Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer For Grade 10 Science 1 Quarterly Examination
Uploaded by
Ken Castro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document provides a reviewer for a 10th grade science exam covering topics related to plate tectonics, earth structure, and earthquakes. It includes over 50 bullet points summarizing key concepts and processes such as Pangaea, sea floor spreading, convection currents, plate movement, earthquake measurement, and plate boundary types. It also provides instructions for locating an earthquake epicenter using data from multiple seismological stations.
Original Description:
Reviewer
Original Title
Reviewer for the Kids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides a reviewer for a 10th grade science exam covering topics related to plate tectonics, earth structure, and earthquakes. It includes over 50 bullet points summarizing key concepts and processes such as Pangaea, sea floor spreading, convection currents, plate movement, earthquake measurement, and plate boundary types. It also provides instructions for locating an earthquake epicenter using data from multiple seismological stations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReviewer For Grade 10 Science 1 Quarterly Examination
Uploaded by
Ken CastroThe document provides a reviewer for a 10th grade science exam covering topics related to plate tectonics, earth structure, and earthquakes. It includes over 50 bullet points summarizing key concepts and processes such as Pangaea, sea floor spreading, convection currents, plate movement, earthquake measurement, and plate boundary types. It also provides instructions for locating an earthquake epicenter using data from multiple seismological stations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
REVIEWER FOR GRADE 10 SCIENCE 1st QUARTERLY EXAMINATION
Notes:
1. I had picked random topics of 1st Quarter for this reviewer. Some topics maybe not here in the
reviewer so you may add notes once you print this or edit it on your laptop, CP and desktop.
2. Please study this reviewer. Sayang ang pagod ni teacher.
3. LASTLY, HONOR BEFORE EXCELLENCE. DANGAL BAGO HUSAY. <3
Good luck, mga aking estudyante!
Scientists rejected Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis because he could not
explain the force that pushes or pulls the continents.
During sea-floor spreading, molten material rise along the mid-ocean ridge and
erupt from the mantle.
Scientists drilled rock samples to know the ages of rocks in the mid-ocean ridges.
Pangaea is the supercontinent composed of nowadays India, Antarctica, Australia,
South America and Africa.
Fossils, rocks, glaciers and puzzle-fit of continents were used by Alfred Wegener to
prove his Theory of Continental Drift.
Cartographers are map-makers; they are interested on shapes of continents and
countries in making their maps.
After million years, Pangaea was broken down into two large continents: Laurasia
and Gondwanaland. Laurasia became the Europe and Asia; Gondwanaland became
the Africa, Antarctica, Australia, India and South America.
Harry Hess and Robert Dietz proposed the theory of seafloor spreading.
Convection currents in the asthenosphere/mantle are the reason why the plates are
moving in the lithosphere.
The lithospheric plates are believed to be moving slowly because of convection
currents in the mantle.
The continents will not be located in the same place compared today because they
are constantly moving.
Convection currents in the mantle cause ridges because they are part of divergent
boundaries.
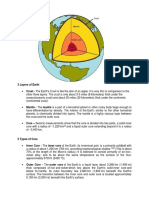
The core of the earth controls its magnetic field.
P-waves are refracted and S-waves are absorbed in the outer core, making a P-wave
shadow zone.
Inner core is solid because of high temperature and high pressure (pressure
freezing).
The mantle is less dense than the core but denser than the crust. It occupies most
of the Earth’s volume.
Because of S-wave shadow zones, we can identify the outer core as liquid state.
For rocks and minerals, people dig into the crust.
The inner core is greatly composed of iron and nickel.
Lithosphere is made up of crust and upper mantle. Meanwhile, asthenosphere is the
weak, plastic layer in the mantle.
Smaller hotspot volcano means it is old compared to bigger ones.
To make a hotspot volcano, magma travels to Earth's surface through an upward
tunnel from deep within Earth.
Subduction zones (oceanic crust-oceanic crust) form volcanic arcs/volcanoes
because it starts to melt rocks and form magma that will go to the surface of Earth.
Tsunamis or “harbor waves” in Japanese are one of the dangers resulted from
earthquakes beneath the ocean floor.
Oceanic crust is denser that continental crust.
Convergent : volcanoes, mountain ranges, earthquakes, trenches, islands
Divergent: new crust, rift valleys, ridges, weak earthquakes
Transform: earthquakes, faults (transform)
Crustal plates move for about 1 centimeter (cm) per day.
Philippine plate and Eurasian plate move together.
Nazca and African plates move together.
Trenches go deeper when subduction zones are active.
Transform faults generate earthquake.
Trenches and volcanic arcs are parallel to one another.
Earth is divided by lithospheric plates because of volcanism, seismicity and
formation of mountain ranges.
distance of the epicenter (km) = (Td / 8 seconds) X 100 km
* Td = time difference of P and S waves
We need to know the epicenter of an earthquake to know the active
fault lines within the area.
To locate the epicenter:
1. Obtain data from three different seismological stations.
2. Determine the difference in the arrival time of S and P waves
recorded from each of the seismological stations.
