Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bolt
Uploaded by
ArfanAli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageBolt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBolt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageBolt
Uploaded by
ArfanAliBolt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
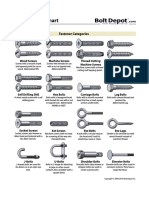
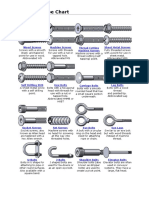
Anchor bolt - Bolt designed to allow objects to be attached to concrete.
The bolt head is usually placed in concrete before it
has cured, leaving the threaded end exposed.
Arbor bolt - Bolt with a washer permanently attached and reversed threading. Designed for use in miter saw and other tools to
auto tighten during use to prevent blade fall out.
Carriage bolt - Bolt with a smooth rounded head and a square section to prevent turning followed with a threaded section for a
nut.
Elevator bolt - Bolt with a large flat head used in conveyor system setups.
Hanger bolt - Bolt that has no head, machine threaded body followed by a wood threaded screw tip. Allow nuts to be attached
to what is really a screw.
Hex bolt - Bolt with a hexagonal head and threaded body. Section immediately under head may or may not be threaded.
J bolt - Bolt shaped like the letter J. Used for tie downs. Only the non curved section is threaded for a nut to be attached.
Lag bolt - Also known as lag screw. Not a true bolt. Hex bolt head with thread screw tip for use in wood.
Rock bolt - Used in tunnel construction to stabilize walls.
Sex bolt or Chicago Bolt - Bolt that has a male and female part with interior threads and bolt heads on either end. Commonly
used in paper binding.
Shoulder bolt or Stripper bolt - Bolt with a broad smooth shoulder and small threaded end used to create a pivot or attachment
point.
U-Bolt - Bolt shaped like the letter U where the two straight sections are threaded. A straight metal plate with two bolt holes is
used with nuts to hold pipes or other round objects to the U-bolt.
You might also like
- Screw FastenersDocument7 pagesScrew FastenersKristian MarajNo ratings yet
- Jewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsFrom EverandJewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Screws and BoltsDocument27 pagesScrews and BoltsCelestine OzokechiNo ratings yet
- The Pochade and Wet Panel Carrier Do It Yourself PlanFrom EverandThe Pochade and Wet Panel Carrier Do It Yourself PlanRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pojedini Tipovi VijakaDocument4 pagesPojedini Tipovi Vijakaserzo75No ratings yet
- Structural Steel Work: Structural Steelwork Is Generally Used To Form A The 'Skeleton'Document23 pagesStructural Steel Work: Structural Steelwork Is Generally Used To Form A The 'Skeleton'Status BatchNo ratings yet
- Lee - Machdesign2dDocument3 pagesLee - Machdesign2dLee AdrielNo ratings yet
- 1 WC Type-ChartDocument1 page1 WC Type-ChartlumpertNo ratings yet
- Type of Screws-Chart PDFDocument4 pagesType of Screws-Chart PDFBoy Sacnamud0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Ameer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Type ChartDocument4 pagesType Chartمحمد فطري فيك نظامNo ratings yet
- Bolt Depot - Fastener Type ChartDocument5 pagesBolt Depot - Fastener Type Chartvijayjain1No ratings yet
- Fasteners: v. Aug. 7, 2011Document3 pagesFasteners: v. Aug. 7, 2011Sam DichosoNo ratings yet
- Pop RivetDocument3 pagesPop RivetKaran SharmaNo ratings yet
- Artifact DissectionDocument13 pagesArtifact DissectionPrashant TolaniNo ratings yet
- Nail (Fastener) : Cam Dowels ConformatDocument9 pagesNail (Fastener) : Cam Dowels Conformatsheshe_19No ratings yet
- أنواع المسامير والكوبلنجDocument16 pagesأنواع المسامير والكوبلنجOmar AlharthiNo ratings yet
- Sketching of Machine ComponentsDocument78 pagesSketching of Machine ComponentsSaurabh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Nut and Bolts: Trem PaperDocument15 pagesNut and Bolts: Trem Papershams0% (1)
- Rivets, Welded Joints, Pin JointsDocument69 pagesRivets, Welded Joints, Pin JointsSiddharth KotechaNo ratings yet
- V Blocks and Clamps: Hold Square or Round Work 2 Inch Round-1 7/16 Inch Square Hardened and Ground NO. 568Document1 pageV Blocks and Clamps: Hold Square or Round Work 2 Inch Round-1 7/16 Inch Square Hardened and Ground NO. 568Chris McLeanNo ratings yet
