Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical No:1 Title: Zoonotic Disease of Poultry and Their Control Measure
Uploaded by
Shiva KhanalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical No:1 Title: Zoonotic Disease of Poultry and Their Control Measure
Uploaded by
Shiva KhanalCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical no:1
Title: Zoonotic disease of poultry and their control measure
Objectives
To get acquainted with poultry zoonosis
To know different infectious agents responsible for poultry zoonosis
To know mode of transmission of zoonosis
To know prevention and control measures of poultry zoonosis
Theory
A poultry zoonosis is any disease or infection that is naturally transmissible from poultry to
humans. Avian zoonotic diseases can be divided into two major groups
1. Those exclusively from birds
2. Those that can also originate from other animals.
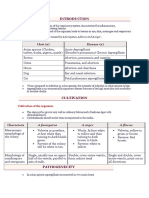
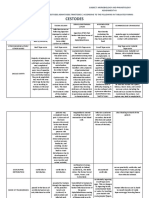
Zoonoses exclusive from birds
Disease Etiology Transmissiom Signs and Symptoms
Avian H5N1 avian Direct contact, raw or Respiratory symptoms
influenza influenza virus undercooked poultry and
poultry products
Ranikhet Paramyxo virus Direct contact, through Eye infection
dropping and nasal
discharge
Chlamydiosis Chlamydia Inhalation or ingestion Fever, headache, dry
psittaci, especially dry cough
submicroscopic contaminated
bacteria materials (dust)
Histoplasmosis Fungus Spore Inhalation Fever, chills, chest
Histoplasma from contaminated discomfort
capsulatum soil/material
West Nile Virus Genus Flavivirus. Birds are Flu-like
mosquito vector reservoirs. condition in humans
(Culex species).
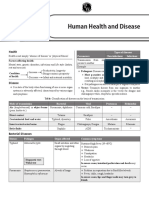
Zoonoses not exclusive to birds
Disease Etiology Transmissiom Signs and Symptoms
Salmonellosis S. enteritidis, S Undercooked meat Diarrhoea, vomiting,
typhimurium, S and egg products abdominal cramps
new port from infected birds
Campylobacteri Mainly C. Contact or ingestion Enteritis and
o jejuni. of undercooked, diarrhoea
sis contaminated meat
Colibacillosis E. coli fecal/oral route Bloody diaeehoea
Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Inhalation - agent in Coughing more than 3
avium complex dried droppings and weeks, blood in sputum
(MAC) contaminated soil
Pasteurellosis P. Multocida Wounds, bites or scratches Local infection, may
cause acute
pneumonia
Listeriosis L. Oral route. Causes Fever, stiff neck,
monocytogenes bacteraemia, weakness, vomiting
septicaemia
Erysipelas Erysipelothrix Cuts or abrasions contact Swollen, red and shiny
rhusiopathiae animals, tissues and muscle skin
Control measures for poultry zoonosis
1) Farm Sanitation
Fumigation with disinfectants
Proper disposal of litter and manure
Cleansing and disinfection of soiled equipments
2) Use of personal protective equipments while dealing with poultry (coveralls, boots, mask,
goggle etc)
3) Control of vectors (Eg. Control of mosquito for west nile virus)
4) Strict biosecurity
Isolation
Traffic control
Sanitation
5) Proper disposal of infected carcass (burning or incineration preferred)
6) Sanitation and disinfection of slaughterhouse
7) Periodic surveillance and monitoring of poultry farm, slaughterhouse and retail meat shop
8) Vaccination of poultry for zoonotic disease
9) Controlling slaughter of sick and deliberated birds
10) Good sanitation and hygiene during food preparation
11) Eliminating cross contamination of food with meat
12) Cooking meat at safe temperature
13) Use preservatives (salt, nitrates etc) and refrigerate meat for prolong storage
14) |Strict quarantine measure to control of spread of disease
15) Raising awareness to students, farmers, shopkeepers and consumers through newspaper, TV,
leaflets, pamphlets for control of poultry zoonosis
You might also like
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Human Health and Disease-1Document12 pagesHuman Health and Disease-1Ananya MoniNo ratings yet
- Poultry diseases: Causes, symptoms and treatment, with notes on post-mortem examinationsFrom EverandPoultry diseases: Causes, symptoms and treatment, with notes on post-mortem examinationsNo ratings yet
- Environmentally Transmitted Pathogens CH 22 - 2018Document24 pagesEnvironmentally Transmitted Pathogens CH 22 - 2018reprano PNo ratings yet
- Common Poultry DiseasesDocument10 pagesCommon Poultry DiseasesDebbie Samar BoragayNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Activity Protozoans & NematodesDocument16 pagesParasitology Lab Activity Protozoans & NematodesJollan Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Zoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKDocument64 pagesZoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKakun internetNo ratings yet
- Aspergillosis in Poultry and Other SpeciesDocument3 pagesAspergillosis in Poultry and Other SpeciesVedha VincyNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Diseases Found in Captivity FinalDocument45 pagesMammalian Diseases Found in Captivity Finalapi-250146149No ratings yet
- Pathologic and NonDocument11 pagesPathologic and NonAisha DoreenNo ratings yet
