels, roads, railways, asphalting, pneumatic 16 10
caissons, electrical installations and lifts. Safety in
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 18 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Prevention and Protection at Work Site including the
collapsing of the structure.
Project Management in Constructions Safety:
Introduction, Manpower and material utilization-
equipment and tools.
Safety in use and handling of explosives: Open cost
machinery, quarrying.
Special precautions for works of Engineering
construction: like distilling / fractionating columns,
5 chimney, silos-oil and gas installations, transmission/ 16 10
communication lines, Cooling towers, cable car
installations, air fields.
Safety in Demolition Operations: Planning and
Permit, sequence of demolition, Safety Precautions to
6 16 10
be taken for and during demolition carrying out
repairs, additions and alterations.
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 Checklist for pneumatic hammer working
2 Development of a checklist for elevated platform
3 List out the Hazards for working at height
4 Development of Tool Box Talks for Construction Activity
5 JSA for excavation Activity
6 Prepare Safety Rules for Safe Construction activity
7 Checklist for Shuttering and shoring working
8 List out the Hazards in excavation in the premises of chemical unit
9 Prepare work permit for working at height on fragile roof
10 List out the statutory provisions for construction activity
11 Prepare PPE Matrix for working at Construction site-activity wise
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 The Chain Testers’ -- Chain Testers Association
Handbook of Great Britain, 430
Barking Road, London.
2 Rigging Manual -- Construction Safety
Association of Ontario,
Ontario, Canada
3 Handbook of Rigging for W.E. Rossnagel McGraw- Hill Book Co.,
Construction and 1221, Avenue of the
Industrial Operations Americans, New York,
N.Y. 10020
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 19 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
4 Report No. 67 (1945) N.C. Weston Great Britain Medical
Research Council
Industrial Heath Research
Board
5 Illumination Engineering H.R Blackwoll --
Vol. 54,
P-317-353, 1959.
6 Ind. J. of Tech. Vol. 2 No. V R & B.K.S --
3, P. 102-106, 1964
7 Forthlight roofs V.R & B.K.S Ind. J. of Tech. Vol. 3. No.
3, Pg. 72-74, 1965
8 Rigging Manual -- Construction Safety
Association of Ontario,
Ontario, Canada
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 20 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : CHEMICAL AND PROCESS SAFETY MANGEMENT
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
Study the nature and functions of chemicals, chemical processes, receiving, storage and
handling of chemicals and understand the occupational health, safety and environment
systems to be implemented for sustainable development.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 21 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Prevention and control of fire, explosion, unintended release of flammable/toxic
Application gases and imminent harm to health, community, property and environment
Start-up and Use of Identification UN classification
Procedures shut-down MSDS by of all hazards and safe
procedures training and and control of transportation of
education risks chemicals
Criteria for plant
Properties of Applicable Statutes for siting, layout and
Principles
chemicals standards and storage, instrumentation
codes handling and for process safety
transportation
Safety, Safe operations
Occupational
Concepts Compatibility of protection of and the concern
health and
chemicals occupational for employees
safety-related
health and and community
information
environment
Siting and layout
MSDS for Receive, store,
Facts Chemicals of plants
hazardous handle and
materials transport
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 22 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Process Safety Management (PSM)
Purpose of PSM, its elements and Risk-Based
Process Safety Management (RBPSM): (1) Process
safety culture, (2) Compliance with standards, (3)
Process safety competency, (4) Workforce
involvement, (5) Stakeholder outreach, (6) Process
knowledge management, (7) Hazard Identification
and Risk Assessment (HIRA), (8) Operating
procedures, (9) Safe work practices, (10) Asset
integrity and reliability, (11) Contractor
Management, (12) Training and Performance
Assurance, (13) Management Of Change (MOC),
(14) Operational readiness, (15) Conduct of
operations, (16) Emergency management, (17)
1 Incident investigation, (18) Measurement and 20 14
metrics, (19) Auditing, (20) Management review and
continuous improvement.
Major Industrial Disasters (Case Studies)
Flixborough disaster (1974), Seveso dioxin disaster
(1976), Mexico LPG tank farm fire and explosion
(1984), Bhopal disaster (1984), Sandoz-Basel
disaster (1986), etc.
Enhancing safety in chemical industry
Criteria for siting and layout of chemical plants
Hazardous Area Classification (HAC)
Layers Of Protection Analysis (LOPA)
Instrumentation for safe and efficient operation of
plants
Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
Unit operations and process hazards
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID),
Various unit operations and their associated hazards,
Control, precautions and prevention, specific safety
measures for certain chemical industries like
fertilisers, insecticides/pesticides, chlor-alkali,
2 explosives, paints, petrochemicals, petroleum 16 10
refineries, pharmaceuticals, etc.
Sampling techniques for toxic and flammable
chemicals, pharmaceuticals, etc. Precautions in the
processes and operations involving explosives,
flammables, toxic substances, dusts, gases, vapour
cloud formations and combating
Safe Handling of chemicals
Safety in receiving, storage and handling of
3 chemicals 16 10
Nitrogen blanketing of flammable liquid storage
tanks
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 23 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Use of Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and
understanding the terminology used in MSDS,
Chemical compatibility considerations
Transportation of hazardous materials, Safety
Precautions for transporting hazardous/ toxic/
flammable/explosive/ radioactive substances by all
modes, U.N. classification of dangerous goods
Transfer of chemicals by pipelines within and outside
the installation (aboveground, underground and
submarine), Pigging operation of pipelines including
intelligent pigging, Cathodic protection of
underground pipelines
Safety in plant operation and maintenance
Safe procedures for plant start-up and shut-down,
Pipeline colour coding for identification of contents,
Safety precautions for working on pipelines, Safety
4 16 10
in preventive and emergency maintenance work,
Pressure relief systems and breather valves, Flare
system, Mechanism of Mechanical Failure that lead
to a Loss of containment. Prevention strategy.
Fire and explosion :
Industrial fires, Dispersion modelling, Chemistry of
fire
Classification of fires, Deflagration and detonation,
Unconfined Vapour Cloud Explosion (UVCE),
Runaway reaction and control methods, Boiling-
Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosion (BLEVE),
Common causes of industrial fires, Dust explosion,
factors of pentagon, causes of dust explosions and
controls
Fire protection: Design of building, plant, exits, etc.
for fire safety, Fire-resistance of building materials,
Fire-doors and firewalls, Determination of fire load,
5 16 10
Dow Fire and Explosion Index, Salient features of
fire, explosion and toxicity index
Fire detection and alarm system: Various types of
fire detection and alarm system, Special safety
measures for control of fire and explosion in
handling / processing of flammable gases, liquids,
vapours, mists, solids, dusts and flying.
