Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Creep Through Demo
Uploaded by
Viswanadhapalli Himasree mm17b113Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding Creep Through Demo
Uploaded by
Viswanadhapalli Himasree mm17b113Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: V.
Himasree(MM17B113)
Instructor’s name: Anand Krishna Kanjarla
13 April 2019
Creep Demo
AIM: To understand the concept of creep.
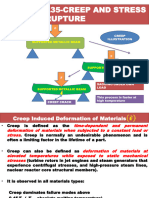
THEORY: Creep is a time dependent deformation on applying certain load.Generally
it occurs at finite temperatures but for some materials it can also happen at room
temperatures.Creep is likely to occur when temperature reaches homologous temperature (0.5
times melting point). In creep, the material undergoes a time dependent decrease in length
which is dangerous. In creep strain vs time curve is plotted. The slope of the line in this curve
is called creep rate(rate of deformation). Materials with high melting point, high elastic
modulus and large grain sizes generally avoid creep failure. The three stages of creep are
primary creep, secondary creep and tertiary creep.
• Primary creep: The creep rate (slope) decreases with time, this indicates the work
hardening of the material. Minimum creep rate is reached at the end of the primary creep
which is maintained in the secondary creep.
• Secondary creep: The creep rate (slope) is constant. This is steady state, that is the
work hardening and the recovery of the material is well balanced.
• Tertiary creep: The creep rate (slope) increases with time. We observe formation of
voids, internal cracks, etc. Rapidly accelerates strain rate up to the failure. The sample is
pulled apart at a time t=tR
There are different creep mechanisms. Dislocation related creep mechanism are cross-
slip, climb, glide. Diffusional related creep mechanisms are Nabarro-Herring creep, Coble
creep, Dissociation core diffusion creep, interface-reaction controlled diffusional flow. Grain
boundary sliding creep. Let’s discuss about Nabarro-Herring creep, Coble creep, Dislocation
climb and Thermally activated glide.
CREEP TEST DEMO "1
• Nabarro-Herring creep: In Nabarro-Herring creep or bulk diffusion, the creep
rate increases as the grain size decreases. This mechanism is lattice diffusion controlled.
• Coble creep: In coble creep, the creep rate is strongly dependent on the grain size
compared to the Navarro-Herring creep. Coble creep is grain boundary diffusion
controlled.
• Dissociation climb: In this mechanism, the movement of dislocations control the
creep rate.
• Thermally activated glide: This is generally observed in polymers and some
viscoelastic materials.
CREEP TESTING:
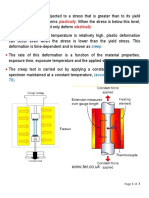
Sample used for creep testing is generally cylindrical. Strain versus time is been plotted
at constant load and temperature at relatively low creep rate and load. Test is carried out at
CREEP TEST DEMO "2
less than 0.5% strain. It usually takes 2000 to 10000 hours. It is performed inside a chamber
to control heating. To minimise the thermal expansion effects on the sample temperature
control is essential. Before loading the sample is heated to the temperature T that is required
and gauge length is measured then load is applied without any shock quickly. Strain is
observed at frequently regular intervals.
