Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics: Paper-I 1 Linear Algebra and Matrix: Vector Spaces, Sub Spaces, Basis and
Uploaded by
Ahmed K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pageshh
Original Title
uggmhjj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesMathematics: Paper-I 1 Linear Algebra and Matrix: Vector Spaces, Sub Spaces, Basis and
Uploaded by
Ahmed Khh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
5.
MATHEMATICS: PAPER-I
1 Linear Algebra and Matrix : Vector spaces, Sub Spaces, basis and
dimensions,
Quotient. space, co-ordinates, linear transformation, rank and nullity of a
linear
transformation, matrix representation of linear transformation, linear
functionals, dual
space, transpose of a linear transformation, characteristic values, annihilating
polynomials, Cayley-Hamilton theorem, Inner product spaces, Cauchy-
Schwarz
inequality, Orthogonal vectors, orthogonal complements, orthonormal sets
and bases,
Bessel's inequality of finite dimensional spaces,Gram-Schmidt
orthogonalisation process.
Rank of Matrix, Echelon form, Equivalence, congruence and similarity,
Reduction to canonical form, orthogonal, symmetrical, skew-symmetrical,
Hermitian and
skew-Hermitian matrices, their eigen values, orthogonal and unitary
reduction of quadratic
and Hermitian form, Positive definite quadratic forms, simultaneous
reduction.
2. Calculus : Limits, continuity, differentiability, mean value theorems,
Taylor's theorem,
indeterminate forms, maxima and minima, tangent and normal, Asymptotes,
curvature,
envelope and evolute, curve tracing, continuity and differentiability of
function of several
variables Interchangeability of partial derivatives, Implicit functions theorem,
double and
tripple integrals. (techniques only), application of Beta and Gamma functions,
areas,
surface and volumes, centre of gravity.
3. Analytical Geometry of two and three dimensions: General equation of
second
degree, system of conics, confocal conics, polar equation of conics and its
properties.
Three dimensional co-ordinates, plane, straight line, sphere, cone and
cylinder. Central
conicoids, paraboloids, plane section of conicoids, generating lines, confocal
conicoids.
4. Ordinary differential equations: Order and Degree of a differential
equation, linear,
and exact differential equations of first order and first degree, , equations of
first order but
not of first degree, Singular solutions, Orthogonal trajectories, Higher order
linear
equations with constant coefficients, Complementary functions and particular
integrals.
Second order linear differential equations with variable coefficients: use of
known solution to find another, normal form, method of undetermined
coefficients method
of variation of parameters.
5. Vector and Tensor Analysis: Vector Algebra, Differentiation and
integration of vector
function of a scalar variable gradient, divergence and curl in cartesian,
cylindrical and
spherical coordinates and their physical interpretation, Higher order
derivates, vector
identities and, vector equations, Gauss and stoke's theorems, Curves in Space,
curvature
and torsion, Serret-Frenet's formulae.
Definition of Tensor, Transformation of coordinates, contravariant and
covariant
tensors, addition and outer product of tensors. Contraction of tensors, inner
product
tensor, fundamental tensors, Christoffel symbols, covariant differentiation,
gradiant,
divergence and curl in tensor notation.
6. Statics and Dynamics: Virtual work, stability of equilibrium. Catenary,
Catenary of
uniform strength, equilibrium of forces in three dimensions.
Rectilinear motion, simple harmonic motion, velocities and accelerations
along
radial and transverse directions and along tangential and normal directions,
Motion in
resisting Medium, constrained motion, motion under impulsive forces,
Kepler's laws,
orbits under central forces, motion of varying mass.
MATHEMATICS
Paper-II
1. Algebra: Groups, Cyclic groups, subgroups, Cosets of a subgroup,
Lagrange's
theorem, Normal subgroups, Homomorphism of groups, Factor groups, basic
Isomorphism theorems, Permutation groups, Cayley's theorem.
Rings, Subrings, Ideals, Integral domains, Fields of quotients of an integral
domain, Euclidean domains, Principal ideal domains, Polynomial rings over a
field,
Unique factorization domains.