- Nut and BoltsDocument10 pagesNut and BoltsSam33% (3)
- MTE 305 Topic 6Document11 pagesMTE 305 Topic 6israelkolawole599No ratings yet
- MDPLT7 PRB5Document3 pagesMDPLT7 PRB5Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoNo ratings yet
- Bolt (Fastener) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesBolt (Fastener) - WikipediaaravindNo ratings yet
- Screwdriver Cross ScrewdriverDocument14 pagesScrewdriver Cross ScrewdriverMa Lorielyn E. NieraNo ratings yet
- Types of Bolts and Their Uses in Construction and AssemblyDocument3 pagesTypes of Bolts and Their Uses in Construction and AssemblyGeraldVirgilioAcusaNo ratings yet
- Metal Vidalama EngDocument12 pagesMetal Vidalama EngJohann Sebastian BachNo ratings yet
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument28 pagesForging New Generations of Engineersravindranath1989No ratings yet
- Report - JOINERY HARDWAREDocument16 pagesReport - JOINERY HARDWAREKeya JainNo ratings yet
- Fastener Type Chart: Wood Screws Machine Screws Thread Cutting Machine Screws Sheet Metal ScrewsDocument4 pagesFastener Type Chart: Wood Screws Machine Screws Thread Cutting Machine Screws Sheet Metal Screwslemuel bacsaNo ratings yet
- 1 Tools, Equipment and Devices For RepairingDocument31 pages1 Tools, Equipment and Devices For RepairingBerlin AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- Types of bolts, screws, nuts and their usesDocument4 pagesTypes of bolts, screws, nuts and their usesNakanakanaknakNo ratings yet
- Screw Fastenings and RivetsDocument53 pagesScrew Fastenings and RivetsAJ BantayNo ratings yet
- Design of Nut & BoltDocument4 pagesDesign of Nut & BoltJyoti Kale0% (1)
- Types of Screws and Bolts: Fasteners With A Tapered Shank (Self-Threading Screws)Document8 pagesTypes of Screws and Bolts: Fasteners With A Tapered Shank (Self-Threading Screws)Saiful AmreeNo ratings yet
- CP3 - Free Hand SketchDocument181 pagesCP3 - Free Hand SketchHrishikesh deshpandeNo ratings yet
- WORKHOLDING DEVICES FOR DRILLING AND MILLINGDocument4 pagesWORKHOLDING DEVICES FOR DRILLING AND MILLINGKeith Tanaka Magaka100% (1)
- FastenersDocument28 pagesFastenersthulasi_krishnaNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF PIN AND COMMONLY USEDDocument3 pagesTYPES OF PIN AND COMMONLY USEDdevmarineacademyNo ratings yet
- 2837-Screws & How To Fit ThemDocument1 page2837-Screws & How To Fit ThemSandra Barnett CrossanNo ratings yet
- What Are Fasteners?Document16 pagesWhat Are Fasteners?MITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Hand tools and power tools under 40 charactersDocument153 pagesHand tools and power tools under 40 charactersMa Lorielyn E. NieraNo ratings yet
- Identifying Basic Hand Tools and Test EquipmentDocument14 pagesIdentifying Basic Hand Tools and Test EquipmentDiana ParkerNo ratings yet
- Nut BoltsDocument3 pagesNut Boltsdanish_shoaib6874No ratings yet
- Lect5 Detachable Fastener Bolt Nut Locking FoundationDocument36 pagesLect5 Detachable Fastener Bolt Nut Locking FoundationPramodVermaNo ratings yet
- 'Identifying Basic Hand Tools and Test Equipment: General ClassificationDocument15 pages'Identifying Basic Hand Tools and Test Equipment: General ClassificationGaming AmbinNo ratings yet
- Types of BoltsDocument3 pagesTypes of BoltsAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ToolsDocument241 pagesPlumbing ToolsAngel NuevoNo ratings yet
- EssentialsDocument66 pagesEssentialsHarold GalopeNo ratings yet
- Screw FastenersDocument17 pagesScrew FastenersZojj UliNo ratings yet
- Fish Mouth Jig For The LatheDocument5 pagesFish Mouth Jig For The Latheradio-chaserNo ratings yet
- Connection With Using BOLT: The Threaded Bolt FullDocument7 pagesConnection With Using BOLT: The Threaded Bolt FullThirza AdelaideNo ratings yet
- Types Of BoltsDocument15 pagesTypes Of BoltsMuhammad MedhatNo ratings yet
- Type of Bolts and Their Uses PDFDocument15 pagesType of Bolts and Their Uses PDFEdwin Barahona FerrufinoNo ratings yet
- 1 Fitting 4Document1 page1 Fitting 4Sanjay Gheji100% (1)
- Workshop Technology Eim 118 Module 2: Hand Tools: Dzanya M.TDocument18 pagesWorkshop Technology Eim 118 Module 2: Hand Tools: Dzanya M.TBriaydon TawandaNo ratings yet