CREEP TEST DEMO "3
You might also like
- Creep Test Complete PDFDocument8 pagesCreep Test Complete PDFKalKatu MaLam50% (6)
- 13 Creep and Stress RuptureDocument25 pages13 Creep and Stress RuptureZdravko IvancicNo ratings yet
- Air Liquide MRPL Overview and Air Liquide Geismar Utility ServicesDocument15 pagesAir Liquide MRPL Overview and Air Liquide Geismar Utility ServicesPland SpringNo ratings yet
- Book - Chap 05 Creep TestDocument27 pagesBook - Chap 05 Creep TestHamdani NurdinNo ratings yet
- Creep Failure Mechanisms and TestingDocument42 pagesCreep Failure Mechanisms and TestingNilesh Balkrishna Sunita Apte0% (1)
- Stress Rupture and Elevated Temparature Fatigue: Shaik Fharaz 18Md07Document16 pagesStress Rupture and Elevated Temparature Fatigue: Shaik Fharaz 18Md07santhosh smartNo ratings yet
- ABS Acceptance of Filler Metals To AWSDocument2 pagesABS Acceptance of Filler Metals To AWSgeorgekc77No ratings yet
- CCS in The Cement IndustryDocument19 pagesCCS in The Cement IndustryJohn Giannakopoulos100% (1)
- A - One Polar LimitedDocument20 pagesA - One Polar LimitedinfoNo ratings yet
- Creep IntroductionDocument56 pagesCreep IntroductionayushdbcNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument26 pagesCreepOsu AmpawanonNo ratings yet
- Creep Fracture Mechanisms ExplainedDocument38 pagesCreep Fracture Mechanisms ExplainedclaradwisNo ratings yet
- MTPE22 - High Temperature MaterialsDocument11 pagesMTPE22 - High Temperature MaterialsSatyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On " Creep Test": Rupendra S. Tanwar, Assistant Professor, MED IPS Academy IES IndoreDocument13 pagesPresentation On " Creep Test": Rupendra S. Tanwar, Assistant Professor, MED IPS Academy IES IndoreRupendra Tanwar IPSANo ratings yet
- CreepDocument60 pagesCreepUsama SaoodNo ratings yet
- Creep Testing: Test Name PrincipleDocument2 pagesCreep Testing: Test Name PrinciplerohitNo ratings yet
- Polymer Creep Test Stages and EffectsDocument12 pagesPolymer Creep Test Stages and EffectsMONIRUZZAMAN MONIR100% (1)
- 34-Creep Deformation-31-10-2023Document22 pages34-Creep Deformation-31-10-2023NandiniNo ratings yet
- Creep Deformation of MetalsDocument12 pagesCreep Deformation of Metalssagardeshpande60No ratings yet
- Temperature Dependence: o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument3 pagesTemperature Dependence: o o o o o o o o o o o oZoe FallurinNo ratings yet
- Creep in MaterialsDocument2 pagesCreep in MaterialsAnonymous pmPNWGpNo ratings yet
- Creep (Deformation)Document5 pagesCreep (Deformation)Carlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Plastically. Elastically.: CreepDocument7 pagesPlastically. Elastically.: CreepSheikh UbaidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Creep and RuptureDocument8 pagesLecture 8 Creep and RuptureAzhar AliNo ratings yet
- Lab MMTDocument30 pagesLab MMTSaad khanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Creep)Document3 pagesLab Report (Creep)Aleem RiderNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Creep) Analyzes Polymer Strain Under LoadDocument3 pagesLab Report (Creep) Analyzes Polymer Strain Under LoadAleem RiderNo ratings yet
- 7 اشي مفخرهDocument5 pages7 اشي مفخرهosama.ammer2002No ratings yet
- Conversion Table & Chart: The Table Gives The Conversion Between DPH, Rockwell Hardness and Brinell HardnessDocument10 pagesConversion Table & Chart: The Table Gives The Conversion Between DPH, Rockwell Hardness and Brinell HardnessAsifMutahirNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Materials: Samir Fernando Castilla Acevedo Chem E., M. Eng., Ph.D. StudentDocument21 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials: Samir Fernando Castilla Acevedo Chem E., M. Eng., Ph.D. StudentMateo PerezNo ratings yet
