Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, See
Uploaded by
hoggasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, See
Uploaded by
hoggasCopyright:
Available Formats
Egypt
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigationJump to search
For other uses, see Egypt (disambiguation).
Coordinates: 26°N 30°E
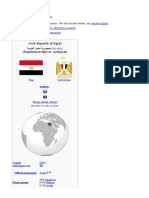
Arab Republic of Egypt
[جمهورية مصر العربيةshow]
Flag
Coat of arms
Anthem: "Bilady, Bilady, Bilady"
" بالدي، بالدي،"بالدي
"My country, my country, my country"
MENU
0:00
Capital Cairo
and largest city 30°2′N 31°13′E
Official languages Arabic
National language Egyptian Arabic[a]
Religion See Religion in Egypt
Demonym(s) Egyptian
Government Unitary semi-presidential
republic
• President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi
• Prime Minister Mostafa Madbouly
• House Speaker Ali Abdel Aal
Legislature House of Representatives
Establishment
• Unification of Upper c. 3150 BC
and Lower Egypt[1][2][b]
• Muhammad Ali 9 July 1805[3]
dynastyinaugurated
• Independence from 28 February 1922
United Kingdom
• Revolution Day 23 July 1952
• Republic declared 18 June 1953
• Current constitution 18 January 2014
Area
• Total 1,010,408[4] km2(390,121 sq mi) (29th)
• Water (%) 0.632
Population
• 2017 census 94,798,827[5]
• Density 96/km2 (248.6/sq mi) (118th)
GDP (PPP) 2019 estimate
• Total $1.391 trillion[6](21st)
• Per capita $14,028[6] (94th)
GDP (nominal) 2019 estimate
• Total $300 billion[6](43rd)
• Per capita $3,019[6] (130th)
Gini (2015) 31.8[7]
medium · 51st
HDI (2017) 0.696[8]
medium · 115th
Currency Egyptian pound (E£) (EGP)
Time zone UTC+2[c] (EET)
Driving side right
Calling code +20
ISO 3166 code EG
Internet TLD .eg
.مصر
a. ^ Literary Arabic is the sole official language.[9] Egyptian
Arabic is the national spoken language. Other dialects and
minority languages are spoken regionally.
b. ^ "Among the peoples of the ancient Near East, only the
Egyptians have stayed where they were and remained what they
were, although they have changed their language once and their
religion twice. In a sense, they constitute the world's oldest
nation".[10][11] Arthur Goldschmidt Jr.
c. ^ See Daylight saving time in Egypt.
Egypt (/ˈiːdʒɪpt/ ( listen) EE-jipt; Arabic: مِ صرMiṣr, Egyptian Arabic: َمصرMaṣr, Coptic: Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ Khēmi),
officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the northeast corner of
Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is
a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and
the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba
lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean
lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.
Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage back to the 6th–4th millennia
BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of
writing, agriculture, urbanisation, organised religion and central government.[12] Iconic monuments such
as the Giza Necropolis and its Great Sphinx, as well the ruins of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak, and
the Valley of the Kings, reflect this legacy and remain a significant focus of scientific and popular
interest. Egypt's long and rich cultural heritage is an integral part of its national identity, which has
endured, and often assimilated, various foreign influences,
including Greek, Persian, Roman, Arab, Ottoman Turkish, and Nubian. Egypt was an early and
important centre of Christianity, but was largely Islamised in the seventh century and remains a
predominantly Muslim country, albeit with a significant Christian minority.
From the 16th to the beginning of the 20th century, Egypt was ruled by foreign imperial powers: The
Ottoman Empire and the British Empire. Modern Egypt dates back to 1922, when it gained nominal
independence from the British Empire as a monarchy. However, British military occupation of Egypt
continued, and many Egyptians believed that the monarchy was an instrument of British colonialism.
Following the 1952 revolution, Egypt expelled British soldiers and bureaucrats and ended British
occupation, nationalized the British-held Suez Canal, exiled King Farouk and his family, and declared
itself a republic. In 1958 it merged with Syria to form the United Arab Republic, which dissolved in
1961. Throughout the second half of the 20th century, Egypt endured social and religious strife and
political instability, fighting several armed conflicts with Israel in 1948, 1956, 1967 and 1973,
and occupying the Gaza Strip intermittently until 1967. In 1978, Egypt signed the Camp David Accords,
officially withdrawing from the Gaza Strip and recognising Israel. The country continues to face
challenges, from political unrest, including the recent 2011 revolution and its aftermath, to terrorism
and economic underdevelopment. Egypt's current government is a presidential republic headed by
President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, which has been described by a number of watchdogs as authoritarian.
