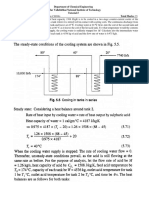
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinetics
Uploaded by
Vince SantosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetics
Uploaded by
Vince SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES
CHE 411 MIDTERMS ASSIGNMENT
1. The irreversible reaction 2A → B takes place in the gas phase in a constant temperature plug flow reactor. Reactant A and diluents
gas are fed in equimolar ratio, and the conversion of A is 85 percent. If the molar feed rate of A is doubled, what is the conversion of
A assuming the feed rate of diluents is unchanged?
2. Consider the reversible first-order reaction of A ↔ B in a CSTR of volume V = 2L with forward and reverse rate constants of k1 =
2.0 /min and k2 = 1.0 /min. At time t = 0, the concentrations of A and B in the tank are both zero. The incoming stream of A has a
volumetric flow rate of 3 L/min at concentration Cao=2 mol/L. Find the concentrations of A and B in the tank.
3. Ethyl Acetate (A) reacts with OH – (B) to produce ethanol and acetate ion. The reaction is first-order with respect to each reactant,
with ka= 0.10 L/mol-s at 298 K. Determine the reactor volume for Xa = 0.90, given that vo is 75 L/min, Cao is 0.050 mole/L, and Cbo
is 0.10 mol/L. Assume isothermal, isobaric conditions.
4. A gas-phase hydrogenation reaction C2H4 (A) + H2 → C2H6, is conducted under isothermal and isobaric conditions in a CSTR.
The feed, consisting of equimolar amounts of each reactant and an inert is fed to the reactor at a rate of of 1.5 mol H2/min with Cao =
0.40 mol/L. Determine the volumetric flow rate at the inlet of the reactor and the mean residence time or holding time if the desired
fractional conversion is 0.85 and the reaction is first-order with respect to each reactant (ka= 0.5 L/mol-min.
5. A mixed flow reactor is being used to determine the kinetics of a reaction whose stoichiometry is A R. For this purpose
various flow rates of an aqueous solution of 100 mmol A/liter are fed to a 1-liter reactor, and for each run, the outlet concentration of
A is measured. Find a rate equation to represent the following data. Also assume that reactant alone affects the rate.
, liter/min 1 6 24
Ca, mmoll/liter 4 20 50
6. Determine the volume of a CSTR required to obtain 65% conversion of A in A →P, given that vo = 5L/s, the density of the system
is constant,Cao = 4 mol/L, and ka = 2.5 x 10 – 3 /s.
7. A gas-phase hydrogenation reaction, C2H4 (A) + H2 →C2H6, is conducted under isothermal and isobaric conditions in a CSTR. The
feed, consisting of equimolar amounts of each reactant and an inert, is fed to a reactor at a rate of 1.5 mole H 2 / min.,with Cao = 0.40
mole/L. Determine the volumetric flow rate at the inlet of the reactor and mean residence time, if the desired fractional conversion, Xa
is 0.85,and the reaction is first-order with respect to each reactant (ka = 0.5 mol/min).
8. An aqueous solution of ethyl acetate (A) with a concentration of 0.3 moles/L and flowing at 0.5 L/s, mixes with an aqueous
solution of sodium hydroxide (B), of concentration 0.45 moles/L and flowing at 1.0 L/s, and the combined stream enters a CSTR of
volume 500 L, if the reactor operates at steady-state and the fractional conversion of A in the exit stream is 0.807, Find the volume of
a PFR to effect this conversion. 𝐴 + 𝐵 → 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑠.
9. A substrate is converted to a product by the catalystic action of an enzyme. The reaction is given as
A product, -ra = 13Ca / (0.03 + Ca)
(a) What should be the size of a steady-state CSTR to convert 95% of incoming substrate (Ca0 = 10M) with a flow rate of 10
L/h. (b) The volume of PFR if used instead of a CSTR.
10. The concentration of diethyl peroxydicarbonate (DEPDC) in the feed to the CSTR was 0.30 mmol. Because of this very low
concentration, constant fluid density can be assumed. At 70ºC and a space time of 10 min, the fractional conversion of DEPDC was
0.21. At 70ºC and a space time of 30 min, the fractional conversion of DEPDC was 0.44. The rate equation for DEPDC decomposition
is believed to have the form - r (DEPDC) = k [DEPDC]n . What is the value of n? The activation energy of the decomposition
reaction is 132 kJ/mol. What is the value of rate constant k at 85ºC?