Fire-fighting systems: Different types of portable
fire extinguishers, their installation, periodic
inspection and operation, Replacement of Halon with
safer substitutes, Fire hydrant system, Fire monitors,
sprinkler system and deluge system, Carbon-dioxide
flooding system, Foam Pourer system
Pressure vessels: Pressure vessels (unfired) codes of
6 16 10
practices governing their safety, Assessment of
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 24 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
reliability of pressure vessels and their testing,
Inspection techniques for plants, reaction vessels,
Checklist for routine inspection; checklist for specific
maintenance,
Pressure System Hazards and Controls : Principle
of pressure system, Pressure, Hazards of steam,
Mechanism of Steam explosion, Properties of Liquid
Petroleum Gas, Liquefaction of gases for bulk
storage under pressure, Pressure system, meaning of
relevant fluids, key components and safety features
of pressure system, Failure of pressure system,
Hazards of overpressure and over temperature in
pressure system,
Corrosion causes and protection
Corrosion and erosion, location, causes inspection
and prevention, Cathodic protection of underground
tanks/pipelines, Sacrificial anode, Protective cladding
and lining
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 Sampling of liquefied flammable gas
2 Safe unloading of a flammable liquid tank-lorry
3 Explain the different types of pressure relief systems provided in your plant
4 Explain the fire-fighting systems provided in your plant
5 Statutory requirements for pressure vessels
6 Working of nitrogen blanketing of a storage tank
7 Sprinkler system for a flammable hydrocarbon storage tank
8 Safety features of LPG tank farm
9 Safety and process control system for a continuous distillation column
10 Preparing a reactor for confined space entry for repair work
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 Risk Based Process Safety -- John Wiley & Sons Inc.,
By Center for Chemical Somerset, NJ (USA)
Process Safety (CCPS),
American Institute of
Chemical Engineers
(AIChE)
(ISBN: 978-0-470-16569-
0)
2 Accident Prevention -- National Safety Council
Manual (Vol. 1 & 2) 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912135- Itasca, Illinois 60143
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 25 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
8) (USA)
3 Accident Prevention -- National Safety Council
Manual for Industrial 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
Operations (ISBN: 978- Itasca, Illinois 60143
08-7-912024-5) (USA)
4 Supervisors’ Safety -- National Safety Council
Manual 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912288- Itasca, Illinois 60143
1) (USA)
5 Prevention of Major -- International Labour
Industrial Accidents Office (ILO),
(ISBN: 92-2-107101-4) Geneva (Switzerland)
6 Loss Prevention in the Frank P. Lees Butterworth-Heinemann
Process Industries (Vol. 1, Waltham, Massachusetts
2 & 3) (USA)
(ISBN: 0-7506-1547-8)
7 Chemical Process Center for Chemical
Quantitative Risk Analysis Process Safety,
(ISBN-13: 978-08-1- American Institute of
690720-5) Chemical Engineers, New
York, N.Y. (USA)
8 Loss Control Management Frank E. Bird, Jr. & Institute Press, Loganville,
(ISBN: 0824784790) Robert G. Loftus Georgia (USA)
9 Management Guide to Frank E. Bird, Jr. Institute Press, Loganville,
Loss Control Georgia (USA)
(ISBN: 978-09-0-912600-1)
10 Techniques of Safety Dan Petersen McGraw-Hill Book Co.
Management Ltd., New York, N.Y.
(ISBN: 978-18-8-558139- (USA)
6)
11 Transport of Dangerous -- United Nations,
Goods – New York, N.Y. (USA)
Recommendations of the
Committee of Experts of
Transportation of
Dangerous Goods
(ISBN: 978-92-1-139136-
7)
12 Agrochemicals Handbook Douglas Hartley and Royal Society of
(ISBN: 978-08-5-186416- Hamish Kidd Chemistry,
7) University of Nottingham
(U.K.)
13 The Merck Index – An -- Merck & Company,
Encyclopedia of Rahway,
Chemicals New Jersey, N.Y. (USA)
(ISBN: 978-1-84973-670-
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 26 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1)
14 Hazardous Chemical Data G. Weiss Noyes Data Corporation,
Book Park Ridge,
(ISBN:081-551072-1) New Jersey, N.Y. (USA)
15 Threshold Limit Values -- American Conference of
for Chemical Substances Governmental Industrial
in Work Environment Hygienists, Cincinnati,
Adopted by ACGIH Ohio (USA)
(Published every year)
16 NIOSH Pocket Guide to -- U.S. Department of Health
Chemical Hazards and Human Services,
By National Institute of Washington, D.C. (USA)
Occupational Safety &
Health (ISBN: 978-15-9-
042586-2)
17 Major Hazard Control: A -- International Labour
Practical Manual Office,
By ILO (ISBN: 978-92-2- Geneva (Switzerland)
106432-9)
18 Industrial Safety and A.K. Gupta Laxmi Publications,
Environment New Delhi
(ISBN: 978-81-3-180454-
4)
19 Industrial Safety: K.T. Kulkarni Pune Vidyarthi Griha
Concepts and Practices Prakashan,
1786, Sadashiv Peth, Pune
- 411 030
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 27 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
This subject deals with environment management system as well as environmental policy,
laws, economics which are very much essential from the point of view of today’s
environmental problems.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 28 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Effective Management of Environmental practices system to protect the
Application
Environment.
Environment Checklists, tag
Management Identification Compliance system, audits,
System of pollutant with statutory pollution
Procedures immediate and requirements control, etc.
basic causes
Environmental
Environment Environment Analysis and
Aspect and
Pollutant Act & Rules investigation
Impact
Principles measurement
Assessment
Environmenta Corrective Non -compliance, Environment
l Aspects action Environment Audits
Concepts
compliance
Environmental Control Measurement Environmental
Facts Impact Measures and Analysis activities at site
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 29 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Environmental Management Systems
EMS Audit- ISO 14001: 2015, Aspects and impact of
Environment Management, Environmental Policy,
Environment Management Programmes,
Administrative Procedure for Environmental
Clearances, Environmental Impact Assessment
(EIA), Process and Methodologies. Air Pollution and
control measures, Water Pollution and control
1 measures, Soil Pollution and Control measures, 20 14
Plastic Pollution & control measures. Ecosystem’ and
the components of ecosystem.
Concept of Common Effluent Treatment Plant
(CETP). Floating aquatic plant system and its design
and operation. Sludge characteristics and disposal
methods –design and operation of sludge drying bed.
Design and operation of treatment plant. Trouble
shooting and trouble free operation.
Environmental Important Regulations :
Water and Air Acts and Rules, Environment
(Protection) Act and Rules, Water Cess Act & Rules,
Public Liability Act & Rules, MSIHC Rule 1989,
Role of State Pollution Control Board under Water
and Air Act.
Environmental Monitoring :
2 Environment related terms/definitions, Principles & 16 10
practices for monitoring of air pollution, water
pollution, solid waste management. Cleaner
technologies. Ambient Air quality, Environmental
Noise Pollution, Stack Monitoring, Effluent
Monitoring, Effluent Treatment Plant-Key process,
Air Pollution Control Devices, Scrubber System,
Parameters of Effluent monitored.
Waste Management :
Statutory Provisions for Bio Medical Wastes, E
waste management, Battery waste management,
treatment, transportation and disposal. Hazardous
Waste Management: Hazardous waste, PCB
3 16 10
requirements and transportation of hazardous wastes,
Manifest, TREM Card, Solid Waste management,
ETP and STP , Management of Hazardous waste by
industries. Four R-Concept: Reduce, Recycle, Reuse
& Reprocessing of Waste.
Global Warming:
Carbon Emission Atmospheric gases, Greenhouse
4 gases 16 10
Kyoto protocol, Acid rains, Effects on Human
beings, wild life and Natures Mitigation measures of
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 30 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Global warming. Deforestation, Tree Plantation, Bio
Diversity, Carbon Credit, Ozone depleting substances
and its impact on the Environment , Restrictions for
development in Coastal Zone as per CRZ regulations.
