Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbial Cardiovascular and Systemic Diseases: Aerobes Facultative Anaerobes
Uploaded by
Christine Ranoa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesMicro
Original Title
Microbial Diseases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesMicrobial Cardiovascular and Systemic Diseases: Aerobes Facultative Anaerobes
Uploaded by
Christine RanoaMicro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
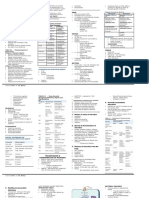
MICROBIAL CARDIOVASCULAR AND SYSTEMIC DISEASES
DISEASES DESCRIPTION CAUSATIVE AGENT VIRULENCE FACTOR/S TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Presence of microbial Neisseria meningitides: G(-)
Form capsules
infection of the blood aerobes
Endotoxin: released from
and can lead to E.coli and speacies of Salmonella:
Septicemia Gram-negative bacteria
lymphangitis Facultative anaerobes Intravenous fluid replacement to
Bacteremia and Siderophores: steal iron
Bacterial septicemia Bacteroides: anaerobic species mitigate fluid loss
Toxemia Destroying erythrocyte:
Bacteria remain fixed at S. aureus and Streptococcus
release iron from
site of infection and pneumonia: G(+)
hemoglobin into blood
release toxin in blood Streptococcus pyogenes: Toxic-
shock-like syndrome
Viridans streptococci: green
pigment when cultured on blood
Bacterial colonization of
S. aureus and S. epidermidis: skin
endocardium triggers
Streptococcus pneumonia: pharynx Intravenous antibacterial drugs
inflammation and formation of
Endocarditis Enterococcus and Escherichia: Not highly invasive Prophylactic antibiotics for high-
vegetation (bulky masses of
digestive tract risk patients when needed
platelets and clotting proteins
Neisseria, Pseudomonas,
that surround and bury
Bartonella, Mycobacterium and
bacteria)
Mycoplasm
Brucellosis Brucella: G(-) coccobacilli
(Bang’s disease: Brucella melitensis: goats and No treatment
Disease of animals that can Endotoxin
Bernhard Bang; Malta sheep Doxycycline and rifampicin or
transfer to humans Has ability to grow and
fever, Rock fever of B. abortus: cattle streptomycin
multiply
Gibraltar and fever of B. suis: swine Attenuated vaccine for animals
Crete) B. canis: dogs, foxes and coyotes
Francisella tularensis: small, Streptomycin or gentamycin and
Lipid capsule
Tularemia Zoonotic disease nonmotile, aerobic, G(-) Tetracycline
Endotoxin
coccobacillus Vaccine
Adhesins - attachment
Caused great pandemics Type III secretion system –
Bubonic plague: enlarged inject antiphagocytic proteins
lymph nodes called buboes into dendritic celss,
Pneumonic plague: occurs neutrophils or macrophages
Plague Yersinia pestis: G(-), rod-shaped Streptomycin or Gentamycin
when the bacterium spreads to Capsule
the lungs Antiphagocytic proteins
Difficulty breathing can develop Endotoxin – trigger
rapidly inflammation, fever and
blood clotting
MICROBIAL CARDIOVASCULAR AND SYSTEMIC DISEASES
Three phases in untreated Uses magnesium instead of
patients: iron ELISA and western blot test
Borrelia burgdorferi: uses
Lyme Disease Bull's-eye rash at infection site Active endotoxin Doxycycline, Cefuroxime or
Manganese
Neurological symptoms Changes outer membrane Amoxicillin
Severe arthritis antigens frequently
Ehrlichia chaffeensis causes
ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis (Human
Tick-borne human disease Anaplasma phagocytophilum
monocytic
Resemble the flu (Ehrlichia equ) causes Endocytosis (internalization
ehrlichiosis HME) and Doxycycline
Leukopenia (decrease on anaplasmosis by a cell)
Anaplasmosis Serological testing
WBC) and thrombocytopenia Rickettsias, G(-), highly Prevent fusion of lysosomes
(Human granulocytic
(decrease of platelets) pleomorphic, obligate
anaplasmosis HGA)
intracellular parasites of
eukaryotic cells
Icosahedral capsid
Fluorescent antibodies againt
Infectious Suppressed apoptosis
Interaction of patient’s cellular anti-EBV immunoglobulin
Mononucleosis Human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4) or EBV infection: Chronic
immune system infected B ELISA Test
(Kissing disease or Epstein-Barr virus: dsRNA fatigue syndrome, B cell