You might also like
- Ideal Reactors Part 2 Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesIdeal Reactors Part 2 Solved ProblemsWaldi SagalaNo ratings yet
- Levenspiel C5 Problemas PDFDocument7 pagesLevenspiel C5 Problemas PDFbete_azmaveteNo ratings yet
- Rawr PDFDocument3 pagesRawr PDFGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption Problems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesGas Absorption Problems and Solutionskokorojiminie connect100% (1)
- Gas Absorption and Gas StrippingDocument14 pagesGas Absorption and Gas StrippingEK63No ratings yet
- TareaDocument3 pagesTareaAydee GarciaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problem Question (Gas Ab)Document2 pagesSolved Problem Question (Gas Ab)Seruzna IshxNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DistillationDocument3 pagesTutorial DistillationManu Indivare Nundoolall100% (1)
- CHEM3002 5 Liquid ExtractionDocument28 pagesCHEM3002 5 Liquid ExtractionResty Ramirez BritaniaNo ratings yet
- P4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperatureDocument7 pagesP4E2: Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction in Batch and Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor at Two Different TemperaturejayaprinaNo ratings yet
- 9A23401 Mass Transfer OperationsDocument8 pages9A23401 Mass Transfer OperationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Distillation Example 4 and 5Document2 pagesDistillation Example 4 and 5DirkMyburghNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems On Ideal Reactor ModelsDocument7 pagesSample Problems On Ideal Reactor ModelsGirllietopsyNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument177 pagesEconomicsOscar CamposNo ratings yet
- RXN CH 5Document68 pagesRXN CH 5Yonas AddamNo ratings yet
- Lab #2 - Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate & Reaction Rates - FinalDocument13 pagesLab #2 - Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate & Reaction Rates - FinalMargaritavillejack83% (6)
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction Processes and EquilibriumDocument52 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction Processes and EquilibriumThelunatic ModNo ratings yet
- CHE504 - Lab Report On Distillation ColuDocument27 pagesCHE504 - Lab Report On Distillation ColuMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- Workshop IDocument6 pagesWorkshop IValentina GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Rate Law and Stoichiometry-Part 2Document17 pagesLecture 5 - Rate Law and Stoichiometry-Part 2Nizam JumadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)Document41 pagesChapter 5 - Absorption (Part 1)La Casa JordanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Stage and Continuous Gas Liquid Separation Processes PDFDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Stage and Continuous Gas Liquid Separation Processes PDFazim100% (1)
- MSOCHA3 Tutorial 1 Multicomponent AbsorptionDocument5 pagesMSOCHA3 Tutorial 1 Multicomponent AbsorptionTshwarelo MahlakoaneNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 NewDocument19 pagesExperiment 5 NewsaramanaeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Leaching 2017Document11 pagesTutorial Leaching 2017Victor M. Jaki100% (1)
- Enzymatic Reaction Mechanisms & Kinetics in Batch & CSTR BioreactorsDocument2 pagesEnzymatic Reaction Mechanisms & Kinetics in Batch & CSTR BioreactorsAditya Whisnu Heryudhanto0% (1)
- Distillation Problem SetDocument1 pageDistillation Problem SetEfraim Abuel100% (1)
- (P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Document11 pages(P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Addison JuttieNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Thermo ProbsetDocument20 pages10.2 Thermo ProbsetJan Rommel DuterteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2deepika snehi100% (1)
- Challenge 2Document9 pagesChallenge 2James Curley100% (1)
- CSTR Experiment: Effects of Process Variables on Reaction RateDocument17 pagesCSTR Experiment: Effects of Process Variables on Reaction RateAllyssa BadilloNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Vapor-Liquid Separation (Multicomponent Distillation)Document19 pagesWeek 4 - Vapor-Liquid Separation (Multicomponent Distillation)psychopassNo ratings yet
- CRE1 PAPER - Alif - Farhandi - HannahDocument53 pagesCRE1 PAPER - Alif - Farhandi - HannahFarhandi Fadillah FedrizalNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40LDocument16 pagesCSTR 40LhishamNo ratings yet
- Cre 1 IntroductionDocument4 pagesCre 1 IntroductionEvangeline LauNo ratings yet
- Calculate Number of Ideal Stages for Absorption ColumnDocument2 pagesCalculate Number of Ideal Stages for Absorption Columnvijendra mauryaNo ratings yet
- Final Report PFRDocument12 pagesFinal Report PFRmark_ancotNo ratings yet