Energy Conservation :
Key elements of energy management system ISO
50001, use of clean technologies, energy
conservation measures Water Conservation,
Recycling, Harvesting, Power Saving Measures,
5 16 10
Paper Saving measures, Raw Material Saving,
Depletion of natural resources, Renewable Energy,
Life Cycle Assessment, Product Stewardship, Green
Supply Chain, Eco Friendly environment good
practices & innovations, etc.
Sustainability Reporting:
Elements of Sustainability Reports, Purpose &
6 advantages of Sustainability Reporting. GRI G 4 16 10
guidelines, Eco system, concept and structure,
Monitoring and analysis of industrial effluents
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 Preparation of a model EIA
2 Preparation of a model Environmental Policy
3 Checklist for Air monitoring
4 Bio medical waste checklist
5 List out various consent parameters
6 Checklist for a ETP
7 List out various Energy Saving practices
8 List out elements of Sustainability Reporting
9 List out the equipment required for stack monitoring
10 List out various Water Saving practices
11 Assignment of Internal Audit of any unit based on ISO 14001
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 The Environment -- Bare Act
Protection Act & Rule
2 Guide for Environment -- Bare Act
Clearance
3 Environment Impact -- Bare Act
Assessment
4 Standard ISO: 14001 -- ISO
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 31 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
5 Environmental Venugopal Rao Prentice-Hall of India Pvt.,
Engineering New Delhi
6 Environmental Studies N K Uberoi Excel Books, New Delhi
7 Environment Management R K Sapru Ashish Publishing House,
in India New Delhi
8 Environmental Studies Daniel & Krishnaswamy John Willey and Sons Inc,
New Jersey, USA
9 Environmental Health & Nicholas & Madelyn Jaico Publishing House,
Safety Management Mumbai
10 Text book of Erach Bharucha Universities Press (India),
Environmental Studies Hyderabad
11 Environmental Studies R. Rajgopalan Oxford University Press,
New Delhi
12 Wastewater Engineering: Metcalf & Eddy Inc.4th ed. TMGHl, New
Treatment, disposal, Reuse Delhi, 2003.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 32 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : QUALITY CONTROL IN OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
It aims to equip the student with skills and techniques for preventing accidents and
minimising losses.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 33 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Application Effective Quality Control in occupational health, safety and environment
management system to prevent accidents and losses
Quantitative & Checklists, tag
qualitative risk Identification Compliance system, audits,
Procedures assessment and of key factors with statutory total loss control,
control, HAZOP immediate and requirements etc.
study, FMEA, etc basic causes
Hazard
Rules of HSE Principle of Analysis and
identification
and risk minimisation investigation
Principles of injuries and
assessment
techniques frequency of
accidents
Hazard Corrective
identification Reportable and Safety rules,
Concepts &risk action non-reportable safety audits and
assessment Accidents surveys
Risk Appraisal and Measurement Safety
Facts Control and Analysis
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 34 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Safety Appraisal & Control Techniques:
Plant safety rules and procedure, Safe operating
systems, Safety checklist, Safety tag system, Plant
Safety Inspection (PSI), Safety sampling, Safety
surveys and safety tours, Safety inventory system,
Product safety, Total Loss Control (TLC)
1 Permit to work Systems : 20 14
Types of Work Permit – Hot Work, Cold Work,
Working at height, Electric Isolation, Confined Space
Entry, Excavation, Working on Fragile Roof.
Contents of Work Permits, Process for execution and
closure of work permit, Lock Out and Tag Out
(LOTO) system.
Accident / incident / near-miss / dangerous
occurrence reporting, investigation :
Accident/incident reporting and investigation,
purpose and process. Accident Report forms,
Accidents reportable under various statutes like
2 16 10
Factories Act 1948, the BOCW Act 1996, the ESI
Act 1948, etc., Agencies investigating accident.
Identifying the key factors and the immediate and basic
causes, Accident investigation report, Corrective Action
and Preventive Action (CAPA).
Measurement and evaluation of safety
performance
Indian standard IS-3786 and its salient features,
Definition of terminology used- Accident, incident,
near-miss incident, dangerous occurrence, disabling
(lost-time) injury, non-disabling injury, reportable
lost-time injury, non-reportable lost-time injury, days
of disablement (lost time), partial disablement,
temporary partial disablement, permanent partial
disablement, total disablement, temporary total
disablement, permanent total disablement, man-hours
worked/ exposure hours, scheduled charges for
3 16 10
disabilities, statistical period, Restricted Work Case
(RWC), first-aid case, etc.
Safety performance indicators: Frequency Rate
(FR), weighted frequency rate, Severity Rate (SR),
incidence rate, Frequency-Severity Index (FSI), Safe-
T-Score, cost factor, cost severity rate, activity rate,
Fatal Accident Frequency Rate (FAFR), time charges
in the Employee’s Compensation Act, 1923, Leading
& Lagging indicators.
Classification of industrial accidents and special
cases according to IS-3786: Classification of
accidents as per IS-3786:1983, Assessment of special
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 35 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
cases: (1) Inguinal hernia, (2) Back injury, (3)
Aggravation of pre-existing condition, (4)
Aggravation of a minor injury, (5) Cardio-vascular
diseases, (6) Miscellaneous, (7) Other disabilities
Accident/incident analysis: Methods of collating
and tabulating data, Record-keeping, Accident/
incident/ occupational illness trend analysis
Hazard identification, Risk assessment and
control
Hierarchy of hazard control, Hazard Identification
and Risk Assessment (HIRA), HAZard ANalysis
(HAZAN), Maximum Credible Accident Analysis
(MCAA)/ Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)
Hazard identification and risk control approaches
and techniques : Reactive approach: Incident recall
technique (after-the-event approach), Proactive
4 approaches: Critical incident review technique 16 10
(before-the-event approach), Deductive technique,
Inductive technique
Cause/consequence finding techniques
What-if, Fishbone, Why-Why, Root Cause Analysis
(RCA), Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), Event Tree Analysis
(ETA), Cause-Consequence Analysis (CCA),
Management Oversight and Review Technique (MORT),
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Job Safety
Analysis (JSA).
Major Accident Hazards (MAH) Control System :
Major Accident Control, Definition of major accident
hazards, Identification and assessment of MAH
installations, Roles of Government, Management,
Local Authorities and Public, ILO Code of Practice
5 for major accident control. 16 10
Emergency Preparedness and response plans
On-site emergency response plan, Off-site
emergency response plan Mutual Accident Response
Group (MARG), Major accident control system at
local, state, national and international levels
Occupational Health and Safety Audits
Occupational health and safety audits IS-14489:
1998, Different types of audits: Internal, External
audits and Integrated Management System (IMS) IS-
6 16 10
18001:2007/ OHSAS 18001:2007/ISO 45001, Safety
Report as per Rule 10 of the Manufacture, Storage
and Import of Hazardous Chemicals (MSIHC)
Rules, 1989.
