Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Findings - RBC
Laboratory Findings - RBC
Uploaded by
Varshaa Bharathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Laboratory findings - RBC.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesLaboratory Findings - RBC
Laboratory Findings - RBC
Uploaded by
Varshaa BharathiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
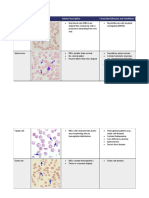
Laboratory Sickle cell disease Thalassemia Iron Megaloblastic Chronic ITP Aplastic
findings deficiency anemia anemia
anemia
Peripheral Blood
Hemoglobin Decreased Markedly Decreased Decreased - Decreased
reduced
Hematocrit Decreased Markedly Decreased Decreased - -
reduced
Red Cell Indices:
MCH - Decreased Decreased Increased - -
MCHC - Decreased Decreased Increased - -
RDW - - Increased, - - -
Earliest sign
of iron
deficiency
Others Reticulocyte Count: RBC Count: Reticulocyte Reticulocyte Platelet Packed
Increased Increased Count: low for Count: count: volume:
ESR: /normal the degree of Normal or low Markedly Decreased
Decreased Reticulocyte anemia reduced Reticulocyte
Count: count:
Increased Markedly
decreased
Peripheral Smear
RBCs: Normocytic Microcytic Microcytic Egg-Shaped Chronic Pancytopenia
normochromic to hypochromic and macro- blood loss , ,
mildly hypochromic, anemia, hypochromic, ovalocytes, lead to Normocytic
Anisopoikilocytosis, Target cells, Moderate Lack the central microcytic normochromi
Sickle cell, Basophilic anisocytosis pallor, hypochrom c anemia
Target cells, stippling, and anisopoikilocyto ic anemia
ovalocytes, Nucleated red poikilocytosis, sis,
polychromatophilia, cell precursors Severe – Basophilic
Howell jolly bodies Ring/pessary stippling,
cells cabot ring and
Howell jolly
bodies
WBCs Mildly increased Leukocytosis Normal; WBC count Normal Pancytopenia
with shift to left with mild left eosinophilia decreased, ,
shift in hook worm Hypersegmente Neutrophils
infestations d neutrophils markedly
diminished
Platelets Mildly increased Normal Normal Decreased Markedly Pancytopenia
reduced, ,
Abnormally Decreased
large sized
platelets
Bone Marrow
Cellularity Hypercellular Markedly Moderately Markedly Hypercellul Marrow
hypercellular hypercellular hypercellular ar aplasia (bone
marrow
biopsy)
Markedly
hypocellular
M:E ratio - 1:1 to 1:5 2:1 to 1:2 1:1 to - -
ratio 1:6(Normal: 2:1
to 4:6)
Erythropoiesis Compensatory Normoblastic Micronormobl Megaloblastic Prolonged -
normoblastic with marked astic type bleeding
erythroid erythroid maturation *Megaloblasts lead to
hyperplasia hyperplasia * Ineffective normoblast
erythropoiesis ic erythroid
hyperplasia
, Constant
bleeding to
iron
deficiency
and
micronorm
oblastic
erythroid
hyperplasia
Myelopoiesis Normal Normal Normal *Myeloid cells Normal -
adequate in
number
*Giant
metamyelocytes
and band forms
Megakaryopoiesis Normal Normal Normal Normal or Moderate -
increased in increase in
number number of
both
immature
and mature
forms of
megakaryo
cytes,Imma
ture
megakaryo
cytes
predomina
te large
non
lobulated
single
nuclei and
basophilic
cytoplasm
Bone marrow iron Usually Increased Markedly Absence of Moderately - -
increased bone marrow increased
iron: “Gold
standard”
test,
demonstrated
by –ve
Prussian blue
reaction
Hematopoiesis - - - - - Marrow
aplasia(bone
marrow
biopsy)Paucit
y of all
erythroid,
myeloid and
megakaryocyt
ic precursors
Others Exramedullary - - - Bleeding Marrow
hematopoiesis time: aplasia(bone
Prolonged, marrow
Clotting biopsy
time,PT Other cells:
and PTT: Lymphocytes
Normal, and plasma
Tournique cells are
test and prominent
tests for
platelet
autoantibo
dies: +ve
You might also like
- Sample Test Questions For The CPC ExamDocument8 pagesSample Test Questions For The CPC ExamHarikaSabbineni100% (1)
- PoikilocytosisDocument3 pagesPoikilocytosisJasonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFAmeer MattaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of AnemiaDocument14 pagesDiagnosis of AnemiaAnggie AnggriyanaNo ratings yet
- Anemia DX TXDocument2 pagesAnemia DX TXProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsDocument72 pagesSystematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsSukma Eka PratiwiNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Anemia: Brad Lewis Director Hematology San Francisco General HospitalDocument47 pagesAn Approach To Anemia: Brad Lewis Director Hematology San Francisco General HospitalyapponNo ratings yet