lymphocytes Chemotherapy
mono) lymphomas and oral hairy
leukoplakia
ELISA tests and DNA probes
Ganciclovir: slow release of CMV
Cytomegalovirus: enveloped, Remains in a latent state
Cytomegalovirus but do not affect the course of
Cells infected are enlarged dsRNA with an icosahedral until immune system is
(CMV) disease
capsid compromised
Formivirsen: inhibit replication of
CMV in retinal cells (eye infection)
First stage: fever, headache,
muscle aches
Second stage: period of
Genus: Flavivirus
remission
Family: Flaviviridae ELISA or Viral Nucleic Acid via
Third stage: delirium, seizures, Intracellular replication cycle;
Yellow Fever Yellow fever virus: (+) ssRNA , PCR
coma, hemorrhaging Adhesins
arbovirus, with an icosahedral Vaccine
Hemorrhaging in the intestines
capsid
may result in “black vomit”
Liver damage “Yellow Jack”
causes jaundice
Dengue fever and Dengue fever
Dengue virus: enveloped, (+) Aedes: vectors of all four
Dengue Hemorrhagic First phase: fever, edema, head No specific treatment available
ssRNA with icosahedral capsids strains of dengue viruses
Fever and muscle pain
MICROBIAL CARDIOVASCULAR AND SYSTEMIC DISEASES
Second phase: return of fever
and red rash
Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Internal bleeding, shock, and
possibly death
Ebolavirus or Marburgvirus:
unsegmented, -ssRNA: must Enveloped viruses have long
African Viral Ebola and Marburg Supportive care involving fluid and
convert into mRNA before an filamentous capsids which
Hemorrhagic Fever hemorrhagic fevers electrolyte replacement
infected cell can transcribe viral curve back upon themselves
polypeptides
Reproductive cycle hides
parasite from immune
surveillance
Associated with parasite's life in Malaria secretome injects
erythrocytes toxins into host cells
Plasmodium: exoerythrocytic
Fever, chills, diarrhea, Adhesins allow red blood Chloroquine
Malaria phase, erythrocytic phase,
headache cells to adhere to certain Pyrimethamine + Artesunate
sporogonic phase
Anemia, weakness, and fatigue tissues
gradually occur Merozoites form within
vesicles and avoid detection
Changes in body chemistry
attract other mosquitoes
Ability of oocysts and of
Major disease in AIDS
pseudocysts to parasitize a
Fetal infections can cause Clindamycin
Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasma gondii: apicomplexan wide variety of hosts
numerous conditions, including Pyrimethamine
(Toxo) protozoan Infect many different cells
spontaneous abortion or Sulfonamides
within a host
stillbirth
Survive intracellularly
Swelling at infection site and Intracellular life
nonspecific symptoms Trypanosoma cruzi: flagellated Antigen switching Benznidazole
Chagas’
Chronic manifestations can protozoan Synthesis of protein that Nifurtimox
occur years after infection inhibits immunity
Swimmer's itch may occur at Schistosoma mansoni: Caribbean,
infection site South American, and Africa
Can burrow through human
Schistosomiasis Eggs deposited throughout S. haematobium: Africa and India Praziquantel
skin
body can cause other S. japonicum: Asia, parasitic
symptoms helminth
You might also like
- Le 2 - Microbio SupertableDocument9 pagesLe 2 - Microbio Supertabletocinolover0102No ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment. ADocument26 pagesMicrobiology Assignment. ACynthia AbbangNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Bacteria TableDocument11 pagesWuolah Free Bacteria TableELENA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- تَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?Document10 pagesتَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٣?سلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- Jocel D. Oclarit-Pbs5 Finals ProjectDocument5 pagesJocel D. Oclarit-Pbs5 Finals ProjectJocel OclaritNo ratings yet
- Identification by Microimmunofluorescence Test: AKA "Woolster's Disease" Incubation For C. Anthrax Is 1-15 DaysDocument10 pagesIdentification by Microimmunofluorescence Test: AKA "Woolster's Disease" Incubation For C. Anthrax Is 1-15 DaysizzmichikoNo ratings yet
