Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LlgasAssignment in S-WPS Office
Uploaded by
John Paolo Perma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesEnjoy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnjoy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesLlgasAssignment in S-WPS Office
Uploaded by
John Paolo PermaEnjoy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
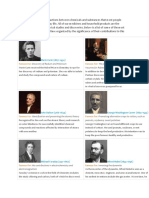
Assignment in Science
Submitted by: Junel G. Llagas
Paul Dirac published
numerous books in his
lifetime, many of which
are still seen today as
the standard bearer
texts in the field of
physics. His most
famous books are:
Quantum Theory of the
Electron (1928) The
principles of quantum
mechanics (1930).
Alan Guth is an
American theoretical
physicist and
cosmologist. Guth has
researched elementary
particle theory. He is
Victor Weisskopf
Professor of Physics in
the Massachusetts
Institute of Technology
Phoebus Aaron
Theodore Levene was
an American
biochemist who studied
the structure and
function of nucleic
acids. He characterized
the different forms of
nucleic acid, DNA from
RNA, and found that
DNA contained adenine,
guanine, thymine,
cytosine, deoxyribose,
and a phosphate group.
Sir James Chadwick, CH,
FRS was a British physicist
who was awarded the 1935
Nobel Prize in Physics for
his discovery of the neutron
in 1932. In 1941, he wrote
the final draft of the MAUD
Report, which inspired the
U.S. government to begin
serious atomic bomb
research efforts.
Prof Hugo Marie de Vries
FRS HFRSE was a Dutch
botanist and one of the first
geneticists. He is known
chiefly for suggesting the
concept of genes,
rediscovering the laws of
heredity in the 1890s while.
Mikhail Semyonovich Tsvet
was a Russian-Italian
botanist who invented
adsorption chromatography.
His last name is Russian for
both "colour" and "flowering.
"
Jaroslav Heyrovský was a
Czech chemist and inventor.
Heyrovský was the inventor
of the polarographic
method, father of the
electroanalytical method,
and recipient of the Nobel
Prize in 1959 for his
discovery and development
of the polarographic
methods of analysis. His
main field of work was
polarography.
Fritz Zwicky was a Swiss
astronomer. He worked
most of his life at the
California Institute of
Technology in the United
States of America, where
he made many important
contributions in theoretical
and observational
astronomy.
Murray Gell-Mann is an
American physicist who
received the 1969 Nobel
Prize in physics for his work
on the theory of elementary
particles.
Neil Bartlett (15 September
1932 – 5 August 2008) was
a chemist who specialized
in fluorine and compounds
containing fluorine, and
became famous for
creating the first noble gas
compounds. He taught
chemistry at the University
of British Columbia and the
University of California,
Berkeley.
You might also like
- The Top 10 Most Famous Chemists of All Time - 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Top 10 Most Famous Chemists of All Time - 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- 10 Scientist Contributed in ChemistryDocument4 pages10 Scientist Contributed in ChemistryJefferd PaetNo ratings yet
- Thirty Years that Shook Physics: The Story of Quantum TheoryFrom EverandThirty Years that Shook Physics: The Story of Quantum TheoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Foreign ChemistDocument2 pagesForeign ChemistmahyoolNo ratings yet
- Scientists CompressedDocument12 pagesScientists CompressedDio PrantisaNo ratings yet
- Worlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFDocument15 pagesWorlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFFadewNo ratings yet
- Foreign ScientistsDocument24 pagesForeign ScientistsAlexander Bermejo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Discoveries of early chemistsDocument5 pagesDiscoveries of early chemistsAlemar Soriano MalintadNo ratings yet
- Werner Heisenberg:: TH THDocument1 pageWerner Heisenberg:: TH THDilip TheLipNo ratings yet
- The Study of Life: An Introduction to BiologyDocument30 pagesThe Study of Life: An Introduction to BiologyJamesInocencioNo ratings yet
- Discoverers ProfileDocument2 pagesDiscoverers ProfileJan Cyril SerradoNo ratings yet
- ( T y Ə ɅDD̥ƏSNN̩ Bd̥ʁɑ ) : Tycho Brahe (Document6 pages( T y Ə ɅDD̥ƏSNN̩ Bd̥ʁɑ ) : Tycho Brahe (Romanuvel ShankarNo ratings yet
- Famous ChemistsDocument22 pagesFamous ChemistsDanica JadeNo ratings yet
- Robert HookeDocument4 pagesRobert Hookebmfgeorgin2100% (5)
- Famous Chemists Who Shaped Modern ChemistryDocument4 pagesFamous Chemists Who Shaped Modern ChemistryRommel Villaroman EstevesNo ratings yet
- Top Chemists ListDocument13 pagesTop Chemists ListMavzkyNo ratings yet
- DemocritusDocument2 pagesDemocritusMaria Teresa Casili - PerezNo ratings yet
- The Famous ChemistsDocument5 pagesThe Famous ChemistsDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- John DaltonDocument3 pagesJohn DaltonShyrill Mae MarianoNo ratings yet
- Take Home Exam Chemistry Essay RevisedDocument3 pagesTake Home Exam Chemistry Essay RevisedDanita AllenNo ratings yet
