Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traditional Japanese Houses: Clues Main Notes
Uploaded by
Uchiha GhiffariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Traditional Japanese Houses: Clues Main Notes
Uploaded by
Uchiha GhiffariCopyright:
Available Formats
Ghiffari Notes
Thursday, September 19, 2019
2:34 PM
Traditional Japanese
Houses
Clues Main Notes
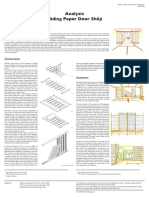
Minka? Minka (traditional Japanese houses), are characterized by sliding doors, tatami mat
flooring, and wooden engawa.
Characteristic traditional Japanese buildings is the dominance of wood, because of the risk of
earthquakes. Japan’s Shinto and Buddhist beliefs influenced architecture right down to
the residential level, with buildings reflecting a strong emphasis on humans’
with nature.
Tatami? is a type of mat used as a flooring material in traditional Japanese-style rooms. Made
using rice straw to form the core.
Genkan? an entrance hall where people remove their footwear. After removal, shoes are put in
the getabako, or wooden clogs cabinet.
Fusuma, and Shōji Rooms are divided by partitions made from washi, Japanese paper. To enter, slide the
door along its wooden rail. There is fusuma and shōji,
• Fusuma use heavier paper or sometimes cloth and are opaque, serving as a
more distinct barrier.
• Shōji are lighter than fusuma, paper affixed to a wooden lattice. They prevent
people from seeing through, but brighten up rooms by allowing light to pass.
Engawa Is a wooden veranda that runs around the outside edge of the house, like an outdoor
corridor.
Futon Bed Futon are traditional Japanese bedding. Put on the floor at night for sleeping. They
could be easily rolled up during the day when they were not needed.
Summary
Traditional Japanese houses ( Minka ) are dominance of wood. The reason why the wood
material is used for reduce the risk of earthquake. Traditional japanese architecture also
reflecting a strong humans relationship with nature. Some elements that can found in the
Minka, just like Tatami, Genkan, Engawa, Fusuma and Shōji, the last is Futon.
Traditional Japanese Page 1
You might also like
- Japan Style: Architecture + Interiors + DesignFrom EverandJapan Style: Architecture + Interiors + DesignRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Japanese Furniture: VIDHYAMBIKA 173712005 DAPHNE PINTO 173713046Document8 pagesJapanese Furniture: VIDHYAMBIKA 173712005 DAPHNE PINTO 173713046sri vidhya Ambika0% (1)
- Traditional Japanese HouseDocument4 pagesTraditional Japanese HouseJohn Michael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Japanese ArchitectureDocument6 pagesJapanese ArchitectureMA. LOU ANGELICA ANGCAYANo ratings yet
- Interior DesignDocument5 pagesInterior DesignGAURAV R 20BAR0045No ratings yet
- 1.4 Japanese ArchitectureDocument147 pages1.4 Japanese ArchitectureeinadrolinebidarNo ratings yet
- HikidoDocument5 pagesHikidoanindya.partha100% (1)
- Presentation 2Document17 pagesPresentation 2Swostika ThapaNo ratings yet
- Japan House Traditonal PresentationDocument25 pagesJapan House Traditonal PresentationbagasNo ratings yet
- HSDA2Document1 pageHSDA2GAURAV R 20BAR0045No ratings yet
- Architecture of Japan Part 1 PDFDocument15 pagesArchitecture of Japan Part 1 PDFAj EstradaNo ratings yet
- Japanese ArchitectureDocument1 pageJapanese ArchitectureJared Marc MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Shoji Analysis MaeIÌ Va MaiIÌ Lys ArthurDocument1 pageShoji Analysis MaeIÌ Va MaiIÌ Lys Arthurarthur stepNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Japanese House PDFDocument2 pagesPresentation of Japanese House PDFmalpontNo ratings yet
- Things Japanese: Everyday Objects of Exceptional Beauty and SignificanceFrom EverandThings Japanese: Everyday Objects of Exceptional Beauty and SignificanceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Japan: Culture of Japanese House 1. The Structure of Japanese HouseDocument3 pagesJapan: Culture of Japanese House 1. The Structure of Japanese Housetri188No ratings yet
- Traditional Indigenous MaterialsDocument14 pagesTraditional Indigenous MaterialsJeannielyn MusniNo ratings yet