Islam is the official religion of Egypt and Arabic is its official language.[13] With over 95 million
inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in North Africa, the Middle East, and the Arab world,
the third-most populous in Africa (after Nigeria and Ethiopia), and the fifteenth-most populous in the
world. The great majority of its people live near the banks of the Nile River, an area of about 40,000
square kilometres (15,000 sq mi), where the only arable land is found. The large regions of
the Sahara desert, which constitute most of Egypt's territory, are sparsely inhabited. About half of
Egypt's residents live in urban areas, with most spread across the densely populated centres of
greater Cairo, Alexandria and other major cities in the Nile Delta.
The sovereign state of Egypt is a transcontinental country considered to be a regional power in North
Africa, the Middle East and the Muslim world, and a middle power worldwide.[14] Egypt's economy is
one of the largest and most diversified in the Middle East, and is projected to become one of the
largest in the world in the 21st century. In 2016, Egypt overtook South Africa and became Africa's
second largest economy (after Nigeria).[15][16] Egypt is a founding member of the United Nations, Non-
Aligned Movement, Arab League, African Union, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
You might also like
- Hidden Codes of The Illuminati Codex Magica Texe MarrsDocument588 pagesHidden Codes of The Illuminati Codex Magica Texe Marrsstingray357100% (3)
- Kelly JB. The Determination of Child CustodyDocument23 pagesKelly JB. The Determination of Child CustodymmaNo ratings yet
- EgyptDocument121 pagesEgyptAmjad PervazNo ratings yet
- 100 Tips For Architecture Students 1 PDFDocument108 pages100 Tips For Architecture Students 1 PDFBhargavi H Chandrashekar100% (1)
- Israel: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia This Article Is About The Modern Country. For Other Uses, See .Document45 pagesIsrael: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia This Article Is About The Modern Country. For Other Uses, See .baktinusantaraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self: Module inDocument75 pagesUnderstanding The Self: Module inRojim Asio DilaoNo ratings yet
- NIGERIA: THE GIANT OF AFRICADocument60 pagesNIGERIA: THE GIANT OF AFRICAamanblr12100% (1)
- Egypt - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureFrom EverandEgypt - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cusanus EriugenaDocument14 pagesCusanus EriugenaDaniel Jones100% (1)
- Arctic Community Nunavut Unit PlanDocument6 pagesArctic Community Nunavut Unit Planapi-402508151No ratings yet
- Course Book Evaluation ChecklistDocument8 pagesCourse Book Evaluation ChecklistDumitriţa Chirica100% (2)
- Egypt: Arab Republic of EgyptDocument4 pagesEgypt: Arab Republic of EgyptLEAHCIM B. DRAGNEELNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Arab Republic of Egypt ةيبرعلا رصم ةيروهمجDocument3 pagesEgypt: Arab Republic of Egypt ةيبرعلا رصم ةيروهمجClaireNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Ancient Civilization and Modern CountryDocument25 pagesEgypt's Ancient Civilization and Modern CountryUpendra ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Egypt - WikipediaDocument40 pagesEgypt - WikipediaMonicaNo ratings yet
- Arab Republic Of Egypt ةّيروهمج رْصِم ةّيبرعلا: Gumhūriyyat Mi R Al-ʿArabiyyaDocument48 pagesArab Republic Of Egypt ةّيروهمج رْصِم ةّيبرعلا: Gumhūriyyat Mi R Al-ʿArabiyyapovseyNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Ǧumhūriyyat Ma R Al - ArabiyyahDocument8 pagesEgypt: Ǧumhūriyyat Ma R Al - ArabiyyahSyafiqah SaleamNo ratings yet
- Egypt Brief DescriptionDocument11 pagesEgypt Brief DescriptionMelchor Sumaylo PragaNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and The World Youth ForumDocument1 pageOrganisation of Islamic Cooperation and The World Youth ForumCAT LABNo ratings yet