- Gregorio Zara's accomplishments and awardsDocument6 pagesGregorio Zara's accomplishments and awardshazelbite_No ratings yet
- Faculty of Entrepreneurship, Business Engineering and Management Politehnica University of BucharestDocument12 pagesFaculty of Entrepreneurship, Business Engineering and Management Politehnica University of BucharestMădălina ŞuţuNo ratings yet
- QawefthujklosdfghjkDocument3 pagesQawefthujklosdfghjkChristian MartinezNo ratings yet
- General Knoweledge RefresherDocument59 pagesGeneral Knoweledge Refreshernaveenchand_a6No ratings yet
- Famous For: Famous For:: Marie Curie (1867-1934) Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)Document4 pagesFamous For: Famous For:: Marie Curie (1867-1934) Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)Wilfred MartinezNo ratings yet
- NamethescientistDocument31 pagesNamethescientistRanniel Espina BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Timeline: Key Discoveries from Democritus to ChadwickDocument5 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline: Key Discoveries from Democritus to ChadwickMaj AquinoNo ratings yet
- John Burdon Sanderson Haldane biographyDocument8 pagesJohn Burdon Sanderson Haldane biographyADRIAN GamingNo ratings yet
- The 10 Best Physicists PDFDocument5 pagesThe 10 Best Physicists PDFemNo ratings yet
- Women in Science: by Shelby KuhnDocument10 pagesWomen in Science: by Shelby KuhnsuzanneNo ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument2 pagesScientistsanon-59051No ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument4 pagesScientistsMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument3 pagesIsaac NewtonBlue Heavens100% (1)
- Albert EinsteinDocument18 pagesAlbert EinsteinRonnelMananganCorpuzNo ratings yet
- Otto Hahn - EncycloipediaDocument19 pagesOtto Hahn - EncycloipediaMynamabatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry As Scienceaazzqqww: The Sceptical ChymistDocument2 pagesChemistry As Scienceaazzqqww: The Sceptical Chymistterran2020No ratings yet
- Chemistry As Scienceaazzqq: The Sceptical ChymistDocument2 pagesChemistry As Scienceaazzqq: The Sceptical Chymistterran2020No ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument14 pagesIsaac NewtonDeath BringerNo ratings yet
- 5 Great Scientists Who Never Won A Nobel PrizeDocument5 pages5 Great Scientists Who Never Won A Nobel PrizeAniket MitraNo ratings yet
- Niels BohrDocument3 pagesNiels Bohrjepibe5134No ratings yet
- Science, Technology and SocietyDocument8 pagesScience, Technology and SocietyCanindo, Claries MargaretNo ratings yet
- Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsDocument5 pagesJohann Wolfgang Döbereiner: TriadsMikeLesterCalolotNo ratings yet
- Chemistry As Science: The Sceptical ChymistDocument2 pagesChemistry As Science: The Sceptical Chymistterran2020No ratings yet
- WW1 ScientistDocument6 pagesWW1 ScientistAlyssa BonabonNo ratings yet
- Timeline On History and Philosophy of Science and MathematicsDocument10 pagesTimeline On History and Philosophy of Science and MathematicsCelRuizLabao100% (1)
- Victor Weisskopf: Pioneer Physicist and Advocate for ScienceDocument27 pagesVictor Weisskopf: Pioneer Physicist and Advocate for ScienceriskycodeNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument3 pagesAristotleAmhyr De Mesa DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Physics Famous ScientistDocument14 pagesPhysics Famous ScientistUsama mughal Usama mughalNo ratings yet
- 12 Amazing Women Who Totally Rocked It in ScienceDocument15 pages12 Amazing Women Who Totally Rocked It in Science3naagathaboladoNo ratings yet
- Project in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaDocument4 pagesProject in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaMichelle Armenta MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Greatest PeopleDocument11 pagesGreatest PeopleKuya KimNo ratings yet
- Discoverers of the Periodic TableDocument5 pagesDiscoverers of the Periodic TableJoneil TorioNo ratings yet
- Teaching of General Science 1 NewDocument18 pagesTeaching of General Science 1 Newapi-231516879No ratings yet
- Louis de Broglie's Wave Theory of ElectronsDocument11 pagesLouis de Broglie's Wave Theory of ElectronsNikhil ChariNo ratings yet
- ModernchemistryDocument7 pagesModernchemistryprinceuduma2021No ratings yet
- Foreign Scientists: Marie Skłodowska-Curie / Marie CurieDocument4 pagesForeign Scientists: Marie Skłodowska-Curie / Marie CurieMaria Anna M LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Physics HistoryDocument5 pagesPhysics HistorybigbossNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Modern Chemistry. in The Hands of The "Oxford Chemists" (Robert Boyle, RobertDocument2 pagesEvolution of Modern Chemistry. in The Hands of The "Oxford Chemists" (Robert Boyle, RobertЮля ПавлущикNo ratings yet
- Henry FordDocument2 pagesHenry FordIvan EsperónNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension StrategiesDocument11 pagesReading Comprehension StrategiesNur InsaniaNo ratings yet