Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surveying PDF
Uploaded by
Aileen AntipoloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surveying PDF
Uploaded by
Aileen AntipoloCopyright:
Available Formats
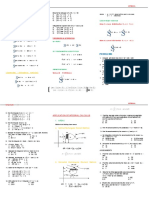
Measurement measure lay-out too long Effect of Curvature & Refraction
too long add subtract e Azimuth
Corrections too short subtract add
CD = MD (1 + )
TL hcr = 0.067K 2 from South
Due to temperature: too short
e D2
(add/subtract); measured length Probable Errors h = h2 + (h − h2 ) − 0.067D1 D2
CD = MD (1 − ) D1 + D2 1
C = αL(T2 − T1 ) TL Reduction to
Probable Error (single):
Sea Level
Due to pull: Stadia Measurement Leveling
(add/subtract); measured length ∑(x − x̅) CD MD
E = 0.6745√ Horizontal: =
(P2 − P1 )L n−1 Elev𝐵 = Elev𝐴 + 𝐵𝑆 − 𝐹𝑆 R R+h
C=
EA D = d + (f + c) Inclined Upward:
Probable Error (mean):
Due to sag: 𝑓 error/setup = −eBS + eFS
(subtract only); unsupported length D = ( )s +C Subtense Bar
E ∑(x − x̅) 𝑖 Inclined Downward:
w 2 L3 Em = = 0.6745√ D = Ks + C error/setup = +eBS − eFS θ
C= √n n(n − 1) D = cot
24P 2 Inclined: Total Error: 2
Proportionalities of weight, w: eT = error/setup ∙ no. of setups
Due to slope: D = Ks cos θ + C
(subtract only); measured length E=error; d=distance; n=no. of trials
1 1 H = D cos θ
C 2 = S 2 − h2 Double Meridian Distance Method DMD
𝑤∝ 𝑤∝ 𝑤∝𝑛 V = D sin θ
𝐸2 𝑑 DMD𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 = Dep𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡
Normal Tension:
DMD𝑛 = DMD𝑛−1 + Dep𝑛−1 + Dep𝑛
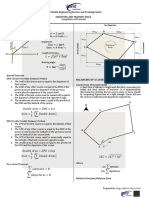
0.204W√AE Area of Closed Traverse Area of Irregular Boundaries
PN = DMD𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡 = −Dep𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡
√PN − P Trapezoidal Rule: 2A = Σ(DMD ∙ Lat)
Lat = L cos α
Dep = L sin α d
A= [h + hn + 2Σh]
Error of Closure:
2 1 Double Parallel Distance Method DPD
Parabolic Curves Simpson’s 1/3 Rule:
= √ΣL2 + ΣD2 DPD𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 = Lat𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡
Symmetrical: d DPD𝑛 = DPD𝑛−1 + Lat 𝑛−1 + Lat 𝑛
Relative Error/Precision: A = [h1 + hn + 2Σh𝑜𝑑𝑑 + 4Σh𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛 ]
L Error of Closure 3 DPD𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡 = −Lat 𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡
H = (g1 + g 2 ) =
Perimeter Note: n must be odd 2A = Σ(DMD ∙ Dep)
8
L 2
x 2 ( 2) 1 acre = Simple, Compound & Reverse Curves Spiral Curve
= L 4047 m2
y H 1
Unsymmetrical:
L1 L2
H= (g + g 2 )
2(L1 +L2 ) 1
g 3 (L1 +L2 ) = g1 L1 + g 2 L2
Note: Consider signs.