TOTAL 100 64
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 36 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 HIRA
2 HAZOP
3 JSA
4 FR,SR and Index
5 Safety Audit element
6 FTA (fault tree analysis)
7 Designing Accident Report Form
8 Designing Accident Investigation Form
9 List any Ten Safety Rules followed in your company
10 Prepare model permit for Confined Space Entry Permit
11 Prepare model permit for Hot Work Permit
12 Prepare model permit for Work at height
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 Industrial Accident H.W. Heinrich, Dan McGraw-Hill Book
Prevention Petersen, and Nestor Roos Company, New York /
New Delhi
2 Accident Prevention -- National Safety Council
Manual (Vol. 1 & 2) 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912135- Itasca, Illinois 60143
8) (USA)
3 Accident Prevention -- National Safety Council
Manual for Industrial 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
Operations (ISBN: 978- Itasca, Illinois 60143
08-7-912024-5) (USA)
4 Supervisors’ Safety -- National Safety Council
Manual 1121, Spring Lake Drive,
(ISBN: 978-08-7-912288- Itasca, Illinois 60143
1) (USA)
5 Prevention of Major -- International Labour
Industrial Accidents Office (ILO),
(ISBN: 92-2-107101-4) Geneva (Switzerland)
6 Loss Prevention in the Frank P. Lees Butterworth-Heinemann
Process Industries Waltham, Massachusetts
(Vol. 1, 2 & 3) (USA)
(ISBN: 0-7506-1547-8)
7 Chemical Process Center for Chemical
Quantitative Risk Analysis Process Safety,
(ISBN-13: 978-08-1- American Institute of
690720-5) Chemical Engineers, New
York, N.Y. (USA)
8 Loss Control Management Frank E. Bird, Jr. & Institute Press, Loganville,
(ISBN: 0-8247-8479-0) Robert G. Loftus Georgia (USA)
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 37 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
9 Management Guide to Frank E. Bird, Jr. Institute Press, Loganville,
Loss Control Georgia (USA)
10 Techniques of Safety Dan Petersen McGraw-Hill Book Co.
Management (ISBN: 978- Ltd., New York, N.Y.
18-8-558139-6) (USA)
11 Industrial Safety and A.K. Gupta Laxmi Publications,
Environment New Delhi
12 Industrial Safety: K.T. Kulkarni Pune Vidyarthi Griha
Concepts and Practices Prakashan,
1786, Sadashiv Peth, Pune
- 411 030
13 A Course in Industrial K.U. Mistry NKM Publishers,
Safety Ahmedabad
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 38 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : SAFETY, HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL LEGISLATION
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 01 -- 03 100 -- -- -- 100
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
Eight Assignments pertaining to the subject shall be completed in the tutorials.
RATIONALE
To acquaint the student with National and International Acts, Rules, Conventions pertaining
to Safety, Health and Environment.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 39 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Effective compliance of SHE Legislation at work and prevention of injury, accident and
Application danger to Health and Property and Environment.
Procedures Compliance Awareness National and Education,
with the Status and International Training System
and Interaction Education Deliberation Changes and
Quality Control
Acts and Act and Rules of
Principles Rules of ISO
ESI, Public ILO, WHO, BIS
Legislative Liability, Insurance, UNEP, UNDP, IS :
Workmen’s EPA, WTO Codes of SHE
Compensation
Prevention and Minimum
Accountability Safety, Health and National
Concepts Control of Injury Environment Standards
and Accidents
Acts Convention Standards
Facts Social Security
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 40 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
The Factories Act, 1948 and Rules :
Provisions relating to Safety, Health and welfare,
under the Act and Factories Rules made there-under,
1 20 14
Amendments Process to the Act and Rules, The
Maharashtra Factories Safety Audit Rule 2014,
Important Case Laws under the Factories Act, 1948,
The Building and other Construction Workers
(Regulation of Employment and Conditions of
Service) Act, 1996, and Central Rules, 1998 and
State Rules
2 16 10
The Building and other Construction Worker’s
Welfare Cess Act, 1996 and State Rules, 1998,
Maharashtra Fire Prevention and Life Saving Act,
2007 and Rules.
Environment Protection Legislations :
Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act 1974
and Rules.
Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act 1981
and1982 and Rules.
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 and Rules.
3 16 10
Manufacture Storage and Import of Hazardous
Chemical Rules, 1989, Noise Pollution Act, 1998,
Bio-Medical Waste, E-Waste Rule, Batteries Rule,
Hazardous Waste Management (Trans boundary)
Rules, Chemical Accidents (Emergency
Preparedness, Planning and Response) Rules 1996
Safety, Health and Environment (SHE) related
Important Legislation:
Sections pertaining to SHE in Indian Boilers Act,
1923 with allied Regulations, 1961, Indian Electricity
Act, 2003 and Rules, latest CEA guidelines, Indian
Explosives Act, 1984 and Rules. Petroleum Act and
4 Rules, Gas Cylinders Rules. Calcium Carbide Rules, 16 10
The Insecticides Act and Rules. Radiation Protection
Rules, Hazardous Materials Transportation Rules,
Static and Mobile (Unfired) Pressure Vessel Rules,
1981 as amended in 2000.
The Dock Workers (Safety, Health & Welfare) Act
1996 and Rules and Regulations.
Social Security Legislations
Employees Compensation Act and Rules, ESIC Act
and Rules, Contract Labour (Abolition and
Conditions of Service) Act and Rules, Public
5 16 10
Liability Insurance Act, 1991 and Rules, Responsible
Care (RC), Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 and Rules
The Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, The
Maharashtra Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, Transport
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 41 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
of Hazardous Goods by Road Rules, Fire Prevention
and life Safety Measures Act 2006 and rules.
ILO Convention and Recommendation
concerning Occupational Health & Safety
Relevant Conventions and Recommendation of ILO
6 16 10
in the furtherance of Safety, Health and Environment
(SHE). SHE a human right issue. Trade Policy
affecting OHS.
TOTAL 100 64
LIST OF ASSIGNMENTS (Attempt any 8)
SR. ASSIGNMENT
NO.
1 List out the Health Provisions under Factories Act / Rule
2 Identify the Duties of Occupier under Factories Act / Rule
3 List out the Key Statutory Provisions under BOCW Act / Rule
4 List out the rules under Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
5 Case Law on Social Security Act
6 Case Law on Dock Safety Act, 1986
7 Case Law on Factories Act
8 List out the Provisions under Factories Act /Rule for Hazardous Process
9 Duties Of Safety Officer
10 List out the Key Elements in PCB Consent to Operate
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 The Factories Act, 1948 & -- Bare Act
Factories Rules
2 Environment (Protection) -- Bare Act
Act, 1986 and Rules
3 The Building and other -- Bare Act
Construction Workers
(Regulation of
Employment and
Conditions of Service)
Act, 1996, and Central
Rules, 1998 and State
Rules
4 Employees Compensation -- Bare Act
Act, 1923 and Rules
5 Indian Electricity Act, -- Bare Act
2003 and Rules CEA
guidelines, Indian
Explosives Act, 1984 and
Rules.
6 The Petroleum Act & -- Bare Act
Rules
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 42 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
7 The Dock Workers -- Bare Act
(Safety, Health &
Welfare) Act 1996 and
Rules and Regulations.
8 Indian Boilers Act, 1923 -- Bare Act
with allied Regulations,
1961.
9 The Maharashtra Fire -- Bare Act
Prevention and life Safety
Measures Act 2006 and
Rules
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 43 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE AND OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME:
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
02 -- 02 03 100 -- 50# -- 150
NOTE
Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by MSBTE.
Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 100 and to be
entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work (SW)
RATIONALE
Acquire knowledge of interaction of Man and Machine to maintain Hygiene and Health while
working to prevent exposure to dangers.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 44 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
Application Designing proper work station based on ergonomics and hygiene and
protect health while working.
