Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suspension System: Ali Raza Chang-Baluch
Uploaded by
Zahid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesautomobile
Original Title
Suspension System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentautomobile
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesSuspension System: Ali Raza Chang-Baluch
Uploaded by
Zahidautomobile
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
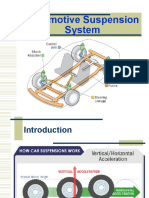
Suspension System
Ali Raza Chang-Baluch
The purpose of the complete suspension system is to
isolate the vehicle body from road shocks and vibrations
which would otherwise be transferred to the passengers
and load. It must also keep the tires in contact with the
road, regardless of road surface.
Solid and Independent Suspension
Solid, or beam, axles connect the wheels on each side of the vehicle. This means the
movement of a wheel on one side of the vehicle is transferred to the wheel on the other
side.
With independent suspension, the wheels can move independently of each other, which
reduces body movement. This prevents the other wheel being affected by movement of
the wheel on the opposite side, and this reduces body movement.
When a wheel strikes a bump, there is a reaction force, and energy is transferred to the
spring which makes it oscillate. Oscillations left uncontrolled can cause loss of traction
between the wheel and the road surface.
Shock absorbers dampen spring oscillations by forcing oil through small holes. The oil heats
up, as it absorbs the energy of the motion. This heat is then transferred through the body of
the shock absorber to the air.
When a vehicle hits an obstruction, the size of the reaction force depends on how much
unsprang mass is at each wheel assembly.
Sprung mass refers to those parts of the vehicle supported on the springs. This includes the
body, the frame, the engine, and associated parts.
Unsprang mass includes the wheels, tires, brake assemblies, and suspension parts not
supported by the springs.
Vehicle ride and handling is improved by keeping unsprang mass as low as possible.
Wheel and brake units that are small and light follow the road contours without a large
effect on the rest of the vehicle.
Modern Suspension Systems being currently
used
Air suspension :- is a type of vehicle suspension powered by an electric or
engine-driven air pump or compressor. This compressor pumps the air into a
flexible bellows, usually made from textile-reinforced rubber. The air
pressure inflates the bellows, and raises the chassis from the axle. The
purpose of air suspension is to provide a smooth, constant ride quality, but
in some cases is used for sports suspension. Modern electronically controlled
systems in automobiles and light trucks almost always feature self-
levelling along with raising and lowering functions. Although traditionally
called air bags or air bellows, the correct term is air spring.
Magnetorheological fluid :-A magnetorheological fluid (MR fluid) is a type
of smart fluid in a carrier fluid, usually a type of oil. When subjected to
a magnetic field, the fluid greatly increases its apparent viscosity, to the
point of becoming a viscoelastic solid (MagneRide)
Audi’s Latest Researched Suspension
Systems
Dynamic Ride Control:- Audi currently offers Dynamic Ride Control
technology in the RS 5, among other models. DRC is a purely mechanical,
and thus fully lag-free, system for reducing body roll and pitch around the
transverse and longitudinal axes.
Audi magnetic ride:-Audi magnetic ride is a suspension technology
employed in the A3, TT and R8 families. This system continually adapts the
function of the shock absorbers to the road profile and the driver’s style.
A synthetic hydrocarbon oil containing tiny magnetic particles between 3
and 10 thousandths of a millimetre in diameter – one tenth the thickness of
a human hair – circulates in the shock absorber pistons. When voltage is
applied to a coil integrated in the damper, a magnetic field is produced
and the particles realign. They orient themselves crosswise with respect to
the direction of oil flow in the piston channels, obstructing its flow. The
process is completed in a few milliseconds.
.
Audi’s adaptive air Suspension
Audi’s Magnetic Ride system
You might also like
- C. Calvin Jones - Big Blue Book of Bicycle Repair-Park Tool Company (2013) PDFDocument228 pagesC. Calvin Jones - Big Blue Book of Bicycle Repair-Park Tool Company (2013) PDFHector Valdez93% (14)
- Automotive Brake Efficiency Formulas & Hydraulic Brake System DesignDocument45 pagesAutomotive Brake Efficiency Formulas & Hydraulic Brake System DesignAjit100% (1)
- 1998 Dodge Ram 1500 Quad Cab Specs & Performance - NADAguidesDocument3 pages1998 Dodge Ram 1500 Quad Cab Specs & Performance - NADAguidesDantes Kebreau0% (1)
- Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) For Buses and Trucks With CAN II (SAE 1939) Maintenance 0Document27 pagesElectronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) For Buses and Trucks With CAN II (SAE 1939) Maintenance 0Miller Andres Aroca100% (1)
- BMW E Series CodingDocument8 pagesBMW E Series CodingJB0% (1)
- 02 MT (R150)Document7 pages02 MT (R150)Carlos MachadoNo ratings yet
- t5R55W-S - Oil Line A Body ValveDocument11 pagest5R55W-S - Oil Line A Body ValveaxallindoNo ratings yet
- Basic Guide On Train OperationDocument226 pagesBasic Guide On Train OperationAmar Singh67% (6)
- Anti Lock Brakes ReportDocument23 pagesAnti Lock Brakes Reportjyoti ranjan nayak90% (10)
- 2003 Audi A8 Wiring DiagramsDocument98 pages2003 Audi A8 Wiring Diagramsmike0% (2)
- Suspension ReportDocument10 pagesSuspension ReportAlbin SibyNo ratings yet
- Manual de Taller Escape y Escape HibridDocument46 pagesManual de Taller Escape y Escape HibridCarlos Sandoval100% (1)
- Car Suspension - An Introduction!Document54 pagesCar Suspension - An Introduction!Siddharth Garkhail100% (1)
- Ecu Programming Tool User ManualDocument142 pagesEcu Programming Tool User ManualNicolas SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Automotive Suspension SystemDocument32 pagesAutomotive Suspension SystemMoniruzzaman Shuvo100% (2)
- NTS Testz-2 PDFDocument256 pagesNTS Testz-2 PDFvik0580% (10)
- Compressor Selection GuidelineDocument46 pagesCompressor Selection Guidelinemohammad basuki0% (1)
- To Whom It May ConcernDocument96 pagesTo Whom It May ConcernKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Active Suspension System Power Point PresentationDocument30 pagesActive Suspension System Power Point PresentationJAYNo ratings yet
- Naloop Bikestability-ForkrakeDocument5 pagesNaloop Bikestability-Forkrakevignesh kumarNo ratings yet
- ATT Brakes - Example TextbookDocument15 pagesATT Brakes - Example TextbookSooraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mini Spares Catalogue PDFDocument55 pagesMini Spares Catalogue PDFFrederick REPOSNo ratings yet
- Prepositions After Verbs Explanation and ExercisesDocument9 pagesPrepositions After Verbs Explanation and Exercisesbondarel12100% (1)
- Rear Absorber::: International Islamic University Malaysia Cocuricular Activities CenterDocument7 pagesRear Absorber::: International Islamic University Malaysia Cocuricular Activities CenterKhirNo ratings yet
- Automatic Air Suspension System Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesAutomatic Air Suspension System Seminar ReportKaushik SheetNo ratings yet
- Understanding Brakes and Their TypesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Brakes and Their TypesMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- Federal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaDocument13 pagesFederal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Aking and Suspension SystemDocument36 pagesAking and Suspension Systemss822054No ratings yet
- Automatic Air Suspension System ReportDocument18 pagesAutomatic Air Suspension System ReportNarayana Sarma MarthiNo ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument14 pagesBrake SystemC/wali Axmed NuurNo ratings yet
- Automotive Suspension SystemDocument83 pagesAutomotive Suspension SystemTanzim Rafat AyonNo ratings yet
- WHAT IS BRAKEDocument3 pagesWHAT IS BRAKESOMOSCONo ratings yet
- 汽车底盘中英文翻译【共18页】493KBDocument18 pages汽车底盘中英文翻译【共18页】493KBnightweisoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document34 pagesUnit 5A ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Automobile EngieeringDocument28 pagesAutomobile EngieeringYogesh Kumar GaurNo ratings yet
- Brake Task 1'Document8 pagesBrake Task 1'Shiva JadhaoNo ratings yet
- Project PBLDocument19 pagesProject PBLAdam LuqmanNo ratings yet
- System Under ChassisDocument6 pagesSystem Under ChassisrheyNo ratings yet
- Active Suspension System - A Mechatronic SystemDocument11 pagesActive Suspension System - A Mechatronic SystemPravin JawarkarNo ratings yet
- Automotive TerminologyDocument13 pagesAutomotive TerminologyMohith ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Design & Fabrication of Suspension Systems: A Report ONDocument13 pagesDesign & Fabrication of Suspension Systems: A Report ONSrinivas DsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Braking SystemDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic Braking SystemGallant Info100% (1)
- Automatic Air SuspentionDocument18 pagesAutomatic Air Suspentionashu047No ratings yet
- 15 Braking System PDFDocument8 pages15 Braking System PDFNishant ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Brake13 Terms PDFDocument0 pagesBrake13 Terms PDFPushkar NathNo ratings yet
- Automotive Glossary 2015 04Document14 pagesAutomotive Glossary 2015 04Antonio Montesinos ChavarríaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Suspension and Steering SystemsDocument11 pagesAutomobile Suspension and Steering Systemspawan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Braking SystemDocument11 pagesBraking SystemOne Love Jah LoveNo ratings yet
- Shock Absorber ReportDocument48 pagesShock Absorber ReportGiani Siva Prasad Sabbavarapu33% (6)
- Adaptive Air Suspension Case Study of AUDI A8Document5 pagesAdaptive Air Suspension Case Study of AUDI A8Bonny SidhuNo ratings yet
- Bài 1 Rack and Pinion Steering SystemDocument34 pagesBài 1 Rack and Pinion Steering SystemPham DuyNo ratings yet
- Automotive (2) Lab: Braking SystemDocument5 pagesAutomotive (2) Lab: Braking SystemMohammad YahyaNo ratings yet
- Baithi AVCNDocument41 pagesBaithi AVCNtranconghia1150No ratings yet
- Friction Kinetic Energy Heat: Frictional Brakes Are Most Common and Can Be Divided Broadly Into "Shoe" or "Pad" BrakesDocument3 pagesFriction Kinetic Energy Heat: Frictional Brakes Are Most Common and Can Be Divided Broadly Into "Shoe" or "Pad" BrakesNikhilVinayNo ratings yet
- Braking System-Wps OfficeDocument7 pagesBraking System-Wps OfficerkNo ratings yet
- Kaushik Sheet: " Automatic Air Suspension System "Document19 pagesKaushik Sheet: " Automatic Air Suspension System "Kaushik SheetNo ratings yet
- Eco Task Braking 1.2Document4 pagesEco Task Braking 1.2ArpanNo ratings yet
- An Anti-Lock BR-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesAn Anti-Lock BR-WPS OfficeKaiRae AsakuraNo ratings yet
- Baithi AVCN 2Document37 pagesBaithi AVCN 2Khanh ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Drum Brake System Backing Plate: Braking PrincipleDocument3 pagesDrum Brake System Backing Plate: Braking PrincipleSamiullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- The Audi TT Is A Cult CarDocument2 pagesThe Audi TT Is A Cult CarvancozNo ratings yet
- TO Automotive Steering SystemDocument22 pagesTO Automotive Steering SystemJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Quá-trình_AVCN-2Document37 pagesQuá-trình_AVCN-2tranquangg0608No ratings yet
- Automotive Brake Systems Experiment ReportDocument6 pagesAutomotive Brake Systems Experiment Reportpratik thakareNo ratings yet
- Hydro Pneumatic Braking SytemDocument11 pagesHydro Pneumatic Braking Sytempramo_dass100% (1)
- Res ResDocument24 pagesRes ResEfjay LagdaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Braking SystemDocument9 pagesHydraulic Braking SystemPrathmesh KoreNo ratings yet
- Asb EngDocument11 pagesAsb Engkrushna NikamNo ratings yet
- SubjectDocument11 pagesSubjectkrushna NikamNo ratings yet
- Res ResDocument26 pagesRes ResEfjay LagdaNo ratings yet
- Autonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)Document11 pagesAutonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)SouravNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1From Everand10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1No ratings yet
- The Dual Wheel Journey Motorcycle Terms Dictionary and Phrasebook: DWJ Dictionary, #2From EverandThe Dual Wheel Journey Motorcycle Terms Dictionary and Phrasebook: DWJ Dictionary, #2No ratings yet
- Fesco Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesFesco Syllabus PDFZahidNo ratings yet
- ME 322 Ideal Rankine Cycle ExampleThe title "TITLE ME 322 Ideal Rankine Cycle ExampleDocument20 pagesME 322 Ideal Rankine Cycle ExampleThe title "TITLE ME 322 Ideal Rankine Cycle ExampleAntonio Montesinos ChavarríaNo ratings yet
- CAA's Professional Team OpportunityDocument3 pagesCAA's Professional Team OpportunityimranjamiNo ratings yet
- Caa SyllabusDocument1 pageCaa SyllabusZahidNo ratings yet
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Çengel BolesDocument20 pagesVapor and Combined Power Cycles: Çengel BolesZahidNo ratings yet
- KIPS Essays PDFDocument58 pagesKIPS Essays PDFMujahidNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economy Challenges ProspectsDocument14 pagesPakistan Economy Challenges ProspectsArslan AwanNo ratings yet
- Open Minds: Briefing Manual On Current AffairsDocument79 pagesOpen Minds: Briefing Manual On Current AffairsZahidNo ratings yet
- 5 - Pakistan's Foreign PolicyDocument22 pages5 - Pakistan's Foreign PolicyDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For Current Affairs in CSS and Other Competitive ExamsDocument3 pagesHow To Prepare For Current Affairs in CSS and Other Competitive ExamsZahidNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Affairs Solved MCQSDocument51 pagesPakistan Affairs Solved MCQSUsman UbairNo ratings yet
- CV Electrical EngineerDocument2 pagesCV Electrical EngineerZahidNo ratings yet
- Parametres & Princ of UGDocument15 pagesParametres & Princ of UGAdeel Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Communication and Report Writing Multiple ChoiceDocument23 pagesBusiness Communication and Report Writing Multiple ChoicesulemanNo ratings yet
- Case I: When Fuel Switch Over Seamlessely Done From KNR To KPDDocument2 pagesCase I: When Fuel Switch Over Seamlessely Done From KNR To KPDZahidNo ratings yet
- FIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteDocument6 pagesFIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Batch Two - FRL101 - 2 PDFDocument3 pagesBatch Two - FRL101 - 2 PDFAtiqa SafdarNo ratings yet
- FIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteDocument6 pagesFIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Description of TagsDocument2 pagesDescription of TagsZahidNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Car 13ME67Document12 pagesHybrid Car 13ME67ZahidNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics ProjectDocument1 pageMechatronics ProjectZahidNo ratings yet
- Arduino and Processing Program GuidelinesDocument1 pageArduino and Processing Program GuidelinesZahidNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics ProjectDocument1 pageMechatronics ProjectZahidNo ratings yet
- FIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteDocument6 pagesFIA Act (Orignal Document On National Assembaly's SiteAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- 3) .Identification of HazardsDocument10 pages3) .Identification of HazardsZahidNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: by Azizullah ChannaDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment: by Azizullah ChannaZahidNo ratings yet
- VW NBD Tiguan Allspace R Line Service Pricing GuideDocument1 pageVW NBD Tiguan Allspace R Line Service Pricing GuideNizamNo ratings yet
- Suspension SystemDocument26 pagesSuspension Systemchandresh ranaNo ratings yet
- John Deere equipment codes and specificationsDocument17 pagesJohn Deere equipment codes and specificationsAC IMPORTNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue: DR-Z70 K8 DR-Z70 K9 DR-Z70 L0Document62 pagesParts Catalogue: DR-Z70 K8 DR-Z70 K9 DR-Z70 L0CRISTHIAN DAVID JURADO MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Front Axle ManitouDocument3 pagesFront Axle ManitouYakob PangihutanNo ratings yet
- About CompanyDocument13 pagesAbout CompanyDivya ChokNo ratings yet
- Cambio y Rellenado Aceite de Transmision Al4Document2 pagesCambio y Rellenado Aceite de Transmision Al4Paulina GarciaNo ratings yet
- MTN320-A: Owner'S ManualDocument100 pagesMTN320-A: Owner'S ManualRizky TahirNo ratings yet
- Toyota's Americanization and Focus on Innovation and DesignDocument7 pagesToyota's Americanization and Focus on Innovation and DesignAnil SinghNo ratings yet
- 2017 Full Stability and The Road Map To The FutureDocument48 pages2017 Full Stability and The Road Map To The Futurev53No ratings yet
- Automatic Transaxle Assembly ComponentsDocument1 pageAutomatic Transaxle Assembly ComponentsSergio JachoNo ratings yet
- Mustang Evo 2 Parts ManualDocument6 pagesMustang Evo 2 Parts ManualRashid HussainNo ratings yet
- Myferrari - Ferrari Roma - fkpS1q9Document11 pagesMyferrari - Ferrari Roma - fkpS1q9BartNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator HitachiDocument10 pagesVoltage Regulator HitachiUmer NawazNo ratings yet
- XDR80T中英文Document4 pagesXDR80T中英文abangNo ratings yet
- 2018-08-01 Mopar Collector S GuideDocument100 pages2018-08-01 Mopar Collector S Guideedoy bmxNo ratings yet
- Momtacarga JGM751FT18Document7 pagesMomtacarga JGM751FT18Betty CuperNo ratings yet
- Amortisseur Ressort EtudeDocument11 pagesAmortisseur Ressort EtudeSliim AmiriNo ratings yet