- TrW-Guwv 0g VwhuPGl65PBCquGkt3j5Document65 pagesTrW-Guwv 0g VwhuPGl65PBCquGkt3j5Shikhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Degenevie - HematologyDocument71 pagesDegenevie - Hematologykkq7fhkwvkNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pancytopenia (3) - 1Document37 pagesApproach To Pancytopenia (3) - 1RahulNo ratings yet
- RED CELL MORPHOLOGY Tabulation SummaryDocument6 pagesRED CELL MORPHOLOGY Tabulation SummaryStephen YorNo ratings yet
- Blood FilmDocument2 pagesBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDocument3 pagesRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Anemia 1Document30 pagesAnemia 1Aishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan DarahDocument11 pagesPemeriksaan DarahJems BoruNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab V2Document14 pagesPhysiology Lab V2Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- HO Notecards3 IncompleteDocument12 pagesHO Notecards3 IncompleteMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Poikilocytosis Review TableDocument5 pagesPoikilocytosis Review Tablekat100% (1)
- Hematology Part 1 NotesDocument23 pagesHematology Part 1 NotesDr. Benson BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Super Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevDocument500 pagesSuper Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevMohd SaquibNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Document3 pagesPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)Document38 pagesCBC (Complete Blood Count)yeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Differential (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesDifferential (AutoRecovered)Trizian ManaliliNo ratings yet
- RBC Anomalies TableDocument7 pagesRBC Anomalies TableMa. Aida Ysabel CariñoNo ratings yet
- DR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistDocument31 pagesDR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- Hematology 4Document21 pagesHematology 4saad samyNo ratings yet
- Hema FinalsDocument12 pagesHema FinalsHANA LUNARIANo ratings yet
- Lecture Lesson 9. Red Blood Cell DisordersDocument7 pagesLecture Lesson 9. Red Blood Cell DisordersHANA LUNARIANo ratings yet
- Result Reporting: Subjectively Graded As Few, Moderate, ManyDocument5 pagesResult Reporting: Subjectively Graded As Few, Moderate, ManyMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- Dr. Sailendra Nayak Assistant Professor MedicineDocument49 pagesDr. Sailendra Nayak Assistant Professor MedicineAishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestDocument15 pagesApproach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestJanella SuerteNo ratings yet
- RBC anomalies-ANEMIADocument19 pagesRBC anomalies-ANEMIAJeremiahNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Aubf Topic 2Document16 pagesAubf Topic 2Bernadette VillegasNo ratings yet
- Patho HematologyDocument39 pagesPatho HematologyCastleKGNo ratings yet
- Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageAnemia ApproachLanaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageHematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachEugen MNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Diagnostic ApproachDocument36 pagesAnemia: Diagnostic ApproachRizky LumalessilNo ratings yet
- Anemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaDocument61 pagesAnemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaSamuel ManurungNo ratings yet
- AUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Document13 pagesAUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Anya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To HematologyReba PhiliposeNo ratings yet
- Anemia TutoringDocument28 pagesAnemia TutoringngNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Hematology Week 8Document3 pagesHematology Week 8Rose Neil LapuzNo ratings yet
- CBC Arikod HoimaDocument37 pagesCBC Arikod Hoimadaniel arikodNo ratings yet