- Bacteri Pathology&pathogenesisDocument22 pagesBacteri Pathology&pathogenesisAsem AlhazmiNo ratings yet
- Micro BioDocument60 pagesMicro BioShanna Charlyn Madridano MadanloNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-148-184Document37 pagesUSMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-148-184mariana yllanesNo ratings yet
- Bacteria ChartsDocument11 pagesBacteria ChartsFlowerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology MnemonicsFritzel SusbillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFRitz Celso100% (1)
- Fungi Gram Positive Bacteria Viruses: Non-Tuberculous MycobacteriaDocument1 pageFungi Gram Positive Bacteria Viruses: Non-Tuberculous MycobacteriaImperium503No ratings yet
- Espectro Antimicrobiano PenicilinaDocument3 pagesEspectro Antimicrobiano PenicilinaVALENTINA ZAMBRANO ROMERONo ratings yet
- Micorbiology Overview (Bacteria, Viruses, Laboratory Diagnosis)Document88 pagesMicorbiology Overview (Bacteria, Viruses, Laboratory Diagnosis)nikoleta.2604.zhekovaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinSijo SunnyNo ratings yet
- Flash Notes Billie-GeneticsDocument29 pagesFlash Notes Billie-GeneticsschxzerrydawnNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci - Ref - Canvas PDFDocument5 pagesStaphylococci - Ref - Canvas PDFacademics pdfNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet - Capsule StainingDocument2 pagesLab Sheet - Capsule Stainingbliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DenguePLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- TR 2 138Document17 pagesTR 2 138Rakhmat RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- BacteDocument12 pagesBacteNinolouise Alvarez JustoNo ratings yet
- PENAFIEL M6 April21-2023Document21 pagesPENAFIEL M6 April21-2023Precious Valerie PenafielNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DengueKevin50% (2)
- Bergey'S Manual Classification of BacteriologyDocument7 pagesBergey'S Manual Classification of BacteriologyItsMeAffaNo ratings yet
- Other Bacteria: Gram-NegativeDocument18 pagesOther Bacteria: Gram-NegativeZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Chronic InfectionsDocument55 pages4 - Chronic InfectionsAlexa GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument4 pagesCommunity Health NursingOnurNo ratings yet
- PIODERMIASDocument97 pagesPIODERMIASAlejandra GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Document39 pagesLecture 10 Antibiotics & Antiinfectives-1Dr Haris AwanNo ratings yet
- Important Terms - Tropical InfectionDocument8 pagesImportant Terms - Tropical InfectionTimothy JordanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification and Disease: An Organ System ApproachDocument33 pagesBacterial Classification and Disease: An Organ System ApproachSyed ShahNo ratings yet
- Bordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andDocument38 pagesBordetella: Drying - Highly Susceptible To Toxic Substance andkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Table of BacteriaDocument10 pagesPart 2 Table of BacteriaTeresa Mae Dimen BautistaNo ratings yet
- Medically Important BacteriaDocument2 pagesMedically Important BacteriaAhmad MsalmahNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics &anti-Infective AgentsDocument39 pagesAntibiotics &anti-Infective AgentsKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesChapter 8 - Infectious DiseasesAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside & Macrolide Antibiotics Classification:: Systemic AminoglycosidesDocument5 pagesAminoglycoside & Macrolide Antibiotics Classification:: Systemic AminoglycosidesSai VamshiNo ratings yet
- Causes of Neonatal Pneumonia by Route - UpToDateDocument2 pagesCauses of Neonatal Pneumonia by Route - UpToDateThảo Nguyên Phan NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Table - Respiratory - Bacterial, Viral Fungal InfectionsDocument9 pagesTable - Respiratory - Bacterial, Viral Fungal InfectionsSondos MohammadNo ratings yet
- Bacteria TableDocument4 pagesBacteria TableBrittany Lynn MyersNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PinkDocument3 pagesMicrobiology PinkBenjamin GaliaNo ratings yet