Earthworks
𝑑𝐿 0 𝑑𝑅
±𝑓𝐿 ±𝑓 ±𝑓𝑅 L2 180°
θ= ∙
f w I 2RLs π
A= (d + dR ) + (fL + fR ) T = R tan
2
2 L 4 θ Ls 2
I i= ; p=
Volume (End Area): E = R [sec − 1] 3 24R
2
L I
L3
Ve = (A1 + A2 ) m = R [1 − cos ] x=
2 2 6RLs
Volume (Prismoidal): L = 2R sin
I L5 LT → long tangent
ST → short tangent
2 Y=L− 2 R → radius of simple curve
L 40R2 Ls L → length of spiral from TS to any point
VP = (A1 + 4Am + A2 ) π along the spiral
6 Lc = RI ∙ Ls I Ls → length of spiral
180° Ts = + (R + p) tan I → angle of intersection
I c → angle of intersection of the simple
Prismoidal Correction: 2 2 curve
20 2πR p → length of throw or the distance from
= I tangent that the circular curve has been
L D 360° Es = (R + p) sec − R offset
CP = (c − c2 )(d1 − d2 ) 2 x → offset distance (right angle
12 1 1145.916 distance) from tangent to any point on
R= 0.036k 3 the spiral
xc → offset distance (right angle
VP = Ve − Cp D Ls = distance) from tangent to SC
R Ec → external distance of the simple
Volume (Truncated): 0.0079k 2
curve
θ → spiral angle from tangent to any
Σh e= point on the spiral
VT = ABase ∙ Have = A( ) R θS → spiral angle from tangent to SC
n i → deflection angle from TS to any point
A D L on the spiral
is → deflection angle from TS to SC
VT = (Σh1 + 2Σh2 + 3Σh3 + 4Σh4 ) = y → distance from TS along the tangent
n DC Ls to any point on the spiral
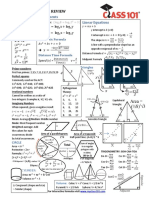
Stopping Sight Distance Parabolic Summit Curve Parabolic Sag Curve Underpass Sight Distance Horizontal Curve
L>S
v2 L>S L>S L>S
S = vt + A(S)2
2g(f ± G) L= 2 A(S)2 A(S)2 h1 + h2 S2
L= L= H= C− R=
a = g(f ± G) (deceleration) 200(√h1 + √h2 ) 122 + 3.5S 800H 2 8M
v L<S L<S L<S L<S
2
tb = (breaking time)
200(√h1 + √h2 ) 122 + 3.5S 800H L(2S − L)
g(f ± G) L = 2(S) − L = 2(S) − L = 2(S) − R=
A A A 8M
f
Eff = (100) L → length of summit curve A → algebraic difference A → algebraic difference of L → length of horizontal
fave S → sight distance of grades, in percent grades, in percent curve
v → speed in m/s h1 → height of driver’s eye L → length of sag curve L → length of sag curve S → sight distance
t → perception-reaction time h1 = 1.143 m or 3.75 ft S → sight distance A(K)2 R → radius of the curve
For passengers comfort,
f → coefficient of friction h2 → height of object L= where K is speed in KPH
M → clearance from the
G → grade/slope of road h2 = 0.15 m or 0.50 ft
395 centerline of the road
You might also like
- Azimuth From South: Subtract AddDocument1 pageAzimuth From South: Subtract Addcristina23No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAeKoe92snvbBv4lCcdxTF9PzyqcDOZ02MrZTTgLuA2bvQ-1iSwmSNflyqLumBIyWZGjyShj02TH0GGn7ZuS65CCbo8 CkP5IDGy6HMGyWaL-Yv cBfwvr2LbLZ3hwe4wfA3UXsVvD20mfPDocument1 pageACFrOgAeKoe92snvbBv4lCcdxTF9PzyqcDOZ02MrZTTgLuA2bvQ-1iSwmSNflyqLumBIyWZGjyShj02TH0GGn7ZuS65CCbo8 CkP5IDGy6HMGyWaL-Yv cBfwvr2LbLZ3hwe4wfA3UXsVvD20mfPHamghad LambasNo ratings yet
- Surveying FormulaDocument8 pagesSurveying FormulaJulie Ann Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- ACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1Document1 pageACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1segun shonaNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter45Document3 pagesSummary Chapter45blalllNo ratings yet
- Aadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVDocument9 pagesAadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVnasserNo ratings yet
- Useful Aerospace FormulasDocument1 pageUseful Aerospace FormulasRadj90No ratings yet
- Midterm 2 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm 2 Cheat SheetwotaddictNo ratings yet
- 2015Document10 pages2015ZaNo ratings yet
- Formula SurveyingDocument3 pagesFormula SurveyingMerrelle Aubrey DeniegaNo ratings yet
- Solutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7Document14 pagesSolutions: 2017 JEE Entrance Examination Advanced/Paper 2 Code 7SUNIL KUMAR JANGRANo ratings yet
- PW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsDocument13 pagesPW - AITS - NT-24: Hint and Solutions PhysicsOfficers IasNo ratings yet
- Ce 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDocument2 pagesCe 201 - Fundamentals of Surveying: Cos SinDaille Wroble GrayNo ratings yet
- Center: Pre-Calculus GuideDocument7 pagesCenter: Pre-Calculus GuideLovEegnia BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Determine The Adjusted Bearing and Lengths of The Following DataDocument13 pagesDetermine The Adjusted Bearing and Lengths of The Following DataJoshua Onin OlivenzaNo ratings yet
