Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Che 421A Clearly State The Sources of Substance Properties. Enclose Final Answers in A Box
Che 421A Clearly State The Sources of Substance Properties. Enclose Final Answers in A Box
Uploaded by
Kaiser Angelo G. LadoresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Che 421A Clearly State The Sources of Substance Properties. Enclose Final Answers in A Box
Che 421A Clearly State The Sources of Substance Properties. Enclose Final Answers in A Box
Uploaded by
Kaiser Angelo G. LadoresCopyright:
Available Formats
ChE 421A
Clearly state the sources of substance properties. Enclose final answers in a BOX
1. Ammonia gas (A) is diffusing at steady-state through N2 (B) by equimolar counter-diffusion in a
circular conduit 1.22 m long at 25C and a total pressure of 101.32 kPa absolute. The partial
pressure of ammonia at the left end is 25.33 kPa and 5.066 kPa at the other end. The conduit has a
diameter of 0.0305 m at the left end and tapering uniformly to 0.0610 m at the right end. The
diffusivity is 0.023 x 10–4 m2/s. Calculate the rate of diffusion of ammonia.
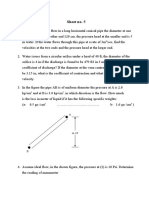
2. An open cylindrical tank is filled with acetone, 2ft from the top. The tank is tapered as shown in the
figure. Air above the tank is adequate to assure negligible concentration of acetone as it leaves the container. The system is at 25°C and
1atm. The price of acetone is $5/L and its molar volume = 74.05 cm3/mol. (a) What is the rate of evaporation of acetone in kg/s (b) how
much is lost in peso after 2 hours of exposure?
4ft
2ft
6ft
3. A 3-cm diameter Stefan tube is used to measure the binary diffusion coefficient of water vapor in air at 20°C at an elevation of 1600m
where the atmospheric pressure is 83.5 kPa. The tube is partially filled with water, and the distance from the water surface to the open
end of the tube is 40cm. Dry air is blown over the open end of the tube so that the water vapor rising to the top is removed immediately
and the concentration of vapor at the top of the tube is zero. In 15 days of continuous operation at constant pressure and temperature,
the amount of water that has evaporated is measured to be 1.23g. Determine the diffusion coefficient of water in the given conditions.
4. A water droplet having a diameter of 0.10 mm is suspended in still air at 320K, 101 kPa, and 20% relative humidity.
a) Calculate the initial rate of evaporation of water
b) Determine the time for the water droplet to evaporate completely.
You might also like
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerMukhzin Rashid100% (3)
- Mass TransferDocument3 pagesMass TransferAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- CL 303-Assignment No.1Document2 pagesCL 303-Assignment No.1Vineeth Dasaraju0% (1)
- Chap 16Document5 pagesChap 16shaito100% (2)
- Mixed TopicDocument105 pagesMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Example From JB SlidesDocument14 pagesExample From JB SlidesSangetha Chelladorai0% (3)
- CCB2053 TuTorial 2Document1 pageCCB2053 TuTorial 2Yassin RoslanNo ratings yet
- SP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022Document2 pagesSP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022ONKAR ARORA0% (1)
- Jnjk'aja J ADocument2 pagesJnjk'aja J AJV CustodioNo ratings yet
- Ccb2053 Assignment 1Document2 pagesCcb2053 Assignment 1Yassin RoslanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3Soon Yung WangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Sums DiffusionDocument11 pagesTutorial-Sums DiffusionHridyaAshokanNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Document15 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Mass Transfer Cairo M5zncomnewuploads20131003pdfm5znDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Mass Transfer Cairo M5zncomnewuploads20131003pdfm5znMm ShdedNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - ProblemsDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics - ProblemsClement Chima50% (2)
- Kmu346-22 HW IDocument1 pageKmu346-22 HW IDevendraa MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer CoefficientDocument6 pagesMass Transfer CoefficientEthan PierceNo ratings yet
- MT-I Question Bank August 2011Document1 pageMT-I Question Bank August 2011Muthu RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Aini LeeNo ratings yet
- Mass Cours 1 2017Document2 pagesMass Cours 1 2017نزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Mass TransferDocument5 pagesTutorial Mass TransferAimy YasminNo ratings yet
- Teaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Document7 pagesTeaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Solin HawreNo ratings yet