- Prion Diseases and Normal Flora MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesPrion Diseases and Normal Flora MicrobiologyHanunNo ratings yet
- Micro by DR - Hesham (GIT)Document65 pagesMicro by DR - Hesham (GIT)abcde990075No ratings yet
- Diseases Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument3 pagesDiseases Microbiology and Parasitologyarsdef tuanNo ratings yet
- Neuro Summaries PDFDocument65 pagesNeuro Summaries PDFBEATRICE SOPHIA PARMANo ratings yet
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNo ratings yet
- AEROBIC, GRAM POS BACILLI NON-SPORE FORMER (Nahaeminrmt)Document7 pagesAEROBIC, GRAM POS BACILLI NON-SPORE FORMER (Nahaeminrmt)Rach ReyesNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Aseptic Meningitis UpToDateDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Aseptic Meningitis UpToDateFf FfNo ratings yet
- Medically Important Bacteria Memorisation SheetDocument7 pagesMedically Important Bacteria Memorisation SheetOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The CardiovascularDocument5 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The CardiovascularToby MapaNo ratings yet
- Coryneform Bacteria, Listeria and Erysipelothrix: Diphtheria Listeriosis ErysipeloidDocument12 pagesCoryneform Bacteria, Listeria and Erysipelothrix: Diphtheria Listeriosis Erysipeloidnour achkarNo ratings yet
- StreptococcusDocument6 pagesStreptococcusAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- Intestinal TB - Diagram IDocument1 pageIntestinal TB - Diagram IJoannNo ratings yet
- FILE - 20200604 - 172043 - High-Concentration Antibacterial Antiviral Pure Nano Silver Solution 200410Document23 pagesFILE - 20200604 - 172043 - High-Concentration Antibacterial Antiviral Pure Nano Silver Solution 200410Le Viet Dung100% (1)
- Normal Body FloraDocument1 pageNormal Body FloraJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Medically Important BacteriaDocument2 pagesMedically Important BacteriaM7md AllahhamNo ratings yet
- Bolesti Obavezne Za PrijavljivanjeDocument14 pagesBolesti Obavezne Za PrijavljivanjeJakić VivienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Echinoderms of Birhen BeachDocument5 pagesEchinoderms of Birhen BeachChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Research Questions: Null Hypothesis: There Is No Relationship Between The Presence of EchinodermsDocument4 pagesStatement of The Research Questions: Null Hypothesis: There Is No Relationship Between The Presence of EchinodermsChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Echinoderms of Birhen BeachDocument5 pagesEchinoderms of Birhen BeachChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Echinoderms of Birhen BeachDocument5 pagesEchinoderms of Birhen BeachChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Social Media On Human Interaction Among Peers As Perceived byDocument30 pagesThe Effect of Social Media On Human Interaction Among Peers As Perceived byChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Org Med Act 3Document33 pagesOrg Med Act 3Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- U OkDocument1 pageU OkChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Echinoderm Diversity and Human Impacts in Intertidal ZonesDocument9 pagesEchinoderm Diversity and Human Impacts in Intertidal ZonesChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Fungal Isolation: Learning Activity No. 11Document25 pagesFungal Isolation: Learning Activity No. 11Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Camphor WaterDocument19 pagesCamphor WaterChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Glycosides Part 2Document9 pagesGlycosides Part 2Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 DDS LABDocument96 pagesActivity 1 DDS LABChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- DDS Paracetamol Elixir (Post-Lab)Document33 pagesDDS Paracetamol Elixir (Post-Lab)Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Intro Pharma Quality ControlDocument80 pagesIntro Pharma Quality ControlChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1:: Inorganic Compounds VS Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesActivity No. 1:: Inorganic Compounds VS Organic CompoundsChristine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Scarlet Fever: Dima Albaik 220150397 Yasmeen Abu Saif 220150502Document11 pagesScarlet Fever: Dima Albaik 220150397 Yasmeen Abu Saif 220150502Dima AlbaikNo ratings yet