Sampling and Monitoring
Assessment Training and and
Procedures Analysis
of Work Maintenance Evaluation
Capacity of PPE Health
Management
Services
Work
Principles Physiology
Environment Selection of Biology of
of Human
Monitoring PPE Disease and
Being
Diagnostic
Method, Acts.
hold limits
Workstation
of affection Protection from Disease
and its design
Concepts for human injuries and
being accident and
health affection
Hygience Ergonomics Personal Occupational
Facts and Health Protective Disease
Equipment
(PPE)
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 45 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
DETAILED CONTENTS
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Industrial Hygiene :
Definition of Industrial Hygiene, Industrial Hygiene:
Control Methods, Substitution, Changing the process,
isolation, wet method, local exhaust ventilation,
personal hygiene, housekeeping and maintenance,
waste disposal, special control measures.
Introduction to chemical hazards, dangerous
properties of chemical, dust, gases, fumes, mist,
vapours, smoke and aerosols.
1 Route of entry to human system, recognition, 16 10
evaluation and control of basic hazards, concepts of
dose response relationship, bio-chemical action of
toxic substances.
Personal Sampler. High Volume Sampler. Midget
Impinger Tubes. Rota meter. Calibration of
Rotameter.
Concept of threshold, limit values TLV-TWA/ PEL
/OEL, STEL, IDLH, LC50, LD50 and air sampling
strategies, personal exposure monitoring.
Personal Protective Equipment :
Need for personal protection equipment, selection,
applicable standards, supply, use, care &
maintenance respiratory and non-respiratory personal
protective equipment. Non-respiratory personal
protective devices: Head protection, Ear protection.
Face and Eye protection. Hand protection, Foot
protection, body protection. Respiratory personal
2 16 10
protective devices :
Classification of hazards: Classification of
respiratory personal protective devices. Selection of
respiratory personal protective devices. Instructions
and training in the use, maintenance and care of self-
containing breathing apparatus. Training in the use of
breathing apparatus (opens circuits and close unit).
Testing Procedures and Standards.
Ventilation and Heat Stress :
Purpose of ventilation. Physiology of heat
regulation. Thermal environment and its
measurement. Thermal comfort. Indices of heat
stress. Thermal limits for comfort, efficiency and
freedom from health risk. Natural ventilation.
3 20 14
Mechanical ventilation. Air conditioning. Control of
heat exposures at source, dilution and local
ventilation. Recommended values for air changes
required for various areas as per Factories Act, 1948
and National Standards.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 46 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
Industrial Lighting & Illumination :
Purpose of lighting. Benefits of good illumination.
Phenomenon of lighting and safety. Lighting and the
work. Sources and types of artificial lighting.
Principles of good illumination. Recommended
optimum standards of illumination. Stroboscopic
Effect, Design of lighting installation. Maintenance.
IS Standards relating to lighting and color.
Noise and Vibration :
Noise and ill-effect of noise on human health-
Auditory & non-auditory, Noise Induced Hearing
Loss (NIHL). Measurement and evaluation of noise.
Control of Noise Hazards- Noise absorption
techniques, silencers. Permissible level of exposure
to noise in Industry. Ill effects of vibration, White
Fingers (Reynolds’s phenomenon), and control
measures of vibration.
Occupational Health :
Definition: As per WHO, Common Occupational
Diseases, Occupations involving risk of contracting
these disease - mode of causation of the diseases and
its effects - diagnostic methods.
Biological monitoring - Method of prevention
Compensation for occupational diseases. Evaluation
of injuries Occupational Health Management
Services at the work place. List of notifiable diseases
Third Schedule of Factories Act, 1948. Occupational
Health Surveillance-Pre employment, Periodical,
Post employment Medical examination, Role of
Factory Medical Officer / Certifying Surgeon.
4 16 10
Occupational exposure & Risk based health
surveillance
Occupational Health Hazards & Occupational
Diseases :
Adverse health effects of noise, vibration, cold, heat
stress, improper illumination, thermal radiation,
ionizing and non-lionizing radiations. Permissible
threshold exposure limits - short term and long term
effects of exposures - Preventive and control
measures.
Common Occupational Diseases as per the Third
Schedule of the Factories Act, 1948 Preventive and
control measures.
First Aid :
Define First Aid, Purpose, Principles of First aid,
5 First Aider-Role & Responsibilities and Qualities. 16 10
Fundamentals of First-Aid- for thermal burns &
chemical burns, Fractures, Fainting, Shock, insects
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 47 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
CHAPTER CONTENTS MARKS HOURS
and animal bites, Suffocation, Toxic Ingestion -
Bleeding Wounds and Bandaging, Artificial
Respiratory, Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR),
Techniques. Victim transportation, Rescue
Techniques. First Aid Box and its contents.
Introduction to Ergonomics:
Definition, Aims and Scope, Man-machine (Job),
Environment System, Constituents of Ergonomics,
Application of Ergonomics in industry for Safety,
Health and Environment. Ergonomics of
Automation/Assembly, Visual Fatigue and
Ergonomics of Rehabilitation while assigning
alternate jobs. Working postures Its effect on cardio-
vascular and musculoskeletal system and
implications on health, Anthropometry and
fundamental of bio-mechanics: Basic and applied
aspects: Anthropometric measurements and their
usefulness in industry, Permissible limits of load for
manual lifting and carrying.
Ergonomic Design of Work Station:
Concept of workstation and its design. Improving
safety and productivity through work station design.
6 Technical and Engineering control measures. 16 10
Economics consideration.
Physiology at Work:
Physiology of respiration, cardiac cycle, muscle
contraction, nerve conduction system etc.
Assessment of Workload based on Human
Physiological reactions. Criteria for fixation limits.
Nutrition and its importance in manual work.
Nutritional requirements and nutritional of diet.
Assessment of Work Capacity Fatigue and Rest
Allowances. Physiological Test for Assessment of
Occupational Health. Nutrition: Nutritional
requirements and the Diets for Exercise, Work and
Physical Fitness Aerobic work capacity (physical
work capacity), methods of its determination (use of
bicycle, ergometer, treadmill, step-stool ergometer).
Factors affecting aerobic capacity and work
performance.
TOTAL 100 64
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 48 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LIST OF PRACTICALS (Minimum 10 experiments)
SR. EXPERIMENTS
NO.
1 Demonstration, Calibration of Sampling Equipment
2 Sampling and Estimation of Gases in Work Environment by Colorimetric Method
Oxides of Nitrogen, Sulfur Dioxide, Ammonia & Chorine
3 Sampling and Estimation of Solvent / toxic vapours in work environment.
Benzene-Sampling by Activities Charcoal and Analysis by Gas Liquid
Chromatography, CO, H2S, CS2 Sampling by Aspiratory Bottle Analysis by
Colorimetric Method.
4 Sampling and Analysis of. Mercury
5 Sampling and Estimation of Dust by Gravimetric Method.
6 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
7 Noise Level Measurement.
(a) Measurement of Sound pressure level in dBA and dB linear.
(b) Frequency analysis of noise.
8 Measurement of Ventilation:
Measurement of thermal
Dry Bulb Temperature
Wet Bulb Temperature Determination of relative humidity and effective corrective
effective.
1) Aspirator Hygrometer.
2) Kata-Thermometer
3) Globe-Thermometer
9 Lung Function Test
Ear Testing on Audiometer
10 Explanation of charts on Industrial noise, notifiable diseases, physical health
hazards, chemical health hazards, industrial dermatoses prevention and control
11 Transportation of Victim
Rescue of Victim,
Bandaging
CPR
12 Anthropometry Practical Measurements of a few body dimensions, its treatment
and application
13 To find out the physical fitness of person by step test
14 Demonstration of Medical equipment such as Titmus Vision tester, Blood Analyser
and Electrocardiograph
15 Measurement of illumination level at working place with the help of digital Lux
meter
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 49 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED FOR PRACTICAL
SR. NAME OF EQUIPMENT
NO.