- HAND TOOL For EASA/CAR - 66 EXAMINATIONDocument201 pagesHAND TOOL For EASA/CAR - 66 EXAMINATIONManish Mishra100% (1)
- Week 6 LectureDocument3 pagesWeek 6 LectureDaniel BognotNo ratings yet
- Welding Present A Ion 1Document87 pagesWelding Present A Ion 1Vishnu KumarNo ratings yet
- Fused Flux For Nickel Based Alloy SteelDocument4 pagesFused Flux For Nickel Based Alloy SteelArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Inspection Plan For Pipe LineDocument4 pagesInspection Plan For Pipe LineArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Product List: Agglomerated Flux (/Product/Agglomerated-Flux/)Document5 pagesProduct List: Agglomerated Flux (/Product/Agglomerated-Flux/)ArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Schweißnahtfehler + Bilder (X)Document12 pagesSchweißnahtfehler + Bilder (X)razerhazerNo ratings yet
- Welding Electrode Classifications 123Document2 pagesWelding Electrode Classifications 123Unnikrishnan RajanNo ratings yet
- Annealing TemperaturesDocument7 pagesAnnealing TemperaturesEmijo.ANo ratings yet
- Types of Corrosion: Dr. Hamdy A. KandilDocument53 pagesTypes of Corrosion: Dr. Hamdy A. KandilAmyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Welding: Drafting and Design Presentation Standards Volume 3: Structural Drafting StandardsDocument12 pagesChapter 6: Welding: Drafting and Design Presentation Standards Volume 3: Structural Drafting StandardsaaronNo ratings yet
- Welder QualificationDocument17 pagesWelder QualificationArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Quality Requirements For Contractors v0Document29 pagesQuality Requirements For Contractors v0ArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Steel Making For Metallurgical EngDocument3 pagesSteel Making For Metallurgical EngArfanAliNo ratings yet
- ML12320A661Document37 pagesML12320A661ArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Weld Defect Acceptance Criteria by CodesDocument17 pagesWeld Defect Acceptance Criteria by CodesMidhun K Chandrabose96% (24)
- Canara Manufacturing ProcessDocument3 pagesCanara Manufacturing ProcessEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNo ratings yet
- ASME P and F Material Numbers ExplainedDocument17 pagesASME P and F Material Numbers ExplainedArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Resigned TextDocument1 pageResigned TextArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Weld Map of Well 32 FLDocument13 pagesWeld Map of Well 32 FLArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Fastener BasicsDocument2 pagesFastener BasicsDigvijay Singh IINo ratings yet
- PPS120 Rev10 0309 PDFDocument2 pagesPPS120 Rev10 0309 PDFArfanAliNo ratings yet
- 4 Heat TreatmentokDocument22 pages4 Heat TreatmentokPramod AthiyarathuNo ratings yet
- Welding Cost Estimator PubDocument8 pagesWelding Cost Estimator Pubrockufool100% (4)
- Radiograph InterpretationDocument12 pagesRadiograph InterpretationnithingrmeNo ratings yet
- 008 SMAW Ready ReviewDocument7 pages008 SMAW Ready ReviewMuhammad Fitransyah Syamsuar PutraNo ratings yet
- Shackle InspectionDocument3 pagesShackle InspectionArfanAliNo ratings yet
- P & F NumberDocument13 pagesP & F NumberArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Nut BotlDocument1 pageNut BotlArfanAliNo ratings yet
- ORF Crane Lift Plan 508Document5 pagesORF Crane Lift Plan 508japv_pasNo ratings yet
- FDocument2 pagesFHenrry Manuel Gonzales DamianNo ratings yet
- Shekhano D # 01tubing Weld Map # 01, Sec-3Document2 pagesShekhano D # 01tubing Weld Map # 01, Sec-3ArfanAliNo ratings yet
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiFrom Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Crochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiFrom EverandCrochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dream Sewing Spaces: Design & Organization for Spaces Large & SmallFrom EverandDream Sewing Spaces: Design & Organization for Spaces Large & SmallRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Friends: The One with the Crochet: The Official Crochet Pattern BookFrom EverandFriends: The One with the Crochet: The Official Crochet Pattern BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Colorful Crochet Knitwear: Crochet sweaters and more with mosaic, intarsia and tapestry crochet patternsFrom EverandColorful Crochet Knitwear: Crochet sweaters and more with mosaic, intarsia and tapestry crochet patternsNo ratings yet