- JAPANESE ARCHITECTURE Group 3Document188 pagesJAPANESE ARCHITECTURE Group 3cyrus mburuNo ratings yet
- Architectural Interiors - Self StudyDocument5 pagesArchitectural Interiors - Self StudyYna Marie GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Japanese Architecture and Korean ArchitectureDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of Japanese Architecture and Korean ArchitectureAlyssa Castro100% (2)
- ArticlesDocument2 pagesArticlesNielfranz MaderazoNo ratings yet
- BT2Document26 pagesBT2Melaine A. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Indigenous MaterialDocument8 pagesIndigenous MaterialAngelica ElboNo ratings yet
- M.ramadhan Armanda 20121008 Tugas B.ingDocument5 pagesM.ramadhan Armanda 20121008 Tugas B.ingMuhammad Ramadhan ArmandaNo ratings yet
- Tea RoomDocument8 pagesTea RoomMinh Tu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Machiya 19.04.12Document25 pagesMachiya 19.04.12Shweta ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Arts in Cordillera RegionDocument71 pagesArts in Cordillera RegionCrisela V. TalabaNo ratings yet
- PhotopaperDocument1 pagePhotopaperShiela CruzNo ratings yet
- K Oshi-Do: A New Entrance To A Master's Studio Comes From The Beginning of His CareerDocument5 pagesK Oshi-Do: A New Entrance To A Master's Studio Comes From The Beginning of His CareersyydeeNo ratings yet
- 9784860993238pr PDFDocument64 pages9784860993238pr PDFjuan100% (2)
- Assign No 4 - Japanese ArchitectureDocument10 pagesAssign No 4 - Japanese ArchitectureElaiza Ann Taguse100% (2)
- Bhutan ArchitectureDocument7 pagesBhutan ArchitectureKripasindhu BordoloiNo ratings yet
- Tea RoomDocument3 pagesTea RoomMinh Tu NguyenNo ratings yet
- CPAR Local MaterialsDocument41 pagesCPAR Local MaterialsKlenn Andrea DimalibotNo ratings yet
- BrunonMunari - Japanese - HouseDocument7 pagesBrunonMunari - Japanese - HouseJenny HoweNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Crafts by Group 2Document44 pagesBamboo Crafts by Group 2Jamika ReyesNo ratings yet
- Group #9 Grade-12-LusterDocument16 pagesGroup #9 Grade-12-LusterRonald DiolandaNo ratings yet
- Hoa ReviewerDocument6 pagesHoa ReviewerShanne ColleraNo ratings yet
- Traditional Houses TableDocument3 pagesTraditional Houses TableIvyNo ratings yet
- Ar 2231 History of Architecture 4 Midterm Reviewer - CompressDocument31 pagesAr 2231 History of Architecture 4 Midterm Reviewer - CompressGlymuel Nino SalemNo ratings yet
- Plate 1 LumberDocument16 pagesPlate 1 LumberAlessandro MacaraigNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledhahatdogNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments MindanaoDocument16 pagesMusical Instruments MindanaoJoanne Jose CastroNo ratings yet
- LandscapeDocument13 pagesLandscapeMd. Hasibul Alam SampodNo ratings yet
- Furniture Design - JDDocument27 pagesFurniture Design - JDRicha SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mayan and Japanese ArchitectureDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Mayan and Japanese ArchitectureSohanNo ratings yet
- MeytriksDocument5 pagesMeytriksCamille RamosNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture NotesDocument2 pagesHistory of Architecture NotesMaureen AlboresNo ratings yet
- Loblolly House - Data in Tabular Form (Ug180499)Document1 pageLoblolly House - Data in Tabular Form (Ug180499)Riddhi DoshiNo ratings yet
- The Dream HomeDocument3 pagesThe Dream HomeYusuf AdiyatmokoNo ratings yet
- Philippines Vernacular ArchitectureDocument6 pagesPhilippines Vernacular ArchitectureFrannie BorrasNo ratings yet
- WoodDocument5 pagesWoodBry Bry ArtsalNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts Week 2Document2 pagesContemporary Arts Week 2April ClaireNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture 4Document10 pagesHistory of Architecture 4Lev PerezNo ratings yet
- Trinoma As A Modern Indigenous ArchitectureDocument13 pagesTrinoma As A Modern Indigenous ArchitectureDeynii C. VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Architecture of Batanes: Ar. Caryll BuenaluzDocument23 pagesArchitecture of Batanes: Ar. Caryll BuenaluzCaryll Soliven BuenaluzNo ratings yet