1 Rotameter
2 Impinger Tube
3 Personal Sampler
4 Multi Gas Detector
5 Gas Detector Tube with pump
6 Lux meter
7 Noise Decibel meter / Sound Level Meter
8 Kata Thermometer
9 Dry Bulb & Wet Bulb Thermometer
10 Psychrometer
11 Audiometer
12 First Aid Box
SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
1 “Health & Safety At -- Department of
Work” Booklets Employment and
Productivity, U.K
2 Model Code of Safety -- ILO
Regulation for Industrial
Establishments
3 Encyclopedia of -- ILO
Occupational Health and
Safety
4 Accident Prevention -- National Safety
Manual for Industrial Council, 444, North
Operations Michigan Avenue,
Chicago, I 11 – 60611.
5 The Chain Testers’ -- the Chain Jesters
Handbook Association of Great
Britain430 Barking Road,
London E 13 BHG
6 Lung function assessment Cotes J.E 3rd Edn. Blackwell
and application in Scientific Publications
Medicine 1969 P.g. 385 to 387
7 Spirometric Standards for Morris J.P. Am. Rev. Resp. Dis.
normal males and females. 1971, 03, 57
8 Predictor equation for Kamath S.R. et all Jr. Ass. Phys. Ind. Vol. 25,
Lung function in Indians Aug. 1977
9 Proper Training, Horvath P.E
Techniques Vital to
pulmonary testing Pg. 23-
27.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 50 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
SR. TITLE AUTHOR PUBLICATION
NO.
10 Biological effects and S.F.Cleary (Ed.), US HEW Report BRH
health implications of (DBE2-70), Rockville,
microwave radiation. 1971
11 Uncortainties in the S.F.Cleary HIth. Phys. 25,
evaluation of the
biological effects of
microwave
12 Biological effects and Polish
health hazards of P.Czerski et. all (Eds.), Medical Publ. Warsaw
microwave radiation. . 1974
13 Biological and Medical R.P. Delahaye Radioprotection, Dunod,
problems raised by the use 12, 199-216, 1977
of radar ultrasound waves.
14 Factories Act & State
Factories Rule
15 National Standards.
IS:3103-1975-Code of
practice for Industrial
Ventilation, National
Building Code Part VIII,
Building Services.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 51 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
COURSE NAME : ADVANCE DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
COURSE CODE : IT
YEAR : FIRST
SUBJECT TITLE : PROJECT
SUBJECT CODE :
TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME
TEACHING SCHEME EXAM SCHEME & MAXIMUM MARKS
PAPER
TH TU PR TH PR OR TW TOTAL
HRS.
-- -- 04 -- -- -- 50# 50@ 100
RATIONALE
The main aim of the preparation of project on industrial safety is to judge the knowledge
gained by the students during their tenure of the industrial safety programme, the transfer of
learning that has taken place as well as their exposure to industrial environment and its
safety; so that many faceted development of the students can be achieved under various skills
of domains such as Personal, social, professional & lifelong learning. The students will be
benefited lot by this exercise of preparation of project on their safety experiences which will
certainly add values in their attitudes such as value for health, work commitment,
hardworking, honesty, problem solving, punctuality, loyalty and independent study. The
Student should also make a brief presentation about the project and the salient observations
and findings.
The Project report should essentially consists of the following
1. TITLE OF THE PROJECT WORK
2. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
3. PREFACE
4. CERTIFICATE FROM THE ORGANISATION
5. CERTIFICATE FROM THE STUDENT THAT PROJECT HAS BEEN DONE BY HIM
6. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
7. INDEX / CONTENTS
8. AIM, OBJECTIVE AND METHODOLOGY
9. INTRODUCTION
10. ABOUT THE ORGANISATION / COMPANY
11. SAFETY, HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL ACTIVITIES IN THE COMPANY
12. OBSERVATIONS AND FINDINGS
13. SUMMARY OF RECOMMENDATIONS
14. REFERENCES / BIBLIOGRAPHY
15. MY KEY LEARNING IN INDUSTRIAL SAFETY AFTER PROJECT
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 52 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
LEARNING STRUCTURE
To develop the students from all faces of various domains of skills
Application such as Personal, social, professional & life long learning and make
them a perfect human being with awareness of all social
responsibilities
Methods of preparation of day- to- day record of actual work done in
Procedures industrial safety. Collection of various related information about the
same. Procedures for preparation of project and its submission.
Principles of record keeping, data collection, scrutiny and selection for
Principles presentation of project.
Data of actual work done, subject data, diagrams and results.
Concepts
Actual safety experiences, work done, subjects, records, presentation
Facts
aids.
IMPLEMENTATION STRATEGY
The project report is to be assessed by external and internal examiners equally for
a) Project assessment – 50 marks (To be reported under title term work – TW)
b) Oral based on Project work – 50 marks (To be reported under title Oral– OR)
IMPORTANT NOTE
There should not be any sort of typographical, diagrammatic, chemical titles, chemical
formulas / structures and any other mistake/s in the final bound copy of the project report
submitted by the candidate.
Refer General Guidelines given below.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 53 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
GUIDELINES FOR PREPARING THE PROJECT REPORT
Project work is a basic requirement for the award of Advance Diploma in Industrial Safety.
Project shall be prepared based on any one of the subjects of the Programme. The project
work should be comprehensive and cover all aspects of the management of occupational
health and Industrial Safety.
1. TITLE OF THE PROJECT WORK
Select an appropriate title, e.g., “Safety in a Petrochemical Plant” or “Safety in a Chlor-Alkali
Plant”, “Safety in an Engineering Company”, etc. The upper half of the first page of the
project report should have the title of the project report in bold block letters and the lower
half some important information like the year, the name of the author (report writer) and the
name of the institute.
2. CONTENTS
On the second page of the project report should be the table of contents. This table can be
prepared after finishing the project report, i.e., when the typing work of the entire project
report has been completed, the pages have been numbered and all annexures appended at the
end.
3. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
It should appear on the third page and the report writer should acknowledge the guidance
provided by the project guide. Here the author may also acknowledge other persons who
might have rendered help or supplied the required data or information for completion of the
project. It should be brief and crisp. Generally, one page should suffice for
acknowledgement.
4. PREFACE, OBJECTIVE AND METHODOLOGY
Preface should describe the choice of selected project work and its objective. The preface
should be limited to one or two pages. It will be prudent to mention the objective and the
methodology used for the project work, e.g., collecting data from various records available in
the company, interviewing certain key employees, questionnaires, etc. Thereafter, briefly
mention the scope of project work. The objective could be, for example, :
(1) To study the safety organisation and safety procedures of the company
(2) To study the underlying causes of accidents and near-miss incidents
(3) To examine and evaluate the safety performance of the company
(4) To give suggestions/recommendations for improving the safety performance of the
company, preventing occupational diseases and conserving the environment.