- Fix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaDocument52 pagesFix PPT Penyakit Kambing DombaGaluh EnggarNo ratings yet
- Avian Diseases Found in Captivity FinalDocument16 pagesAvian Diseases Found in Captivity Finalapi-250146149No ratings yet
- List of Causative AgentDocument26 pagesList of Causative AgentMe2 ModhNo ratings yet
- 4A Group 3 Orthomyxoviridae, PoxviridaeDocument46 pages4A Group 3 Orthomyxoviridae, PoxviridaeLowella Rose C. DonguinesNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument15 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesHarshith HachhuNo ratings yet
- Selected Bacterial and Mycotic Infections of Poultry 10Document90 pagesSelected Bacterial and Mycotic Infections of Poultry 10Iancu SebastianNo ratings yet
- Human Health and Diseases NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Health and Diseases NotesYuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Medical EntomologyDocument39 pagesMedical EntomologyRIZIQ TSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Health and Hygiene - SADocument8 pagesChapter 1. Health and Hygiene - SAPalakNo ratings yet
- GLANDERS: A FATAL DISEASE OF EQUIDAEDocument28 pagesGLANDERS: A FATAL DISEASE OF EQUIDAEMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- q3 Health 8 Notes Infection and CommunicableDocument6 pagesq3 Health 8 Notes Infection and CommunicablecaballesandreanicoleaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disease With Color AtlasDocument45 pagesRespiratory Disease With Color Atlasahmad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Himor - LG3.1 2nd QuaDocument5 pagesHimor - LG3.1 2nd QuaJeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 Q3W8 Animal ProdDocument8 pagesTLE 8 Q3W8 Animal Prodplaq0% (1)
- Human Health & Diseases Short Notes Lakshya NEET 2024Document5 pagesHuman Health & Diseases Short Notes Lakshya NEET 2024Vanshika YadavNo ratings yet
- Final - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsDocument5 pagesFinal - Zoonotic Diseases From Sheep & GaotsVijay JadhavNo ratings yet
- Summary of Farm Animal DiseasesDocument1 pageSummary of Farm Animal DiseasesJerico Mituda ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- Cattle Diseases and ParasitesDocument6 pagesCattle Diseases and ParasitesNorman Rodriguez LlorandoNo ratings yet
- Tdladmin, 50Document7 pagesTdladmin, 50MD shohelNo ratings yet
- HOST-PATHOGEN INTERACTIONSDocument48 pagesHOST-PATHOGEN INTERACTIONSFajar AnshoriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologyRNEE LEYRITANo ratings yet
- Large Ruminant DiseasesDocument96 pagesLarge Ruminant DiseasesJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases and ParasitesDocument47 pagesCommon Diseases and ParasitesJane LabradorNo ratings yet
- Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesHealth and Diseasereet.patidar18No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Medical Entomology, IntroductionDocument57 pagesMedical Entomology, IntroductionKing IvyNo ratings yet
- OtopDocument96 pagesOtopJayzle SaguisiNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases: Posted byDocument4 pagesCommon Diseases: Posted byChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Fungal InfectionsDocument81 pagesOpportunistic Fungal Infectionstummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Safe Handling, Packaging & Shipping of Infectious SubstancesDocument96 pagesSafe Handling, Packaging & Shipping of Infectious SubstancesGeoffrey RufinNo ratings yet
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNo ratings yet
- FP 8 Poultry Diseases ManagementDocument2 pagesFP 8 Poultry Diseases ManagementWellington MabhandeNo ratings yet
- The Chain of InfectionDocument10 pagesThe Chain of InfectionJessica SebastianNo ratings yet
- Micro CH 6 BacteriaDocument58 pagesMicro CH 6 BacteriaBernadette Joyce PascualNo ratings yet
- Key Bacterial DiseasesDocument3 pagesKey Bacterial Diseaseszain hassanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PathogenesisDocument53 pagesBacterial PathogenesisbruhwahatNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - VMICRO 3rd TopicDocument5 pagesReviewer - VMICRO 3rd TopicAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Poultry DiseasesDocument7 pagesPoultry DiseasesJohnMasiveNo ratings yet
- Arthropods and infectious diseasesDocument4 pagesArthropods and infectious diseasesAnnahNo ratings yet
- Reptilian and Amphibious Diseases Found in Captivity FinalDocument12 pagesReptilian and Amphibious Diseases Found in Captivity Finalapi-250146149No ratings yet
- Handouts Infectious Coryza Fall 2020Document3 pagesHandouts Infectious Coryza Fall 2020NabeelNo ratings yet
- Agri 5Document11 pagesAgri 5funhenonNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument5 pagesLumbar PunctureJennifer JaneNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 4 ScienceDocument11 pagesForm 2 Chapter 4 ScienceNajiha Km100% (1)
- Camel Health For DVM StudentsDocument132 pagesCamel Health For DVM Studentsaklilu mamoNo ratings yet