2. Real Analysis : Metric spaces and their topology with special reference to
sequence,
Convergent sequence, Cauchy sequences, Cauchy's criterion of convergence,
infinite
series and their convergence, nth term test, series of positive terms, Ratio and
root tests,
limit comparison tests, logarithmic ratio test, condensation test, Absolute and
conditional
convergence of general series in R, Abel's Dirichlet's theorems. Uniform
convergence of
sequences and series of functions over an interval, Weierstrass M-test, Abel's
and
Dirichlet's tests, continuity of limit function. Term by term integrability and
differentiability.
Riemann's theory of integration for bounded functions, integrability of
continuous
functions. Fundamental theorem of calculus. Improper integrals and
conditions for their
existence, – עtest.
3. Complex Analysis: Analytic functions, Cauchy-Riemann equations,
Cauchy's
theorem, Cauchy's integral formula, Power series representation of an
analytic function.
Taylor's series. Laurent's series, Classification of singularities, Cauchy's
Residue
theorem, Contour integration.
4. Partial Differential Equations: Formation of partial differential equations.
Integrals of
partial differential equations of first order, Solutions of quasi linear partial
differential
equations of first order, Charpit's method for non-linear partial differential
equations of first
order, Linear Partial differential equations of the second order with constant
coefficients
and their canonical forms, Equation of vibrating string. Heat equation. Laplace
equation
and their solutions.
5. Mechanics: Generalized co-ordinates, generalized velocities, Holonomic
and nonholonomic
systems, D'Alembert's principle and Lagrange's equations of motion for
holonomic systems in a conservative field, generalized momenta, Hamilton's
equations.
Moments and products of inertia, Pricipal axes, Moment of inertia about a line
with
direction cosines (l,m,n), Momental ellipsoid, Motion of rigid bodies in two
dimensions.
6. Hydrodynamics: Equation of continuity, Velocity Potential, Stream lines,
Path Lines,
Momentum and energy.
Inviscid flow theory: Euler's and Bernoulli's equations of motion. Two
dimensional fluid motion, Complex potential, Momentum and energy, Sources
and Sinks,
Doublets and their images with respect line and circle.
7. Numerical Analysis: Solution of algebraic and transcendental equations of
one
variable by bisection, Regula-Falsi and Newton-Raphson methods and order
of their
convergence. Interpolation (Newton's and Lagrange's) and Numerical
differentiation
formula with error terms.
Numerical Integration:Trapezoidal and Simpson's rules.
Numerical solutions of Ordinary differential Equations: Euler's method.
Rune-Kutta method.
You might also like
- Workbook PDFDocument110 pagesWorkbook PDFAbdul Munim100% (1)
- Mathematics Main Syllabus: Paper-I Section ADocument4 pagesMathematics Main Syllabus: Paper-I Section AVenkata Harsha Vardhan KinjarapuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesMathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraMahi RaperiaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper-I Section A 1. Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Paper-I Section A 1. Linear Algebrashiva1654No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper-IDocument4 pagesMathematics Paper-ISathish ParlapellyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ACFDocument6 pagesMathematics ACFAhmed KNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument6 pagesMATHEMATICSharidashav22No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper-I Section A 1. Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Paper-I Section A 1. Linear AlgebraMOHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- UPSC Syllabus MathsDocument6 pagesUPSC Syllabus MathsMahesh Narayan NayakNo ratings yet
- CSIR NET Mathematical Sciences SyllabusDocument4 pagesCSIR NET Mathematical Sciences Syllabuskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus for Main ExamDocument4 pagesMathematics Syllabus for Main ExamNIlesh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Maths Optional in Upsc-1Document3 pagesSyllabus For Maths Optional in Upsc-1Shivangi SinghNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis and SequencesDocument1 pageReal Analysis and SequencesVaishnavi BhandariNo ratings yet