3. Determine the distance of the epicenter from the station.
4. Use the triangulation method.
-End of Reviewer-
“Without integrity and honor, having everything means nothing.” -Robin Sharma
“With regard to excellence, it is not enough to know, but we must try to have and use it.” -Aristotle
You might also like
- Words of Radiance: Book Two of The Stormlight Archive - Brandon SandersonDocument6 pagesWords of Radiance: Book Two of The Stormlight Archive - Brandon Sandersonxyrytepa0% (3)
- Plate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleDocument48 pagesPlate Movements and Boundaries Science Presentation in Dark Blue Teal StyleAngeline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Hockney-Falco Thesis: 1 Setup of The 2001 PublicationDocument6 pagesHockney-Falco Thesis: 1 Setup of The 2001 PublicationKurayami ReijiNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory and Evidences That Support Continental Drift TheoryDocument11 pagesContinental Drift Theory and Evidences That Support Continental Drift TheoryChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Science 1st Quarter - Grade 10Document8 pagesScience 1st Quarter - Grade 10Patricia Keith Bautista-PapyrusNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 1 Reviewer G10Document12 pagesScience Quarter 1 Reviewer G10jahri ruzeraNo ratings yet
- The Continental Drift Theory HandoutsDocument3 pagesThe Continental Drift Theory Handoutslorraine baysicNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerLeslie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Ud 1-2 Structure and Dynamics of The EarthDocument97 pagesUd 1-2 Structure and Dynamics of The EarthMónica Rodríguez HernándezzNo ratings yet
- Earths InteriorDocument64 pagesEarths InteriorTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 10 ReviewerAmber RamosNo ratings yet
- Science Discussion NotesDocument4 pagesScience Discussion NotesIvan TroyNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewerDocument16 pagesSci ReviewerLeigh SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift HypothesisDocument4 pagesContinental Drift HypothesisRaymart Dave MirandoNo ratings yet
- Interior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Updated English 11Document10 pagesInterior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Updated English 11Team RaagNo ratings yet
- Module 1 For Week 1 (2 DAYS)Document7 pagesModule 1 For Week 1 (2 DAYS)May Lyn BerondoNo ratings yet
- GeomorphologyDocument37 pagesGeomorphologykalluri ganeshNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer YesDocument5 pagesScience Reviewer YesJeffNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Module 1.1Document34 pagesScience 10 Module 1.1marisNo ratings yet
- Interior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics 751653236350454 PDFDocument11 pagesInterior of Earth Formation of Earth Crust Geomorphic Process Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics 751653236350454 PDFGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- T1 NOTES ScienceDocument8 pagesT1 NOTES Science123r12f1No ratings yet
- 4 Plate Tectonics KDDocument16 pages4 Plate Tectonics KDStephen Richard Kirkley100% (1)
- Reviewer 1ST GradingDocument23 pagesReviewer 1ST Gradingpretty raul100% (2)
- The Earth's Interior: By: Junard A. AsentistaDocument75 pagesThe Earth's Interior: By: Junard A. AsentistaJunard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- ES Q2 Week-4bDocument10 pagesES Q2 Week-4bIrish KriselleNo ratings yet
- The Changing EarthDocument52 pagesThe Changing EarthAnileydi Taveras JimenezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Document43 pages4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Jordan RixNo ratings yet
- Chapt 3 MarshakDocument27 pagesChapt 3 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- Science 10 LESSON 1 and 2Document3 pagesScience 10 LESSON 1 and 2jayyyyyrg16No ratings yet
- Handouts in Science 10Document2 pagesHandouts in Science 10CRISTIAN PORTUGALNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Revision P1Document7 pagesPHYSICS Revision P1Mike JosephineNo ratings yet
- Geology Module 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeology Module 2 ReviewerElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNo ratings yet
- Tektonik IndonesiaDocument8 pagesTektonik IndonesiaArfaq Fauqi RomadlonNo ratings yet
- Elective Summary For IntroductionDocument3 pagesElective Summary For IntroductionFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Module 10 Reviewer Sem1 q2Document4 pagesEarth Science Module 10 Reviewer Sem1 q2John Aiddy VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document53 pagesScience 10jamespfronda0796No ratings yet
- 3 Layers of EarthDocument18 pages3 Layers of EarthDaddyDiddy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science Space and Geology RevisionDocument5 pagesYear 9 Science Space and Geology Revisiondan964No ratings yet
- The Nature of EarthDocument13 pagesThe Nature of Earthgeneabi012No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerMelody Bong ZitaNo ratings yet
- SMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalDocument16 pagesSMS 1201 A K M Mohiuddin FinalA.K.M. MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Sciencestudyguide 3Document3 pagesSciencestudyguide 3api-251436295No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesPlate TectonicsDBSKfangirlNo ratings yet
- Science 1.09 Seafloor Spreading TheoryDocument1 pageScience 1.09 Seafloor Spreading TheoryElijah Gabriel T. MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Global Geological HazardsDocument27 pagesGlobal Geological HazardssalmanNo ratings yet