- Microbial Mechanisms of PathogenicityDocument48 pagesMicrobial Mechanisms of PathogenicitywfNo ratings yet
- Prevent Infections with Proper ControlDocument16 pagesPrevent Infections with Proper ControljasornciolimNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument2 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesSNIGDHA APPANABHOTLANo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 FinalDocument9 pagesAssignment 3 Finalcandido evanNo ratings yet
- Some Common Health Problems of PoultryDocument4 pagesSome Common Health Problems of PoultryTakougalamoNo ratings yet
- Vishnu YogDocument1 pageVishnu YogShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Fodder SummaryDocument6 pagesFodder SummaryShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Fodder SummaryDocument6 pagesFodder SummaryShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Summer CropsDocument2 pagesSummer CropsShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Indigenous BreedDocument3 pagesIndigenous BreedShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Nath YogiDocument1 pageNath YogiShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Santosh GoatDocument1 pageSantosh GoatShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Indigenous BreedDocument3 pagesIndigenous BreedShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Shia YogDocument1 pageShia YogShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Lohmann Alternative SystemDocument68 pagesLohmann Alternative SystemShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Nath YogiDocument1 pageNath YogiShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Nepal Pet Service Center Pvt. LTD.: Swayambhu-15, Buddhapark, Kathmandu, Nepal. Tel No.01-4033742 Email: DateDocument1 pageNepal Pet Service Center Pvt. LTD.: Swayambhu-15, Buddhapark, Kathmandu, Nepal. Tel No.01-4033742 Email: DateShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument1 pageTerm PaperShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- TNPSC VAS Question Bank...Document6 pagesTNPSC VAS Question Bank...malaimax90% (20)
- Response of OatDocument12 pagesResponse of OatShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Growth and Production of Oat and RyeDocument9 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Growth and Production of Oat and RyeShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- 2009161029poultry LayerDocument9 pages2009161029poultry LayerShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- CP Case Record Shiva N NabinDocument4 pagesCP Case Record Shiva N NabinShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Selection & Breeds of GoatsDocument3 pagesSelection & Breeds of GoatsShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- TrialDocument45 pagesTrialShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Bikash AryalDocument4 pagesBikash AryalShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Dog PopulationDocument1 pageDog PopulationShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Nepal Pet Hospital Pvt. LTD.: Owner's Details Animal's DetailsDocument1 pageNepal Pet Hospital Pvt. LTD.: Owner's Details Animal's DetailsShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Bikash AryalDocument4 pagesBikash AryalShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Nepal Pet Hospital Pvt. LTD.: Owner's Details Animal's DetailsDocument1 pageNepal Pet Hospital Pvt. LTD.: Owner's Details Animal's DetailsShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument1 pagePoster PresentationShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Tara DidiDocument1 pageTara DidiShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On Clinical Practice (VCP 411) : Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument1 pageAn Assignment On Clinical Practice (VCP 411) : Submitted By: Submitted ToShiva KhanalNo ratings yet
- Wound and Its ClassificationDocument3 pagesWound and Its ClassificationShiva Khanal100% (1)
- Role and Functions of Beneficial Microorganisms in Sustainable AquacultureDocument7 pagesRole and Functions of Beneficial Microorganisms in Sustainable Aquaculturepig_pink1989No ratings yet
- MicroBioLogy of Periodontal DiseasesDocument104 pagesMicroBioLogy of Periodontal DiseasesKush Pathak75% (4)
- PNMCC Directory of StrainsDocument67 pagesPNMCC Directory of StrainsKing James PalmaNo ratings yet
- Swine Disease Manual, E.J. Neumann, A. Ramirez, and K.J. Schwartz - 5th Edition (2020)Document208 pagesSwine Disease Manual, E.J. Neumann, A. Ramirez, and K.J. Schwartz - 5th Edition (2020)Patricia TorresNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology: Peter Kotsoana Montso, Victor Mlambo, Collins Njie AtebaDocument10 pagesFood Microbiology: Peter Kotsoana Montso, Victor Mlambo, Collins Njie AtebaNithin SakthiNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET A-QuestionsDocument2 pagesMICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET A-QuestionschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Womens Health Care 11th Edition Lowdermilk Test BankDocument38 pagesMaternity and Womens Health Care 11th Edition Lowdermilk Test Bankhenrycpwcooper100% (14)