- IIT JAM Mathematics SyllabusDocument2 pagesIIT JAM Mathematics Syllabusmohit24031986No ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus - Civil Services Mains Exam UPSCDocument4 pagesMathematics Syllabus - Civil Services Mains Exam UPSCtabrezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics scqp19Document3 pagesMathematics scqp19harshitamaggo2006No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentfackname778No ratings yet
- SET Syllabus Common Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences Unit - 1Document4 pagesSET Syllabus Common Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences Unit - 1skumar5267600No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper - I (1) Linear AlgebraDocument2 pagesMathematics Paper - I (1) Linear AlgebraKshitijVermaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Sequences and Series of Real NumbersDocument2 pagesMathematics: Sequences and Series of Real Numbersaishwarya asawaNo ratings yet
- Indian Civil Service Exam MathsDocument4 pagesIndian Civil Service Exam MathskondamudisagarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus 2021: Unit-1: Algebra, Number Theory and Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Syllabus 2021: Unit-1: Algebra, Number Theory and Linear AlgebraPriyadrshani nayakNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra:: Paper-IiDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra:: Paper-IiAdhiyamanPownrajNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus Paper-I (1) Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Syllabus Paper-I (1) Linear AlgebraVaibowNo ratings yet
- MA SyllabiDocument1 pageMA Syllabipiyush upadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraPRAVEEN RAGHUWANSHINo ratings yet
- Jam SyllebusDocument1 pageJam SyllebusSubhajit SenNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Calculus Mains Syllabus BreakdownDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra and Calculus Mains Syllabus BreakdownrakukulappullyNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations, Algebra, Real Analysis Exam TopicsDocument2 pagesLinear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations, Algebra, Real Analysis Exam Topicsdawn.devNo ratings yet
- Cucet Syllabus MSC MathsDocument2 pagesCucet Syllabus MSC MathsSatya SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Maths SyllabusDocument4 pagesMaths SyllabusTanuja RithwikNo ratings yet
- IIT JAM Mthematics SyllabusDocument1 pageIIT JAM Mthematics Syllabusk.d.khodwa2001No ratings yet
- mathmeticascience_syllbusDocument4 pagesmathmeticascience_syllbusjayasankari kumariNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Mains Mathematics Syllabus - 2017-2018 - UPSCsyllabusDocument4 pagesUPSC CSE Mains Mathematics Syllabus - 2017-2018 - UPSCsyllabusashishNo ratings yet
- MA SyllabusDocument1 pageMA Syllabuspranjalcoc35936No ratings yet
- MA SyllabusDocument1 pageMA SyllabusAishwarya SoniNo ratings yet
- 4 - 08-31-2021 - 16-12-27 - Syllabi For Entrance Exam For M.Sc. (Maths), M.SC. (Maths) Under SFS, M.Sc. (Maths With Computer Science) For 2021-22Document7 pages4 - 08-31-2021 - 16-12-27 - Syllabi For Entrance Exam For M.Sc. (Maths), M.SC. (Maths) Under SFS, M.Sc. (Maths With Computer Science) For 2021-22Sanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- JAM2015 MA SyllabusDocument1 pageJAM2015 MA Syllabusrcpuram01No ratings yet
- IAS Mains Mathematics Syllabus Exam PapersDocument2 pagesIAS Mains Mathematics Syllabus Exam Papersvipinvns999No ratings yet
- 213 MathematicsDocument7 pages213 MathematicsNidhi JhaNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument3 pagesMathematicshejan94618No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS (MA) SYLLABUS FOR GATE EXAMDocument2 pagesMATHEMATICS (MA) SYLLABUS FOR GATE EXAMShikha KumariNo ratings yet
- Maths SyllabusDocument3 pagesMaths SyllabusSabari BalaNo ratings yet
- UPPSC Maths Syllabus SummaryDocument2 pagesUPPSC Maths Syllabus SummaryankitNo ratings yet
- Xea Syllabus GATE 2013Document2 pagesXea Syllabus GATE 2013Anonymous 8pCXXsNo ratings yet