- Japanese Architecture (Nihon Kenchiku) : Posts Lintels Load-BearingDocument5 pagesJapanese Architecture (Nihon Kenchiku) : Posts Lintels Load-BearingRj ClimacoNo ratings yet
- HAGELDocument1 pageHAGELHizkia WeskyNo ratings yet
- Traditional Japanese Architecture: An Exploration of Elements and FormsFrom EverandTraditional Japanese Architecture: An Exploration of Elements and FormsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1011 Chapter 3Document38 pages1011 Chapter 3Eman Sarmiento0% (1)
- GP HM A8 X5Document61 pagesGP HM A8 X5ums6120No ratings yet
- Natural Game Compendium (Compact Edition)Document29 pagesNatural Game Compendium (Compact Edition)Hateful8050% (2)
- Sample PowerPoint On Feminist TheoriesDocument30 pagesSample PowerPoint On Feminist TheoriesKathlyn Enciso100% (1)
- Finlay Park PresentationDocument6 pagesFinlay Park PresentationWIS Digital News StaffNo ratings yet
- Armor of God FHEDocument8 pagesArmor of God FHECranial Hiccups100% (8)
- Handout Exercise Upper Inter Future Perfect Simple Vs Continuous PDFDocument3 pagesHandout Exercise Upper Inter Future Perfect Simple Vs Continuous PDFgabyferr100% (1)
- Manual Panasonic Ny MDDocument3 pagesManual Panasonic Ny MDPopescu IonutNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 2, Wk.4 Module 1Document20 pagesEnglish: Quarter 2, Wk.4 Module 1Monaliza PawilanNo ratings yet
- The Day The Dancers CameDocument8 pagesThe Day The Dancers CamehyarojasguliNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2014 Tutorial - Second Level: 3D Modeling: Randy H. ShihDocument26 pagesAutocad 2014 Tutorial - Second Level: 3D Modeling: Randy H. ShihTri BudiNo ratings yet
- Read The Text Carefully in Each Question. Choose The Best Answer A, B or C. For Each Question, Mark The Correct Answer A, B or C On Your Answer SheetDocument9 pagesRead The Text Carefully in Each Question. Choose The Best Answer A, B or C. For Each Question, Mark The Correct Answer A, B or C On Your Answer SheetGirlie ThohNo ratings yet
- National Lampoons Christmas Vacation 1989Document136 pagesNational Lampoons Christmas Vacation 1989joeyjoker17No ratings yet
- Keeler News No. 1Document4 pagesKeeler News No. 1richardpoltNo ratings yet
- Anousen Leonte - Chaos Magick and TalismansDocument14 pagesAnousen Leonte - Chaos Magick and TalismansКлавдий100% (1)
- Welcome Ramadan Activity BookDocument20 pagesWelcome Ramadan Activity Bookapi-257922682100% (2)
- Crazy Advice ColumnDocument2 pagesCrazy Advice ColumnPau LKNo ratings yet
- Patricia Millns: Painting Her Own ScriptDocument5 pagesPatricia Millns: Painting Her Own ScriptShalini SethNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - Worship and Prophecy - Psalm 63Document4 pagesWeek 9 - Worship and Prophecy - Psalm 63kishtal17No ratings yet
- Take Me To Your Heart WorksheetDocument2 pagesTake Me To Your Heart WorksheetotpengNo ratings yet
- National Artists For Film and TheaterDocument65 pagesNational Artists For Film and TheaterClaren Opeña0% (1)
- Homonyms - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesHomonyms - Lesson PlanJefferson McKing FlorNo ratings yet
- Art & Language With Red Krayola - Nine Gross and Conspicuous Errors (1976)Document2 pagesArt & Language With Red Krayola - Nine Gross and Conspicuous Errors (1976)johndsmith22No ratings yet
- Xinxing Cast Iron Pipe CatalogDocument18 pagesXinxing Cast Iron Pipe Catalogbudi budihardjo100% (4)
- Creative Guitar 1Document118 pagesCreative Guitar 1Hykal100% (10)
- English 6 Q4 Summative Test #2Document10 pagesEnglish 6 Q4 Summative Test #2Elc Elc ElcNo ratings yet
- Most Interesting Man in The WorldDocument1 pageMost Interesting Man in The Worldlarson hermanNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PROCESS AND METHODOLOGIES BodyDocument16 pagesARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PROCESS AND METHODOLOGIES BodyAlejandro VidalNo ratings yet
- The Healing School Magazine - November 2019Document16 pagesThe Healing School Magazine - November 2019Healing School NewsNo ratings yet
- Robert Morris. Two Columns, 1973 Refab-Rication of A 1961 OriginalDocument25 pagesRobert Morris. Two Columns, 1973 Refab-Rication of A 1961 OriginalBruno SchiavoNo ratings yet