- Geomorphologynoteslecture2 PDFDocument11 pagesGeomorphologynoteslecture2 PDFAshpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 1b.p-Earth's Structures & Continental DriftDocument17 pages1b.p-Earth's Structures & Continental DriftRicky Vincent TormesNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Tectonics PlateDocument9 pages3 Types of Tectonics PlateJingky MarzanPurisima Lumauig SallicopNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Sci Q1 G10Document27 pagesPlate Tectonics Sci Q1 G10Charlotte Anne FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Daniel Alcides Carrión National University: TOPIC: Tectonic PlatesDocument5 pagesDaniel Alcides Carrión National University: TOPIC: Tectonic PlatesKevin Julca BalvinNo ratings yet
- Magnetic-ReversalDocument19 pagesMagnetic-ReversalThe WeekndNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument5 pagesResearchMacaraeg Kendrick M.No ratings yet
- 16plate TectonicsDocument6 pages16plate TectonicsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Triassic FossilsDocument14 pagesTriassic FossilsRachelle Ann BaldonadeNo ratings yet
- 2 Ocean Basins and Plate Tectonics AMS 2018Document10 pages2 Ocean Basins and Plate Tectonics AMS 2018Brandon PraterNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Structural Geology 2020-23Document65 pagesGroup 1 Structural Geology 2020-23Aeshah RafeequeNo ratings yet
- Handout 13Document2 pagesHandout 13Dione Gale NavalNo ratings yet
- Evidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleDocument6 pagesEvidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleChristopher Shane GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Earth: Surface, Structure and AgeDocument13 pagesThe Earth: Surface, Structure and AgeOlsen SoqueñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5api-286015323No ratings yet
- The Interior of The Earth: Last Modified 01-14-11Document5 pagesThe Interior of The Earth: Last Modified 01-14-11ivan pesebreNo ratings yet
- Geology: A Fully Illustrated, Authoritative and Easy-to-Use GuideFrom EverandGeology: A Fully Illustrated, Authoritative and Easy-to-Use GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- RARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesDocument91 pagesRARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesenoshaugustineNo ratings yet
- GPP Calendar of Activities 2022 23 SdoDocument5 pagesGPP Calendar of Activities 2022 23 SdoRomel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Toolbox TalkDocument14 pagesToolbox Talkcall_mustafas2361No ratings yet
- G10 Lesson2 DLPDocument13 pagesG10 Lesson2 DLPAngeles, Mark Allen CNo ratings yet
- NHD Process PaperDocument2 pagesNHD Process Paperapi-203024952100% (1)
- Grade 7 Nap MayDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Nap Mayesivaks2000No ratings yet
- Carnegie Mellon Thesis RepositoryDocument4 pagesCarnegie Mellon Thesis Repositoryalisonreedphoenix100% (2)
- Evidence Prove DiscriminationDocument5 pagesEvidence Prove DiscriminationRenzo JimenezNo ratings yet
- Very Narrow Aisle MTC Turret TruckDocument6 pagesVery Narrow Aisle MTC Turret Truckfirdaushalam96No ratings yet
- 0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andDocument20 pages0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andJuke LastNo ratings yet
- Circular ConvolutionDocument3 pagesCircular Convolutionseeksudhanshu1No ratings yet
- Safety Bulletin 09 - Emergency Escape Breathing Device - Product RecallDocument2 pagesSafety Bulletin 09 - Emergency Escape Breathing Device - Product RecallMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EthicsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To EthicsMarielle Guerra04No ratings yet
- SEILDocument4 pagesSEILGopal RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Test 2-Module 1 12-10-2017: VocabularyDocument2 pagesTest 2-Module 1 12-10-2017: VocabularySzabolcs Kelemen100% (1)
- Sale Counter List JuneDocument9 pagesSale Counter List Junep6a4nduNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Associated With DiarrheaDocument7 pagesPathogenic Escherichia Coli Associated With DiarrheaSiti Fatimah RadNo ratings yet
- СV Nestor RodriguezDocument28 pagesСV Nestor RodriguezKate BrownNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536Document4 pagesSafety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536BanyuNo ratings yet
- Note!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXDocument4 pagesNote!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXAdityaArnas0% (1)
- Magic Bullet Theory - PPTDocument5 pagesMagic Bullet Theory - PPTThe Bengal ChariotNo ratings yet
- Wealth and Poverty in The Book of Proverbs PDFDocument133 pagesWealth and Poverty in The Book of Proverbs PDFMaahes Cultural Library100% (1)
- Contemporary Strategic ManagementDocument2 pagesContemporary Strategic ManagementZee Dee100% (1)
- Culture 2007 2013 Projects Overview 2018-03-18Document133 pagesCulture 2007 2013 Projects Overview 2018-03-18PontesDeboraNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - TQM 03 2020 0066 PDFDocument23 pages10 1108 - TQM 03 2020 0066 PDFLejandra MNo ratings yet
- Practice - Test 2Document5 pagesPractice - Test 2Nguyễn QanhNo ratings yet
- Educationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeDocument84 pagesEducationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeAnna ModebadzeNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Manila University: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAteneo de Manila University: Submitted byCuster CoNo ratings yet