- ExpoDocument3 pagesExpodoudou91No ratings yet
- EgyptDocument1 pageEgyptsdgragonsNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument4 pagesUntitled PresentationAya Amr MohamedNo ratings yet
- HistorianDocument1 pageHistorianJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- EgiptoDocument29 pagesEgiptoRamón FerrerNo ratings yet
- StoryDocument1 pageStoryshalakasatishNo ratings yet
- Egypt-India - Nepal FullDocument166 pagesEgypt-India - Nepal FullDinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Egypt HistoryDocument4 pagesEgypt HistoryMichael OlympiaNo ratings yet
- Report On Country's Culture: Submitted ToDocument16 pagesReport On Country's Culture: Submitted ToWaliNo ratings yet
- Fathima College: A.NiranjanadeviDocument22 pagesFathima College: A.NiranjanadevisatyajaiNo ratings yet
- Egypt-Israel RelationsDocument5 pagesEgypt-Israel Relationsnamrata_huntNo ratings yet
- Individual EgyptDocument11 pagesIndividual EgyptDmytro HorilenkoNo ratings yet
- Demographics of EgyptDocument3 pagesDemographics of EgyptAnonymous ZSBZhmnI8No ratings yet
- Egypt AssignmentDocument4 pagesEgypt AssignmentJess SamyNo ratings yet
- Geo Graph y Final ShitDocument9 pagesGeo Graph y Final ShitRhod Uriel FabularNo ratings yet
- EgyptDocument3 pagesEgyptJanice DollosaNo ratings yet
- Tunisia Republic FactsDocument4 pagesTunisia Republic Factsfatma ezzahra ben mimounNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa or Addis Abeba (The Spelling Used by The OfficialDocument15 pagesAddis Ababa or Addis Abeba (The Spelling Used by The OfficialnebiyuNo ratings yet
- Class Notes 4Document1 pageClass Notes 4jhvdchjsvNo ratings yet
- Africa: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 pagesAfrica: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchVIOLETA CASARUNo ratings yet
- Israel - SC1Document97 pagesIsrael - SC1amanNo ratings yet
- SudanDocument1 pageSudanpabloNo ratings yet
- AfricaDocument40 pagesAfricamiguelNo ratings yet
- Sudan - Wikipedia PDFDocument161 pagesSudan - Wikipedia PDFmonsfatNo ratings yet
- Greece: Hellenic RepublicDocument7 pagesGreece: Hellenic Republics_bishoymagdyfekryNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Flag, History & CultureDocument7 pagesEgypt's Flag, History & CultureSAASDASDA9682No ratings yet
- Sudan - WikipediaDocument12 pagesSudan - WikipediaoilmanNo ratings yet
- EgyptDocument2 pagesEgyptapi-309342005No ratings yet
- DISS (1)Document2 pagesDISS (1)Jamilla BiancaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument98 pagesDocumentdiana_iuliana_13No ratings yet
- Turkey Not ChipmunkDocument55 pagesTurkey Not ChipmunkRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- Egypt PDFDocument10 pagesEgypt PDFAhmedAbdelZaherNo ratings yet
- Federal Democratic Republic of EthiopiaDocument4 pagesFederal Democratic Republic of EthiopiahoggasNo ratings yet
- Republic of TunisiaDocument7 pagesRepublic of Tunisiafatma dakhliNo ratings yet
- Geography of EgyptDocument2 pagesGeography of EgyptJihad PelminNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Investment AgencyDocument91 pagesEthiopian Investment Agencyabdume74No ratings yet
- Current Issues in EgyptDocument9 pagesCurrent Issues in EgyptshannonNo ratings yet
- Geo Ass 1Document15 pagesGeo Ass 1utopiaamenNo ratings yet
- Egypt: Fast FactsDocument6 pagesEgypt: Fast FactsSourav palitNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Ancient Pharaohs and the Nile CivilizationDocument3 pagesEgypt's Ancient Pharaohs and the Nile Civilizationblumhaghel bogdanNo ratings yet
- Ɪ Z R Eɪ ƏL /: Yisrā'el, IPA:, IPADocument2 pagesꞮ Z R Eɪ ƏL /: Yisrā'el, IPA:, IPAJohn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Algeria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesAlgeria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchJianhengMokNo ratings yet
