Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Johndie Sarmiento0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOriginal Title
The Circulatory System.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Johndie SarmientoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
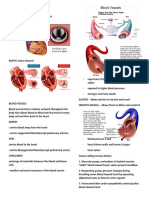
The Circulatory System
The circulatory system is a vast network of organs and vessels that is
responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, hormones, oxygen and other gasses to
and from cells. There are three major parts of the circulatory system. The heart
which pumps blood throughout the body, the blood, and the blood vessels which
are the arteries, capillaries and veins. Circulatory cycle starts when oxygenated
blood is carried from the lungs to the heart to the left atrium of the heart by means
of pulmonary veins, as the left atrium relaxes the bloods goes into the heart, when
the left atrium contracts the left ventricle relaxes simultaneously, the left atrium
pushes the blood into the left ventricle through the one way valve, when the left
ventricle contracts, the blood is pump into the aorta which carries oxygenated
blood to the different parts of the body (except the lungs). Oxygenated blood
reaches the different parts of the body through the blood vessels called arteries, the
arteries gets branch into capillaries which then reaches the different organs of the
body, the blood then becomes deoxygenated goes to the blood capillaries and into
the blood vessels called veins, veins carries deoxygenated blood to the heart, the
blood vessels carried deoxygenated blood to heart are known as venacava, the
deoxygenated blood from different parts of body enters the right upper chamber of
the heart which is called the right atrium, the right atrium gets contracted allowing
the blood to flow into the right ventricle which contracts with the expansion of the
right atrium through the one way valve, the right ventricle then contracts pushing
the blood into the pulmonary artery, the pulmonary artery carries the deoxygenated
blood to the lungs for oxygenation and flows back again to the heart through the
pulmonary vein and start the circulatory cycle again.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Science 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Document33 pagesScience 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Ace AligoraNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Gold Advanced WordlistDocument95 pagesGold Advanced WordlistmarsorianobebNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BasketballDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BasketballJohndie Sarmiento100% (1)
- British Biology Olympiad 2021Document66 pagesBritish Biology Olympiad 2021Yinyin ZhuNo ratings yet
- Oxford Science Fact File 3 Teaching GuideDocument96 pagesOxford Science Fact File 3 Teaching GuideAdnan Roonjha50% (10)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BasketballDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BasketballJohndie Sarmiento100% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BasketballDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BasketballJohndie Sarmiento100% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BasketballDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BasketballJohndie Sarmiento100% (3)
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet For Beginners 20 Day Meal Plan Delicious Recipes For Everyone (Katie Salzmann) (Z-Library)Document144 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Diet For Beginners 20 Day Meal Plan Delicious Recipes For Everyone (Katie Salzmann) (Z-Library)KataVuleticNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Petermann PCLACDocument11 pages7.1 Petermann PCLACbob marley100% (1)
- Research Paper FinalDocument47 pagesResearch Paper FinalKeith Chastine Miraballes100% (1)
- TUNG Alex AcostaDocument74 pagesTUNG Alex AcostaJose Miguel Seguela Flores100% (2)
- ANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologySheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Textbook of Surgery For Dental StudentssDocument399 pagesTextbook of Surgery For Dental StudentssDiana Mihaela Ilie50% (2)
- Rubrics For Practical ExamDocument1 pageRubrics For Practical ExamJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Dangerous DrugsDocument3 pagesDangerous DrugsJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Reflection On DPDDocument4 pagesReflection On DPDJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Consumer ActDocument3 pagesConsumer ActJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- How To Find ResearchDocument1 pageHow To Find ResearchJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- STROKEDocument9 pagesSTROKEJalouis GabalfinNo ratings yet
- GS 201-250Document19 pagesGS 201-250Sara Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of The American Academy of DermatologyDocument56 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of The American Academy of DermatologyMădălina StamateNo ratings yet
- Arteries, veins and capillaries: Structure and functionDocument5 pagesArteries, veins and capillaries: Structure and functionRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Articular System and Joints OverviewDocument9 pagesArticular System and Joints OverviewjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Physiology of CirculationDocument40 pagesPhysiology of Circulationالبحر الاميرNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Chapter 4Document61 pagesBiology 2 Chapter 4Malas Nak TaipNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Dr. D. K. KishoreDocument35 pagesEpistaxis: Dr. D. K. KishorejialeongNo ratings yet
- Burn PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesBurn PathophysiologyAgung Widya PramanaNo ratings yet
- Laptor Case 2 Ikd 5Document28 pagesLaptor Case 2 Ikd 5Faris RahmanNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Restriction Exercise Position Stand: Considerations of Methodology, Application, and SafetyDocument15 pagesBlood Flow Restriction Exercise Position Stand: Considerations of Methodology, Application, and SafetyLuis VargasNo ratings yet
- s.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals NotesDocument40 pagess.3 Biology Transport in Plants and Animals Notesgeofreyvybz95No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Human Coronary Collateral CirculationDocument11 pagesAssessment of The Human Coronary Collateral CirculationSitiMaghfirahHafizNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY AND FUNCTIONchelliNo ratings yet
- Keeping Healthy Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesKeeping Healthy Circulatory Systemsama ahmedNo ratings yet
- Biology Practice Questions on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument9 pagesBiology Practice Questions on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDarshini SankerNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Maternal Physiology Dra. Marla Llanto: UterusDocument12 pagesObstetrics Maternal Physiology Dra. Marla Llanto: UterusIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3rd Weekly TestsDocument10 pages3rd Weekly Testsadrian capilloNo ratings yet
- CVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniDocument27 pagesCVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniSerwan J AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Handheld RelaxationDocument8 pagesHandheld RelaxationSiska Prima OlimvianiNo ratings yet