- FOSFOMYCINDocument29 pagesFOSFOMYCINDreamline de SkyNo ratings yet
- Rohela Mahmud, Yvonne Ai Lian Lim, Amirah Amir - Medical Parasitology - A Textbook (2017, Springer International Publishing)Document198 pagesRohela Mahmud, Yvonne Ai Lian Lim, Amirah Amir - Medical Parasitology - A Textbook (2017, Springer International Publishing)Brant100% (2)
- Bioinoculants in Plant Growth Promotion and Disease ManagementDocument44 pagesBioinoculants in Plant Growth Promotion and Disease ManagementMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- Case Investigation Form: DiphtheriaDocument3 pagesCase Investigation Form: DiphtheriaSalihu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- WIDALDocument17 pagesWIDALNasti YL HardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Table of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021Document3 pagesTable of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021AnthonyNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument26 pagesThe Expanded Program On ImmunizationJudee Marie MalubayNo ratings yet
- 02-06-2021 HMB EnglishDocument63 pages02-06-2021 HMB EnglishMohammed IrfanNo ratings yet
- The Cancer Cure That Worked PDFDocument18 pagesThe Cancer Cure That Worked PDFcorbu_george67% (3)
- Lampung Black Pepper Microbial Test ReportDocument2 pagesLampung Black Pepper Microbial Test Reportsantoso w pratamaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Water: Waterborne Pathogens and Indicator BacteriaDocument15 pagesMicrobiology of Water: Waterborne Pathogens and Indicator BacteriaDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Department of Molecular Biology. Covid 19 Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument4 pagesDepartment of Molecular Biology. Covid 19 Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodGST WEST COMMISSIONERATENo ratings yet
- Untitled 12Document2 pagesUntitled 12Natasa PrelevicNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: What Is It?Document2 pagesHepatitis B: What Is It?DrBertram ForerNo ratings yet
- CiullaparaDocument10 pagesCiullaparaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Widal TestDocument2 pagesWidal Testsarun5832No ratings yet
- Cellulitis Infection Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument11 pagesCellulitis Infection Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAli dhyaaNo ratings yet
- Gusto Niyo Ba NG MagicDocument2 pagesGusto Niyo Ba NG MagicKeannu HavanaNo ratings yet
- Biological WarfareDocument7 pagesBiological WarfareBakhtawar ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Bactalert FN PlusDocument10 pagesBactalert FN PluscassNo ratings yet
- 260002-Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology-IIDocument2 pages260002-Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology-IIchintoo4696No ratings yet
- Study Guide Microbiology Module 1Document6 pagesStudy Guide Microbiology Module 1Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- GPC8 IsDocument1 pageGPC8 IsDrivailaNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicFrom EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicNo ratings yet
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineFrom EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- The HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedFrom EverandThe HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismFrom EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.From EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanFrom EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsFrom EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentFrom EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryFrom EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusFrom EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyFrom EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthFrom EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthNo ratings yet
- Getting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsFrom EverandGetting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- War on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicFrom EverandWar on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthFrom EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefFrom EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefNo ratings yet
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceFrom EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Development of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchFrom EverandDevelopment of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchNo ratings yet
- The War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardFrom EverandThe War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A Good Time to Be Born: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a FutureFrom EverandA Good Time to Be Born: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a FutureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)