5. INTRODUCTION
Brief description of the Organization, the main raw materials used, its processes and the
main features of manufacturing and other key operations, including the potential hazards
shall be the contents. It is recommended to limit the description to about 5 to 10 pages.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 54 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
6. SAFETY, HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL ACTIVITIES IN THE COMPANY
This is the most important part of the project report and forms the main body of the project
report. It needs very comprehensive coverage of all aspects of safety in the plant, industrial
hygiene, environmental conservation, safety in storage and transportation, etc. It will usually
require about 60 to 100 pages. Write-up should include the details mainly in some of the
following areas:
Occupational health, safety and environment policy of the company and its
implementation
Safety organisation
Role of management in promoting safety and striving for continual improvement
Accident and near-miss incidents reporting system
Accident and near-miss incident investigation system
Accident/incident analysis (using data of previous five years at least)
Case-studies (discuss at least five cases of different types of accidents/near-misses)
Selection and training of employees
Safety induction and safety training of employees and contractor personnel
Health and hygiene (including pre-employment and periodic medical examinations)
Environmental conservation
Safety in transportation and training of drivers
Trade union and its role in promoting safety
Plant layout
Facilities and services
Storage and handling of chemicals
Built-in safety measures
Instrumentation for safety of plant and personnel
Fire prevention and fire-fighting measures
Housekeeping
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Pollution control measures
Various safety procedures (e.g., work permit system, working at height, etc.)
Job safety analysis (JSA)
Preventive maintenance
Safe operating procedures (SOPs) and operating manuals
Safety manual, material safety data sheets (MSDS), Tremcards, etc.
Health, safety and environment audits.
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 55 IT
w.e.f Academic Year 2017-18 ‘I’ Scheme
Relevant information and data presented in the form of tables and graphs (e.g., graphs for
injury frequency rates, severity rates, frequency-severity indices, incident rates, fire statistics,
etc.), accident/incident analysis, work permit form, accident/near-miss incident report form,
medical attention form, block diagrams, plant layout, relevant photographs, MSDS, etc.,
which are required to supplement your project report, should be included at the end as
annexures with appropriate references in the main text of the project report. If an annexure is
of more than one page, it should be provided with page numbering. Page numbering should
be done individually for each annexure.
7. RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the project work and study of safety management system, student should identify
areas needing improvement and recommend measures for improvement. The
recommendations should be specific, relevant and practically implementable.
8. PROJECT REPORT FORMAT
Paper Size - A4
Printing - Only on one side of the sheet
Line Spacing of Paragraph - 1½
Font Face - Times New Roman
Font Size - 12 for Normal text, 14 for Sub-headings and 16 for Headings
No of Project Report copies - Two
Binding - Hard bound copies with Black cover (Golden Embossing)
MSBTE Draft Copy Dt.__/__/__ 56 IT
You might also like
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical EducationDocument5 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical EducationKrishna PujeriNo ratings yet
- Final Year MarksheetsDocument3 pagesFinal Year MarksheetsDakhani SohelNo ratings yet
- JOB SATISFACTION of The EmployeesDocument59 pagesJOB SATISFACTION of The EmployeesVarun Sadh100% (1)
- CertificateDocument6 pagesCertificatejassi7nishadNo ratings yet
- Nebosh Command Words BreakdownDocument11 pagesNebosh Command Words Breakdownw hite100% (1)
- Safe Erection of Structures Part 2 - Site Management and Procedures.Document20 pagesSafe Erection of Structures Part 2 - Site Management and Procedures.mannie edetNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Azeem Sarwar: Safety EngineerDocument5 pagesMuhammad Azeem Sarwar: Safety EngineerHareekirishnan LrkNo ratings yet
- Project Report - Role of A Security Guard in Fire and SafetyDocument66 pagesProject Report - Role of A Security Guard in Fire and SafetyReddy KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Grua SanyDocument266 pagesManual de Partes Grua SanyIrving Antonio Flores Alegria0% (2)
- Talha's ResumeDocument1 pageTalha's Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Safety Measure of Workers at Sri Sarvaraya Sugars LTDDocument54 pagesA Study On Safety Measure of Workers at Sri Sarvaraya Sugars LTDRonak JainNo ratings yet
- Air Equipment Compressors Compressor 100 130CFM D XAS 66G Operation ManualDocument40 pagesAir Equipment Compressors Compressor 100 130CFM D XAS 66G Operation ManualCosmin Ion BlajaNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Statement June 2012Document1 pageFood Safety Statement June 2012Mohit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Viddya Ganesh Joshi ProjectDocument55 pagesViddya Ganesh Joshi ProjectkiranbjNo ratings yet
- Truf Management SystemDocument24 pagesTruf Management SystemATHUL P SUDHEERNo ratings yet
- SP-091-C CNC Router SOPDocument1 pageSP-091-C CNC Router SOPBorislav VulićNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training SejalDocument6 pagesIndustrial Training SejalYojana PatkarNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection Exam - Worksite SafetyDocument6 pagesFall Protection Exam - Worksite SafetyIan Jeff Landingin DumayasNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited: Written Test For Officer Trainee and Information Systems Officer RecruitmentDocument2 pagesHindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited: Written Test For Officer Trainee and Information Systems Officer RecruitmentAbdul SubhanNo ratings yet
- Fema Ics 200Document1 pageFema Ics 200api-455495817No ratings yet
- Shakeel CV-Electrical Electronics EngineerDocument3 pagesShakeel CV-Electrical Electronics EngineerFaisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Advance DiplomaDocument16 pagesAdvance DiplomaDevashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- ASWA Career Guidance Chart Shorter Version WebsiteDocument4 pagesASWA Career Guidance Chart Shorter Version WebsiteRavi Babu GNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Format - BCCDocument13 pagesMicro Project Format - BCCMoin PinjariNo ratings yet
- Migration ApplicationDocument1 pageMigration ApplicationAlice JonesNo ratings yet
- ASWA Career Guidance Chart Shorter Version WebsiteDocument4 pagesASWA Career Guidance Chart Shorter Version WebsiteRavi Babu GNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument31 pagesInternship ReportAnkur MallickNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic Inst Mumbai Region - 1Document61 pagesPolytechnic Inst Mumbai Region - 1Sanjay Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Agrinext Consultancy Training CertificateDocument1 pageAgrinext Consultancy Training CertificateSantosh LokhandeNo ratings yet
- GrivanceDocument108 pagesGrivanceAshwani kumarNo ratings yet
- Government of India Prospectus for Advanced Diploma in Industrial SafetyDocument16 pagesGovernment of India Prospectus for Advanced Diploma in Industrial SafetyEHS Plant6No ratings yet
- VLE Insurance Certificate for Soliciting BusinessDocument1 pageVLE Insurance Certificate for Soliciting BusinessPrem SagarNo ratings yet