- Formulae Part ThreeDocument5 pagesFormulae Part ThreeShiva SeshasaiNo ratings yet
- Surveying and Transpo FormulaDocument12 pagesSurveying and Transpo FormulaKent David Relatado100% (1)
- MIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Document15 pagesMIT8 03SCF16 PracticeFinalExam1Gavin BirlaNo ratings yet
- Poster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationDocument1 pagePoster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationPierre NievesNo ratings yet
- Integral - NEUSTDocument3 pagesIntegral - NEUSTJohn vincent SalazarNo ratings yet
- Traverse SheetDocument1 pageTraverse Sheetjeffrobinson782No ratings yet
- Act Math Formulas Interactive 1Document2 pagesAct Math Formulas Interactive 1Isley Quintine YutucNo ratings yet
- Calculation and Design Touch and Step VoltageDocument7 pagesCalculation and Design Touch and Step Voltagenikhilsingh1087No ratings yet
- Trigonometria I.E.P. "Lord Karmel"Document5 pagesTrigonometria I.E.P. "Lord Karmel"foker01No ratings yet
- International Program Giaûi Tích 2: Hut - Department of Math. AppliedDocument12 pagesInternational Program Giaûi Tích 2: Hut - Department of Math. AppliedBell PhamNo ratings yet
- Hezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 7Document11 pagesHezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 7TimelessNo ratings yet
- ACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Document6 pagesACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Waheed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document8 pagesLecture 1Khang DangNo ratings yet
- Metc SesiuneDocument10 pagesMetc SesiuneRazvan 888No ratings yet
- Cap. 11 PDFDocument77 pagesCap. 11 PDFRamón RamalhoNo ratings yet
- Repaso de Reduccion de ÁngulosDocument3 pagesRepaso de Reduccion de ÁngulosAlan CordobaNo ratings yet
- Technical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFDocument13 pagesTechnical Test - 01 - SOL - PDFVamshiNo ratings yet
- Article 4Document7 pagesArticle 4pratiksharma2828No ratings yet
- Diffusion: 2.1 September 5, 2003: 1 D Cartesian and Cylindrical Steady StateDocument20 pagesDiffusion: 2.1 September 5, 2003: 1 D Cartesian and Cylindrical Steady StateFlor MárquezNo ratings yet
- Design Formulas For Full Wave Ei Core Transformer - NewDocument2 pagesDesign Formulas For Full Wave Ei Core Transformer - NewViet Hoang LeNo ratings yet
- QM Equations and Constants Sheet NewDocument2 pagesQM Equations and Constants Sheet NewBinh LamNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B: The College Board: Connecting Students To College SuccessMr. PopoNo ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- PHL BS With Affine DivsDocument8 pagesPHL BS With Affine DivsRaphaël FromEverNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDocument12 pagesMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetCarlos GamioNo ratings yet
- Cartesian 20to 20geodetic 20 - 20borkowskiDocument2 pagesCartesian 20to 20geodetic 20 - 20borkowskiRober Ignacio GarciaNo ratings yet
- Livro Hibbeler - 7 Ed Resistencia Materiais (Soluções) - 4 PDFDocument50 pagesLivro Hibbeler - 7 Ed Resistencia Materiais (Soluções) - 4 PDFIzabel Cristina100% (1)
- Review 3Document2 pagesReview 3xesef93262No ratings yet
- 21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremDocument10 pages21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremNaga ArjunNo ratings yet
- ELEC 353 Formula Sheet - Winter 2009Document1 pageELEC 353 Formula Sheet - Winter 2009Juampi MochenNo ratings yet
- Please Note, This Is A Complementary Aid Only, It Is Not Allowed On Any ExamsDocument2 pagesPlease Note, This Is A Complementary Aid Only, It Is Not Allowed On Any ExamsaradsugerdachriNo ratings yet
- Formula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵDocument5 pagesFormula Page:: Y = X = D (1 - Cosɵ) ˙Y= V = Ωd Sinɵ Ÿ = F = Ω D CosɵPhemi2580No ratings yet
- Aero - Lect8 - 2019 (1) Take Off Aircraft Stability and PerformanceDocument14 pagesAero - Lect8 - 2019 (1) Take Off Aircraft Stability and PerformanceAftab AliNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCalculus 2 Cheat SheetB SotoNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageCalculus 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDauda Sulley DaudaNo ratings yet
- By Type: Search The World's Digital LibraryDocument8 pagesBy Type: Search The World's Digital LibraryIbrahim ZahidNo ratings yet