- Background and Usage: CreepDocument8 pagesBackground and Usage: CreepharicoolestNo ratings yet
- Creep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofDocument2 pagesCreep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofحسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- Creep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofDocument2 pagesCreep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofحسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- Creep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofDocument2 pagesCreep Test: Creep: The Deformation of A Material With The Passage ofحسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- University Of Kirkuk College Of Engineering Performs Creep TestDocument6 pagesUniversity Of Kirkuk College Of Engineering Performs Creep Testعبدالمؤمن خالد محمودNo ratings yet
- Lec 15 (2211)Document9 pagesLec 15 (2211)IshmamNo ratings yet
- Creep - EMM212 - Physical Metallurgy IIDocument34 pagesCreep - EMM212 - Physical Metallurgy IICalebNo ratings yet
- Creep (Deformation) PDFDocument13 pagesCreep (Deformation) PDFAdamRaczNo ratings yet
- Creep Strength: Definitions: Creep Is The Tendency of A Solid Material To Move Slowly or Deform Permanently UnderDocument5 pagesCreep Strength: Definitions: Creep Is The Tendency of A Solid Material To Move Slowly or Deform Permanently UnderUmarDraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Creep Test & Proving RingqDocument9 pagesLecture 4 - Creep Test & Proving RingqabgkkmjqpemmcvfpcuNo ratings yet
- Study of Time DependenceDocument25 pagesStudy of Time DependenceSwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Creep - MSE 305Document46 pagesCreep - MSE 305Badmus AbdulmalikNo ratings yet
- Creep (Deformation) - WikipediaDocument14 pagesCreep (Deformation) - WikipediaMustaqeem NabiNo ratings yet
- Conflong CreepDocument31 pagesConflong CreepAnonymous LMfIjpENo ratings yet
- Material Lab 7Document3 pagesMaterial Lab 721pwind0685No ratings yet
- Creep and Stress RuptureDocument43 pagesCreep and Stress RuptureAlfiansyah DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Creepof CeramicsDocument14 pagesCreepof CeramicsTejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Urvival at High Temperatures: Sub-Topics High Temperature Materials CreepDocument33 pagesUrvival at High Temperatures: Sub-Topics High Temperature Materials CreepessamNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument20 pagesCreepGhaida mohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 - Creep Test FinalDocument6 pages1 - Creep Test Finalosama.ammer2002No ratings yet
- Lect 5Document45 pagesLect 5Hüseyin xNo ratings yet
- Creep Strength: Definitions: Creep Is The Tendency of A Solid Material To Move Slowly or Deform Permanently UnderDocument13 pagesCreep Strength: Definitions: Creep Is The Tendency of A Solid Material To Move Slowly or Deform Permanently UnderupenderNo ratings yet
- Testing hardened mortar propertiesDocument5 pagesTesting hardened mortar propertiesbatteekhNo ratings yet
- Creep Test CurveDocument3 pagesCreep Test CurveAmmar AlmanaseerNo ratings yet
- Topic #3a Creep and FatigueDocument50 pagesTopic #3a Creep and FatigueDaniel Janthinus Kristianto100% (1)
- Creep Properties PDFDocument23 pagesCreep Properties PDFMehmet Soysal100% (1)
- Material Lab 7Document3 pagesMaterial Lab 721pwind0685No ratings yet
- Creep TestingDocument26 pagesCreep Testingsamurai7_77No ratings yet
- Textile Testing & Quality Assurance: Crease RecoveryDocument5 pagesTextile Testing & Quality Assurance: Crease RecoveryTauqeer Raza100% (1)
- Fracture BehaviourDocument58 pagesFracture BehaviournavneeshvNo ratings yet