- Mass TransferDocument58 pagesMass TransferShai Sta Catalina100% (1)
- 6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Document26 pages6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Neybil100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument385 pagesFundamentals of Chemical Reaction Engineeringtesfayregs gebretsadik100% (2)
- Experiment Chemical ReactorDocument4 pagesExperiment Chemical ReactorIboniks Beponpiks DabondatskiNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Self Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesDistillation - Self Study QuestionsEsther MaidenNo ratings yet
- Acetone Production Plant DesignDocument25 pagesAcetone Production Plant DesignSerdar Arıcan100% (1)
- KineticsDocument123 pagesKineticssamueloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-7 SolDocument3 pagesTutorial-7 SolAvengerNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Batch Reactor Unit Operations Lab I (CHEGR3787L) Fall 2004Document5 pagesExperiment: Batch Reactor Unit Operations Lab I (CHEGR3787L) Fall 2004Janice YanNo ratings yet
- Absorption and StrippingDocument60 pagesAbsorption and StrippingMyvizhi Somasundaram100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document43 pagesChapter 4aliNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distillation Column Lab Report (40Document27 pagesContinuous Distillation Column Lab Report (40JimNo ratings yet
- Ion Mobility: Transference Number of Ions (ION) and Analysis of Electrochemical Reactions (ECR)Document16 pagesIon Mobility: Transference Number of Ions (ION) and Analysis of Electrochemical Reactions (ECR)Jan Rommel DuterteNo ratings yet
- CHE201ch12Document25 pagesCHE201ch12chandro57No ratings yet
- Tutorial-5 SolDocument2 pagesTutorial-5 SolAvengerNo ratings yet
- L9b Selectivity Example ProblemsDocument24 pagesL9b Selectivity Example ProblemsMeghna SheoranNo ratings yet
- Stirred Tank Reactor Series Experiment ReportDocument20 pagesStirred Tank Reactor Series Experiment ReportEmonbeifo EfosasereNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Probset (LE4)Document4 pagesKinetics Probset (LE4)Jewls HatudNo ratings yet
- AsdfghjklDocument4 pagesAsdfghjklJV CustodioNo ratings yet
- bài tập cuối kỳ 2Document17 pagesbài tập cuối kỳ 2KHÁNH VÕ ĐĂNGNo ratings yet
- bài-tập-cuối-kỳ môn KTPƯDocument17 pagesbài-tập-cuối-kỳ môn KTPƯSang HoàngNo ratings yet
- bài tập cuối kỳDocument14 pagesbài tập cuối kỳKHÁNH VÕ ĐĂNGNo ratings yet
- Feedback On Module 1 Journal ReviewDocument1 pageFeedback On Module 1 Journal ReviewVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism and Its Ill Intents Towards The Academic LifeDocument2 pagesPlagiarism and Its Ill Intents Towards The Academic LifeVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Zeolite-As-Wastewater-Treatment-In-DyesDocument2 pagesZeolite-As-Wastewater-Treatment-In-DyesVince SantosNo ratings yet
- LechonDocument1 pageLechonVince SantosNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument2 pagesCONCLUSIONVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Racism Towards Aboriginal PeopleDocument5 pagesRacism Towards Aboriginal PeopleVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor FinalDocument6 pagesBatch Reactor FinalVince SantosNo ratings yet
- PoultryDocument1 pagePoultryVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Soil ConditionoingDocument1 pageSoil ConditionoingVince SantosNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Zeolite-Wastewater-For-Heavy-MetalsDocument2 pagesZeolite-Wastewater-For-Heavy-MetalsVince SantosNo ratings yet
- 7-8. Zeolite-As-Feeds-Raw-MaterialsDocument2 pages7-8. Zeolite-As-Feeds-Raw-MaterialsVince SantosNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Zeo-FishkillDocument2 pagesZeo-FishkillVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Zeo-FishkillDocument2 pagesZeo-FishkillVince SantosNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Batch Reactor FinalDocument6 pagesBatch Reactor FinalVince SantosNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Soil ConditionoingDocument1 pageSoil ConditionoingVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor FinalDocument6 pagesBatch Reactor FinalVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Lect 16. Energybal ReactiveDocument18 pagesLect 16. Energybal ReactiveChin RamosNo ratings yet
- Industrial SYNTHESIS of AMMONIADocument10 pagesIndustrial SYNTHESIS of AMMONIAVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Chehade 2019Document37 pagesChehade 2019Vince SantosNo ratings yet
- 3 Gods Purpose in My TalentsDocument21 pages3 Gods Purpose in My TalentsVince SantosNo ratings yet
- FinalLaboratoryExperiment 2Document7 pagesFinalLaboratoryExperiment 2Vince SantosNo ratings yet
- MSDS Ammonia Safety GuideDocument4 pagesMSDS Ammonia Safety Guidedyah ayuNo ratings yet