- RBC Blood TableDocument2 pagesRBC Blood Tablearodriguez_66No ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFBilly AuNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Cara Mendiagnose AnemiaDocument1 pageCara Mendiagnose AnemiaMuchlissatus Lisa MedicalbookNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument8 pagesAnemia SCarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- Kuliah AnemiaaDocument44 pagesKuliah AnemiaaAhmad Umar AfNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - 06 Clinical Pathology Mcqs With Answers 1Document29 pagesQdoc - Tips - 06 Clinical Pathology Mcqs With Answers 1Sandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Pendekatan Diagnosis AnemiaDocument7 pagesPendekatan Diagnosis AnemiaFerry GhifariNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument2 pagesHematologyMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophyzylfielNo ratings yet
- Ana IfDocument101 pagesAna Ifshrikrishnapathlab100% (1)
- BlepharitisDocument2 pagesBlepharitisVarshaa BharathiNo ratings yet
- ChalazionDocument1 pageChalazionVarshaa BharathiNo ratings yet
- HordeolumDocument1 pageHordeolumVarshaa BharathiNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders InvestigationDocument2 pagesBleeding Disorders InvestigationVarshaa BharathiNo ratings yet
- Isbar StrokeDocument1 pageIsbar Strokeapi-688564858No ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingDocument5 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of NursingNessy Nicholle SatruionNo ratings yet
- Secondary Prevention Stroke AHA ChecklistDocument1 pageSecondary Prevention Stroke AHA ChecklistGyörgy HalászNo ratings yet
- Modern Humans Clarification Report 3Document45 pagesModern Humans Clarification Report 3Quake13No ratings yet
- Gall Bladder USGDocument66 pagesGall Bladder USGarina31No ratings yet
- Handout 10 Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesHandout 10 Circulatory SystemKyle QuietaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and SafetyDocument181 pagesOccupational Health and SafetylusiNo ratings yet
- Stock 27 Sept 23Document16 pagesStock 27 Sept 23hadiprayitno.agustusNo ratings yet
- Curricullum Vitae: I. Personal DetailsDocument4 pagesCurricullum Vitae: I. Personal Detailsdwi widyaNo ratings yet
- PLANNERDocument4 pagesPLANNERRoland Ceazar CunananNo ratings yet
- Management of Side Effects and Complication in Medical AbortionDocument10 pagesManagement of Side Effects and Complication in Medical AbortionmariaNo ratings yet
- I PASS MnemonicDocument6 pagesI PASS MnemonicDevina CiayadiNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaDocument5 pagesManagement of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaNurhafizahImfista100% (1)
- Relay For Life NewsletterDocument4 pagesRelay For Life NewsletterJordyn LevineNo ratings yet
- ST George's Healthcare Gazette August 2012Document12 pagesST George's Healthcare Gazette August 2012St George's Healthcare NHS TrustNo ratings yet
- Literary Review of Somanathi Tamra Bhasma PDFDocument4 pagesLiterary Review of Somanathi Tamra Bhasma PDFRamamurthyNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument63 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYYuni IndrianiNo ratings yet
- Femara: (Letrozole Tablets) 2.5 MG Tablets RX Only Prescribing InformationDocument28 pagesFemara: (Letrozole Tablets) 2.5 MG Tablets RX Only Prescribing InformationKirubakaranNo ratings yet
- Jurnal DematitisDocument11 pagesJurnal DematitisRana NurfadillahNo ratings yet
- PHICDocument3 pagesPHICapi-3836762No ratings yet
- Ospe Bank PDFDocument318 pagesOspe Bank PDFMed StudentNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biomechanics and Motion PalpationDocument8 pagesClinical Biomechanics and Motion PalpationsunNo ratings yet
- Treatment Release VOMDocument1 pageTreatment Release VOMTheVOMLadyNo ratings yet
- ChandrachurDocument5 pagesChandrachurUtkarsh GhateNo ratings yet
- Lac TranspDocument13 pagesLac Transpfarinha2009No ratings yet
- Morning ReportDocument14 pagesMorning ReportAyu KristinaNo ratings yet
- Nephrology: World Journal ofDocument18 pagesNephrology: World Journal ofursula_ursulaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Essentials in Emergency MedicineDocument35 pagesOrthopedic Essentials in Emergency MedicineMohd Tarmizi100% (1)
- REM Sleep: The 4 Stages of SleepDocument2 pagesREM Sleep: The 4 Stages of Sleepapi-353153069No ratings yet