- Crochet Pattern Books: The Ultimate Complete Guide to Learning How to Crochet FastFrom EverandCrochet Pattern Books: The Ultimate Complete Guide to Learning How to Crochet FastRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetFrom EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingFrom EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Modern Granny Stitch Crochet: Make clothes and accessories using the granny stitchFrom EverandModern Granny Stitch Crochet: Make clothes and accessories using the granny stitchRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!From EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Crochet Lace: Techniques, Patterns, and ProjectsFrom EverandCrochet Lace: Techniques, Patterns, and ProjectsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsFrom EverandThe Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Coloring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesFrom EverandColoring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (12)
- Delicate Crochet: 23 Light and Pretty Designs for Shawls, Tops and MoreFrom EverandDelicate Crochet: 23 Light and Pretty Designs for Shawls, Tops and MoreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Life in Stitches: Knitting My Way Through Love, Loss, and Laughter - Tenth Anniversary EditionFrom EverandA Life in Stitches: Knitting My Way Through Love, Loss, and Laughter - Tenth Anniversary EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Crochet Collage Garden: 100 patterns for crochet flowers, plants and petalsFrom EverandCrochet Collage Garden: 100 patterns for crochet flowers, plants and petalsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Two Simple Shapes = 26 Crocheted Cardigans, Tops & Sweaters: If you can crochet a square and rectangle, you can make these easy-to-wear designs!From EverandTwo Simple Shapes = 26 Crocheted Cardigans, Tops & Sweaters: If you can crochet a square and rectangle, you can make these easy-to-wear designs!Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Kawaii Crochet Garden: 40 super cute amigurumi patterns for plants and moreFrom EverandKawaii Crochet Garden: 40 super cute amigurumi patterns for plants and moreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Crochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeFrom EverandCrochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Radical Sewing: Pattern-Free, Sustainable Fashions for All BodiesFrom EverandRadical Sewing: Pattern-Free, Sustainable Fashions for All BodiesNo ratings yet
- Origami: The Ultimate Origami Guide - Master Origami in 2 hours. Learn Origami with 20 Step by Step Projects that Inspire YouFrom EverandOrigami: The Ultimate Origami Guide - Master Origami in 2 hours. Learn Origami with 20 Step by Step Projects that Inspire YouRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (15)
- The Basics of Corset Building: A Handbook for BeginnersFrom EverandThe Basics of Corset Building: A Handbook for BeginnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Martha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeFrom EverandMartha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeNo ratings yet
- Edward's Menagerie: Dogs: 50 canine crochet patternsFrom EverandEdward's Menagerie: Dogs: 50 canine crochet patternsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Amigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)From EverandAmigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)No ratings yet
- Modern Crochet…For the Beach Babe Goddess: Easy to Use StitchesFrom EverandModern Crochet…For the Beach Babe Goddess: Easy to Use StitchesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Sew Bags: The Practical Guide to Making Purses, Totes, Clutches & More; 13 Skill-Building ProjectsFrom EverandSew Bags: The Practical Guide to Making Purses, Totes, Clutches & More; 13 Skill-Building ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)