- Re 54 W 57Document3 pagesRe 54 W 57ANAND BIRAJDAR100% (1)
- Major Project Report Format NewDocument6 pagesMajor Project Report Format Newams2011No ratings yet
- Study of Safety Measures Followed in IndustryDocument20 pagesStudy of Safety Measures Followed in IndustryJokerrrr100% (1)
- Vtu Final Year Project Report Front PagesDocument7 pagesVtu Final Year Project Report Front PagesshwethaNo ratings yet
- Qaqc E&i Engineer - AzmatDocument3 pagesQaqc E&i Engineer - AzmatManda Khel Apna DesNo ratings yet
- 4MT17CS007 Aishwarya K InternshipDocument25 pages4MT17CS007 Aishwarya K InternshipPrakash GNo ratings yet
- Drive 15 For KodNestDocument20 pagesDrive 15 For KodNestAnjum Afsana T.ANo ratings yet
- Shruti ResumeDocument2 pagesShruti ResumevractivaNo ratings yet
- Internship at Brainybeam Technologies Pvt. LTD: Ruchit Mukeshbhai PatelDocument51 pagesInternship at Brainybeam Technologies Pvt. LTD: Ruchit Mukeshbhai PatelRandom LoginsNo ratings yet
- Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science: (Affiliated To Jntua, Anantapur)Document1 pageMadanapalle Institute of Technology and Science: (Affiliated To Jntua, Anantapur)Gopi Krishna0% (1)
- "Effectiveness of Epms in Rdcis (Sail) ": Research TopicDocument53 pages"Effectiveness of Epms in Rdcis (Sail) ": Research Topicj4jhnyNo ratings yet
- New Format Mini Project-1Document6 pagesNew Format Mini Project-1Krishna vallabh PatidarNo ratings yet
- Selecstud ReportNew 2Document119 pagesSelecstud ReportNew 2Md Irfan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: "Nano Robotics Embed Technologies"Document34 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: "Nano Robotics Embed Technologies"pradip pokharelNo ratings yet
- Tabrez Alam ExpDocument1 pageTabrez Alam ExpAdnaan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Mba Summer Training Internship ReportDocument46 pagesMba Summer Training Internship Reportmrinalbohra100% (2)
- Work Experience Certificate for M/s BSK Security ServicesDocument1 pageWork Experience Certificate for M/s BSK Security Servicesjmpnv0070% (1)
- 5th Sem-Industrial Training Report FormatDocument7 pages5th Sem-Industrial Training Report FormattarunNo ratings yet
- ATAL FDP CertificateDocument1 pageATAL FDP CertificateAbid HussainNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Resources Industrial Relations in Simplex Metalica, JabalpurDocument50 pagesStudy of Human Resources Industrial Relations in Simplex Metalica, JabalpurluckyNo ratings yet
- College Bonafide Certificate Title GeneratorDocument1 pageCollege Bonafide Certificate Title GeneratorAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- List of Institutes Approved by Joint Committee of AICTE, UGC and DEC in IndiaDocument13 pagesList of Institutes Approved by Joint Committee of AICTE, UGC and DEC in Indiaali100% (3)
- Resume for Safety Officer PositionDocument3 pagesResume for Safety Officer PositionAkshay PotdarNo ratings yet
- Final Year B.Tech Mechanical SyllabusDocument76 pagesFinal Year B.Tech Mechanical SyllabusEr Zubair HabibNo ratings yet
- Robin Stephen: Civil Survey EngineerDocument3 pagesRobin Stephen: Civil Survey EngineerrubanNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Acknowledgement Slip 3Document1 pageIGNOU Acknowledgement Slip 3mdamaan7755No ratings yet
- SignedDocument2 pagesSignedaryanNo ratings yet
- Final Report BangladeshDocument54 pagesFinal Report Bangladesh임동우No ratings yet
- UMT Internship LetterDocument1 pageUMT Internship LetterhammadusmanworkplaceNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument47 pagesInternship ReportDeepaNo ratings yet
- BCC Micro ProjectDocument9 pagesBCC Micro ProjectrakibNo ratings yet
- selecStudFr ReportNewDocument177 pagesselecStudFr ReportNewTayyab SaeedNo ratings yet
- Narayana Engineering College: Nellore: A Study On Capital Budgeting in Sagar Cements PVT LTD, HyderbadDocument65 pagesNarayana Engineering College: Nellore: A Study On Capital Budgeting in Sagar Cements PVT LTD, Hyderbadsaryumba5538No ratings yet
- Dr.C.Ramalingam - Prof - Business Studies ResumeDocument16 pagesDr.C.Ramalingam - Prof - Business Studies ResumeRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- Bio - Data of AmDocument10 pagesBio - Data of AmRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- JSPM's RAJARSHI SHAHU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING INTERNSHIP MANUALDocument39 pagesJSPM's RAJARSHI SHAHU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING INTERNSHIP MANUALShantanuNo ratings yet
- Tentative Vacncy Je 15022019 PDFDocument1 pageTentative Vacncy Je 15022019 PDFaviralNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Horizontal Steam Pressure VesselDocument41 pagesDesign and Analysis of Horizontal Steam Pressure VesselVitor OlivettiNo ratings yet
- KJ's Shock Absorber Test RigDocument12 pagesKJ's Shock Absorber Test RigPrashant JagdaleNo ratings yet
- SCIE Engg SE All PatternDocument10 pagesSCIE Engg SE All PatternPrashant JagdaleNo ratings yet
- Revised Schedule of Second Half 2017 - 7102017Document6 pagesRevised Schedule of Second Half 2017 - 7102017Prashant JagdaleNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lecture 1Document19 pagesR&AC Lecture 1jojovaliaveetilNo ratings yet
- All DatasheetsDocument485 pagesAll Datasheetssflynn79No ratings yet
- Turin Industrial Robot User ManualDocument89 pagesTurin Industrial Robot User ManualAutoman IntertradeNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Fumaric AcidDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Fumaric AcidStephen StantonNo ratings yet
- PSM 25 - Element 20 - Management Review (v1)Document9 pagesPSM 25 - Element 20 - Management Review (v1)Ahmed HamadNo ratings yet
- South Metro Fire Rescue Authority Accreditation ReportDocument50 pagesSouth Metro Fire Rescue Authority Accreditation ReportRonda ScholtingNo ratings yet
- Safe Work Method Statement (York Street EC) 2023.06.23Document8 pagesSafe Work Method Statement (York Street EC) 2023.06.23manuel010478No ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis FMEADocument6 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis FMEAMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Sop Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesSop Risk ManagementKavitha G3No ratings yet
- MSDS Asam Klorida Pekat (Hydrogen Acid) 37%Document8 pagesMSDS Asam Klorida Pekat (Hydrogen Acid) 37%Wahyu OktavianiNo ratings yet
- OSHA 10 Hour Construction Course Fact SheetDocument1 pageOSHA 10 Hour Construction Course Fact SheetMaurice Anthony0% (1)
- Fire Explosion and Toxicity Index (FETI) Various IndicesDocument18 pagesFire Explosion and Toxicity Index (FETI) Various IndicesSayed Ibrahim GhanemNo ratings yet
- Ism ImplementationDocument16 pagesIsm ImplementationnishantNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety ProgramDocument40 pagesRadiation Safety ProgramKhalid AbeedNo ratings yet
- Primer On The DRRM Act of 2010Document22 pagesPrimer On The DRRM Act of 2010Janet Vargas GendranoNo ratings yet
- CSR - Base Coat and Adhesive - SDS - 20.11.2019Document7 pagesCSR - Base Coat and Adhesive - SDS - 20.11.2019jr-nts ntsNo ratings yet
- Schlumberger MSDS J494Document6 pagesSchlumberger MSDS J494sajad gohariNo ratings yet
- NFIRS 5.0 Complete Reference GuideDocument522 pagesNFIRS 5.0 Complete Reference Guidemegscannell100% (3)
- PCQI BrouchureDocument6 pagesPCQI BrouchuresuchivapgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesMaterial Safety Data SheetRio SugengNo ratings yet
- 1 2 4 Trichlorobenzene SDSDocument7 pages1 2 4 Trichlorobenzene SDSMali teaNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide For Cat Terrain For Drilling On The MD6250Document64 pagesInstallation Guide For Cat Terrain For Drilling On The MD6250Sain MezaNo ratings yet
- HEP3 Mec Ang 562Document15 pagesHEP3 Mec Ang 562dedeNo ratings yet