- Cpi Assignment#2Document4 pagesCpi Assignment#2Vince SantosNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise NoDocument14 pagesLaboratory Exercise NoVince SantosNo ratings yet
- Flacs CFD ManualDocument658 pagesFlacs CFD ManualCyanNo ratings yet
- Bio Sem2 EssayDocument2 pagesBio Sem2 EssayEileen WongNo ratings yet
- B Ed 3 Sem Physics Teaching Group C Science 1 Paper 1 Summer 2018Document3 pagesB Ed 3 Sem Physics Teaching Group C Science 1 Paper 1 Summer 2018Rrr KkkNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptDocument72 pagesPharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipient - LastpptFANTANo ratings yet
- Karl Marx'S Philosophy and Its Relevance Today: Haroon RashidDocument14 pagesKarl Marx'S Philosophy and Its Relevance Today: Haroon RashidJuan Carlos LinaresNo ratings yet
- Sponge BobDocument4 pagesSponge BobchabriesNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Headaches in The ED With Lower Cervical Intramuscular Bupivacaine Injections: A 1-Year Retrospective Review of 417 PatientsDocument9 pagesTreatment of Headaches in The ED With Lower Cervical Intramuscular Bupivacaine Injections: A 1-Year Retrospective Review of 417 PatientsLarry B. Mellick, MDNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Motors: Service ManualDocument29 pagesMitsubishi Motors: Service ManualCristobalNo ratings yet
- Cs Project Book ManagementDocument22 pagesCs Project Book ManagementabNo ratings yet
- Oxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopDocument12 pagesOxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopKanjaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food and Beverage IndustryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Food and Beverage IndustryRhyza BehaveNo ratings yet
- EniSpA - The Corporate Strategy of An International Energy Major PDFDocument24 pagesEniSpA - The Corporate Strategy of An International Energy Major PDFAnonymous 9ZMbuR75% (4)
- Acknowledgement For Project Report SampleDocument23 pagesAcknowledgement For Project Report SampleSiddhesh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Memories of HomeDocument14 pagesMemories of HomeMary Francis Edmer SayconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsAira Jane Irarum78% (18)
- Terpin Hydrate Oral SolutionDocument1 pageTerpin Hydrate Oral SolutionAbelard Maria EscrivaNo ratings yet
- Auomotivr Fuel TanksDocument9 pagesAuomotivr Fuel Tankscolumba_mcNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge - Open ElectricalDocument2 pagesPartial Discharge - Open ElectricalBHALAJI BIRLANo ratings yet
- HydrotherapyDocument7 pagesHydrotherapyGialys MoretaNo ratings yet
- 0610 m16 QP 62Document12 pages0610 m16 QP 62faryal khanNo ratings yet
- Design & Operation of Clean Room-1Document39 pagesDesign & Operation of Clean Room-1Hafizur Rahman0% (1)
- FIKE RD Combo With Relief ValvesDocument11 pagesFIKE RD Combo With Relief ValvesAnkit GandhiNo ratings yet
- 5020-Article Text-10917-1-10-20220808Document9 pages5020-Article Text-10917-1-10-20220808indah rumah4No ratings yet
- NOISE ANALYSISDocument16 pagesNOISE ANALYSISDiana Rose TapelNo ratings yet
- OrlDocument186 pagesOrlMuli MaroshiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesDocument20 pagesSeminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesSaikat BadyakarNo ratings yet
- Shat Karma ConciseDocument4 pagesShat Karma ConcisesarikaabhayNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchememuhajireenNo ratings yet
- Full Report-Disinfectant and SanitizerDocument19 pagesFull Report-Disinfectant and Sanitizermohd addinNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFDocument61 pagesChap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFRafael Joshua LedesmaNo ratings yet
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Quiet Zone: Unraveling the Mystery of a Town Suspended in SilenceFrom EverandThe Quiet Zone: Unraveling the Mystery of a Town Suspended in SilenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (23)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (50)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceFrom EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (587)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaFrom EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNo ratings yet
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (241)
- The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914From EverandThe Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)
- 35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980From Everand35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreFrom EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseFrom EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)
- Recording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesFrom EverandRecording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureFrom EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (125)