- UPSC Maths Syllabus GuideDocument5 pagesUPSC Maths Syllabus GuidefghdNo ratings yet
- CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) For Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-Ship Mathematical Sciences Unit 1Document4 pagesCSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) For Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-Ship Mathematical Sciences Unit 1Faiz ImamNo ratings yet
- Upscsdfyllabdsffdsdus - in-uPSjhksfC ChkjhjjkhkSE Mains Mathhfgfematics SylghfglabusDocument2 pagesUpscsdfyllabdsffdsdus - in-uPSjhksfC ChkjhjjkhkSE Mains Mathhfgfematics SylghfglabusShakthidhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Course of M.Phil/Ph.D Session 2010-11: R Z Q Dy P DXDocument2 pagesSyllabus For The Course of M.Phil/Ph.D Session 2010-11: R Z Q Dy P DXRehaan FayazNo ratings yet
- Syl Lab Us Entrance MSCDocument4 pagesSyl Lab Us Entrance MSCRehaan FayazNo ratings yet
- UPSC Maths Syllabus BreakdownDocument3 pagesUPSC Maths Syllabus BreakdownNooman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-PGT - Math FDocument5 pagesSyllabus-PGT - Math Fsahudebashis2000No ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Paper I (1) Linear AlgebraUlta KaamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SyllabusDocument3 pagesMathematics SyllabusAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- MA Mathematics: CalculusDocument2 pagesMA Mathematics: CalculusBala RamNo ratings yet
- Applied MathsDocument8 pagesApplied MathsVinay MishraNo ratings yet
- RET Exam Syllabus PhysicsDocument22 pagesRET Exam Syllabus PhysicsSubhasis SarkarNo ratings yet
- 15.5 Mathematics (Ma)Document1 page15.5 Mathematics (Ma)Sai Tejesh Reddy GurijalaNo ratings yet
- Maths Syllabus SequenceDocument3 pagesMaths Syllabus Sequenceayush.shukla.iitbhuNo ratings yet
- NRTDDocument1 pageNRTDAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Russian WritingDocument4 pagesSection 2 - Russian WritingAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Jhd162A SeriesDocument10 pagesJhd162A SeriesClaudinei JankeNo ratings yet
- ConversionsDocument1 pageConversionsAhmed KNo ratings yet
- UyuDocument2 pagesUyuAhmed KNo ratings yet
- PIR Motion Sensor GuideDocument3 pagesPIR Motion Sensor GuideAbdul Raziq ShadNo ratings yet
- Pir SB0061Document2 pagesPir SB0061samagoustNo ratings yet
- R305 User ManualDocument26 pagesR305 User ManualchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi home security system partsDocument2 pagesRaspberry Pi home security system partsAhmed KNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Atm Block DiagramDocument3 pagesAtm Block DiagramAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Power Supply Security SystemDocument3 pagesRaspberry Pi Power Supply Security SystemAhmed KNo ratings yet
- HydraDocument3 pagesHydraAhmed KNo ratings yet
- ddc45 January 2019 Ca English PDFDocument87 pagesddc45 January 2019 Ca English PDFAmit negiNo ratings yet
- The MagPi Issue 14 enDocument36 pagesThe MagPi Issue 14 enNebojsa MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Scanner - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesFingerprint Scanner - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Security Issues of Atm: Chapter - 4Document60 pagesAnalysis of Security Issues of Atm: Chapter - 4Ahmed KNo ratings yet
- Print TicketDocument2 pagesPrint TicketSean MINo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2542660519300241 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S2542660519300241 MainAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Synchronized Webcam Based Authenticated ATMDocument4 pagesSynchronized Webcam Based Authenticated ATMAhmed KNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1876610218310920 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1876610218310920 MainComputerCoaching ClssesNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1742287619300222 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1742287619300222 MainAhmed KNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Information Management: Paul Brous, Marijn Janssen, Paulien HerderDocument17 pagesInternational Journal of Information Management: Paul Brous, Marijn Janssen, Paulien HerderAhmed KNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Information Management: A A B C D A A e ADocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Information Management: A A B C D A A e AAhmed KNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things: Are You Ready For What 'S Coming?: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesThe Internet of Things: Are You Ready For What 'S Coming?: SciencedirectAhmed KNo ratings yet