- Effect of Environmental Factors On The Growth of MicroorganismsDocument10 pagesEffect of Environmental Factors On The Growth of MicroorganismsHan Hui ChongNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 PseudomonashhjjunDocument8 pagesTopic 1 PseudomonashhjjunRachel Marie M. GaniaNo ratings yet
- Astm E640.21036Document3 pagesAstm E640.21036Ageng Wahyu PatrianitaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PneumoniaDocument31 pagesMicrobiology PneumoniaKartika Rezky100% (1)
- Thesis File PDFDocument42 pagesThesis File PDFSeema GulNo ratings yet
- Chain of Infection For TuberculosisDocument2 pagesChain of Infection For Tuberculosisapi-251961377100% (1)
- Immunohematology MCQsDocument21 pagesImmunohematology MCQsMeerva El-zein86% (21)
- Lab 1 - Blood and Blood Typing: The Circulatory System: Blood, Pages 679-712 (Saladin, 4Document4 pagesLab 1 - Blood and Blood Typing: The Circulatory System: Blood, Pages 679-712 (Saladin, 4math_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Chart PDFDocument1 pageMicrobiology Chart PDFseshadriNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 4 Stains PDFDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 4 Stains PDFOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Team Readiness Assurance Test (TRAT) (Page 1 of 2)Document1 pageTeam Readiness Assurance Test (TRAT) (Page 1 of 2)BahirahNo ratings yet
- Bio310 Lab 1Document19 pagesBio310 Lab 1nursyahirahNo ratings yet
- اكثر من 400 سؤال مع الاجابة أسئلة الهيئة السعودية 2015 للمختصيين بالبكتريا والمياكروبيولجيDocument86 pagesاكثر من 400 سؤال مع الاجابة أسئلة الهيئة السعودية 2015 للمختصيين بالبكتريا والمياكروبيولجيMohsen HaleemNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Massive Blood Loss ManagementDocument8 pagesGuidelines Massive Blood Loss ManagementRatna AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Medicine by Dr. Sharad JohriDocument54 pagesTransfusion Medicine by Dr. Sharad JohriShashwat JohriNo ratings yet
- Blood TestDocument1 pageBlood TestDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Training Report. Kipps (Repaired) Wariongo (Final) )Document47 pagesTraining Report. Kipps (Repaired) Wariongo (Final) )George KipkoechNo ratings yet
- SPREad PlateDocument7 pagesSPREad PlateJermeLou BaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment For The Fourth Semesters Botany Department ST MarysDocument3 pagesAssignment For The Fourth Semesters Botany Department ST MarysRimeiaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Crossword - An SEO-Optimized TitleDocument1 pageMicrobiology Crossword - An SEO-Optimized TitleAbiNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument91 pagesStreptococciDr. Ashish JawarkarNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Operation Theatre SurveillanceDocument7 pagesOperation Theatre Surveillancetummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Mechanisms and ImmunityDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Vaccine Mechanisms and ImmunityAvinash KumbharNo ratings yet
- StaphDocument1 pageStaphPrabhjot Singh BakshiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blood Tests PDFDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Blood Tests PDFKishor SinghNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology DemonstrationsDocument12 pagesBacteriology Demonstrationshamody662002100% (1)
- Cell Culture Based VaccinesDocument2 pagesCell Culture Based VaccinesNithya Kutty100% (1)
- Interpretation of Gram Stains and Other Common Microbiologic Slide Preparations - LibraryDocument4 pagesInterpretation of Gram Stains and Other Common Microbiologic Slide Preparations - Libraryfabriclive15No ratings yet