- Creep (Deformation)Document7 pagesCreep (Deformation)Harianto ArieNo ratings yet
- Process Variables and Ideal Gases: Cheme 101 Module 2 Part 1Document13 pagesProcess Variables and Ideal Gases: Cheme 101 Module 2 Part 1AcademicBMNo ratings yet
- Creep test analysisDocument4 pagesCreep test analysisجعفر ذيابNo ratings yet
- Repair Pocket Guide B31Document2 pagesRepair Pocket Guide B31Adolfo Israel Ayuso SaezNo ratings yet
- TDS Weberanc 405 BFXDocument14 pagesTDS Weberanc 405 BFXTawfeek JadidNo ratings yet
- ITEM 400 Latest 2012 (M) 2 FinalDocument170 pagesITEM 400 Latest 2012 (M) 2 FinalMikhail TabucalNo ratings yet
- Case Study Biomaterials Selection For A Joint ReplacementDocument8 pagesCase Study Biomaterials Selection For A Joint ReplacementBjarne Van haegenbergNo ratings yet
- High Capacity IKN Clinker Coolers - MR Huybens Bernard, IKN PDFDocument9 pagesHigh Capacity IKN Clinker Coolers - MR Huybens Bernard, IKN PDFcassindromeNo ratings yet
- BT 31Document9 pagesBT 31dalton2003No ratings yet
- 2019 - Corani - Ni43-101 - r1 - Final - Compressed (2) - 56-104Document49 pages2019 - Corani - Ni43-101 - r1 - Final - Compressed (2) - 56-104Jheison YunguriNo ratings yet
- HT PoleDocument8 pagesHT PolemanishNo ratings yet
- Bonderite NT-1 (14825190)Document6 pagesBonderite NT-1 (14825190)Nikolas Kolasni Lakenir Ckerde DockosNo ratings yet
- Denture Base PolymersDocument47 pagesDenture Base PolymersAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Fabric Testing and Process Control for Quality Denim ProductionDocument11 pagesImportance of Fabric Testing and Process Control for Quality Denim ProductionBasit KhanNo ratings yet
- GF Indonesia Brochure PR UTS 0417 Garda SuryaDocument12 pagesGF Indonesia Brochure PR UTS 0417 Garda SuryaRival Juney Christian PatrasNo ratings yet
- Inspection Report ALU - Jul-2021 PASS, FAILDocument196 pagesInspection Report ALU - Jul-2021 PASS, FAILHiếu PhanNo ratings yet
- Brett Trade Guide 2020 1Document104 pagesBrett Trade Guide 2020 1ANo ratings yet
- Rate List of 2011 (Physical Lab)Document1 pageRate List of 2011 (Physical Lab)lpdiNo ratings yet
- SHERA Wood CatalogDocument16 pagesSHERA Wood Cataloghk1680% (1)
- Sunwave™ Prismatic Skylights: Product InformationDocument9 pagesSunwave™ Prismatic Skylights: Product InformationAduanas 1No ratings yet
- OMB Gate Valve & Check Valve #800 CatalogDocument4 pagesOMB Gate Valve & Check Valve #800 CatalogEPC Patuha BMJNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tack Coat Application On Interlayer Shear Strength of Asphalt Pavement: A State-Of-The-Art Review Based On Application in The United StatesDocument12 pagesEffect of Tack Coat Application On Interlayer Shear Strength of Asphalt Pavement: A State-Of-The-Art Review Based On Application in The United StatesNgân KimNo ratings yet
- PART 1 - Spring CapeletDocument2 pagesPART 1 - Spring CapeletFabros VanessaNo ratings yet
- 3 - MYP - 1 - Unit - 2 - Chemistry - Week - 4 - SolutionsDocument63 pages3 - MYP - 1 - Unit - 2 - Chemistry - Week - 4 - Solutionsvandana giriNo ratings yet
- Pet Bottle Strips ReinforcementDocument22 pagesPet Bottle Strips ReinforcementJaron FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 13.09 Stream A AxensDocument27 pages13.09 Stream A AxensJorge Ariel QuipildorNo ratings yet
- High Build Epoxy Coating for Hulls and Ballast TanksDocument3 pagesHigh Build Epoxy Coating for Hulls and Ballast Tankskasosei0% (1)
- Thai industrial standard for high carbon steel wire rodsDocument10 pagesThai industrial standard for high carbon steel wire rodsNabeel IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Financial Markets & InstitutionDocument38 pagesAssignment: Financial Markets & InstitutionFaraz AamirNo ratings yet