- Analysis of identifiers in leading IoT platformsDocument13 pagesAnalysis of identifiers in leading IoT platformsAhmed KNo ratings yet
- GogaDocument1 pageGogaAhmed KNo ratings yet
- BW Collective NounsDocument1 pageBW Collective NounsiswanahNo ratings yet
- 3 - Content - Introduction To Java, JVM, JDK PDFDocument8 pages3 - Content - Introduction To Java, JVM, JDK PDFAnonymous zdY202lgZYNo ratings yet
- Inertial Reference Frames: Example 1Document2 pagesInertial Reference Frames: Example 1abhishek murarkaNo ratings yet
- C11 Strategy DevelopmentDocument30 pagesC11 Strategy DevelopmentPARTI KEADILAN RAKYAT NIBONG TEBALNo ratings yet
- Design & Construction of Substation 16P Painting System ComplianceDocument103 pagesDesign & Construction of Substation 16P Painting System ComplianceRamil LazNo ratings yet
- Visualization BenchmarkingDocument15 pagesVisualization BenchmarkingRanjith S100% (1)
- Chronological OrderDocument5 pagesChronological OrderDharWin d'Wing-Wing d'AriestBoyzNo ratings yet
- SMEs, Trade Finance and New TechnologyDocument34 pagesSMEs, Trade Finance and New TechnologyADBI EventsNo ratings yet
- 03 - 42 STCP-Ahm AssetDocument46 pages03 - 42 STCP-Ahm AssetARP MEILNo ratings yet
- Victor Mejia ResumeDocument1 pageVictor Mejia Resumeapi-510300922No ratings yet
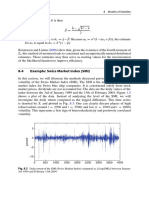
- 8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityDocument3 pages8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityNickesh ShahNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchElsha DamoloNo ratings yet
- Aos Warscroll Fimir WarriorsDocument1 pageAos Warscroll Fimir WarriorsGuido Sebastián AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Understanding HydrocarbonsDocument9 pagesHydrocarbon: Understanding HydrocarbonsBari ArouaNo ratings yet
- Sia Mock+Test 1 Csat Updated CompressedDocument216 pagesSia Mock+Test 1 Csat Updated Compressedpooja bhatiNo ratings yet
- 41 PDFsam Redis CookbookDocument5 pages41 PDFsam Redis CookbookHữu Hưởng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Types of NumbersDocument11 pagesTypes of NumbersbrajanosmaniNo ratings yet
- Barelwiyah, Barelvi Chapter 1 (Part 2 of 5)Document31 pagesBarelwiyah, Barelvi Chapter 1 (Part 2 of 5)Dawah ChannelNo ratings yet
- DCAD OverviewDocument9 pagesDCAD OverviewSue KimNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Report For Mixed Use 2B+G+7Hotel BuildingDocument20 pagesElectrical Design Report For Mixed Use 2B+G+7Hotel BuildingEyerusNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantDocument13 pagesMedicinal PlantNeelum iqbalNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference - HVAC (Part-1) : DECEMBER 1, 2019Document18 pagesQuick Reference - HVAC (Part-1) : DECEMBER 1, 2019shrawan kumarNo ratings yet
- IPO Fact Sheet - Accordia Golf Trust 140723Document4 pagesIPO Fact Sheet - Accordia Golf Trust 140723Invest StockNo ratings yet
- Maths SolutionDocument10 pagesMaths SolutionAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell Selection ReselectionDocument35 pagesCell Selection ReselectionThiaguNo ratings yet
- Kennedy 1945 Bibliography of Indonesian Peoples and CulturesDocument12 pagesKennedy 1945 Bibliography of Indonesian Peoples and CulturesJennifer Williams NourseNo ratings yet
- CP Mother's Day Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCP Mother's Day Lesson PlanAma MiriNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceDocument8 pagesInternal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- WEEK 8. - Gen Math-PortfolioDocument12 pagesWEEK 8. - Gen Math-PortfolioOreo ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Stages of Intimate RelationshipsDocument4 pagesStages of Intimate RelationshipsKrystalline ParkNo ratings yet
- Apps Tables Excel FRMTDocument4 pagesApps Tables Excel FRMTSunil ReddyNo ratings yet