- GeologyDocument41 pagesGeologyNamara TemesgenNo ratings yet
- What Will Happen To The Level of Water in Case 2 and Case 3 in Comparison of Case 1?Document5 pagesWhat Will Happen To The Level of Water in Case 2 and Case 3 in Comparison of Case 1?random noobNo ratings yet
- ME Con-2Document8 pagesME Con-2Divyanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Sample Probs Heat TransferDocument3 pagesSample Probs Heat Transferche.2ndyearNo ratings yet
- Assignment - III (Part-I, II III)Document8 pagesAssignment - III (Part-I, II III)Prerna JainNo ratings yet
- Review Problems From Diff BooksDocument9 pagesReview Problems From Diff BooksHannah AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Mass TotourialsDocument5 pagesMass TotourialsOmr MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Mass Transfer Solved ProblemsDocument22 pagesDiffusion Mass Transfer Solved ProblemsSteph Kier PonterasNo ratings yet
- Assignment-II (PART A)Document4 pagesAssignment-II (PART A)divyanshu.221ch018No ratings yet
- 2012 Problem Set 3Document3 pages2012 Problem Set 3Fiona PuNo ratings yet
- Isentropic Flow - Area VariationDocument11 pagesIsentropic Flow - Area VariationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentUdayNo ratings yet
- Problemas OrdinarioDocument10 pagesProblemas OrdinarioAngelo EdoraNo ratings yet
- AIRCONDITIONING ProblemsDocument28 pagesAIRCONDITIONING Problemsعبدالرحمن منصورNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5Document3 pagesSheet 5Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionDocument25 pagesHomework SolutionHirman De NovaNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption Problem Set 2016Document2 pagesGas Absorption Problem Set 2016Jumar CadondonNo ratings yet
- Power Plant and Industrial Plant Design Pre-Board/RefresherDocument13 pagesPower Plant and Industrial Plant Design Pre-Board/RefresherMark Gil Jalbuena AltezaNo ratings yet
- FM - Assignment 2Document2 pagesFM - Assignment 2Swagata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech - TutorialsDocument19 pagesFluid Mech - Tutorialsiddi5504No ratings yet
- Overall-Problems (Day 2)Document52 pagesOverall-Problems (Day 2)jantskie0% (2)
- Mass Transfer TutorialDocument4 pagesMass Transfer TutorialShashank_PardhikarNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- LTpart 2Document7 pagesLTpart 2Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Tuitorial Pff216b July-2021Document6 pagesTuitorial Pff216b July-2021Enabewhkom OhpmNo ratings yet
- Physics 14 HWDocument2 pagesPhysics 14 HWMelody KimNo ratings yet
- GASES With Varying Path LengthDocument12 pagesGASES With Varying Path LengthKristine Ann VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1John Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CondensationDocument1 pageTutorial Condensationeja70No ratings yet
- Lectut CHN-102 PDF Eq StateDocument3 pagesLectut CHN-102 PDF Eq StateTanmaysainiNo ratings yet
- Tutorials ChE314Document12 pagesTutorials ChE314Nagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Velocity of Sound in Sea Water: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of the Velocity of Sound in Sea Water: Mathematical Tables SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 3 (Expt 8)Document2 pagesChapter 3 (Expt 8)Carlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 16221Document6 pagesS Announcement 16221Carlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Flow of Incompressible Fluids in Conduits and Thin LayersDocument3 pagesFlow of Incompressible Fluids in Conduits and Thin LayersCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Flowrate Vs Headloss: Calibration On An Orifice MeterDocument1 pageFlowrate Vs Headloss: Calibration On An Orifice MeterCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Equity TheoryDocument2 pagesEquity TheoryCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Prevention and MitigationDocument36 pagesDisaster Prevention and MitigationCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- 7 Disaster MitigationDocument23 pages7 Disaster MitigationCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument1 pageHeatCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Mystery." But Are We Even Sure That We Will Witness The Mystery of Tomorrow? IsDocument1 pageMystery." But Are We Even Sure That We Will Witness The Mystery of Tomorrow? IsCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Economy Posts 7.1 Percent GDP Growth in The Third Quarter of 2016Document2 pagesPhilippine Economy Posts 7.1 Percent GDP Growth in The Third Quarter of 2016Carlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- Colloidal DispersionDocument5 pagesColloidal DispersionCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet