100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views23 pagesQuality Control and Standard Operating Procedures
This document discusses quality control and standard operating procedures for medical laboratories. It defines quality control as a statistical process used to monitor laboratory test results. There are two main types of quality control: internal quality control measures precision, while external quality control measures accuracy by analyzing unknown samples from an external source. Quality control results should be monitored graphically over time to detect errors. Standard operating procedures are necessary to standardize processes and ensure quality. Adhering to quality control protocols and standard operating procedures is important for producing reliable patient test results.
Uploaded by
No BodyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
4K views23 pagesQuality Control and Standard Operating Procedures
This document discusses quality control and standard operating procedures for medical laboratories. It defines quality control as a statistical process used to monitor laboratory test results. There are two main types of quality control: internal quality control measures precision, while external quality control measures accuracy by analyzing unknown samples from an external source. Quality control results should be monitored graphically over time to detect errors. Standard operating procedures are necessary to standardize processes and ensure quality. Adhering to quality control protocols and standard operating procedures is important for producing reliable patient test results.
Uploaded by
No BodyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction: Discusses the expectations of quality care in hospitals emphasizing the importance of an effective quality control protocol.
- Quality Control: Explains the use of quality control results to validate patient results, and details the statistical processes involved.
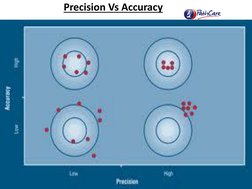
- Types of Quality Control: Describes different types of quality control including internal and external measures emphasizing precision and accuracy.
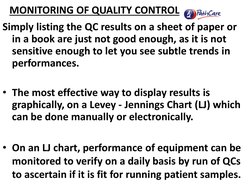
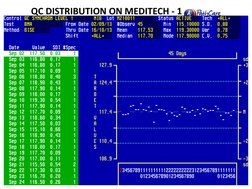
- Monitoring of Quality Control: Discusses methods for effective monitoring of quality control using graphical tools like Levey-Jennings charts.
- Multi-rule Quality Control: Introduces multi-rule quality control methods for evaluating analytical runs in medical laboratories.
- Types of Analytical Errors: Defines and differentiates between random and systematic analytical errors in laboratory processes.
- Quality Control Material: Details the composition and purpose of quality control materials made from matrices similar to patient samples.
- Quality Control Protocol: Describes the importance and establishment of QC protocols to minimize examination result risks.
- Standard Operating Procedures: Details the necessity and structure of standard operating procedures for consistent laboratory performance.
- Importance of SOP: Highlights the critical role of documented SOPs in process standardization and quality management.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the lasting importance of quality over cost in laboratory operations and management.