- Relevant Charts and Formulae: e e e eDocument4 pagesRelevant Charts and Formulae: e e e etehNo ratings yet
- Floating Point Arithmethic - Error AnalysisDocument30 pagesFloating Point Arithmethic - Error AnalysisAlfreda OduroNo ratings yet
- Polarization: Meseret Asrat, Meseret@uchicago - Edu, 02211Document3 pagesPolarization: Meseret Asrat, Meseret@uchicago - Edu, 02211MomoHinamoriChanNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Geodetic Problem Using The Method by BowringDocument2 pagesThe Inverse Geodetic Problem Using The Method by BowringRober Ignacio GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2 Point Function PDFDocument1 page2 Point Function PDFKevin ChenNo ratings yet
- Comp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsDocument16 pagesComp2024 Btest-11 MathematicsTtttNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NDocument19 pagesOperating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NJohnTPNo ratings yet
- Good Practices in Tray DesignDocument7 pagesGood Practices in Tray Designmehul10941100% (2)
- Accessories 162-USDocument20 pagesAccessories 162-USعايد التعزيNo ratings yet
- Prakab Export 20.8.2018 UkDocument260 pagesPrakab Export 20.8.2018 UkREN JTNNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Labeling Waves: NameDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Labeling Waves: NameNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- The Earth's SubsystemsDocument17 pagesThe Earth's SubsystemsAndevie Balili Iguana100% (1)
- Veg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenDocument2 pagesVeg Dum Biryani - Hyderabadi Veg Biryani Recipe - Hyderabadi Biryani - Hebbar's KitchenmusicalcarpetNo ratings yet
- Legend Of Symbols: Chú Thích Các Ký HiệuDocument9 pagesLegend Of Symbols: Chú Thích Các Ký HiệuKiet TruongNo ratings yet
- Onitsuka Tiger PDFDocument67 pagesOnitsuka Tiger PDFAhmad Bilal MawardiNo ratings yet
- ADC ManualDocument47 pagesADC ManualRavi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- BiPAP ST Clinical ManualDocument37 pagesBiPAP ST Clinical ManualEng. Edelson Martins100% (2)
- Outerstellar Self-Impose RulesDocument1 pageOuterstellar Self-Impose RulesIffu The war GodNo ratings yet
- Section 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightDocument4 pagesSection 08630 Metal-Framed SkylightMØhãmmed ØwięsNo ratings yet
- Bitsat Paper 5Document19 pagesBitsat Paper 5pranka5240100% (1)
- Part 3-Chap 2 - Classification of Buildings Based On OccupanciesDocument60 pagesPart 3-Chap 2 - Classification of Buildings Based On Occupanciesfaruque65No ratings yet
- HACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)Document6 pagesHACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)kerem__22No ratings yet
- Brainedema 160314142234Document39 pagesBrainedema 160314142234Lulu LuwiiNo ratings yet
- Ora Laboratory Manual: Section 1 Section 1Document36 pagesOra Laboratory Manual: Section 1 Section 1Ahmed IsmailNo ratings yet
- SFT PresentationDocument16 pagesSFT Presentationapna indiaNo ratings yet
- Aci 522R-06 PDFDocument25 pagesAci 522R-06 PDFaldi raimon100% (2)
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteDocument8 pagesNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielNo ratings yet
- Fo Transfer ProcedureDocument8 pagesFo Transfer ProcedureadityasahayNo ratings yet
- Moldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Document111 pagesMoldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Arwin AgustinNo ratings yet
- Joseph Conrad - Heart of DarknessDocument86 pagesJoseph Conrad - Heart of DarknessCaztor SscNo ratings yet
- ReagentsDocument12 pagesReagentsKimscey Yvan DZ SulitNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Troubleshooting ManualDocument15 pagesMotorcycle Troubleshooting ManualJan Warmerdam100% (1)
- Air Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Document310 pagesAir Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Michael SmallNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris PATDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggris PATNilla SumbuasihNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)Document3 pagesSyllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)shekhusatavNo ratings yet
- Developing Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66Document2 pagesDeveloping Agility and Quickness (Etc.) (Z-Library) - 66guypetro6No ratings yet