- TurkDocument21 pagesTurkashish.nairNo ratings yet
- EgyptDocument4 pagesEgyptSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Lamia EgyptDocument21 pagesLamia EgyptRhea KhaitanNo ratings yet
- Egyptian-Sudanese Relations Amidst Power Struggles in The Middle East and Horn of AfricaDocument18 pagesEgyptian-Sudanese Relations Amidst Power Struggles in The Middle East and Horn of Africaزهرة الزنبق زهرة الزنبقNo ratings yet
- Guinea Bissau PDFDocument28 pagesGuinea Bissau PDFAnonymous BeoWLI3D7QNo ratings yet
- MoroccoDocument6 pagesMoroccoKOMCINo ratings yet
- Arab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesArab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeehoggasNo ratings yet
- Arab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesArab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeehoggasNo ratings yet
- Arab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesArab Republic of Egypt: For Other Uses, SeehoggasNo ratings yet
- Federal Democratic Republic of EthiopiaDocument4 pagesFederal Democratic Republic of EthiopiahoggasNo ratings yet
- FGM Violates Women's RightsDocument5 pagesFGM Violates Women's RightsHillary Grace VeronaNo ratings yet
- Serbian LiteratureDocument3 pagesSerbian Literaturedraganscribd12No ratings yet
- 5 Biggest Challenges of Learning EnglishDocument3 pages5 Biggest Challenges of Learning EnglishRico MoradaNo ratings yet
- Discussion On Application For Interior Space Design and The Application of Interior Design StyleDocument9 pagesDiscussion On Application For Interior Space Design and The Application of Interior Design Stylesusan sansannNo ratings yet
- Soal LM Bhs Inggris XI SMT GNP 1516Document8 pagesSoal LM Bhs Inggris XI SMT GNP 1516Rudianto0% (1)
- Mock Job Interview RubricDocument2 pagesMock Job Interview RubricMylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- HEA/RA/PP-2000-6: NO. Course Code Name of Course Credit Hours Grade ResultDocument1 pageHEA/RA/PP-2000-6: NO. Course Code Name of Course Credit Hours Grade ResultRobert AndersonNo ratings yet
- Vihiga County Peace and Conflict ProfileDocument20 pagesVihiga County Peace and Conflict ProfileLazarus KubasuNo ratings yet
- CJR Pembelajaran Bilingual CHRISTINE DAHLIANA BR TARIGANDocument7 pagesCJR Pembelajaran Bilingual CHRISTINE DAHLIANA BR TARIGANChristine Br Tarigan0% (1)
- Literacy Assessment ReflectionDocument5 pagesLiteracy Assessment Reflectionapi-509057201No ratings yet
- Forum 5Document3 pagesForum 5Jesus Villaflor Jr.No ratings yet
- Special Topics in Asean IntegrationDocument8 pagesSpecial Topics in Asean IntegrationKemberly PecayoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document16 pagesAssignment No 1sabeenNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions for ESL TeachersDocument21 pagesInterview Questions for ESL TeachersEfendi PunjotNo ratings yet
- 2018 Higher Level Paper 1 Response: © David Mcintyre, InthinkingDocument2 pages2018 Higher Level Paper 1 Response: © David Mcintyre, Inthinkingjassi bNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Score Analysis for Grade 10Document3 pagesMAPEH Score Analysis for Grade 10Rodolfo Esmejarda Laycano Jr.No ratings yet
- CV Faizul Giffari GazawaliDocument3 pagesCV Faizul Giffari GazawaliCek GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Grade-7 TOSDocument6 pagesGrade-7 TOSmerlyn m romerovNo ratings yet
- Awakening The People Bhutto SpeechesDocument331 pagesAwakening The People Bhutto SpeechesSani Panhwar100% (1)
- Carlos Saura 1932Document8 pagesCarlos Saura 1932Beray SelenNo ratings yet
- PamelaDocument19 pagesPamelaP DasNo ratings yet
- Anthropology: Desiring The OtherDocument34 pagesAnthropology: Desiring The OtherMary Jane de GuzmanNo ratings yet